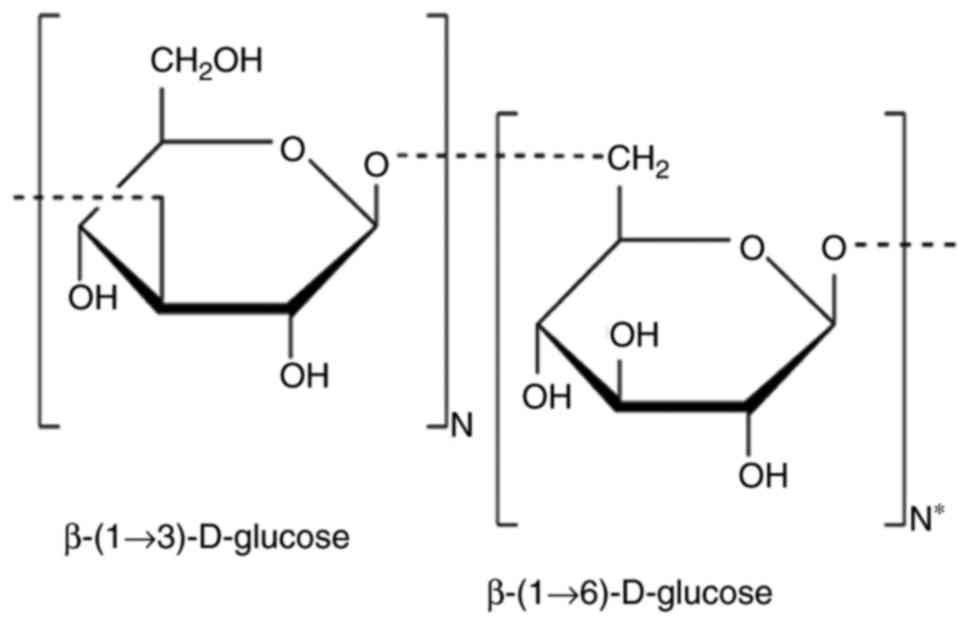
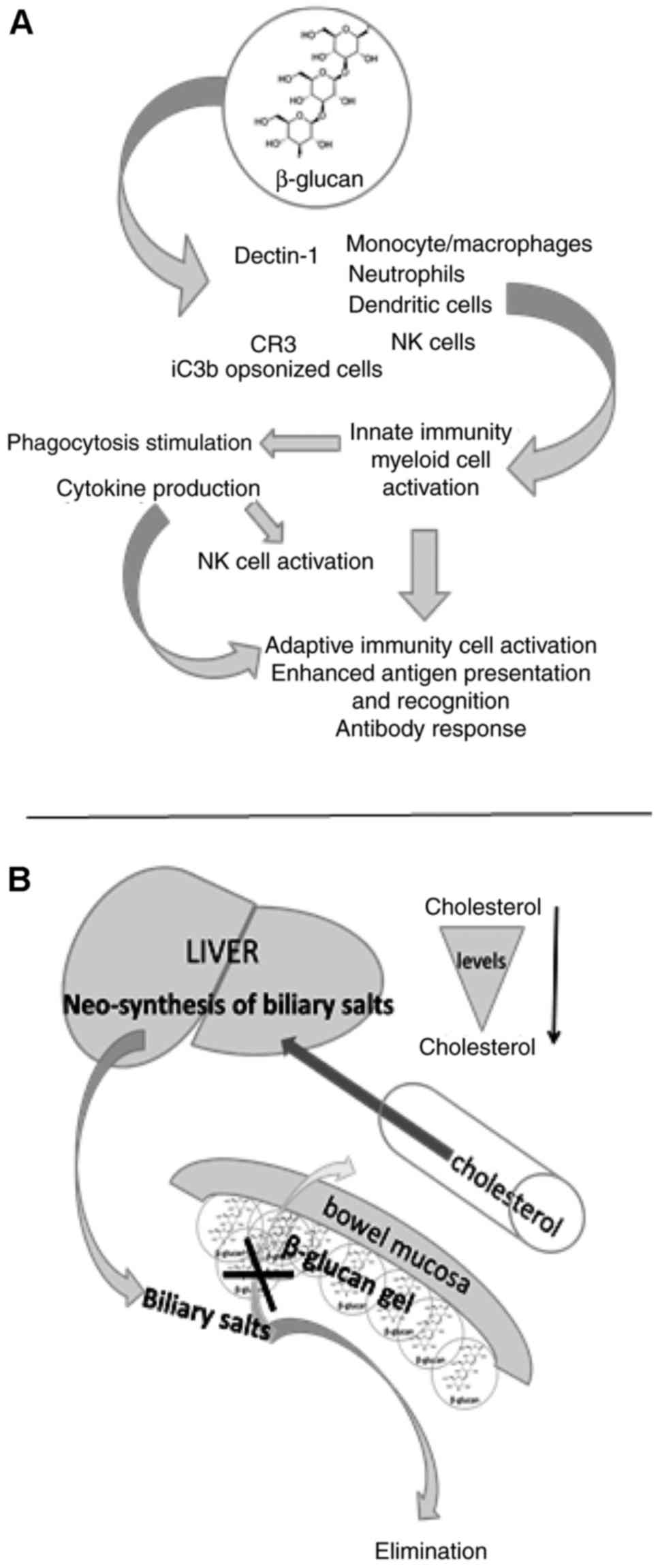
|
1
|
World Health Organization: Cardiovascular
disease. 2016
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization: Obesity and
overweight fact sheet. 2017
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization: Obesity and
overweight fact sheet. 2016
|
|
4
|
CDC, National Center for Chronic Disease
Prevention and Health Promotion and Division for Heart Disease and
Stroke Prevention: Heart Disease Facts and Statistics. CDC;
|
|
5
|
Murray CJ and Lopez AD: Alternative
projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global
Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 349:1498–1504. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oreopoulos A, Padwal R, Kalantar-Zadeh K,
Fonarow GC, Norris CM and McAlister FA: Body mass index and
mortality in heart failure: A meta-analysis. Am Heart J. 156:13–22.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clark JM and Brancati FL: The challenge of
obesity-related chronic diseases. J Gen Intern Med. 15:828–829.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oreopoulos A, Ezekowitz JA, McAlister FA,
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Fonarow GC, Norris CM, Johnson JA and Padwal RS:
Association between direct measures of body composition and
prognostic factors in chronic heart failure. Mayo Clin Proc.
85:609–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bose KS, Gupta SK and Vyas P:
Adipocytokine levels in genetically high risk for type 2 diabetes
in the Indian population: A cross-sectional study. Exp Diabetes
Res. 2012:3865242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olson NC, Callas PW, Hanley AJ, Festa A,
Haffner SM, Wagenknecht LE and Tracy RP: Circulating levels of
TNF-α are associated with impaired glucose tolerance, increased
insulin resistance, and ethnicity: The insulin resistance
atherosclerosis study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:1032–1040. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Emanuela F, Grazia M, Marco de R, Maria
Paola L, Giorgio F and Marco B: Inflammation as a link between
obesity and metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Metab. 2012:4763802012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harland JI: Food combinations for
cholesterol lowering. Nutr Res Rev. 25:249–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnston TP, Korolenko TA, Pirro M and
Sahebkar A: Preventing cardiovascular heart disease: Promising
nutraceutical and non-nutraceutical treatments for cholesterol
management. Pharmacol Res. 120:219–225. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chatzizisis YS, Koskinas KC, Misirli G,
Vaklavas C, Hatzitolios A and Giannoglou GD: Risk factors and drug
interactions predisposing to statin-induced myopathy: Implications
for risk assessment, prevention and treatment. Drug Saf.
33:171–187. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Camerino GM, Musumeci O, Conte E, Musaraj
K, Fonzino A, Barca E, Marino M, Rodolico C, Tricarico D, Camerino
C, et al: Risk of myopathy in patients in therapy with statins:
Identification of biological markers in a pilot study. Front
Pharmacol. 8:5002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Caparros-Martin JA, Lareu RR, Ramsay JP,
Peplies J, Reen FJ, Headlam HA, Ward NC, Croft KD, Newsholme P,
Hughes JD, et al: Statin therapy causes gut dysbiosis in mice
through a PXR-dependent mechanism. Microbiome. 5:952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verhaegh BP, de Vries F, Masclee AA,
Keshavarzian A, de Boer A, Souverein PC, Pierik MJ and Jonkers DM:
High risk of drug-induced microscopic colitis with concomitant use
of NSAIDs and proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
43:1004–1013. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Keefe SJ: Diet, microorganisms and their
metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:691–706. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peters U, Sinha R, Chatterjee N, Subar AF,
Ziegler RG, Kulldorff M, Bresalier R, Weissfeld JL, Flood A,
Schatzkin A, et al: Dietary fibre and colorectal adenoma in a
colorectal cancer early detection programme. Lancet. 361:1491–1495.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao QQ, Lin YW, Chen H, Qin J, Zheng XY,
Xu X and Xie LP: Dietary fiber intake is inversely associated with
risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr.
26:89–96. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohira H, Tsutsui W and Fujioka Y: Are
short chain fatty acids in hut microbiota defensive players for
inflammation and atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:660–672.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hernandez-Rodas MC, Valenzuela R and
Videla LA: Relevant aspects of nutritional and dietary
interventions in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci.
16:25168–25198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burton-Freeman B, Liyanage D, Rahman S and
Edirisinghe I: Ratios of soluble and insoluble dietary fibers on
satiety and energy intake in overweight pre- and postmenopausal
women. Nutr Healthy Aging. 4:157–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adam CL, Thomson LM, Williams PA and Ross
AW: Soluble fermentable dietary fibre (Pectin) decreases caloric
intake, adiposity and lipidaemia in high-fat diet-induced obese
rats. PLoS One. 10:e01403922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Torcello-Gómez A, Fernández Fraguas C,
Ridout MJ, Woodward NC, Wilde PJ and Foster TJ: Effect of
substituent pattern and molecular weight of cellulose ethers on
interactions with different bile salts. Food Funct. 6:730–739.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meneses ME, Martinez-Carrera D, Torres N,
Sánchez-Tapia M, Aguilar-López M, Morales P, Sobal M, Bernabé T,
Escudero H, Granados-Portillo O and Tovar AR: Hypocholesterolemic
properties and prebiotic effects of Mexican Ganoderma lucidum in
C57BL/6 mice. PLoS One. 11:e01596312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hung TV and Suzuki T: Dietary fermentable
fiber reduces intestinal barrier defects and inflammation in
colitic mice. J Nutr. 146:1970–1979. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong Y, Marungruang N, Fak F and Nyman M:
Effects of two whole-grain barley varieties on caecal SCFA, gut
microbiota and plasma inflammatory markers in rats consuming low-
and high-fat diets. Br J Nutr. 113:1558–1570. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo Y, Zhang L, Li H, Smidt H, Wright AG,
Zhang K, Ding X, Zeng Q, Bai S, Wang J, et al: Different types of
dietary fibers trigger specific alterations in composition and
predicted functions of colonic bacterial communities in BALB/c
mice. Front Microbiol. 8:9662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Winglee K and Fodor AA: Intrinsic
association between diet and the gut microbiome: Current evidence.
Nutr Diet Suppl. 7:69–76. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jakobsdottir G, Xu J, Molin G, Ahrné S and
Nyman M: High-fat diet reduces the formation of butyrate, but
increases succinate, inflammation, liver fat and cholesterol in
rats, while dietary fibre counteracts these effects. PLoS One.
8:e804762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vannucci L, Krizan J, Sima P, Stakheev D,
Caja F, Rajsiglova L, Horak V and Saieh M: Immunostimulatory
properties and anti-tumor activities of glucans (Review). Int J
Oncol. 43:357–364. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chanput W, Reitsma M, Kleinjans L, Mes JJ,
Savelkoul HF and Wichers HJ: β-Glucans are involved in
immune-modulation of THP-1 macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res.
56:822–833. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ho HV, Sievenpiper JL, Zurbau A, Blanco
Mejia S, Jovanovski E, Au-Yeung F, Jenkins AL and Vuksan V: The
effect of oat β-glucan on LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol and
apoB for CVD risk reduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of randomized-controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 116:1369–1382. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Caz V, Gil-Ramirez A, Largo C, Tabernero
M, Santamaría M, Martín-Hernández R, Marín FR, Reglero G and
Soler-Rivas C: Modulation of cholesterol-related gene expression by
dietary fiber fractions from edible mushrooms. J Agric Food Chem.
63:7371–7380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barsanti L, Passarelli V, Evangelista V,
Frassanito AM and Gualtieri P: Chemistry, physico-chemistry and
applications linked to biological activities of β-glucans. Nat Prod
Rep. 28:457–466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Anderson JW, Baird P, Davis RH Jr, Ferreri
S, Knudtson M, Koraym A, Waters V and Williams CL: Health benefits
of dietary fiber. Nutr Rev. 67:188–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Van Horn L, McCoin M, Kris-Etherton PM,
Burke F, Carson JA, Champagne CM, Karmally W and Sikand G: The
evidence for dietary prevention and treatment of cardiovascular
disease. J Am Diet Assoc. 108:287–331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: Effects of
yeast-derived beta-glucans on blood cholesterol and macrophage
functionality. J Immunotoxicol. 6:30–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Groot A, Luyken R and Pikaar NA:
Cholesterol-lowering effect of rolled oats. Lancet. 2:303–304.
1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Czop JK: The role of beta-glucan receptors
on blood and tissue leukocytes in phagocytosis and metabolic
activation. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 5:286–296. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Estrada A, Yun CH, Van Kessel A, Li B,
Hauta S and Laarveld B: Immunomodulatory activities of oat
beta-glucan in vitro and in vivo. Microbiol Immunol. 41:991–998.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Torrence PF: Biological response
modifiers: New approaches to disease intervention. Academic Press;
Orlando: pp. 3971985
|
|
45
|
Novak M and Vetvicka V: Beta-glucans,
history, and the present: Immunomodulatory aspects and mechanisms
of action. J Immunotoxicol. 5:47–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: β1,3-Glucan:
Silver bullet or hot air. Open Glycoscience. 3:1–6. 2010.
|
|
47
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: Comparison of
immunological effects of commercially available β-glucans: Part
III. Int J Clin Pathol. 2:2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Würsch P and Pi-Sunyer FX: The role of
viscous soluble fiber in the metabolic control of diabetes. A
review with special emphasis on cereals rich in beta-glucan.
Diabetes Care. 20:1774–1780. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mosikanon K, Arthan D, Kettawan A,
Tungtrongchitr R and Prangthip P: Yeast β-glucan modulates
inflammation and waist circumference in overweight and obese
subjects. J Diet Suppl. 14:173–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Browder W, Williams D, Lucore P, Pretus H,
Jones E and McNamee R: Effect of enhanced macrophage function on
early wound healing. Surgery. 104:224–230. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: Anti-stress
action of an orally-given combination of resveratrol, β-glucan, and
vitamin C. Molecules. 19:13724–13734. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: β-glucan
attenuates chronic fatigue syndrome in murine model. J Nat Sci.
1:e1122015.
|
|
53
|
Sima P, Vannucci L and Vetvicka V: Glucans
and cancer: Historical perspective. Cancer Translational Med.
1:209–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Barbieri A, Quagliariello V, Del Vecchio
V, Falco M, Luciano A, Amruthraj NJ, Nasti G, Ottaiano A, Berretta
M, Iaffaioli RV and Arra C: Anticancer and anti-inflammatory
properties of gano-derma lucidum extract effects on melanoma and
triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Nutrients. 9:pii:E2102017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Richter J, Kral V, Svozil V, Rajnohova DL,
Pohorska JI and Vetvicka V: Effects of transfer point glucan #300
supplementation on children exposed to passive
smoking-placebo-driven double-blind clinical trials. J Nutr Health.
1:1052014.
|
|
56
|
Vetvicka V, Richter J, Svozil V, Rajnohová
Dobiášová L and Král V: Placebo-driven clinical trials of
yeast-derived β-(1-3) glucan in children with chronic respiratory
problems. Ann Transl Med. 1:262013.
|
|
57
|
Brown GD and Gordon S: Immune recognition.
A new receptor for beta-glucans. Nature. 413:36–37. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stambach NS and Taylor ME:
Characterization of carbohydrate recognition by langerin, a C-type
lectin of Langerhans cells. Glycobiology. 13:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Allendorf DJ, Ostroff GR, BAran JT, et al:
Oral WGP beta glucan treatment accelerates myeloid recovery and
survival after irradiation wxposure. BTR 2003: Unified Science
& Technology for Reducing Biological Threats & Counterin
Terrorism Albuquesrque: University of New Mexico; pp. 104–113.
2003
|
|
60
|
Ross GD and Vĕtvicka V: CR3 (CD11b. CD18):
A phagocyte and NK cell membrane receptor with multiple ligand
specificities and functions. Cell Exp Immunol. 92:181–184. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Xia Y, Vetvicka V, Yan J, Hanikyrová M,
Mayadas T and Ross GD: The beta-glucan-binding lectin site of mouse
CR3 (CD11b/CD18) and its function in generating a primed state of
the receptor that mediates cytotoxic activation in response to
iC3b-opsonized target cells. J Immunol. 162:2281–2290.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Legentil L, Paris F, Ballet C, Trouvelot
S, Daire X, Vetvicka V and Ferrières V: Molecular interactions of
β-(1→>3)-glucans with their receptors. Molecules. 20:9745–9766.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Williams DL, Ha T, Li C, Laffan J,
Kalbfleisch J and Browder W: Inhibition of LPS-induced NFkappaB
activation by a glucan ligand involves down-regulation of IKKbeta
kinase activity and altered phosphorylation and degradation of
IkappaBalpha. Shock. 13:446–452. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rogers NC, Slack EC, Edwards AD, Nolte MA,
Schulz O, Schweighoffer E, Williams DL, Gordon S, Tybulewicz VL,
Brown GD and Reis e Sousa C: Syk-dependent cytokine induction by
Dectin-1 reveals a novel pattern recognition pathway for C type
lectins. Immunity. 22:507–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Elcombe SE, Naqvi S, Van Den Bosch MW,
MacKenzie KF, Cianfanelli F, Brown GD and Arthur JS: Dectin-1
regulates IL-10 production via a MSK1/2 and CREB dependent pathway
and promotes the induction of regulatory macrophage markers. PLoS
One. 8:e600862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Větvička V: (Beta)-glucans as natural
biological response modifiers. Nova Science Publishers Inc; New
York: 2013
|
|
67
|
Orth M and Bellosta S: Cholesterol: Its
regulation and role in central nervous system disorders.
Cholesterol. 2012:2925982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li T and Chiang JY: Regulation of bile
acid and cholesterol metabolism by PPARs. PPAR Res.
2009:5017392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Worthmann A, John C, Rühlemann MC, Baguhl
M, Heinsen FA, Schaltenberg N, Heine M, Schlein C, Evangelakos I,
Mineo C, et al: Cold-induced conversion of cholesterol to bile
acids in mice shapes the gut microbiome and promotes adaptive
thermogenesis. Nat Med. 23:839–849. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li T and Chiang JY: Bile acids as
metabolic regulators. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 31:159–165. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: How LDL
receptors influence cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Sci Am.
251:58–66. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Russell DW: The enzymes, regulation, and
genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 72:137–174.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kuipers F, Bloks VW and Groen AK: Beyond
intestinal soap-bile acids in metabolic control. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 10:488–498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gibbons GF, Wiggins D, Brown AM and
Hebbachi AM: Synthesis and function of hepatic
very-low-density-lipoprotein. Biochem Soc Trans. 32:59–64. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Davidson WS and Hilliard GM: The spatial
organization of apolipoprotein A-I on the edge of discoidal high
density lipo-protein particles. J Biol Chem. 278:27199–27207. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
de Oliveira Alvim R, Mourao-Junior CA,
Magalhaes GL, de Oliveira CM, Krieger JE, Mill JG and Pereira AC:
Non-HDL cholesterol is a good predictor of the risk of incfeased
arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women in an urban Brazilian
population. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 72:106–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ,
Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, Jacobs DR Jr, Bangdiwala S and
Tyroler HA: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular
disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation. 79:8–15.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Srinivasan SR, Myers L and Berenson GS:
Distribution and correlates of non-high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol in children: The Bogalusa heart study. Pediatrics.
110:e292002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hoenig MR: Implications of the obesity
epidemic for lipid-lowering therapy: Non-HDL cholesterol should
replace LDL cholesterol as the primary therapeutic target. Vasc
Health Risk Manag. 4:143–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
The National Cholesterol Education
Program. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/atglance.pdf.
|
|
81
|
Masson D, Koseki M, Ishibashi M, Larson
CJ, Miller SG, King BD and Tall AR: Increased HDL cholesterol and
apoA-I in humans and mice treated with a novel SR-BI inhibitor.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:2054–2060. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
White CR, Garber DW and Anantharamaiah GM:
Anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-reducing properties of
apolipoprotein mimetics: A review. J Lipid Res. 55:2007–2021. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Parathasarathy S, Raghavamenon A,
Garelnabi MO and Santanam N: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein.
Methods Mol Biol. 610:403–417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Besler C, Lüscher TF and Landmesser U:
Molecular mechanisms of vascular effects of high-density
lipoprotein: Alternations in cardiovascular disease. EMBO Mol Med.
4:251–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Stary HC: The sequence of cell and matrix
changes in athero-sclerotic lesions of coronary arteries in the
first forty years of life. Eur Heart J. 11(Suppl E): S3–S19. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Sullivan MP, Cerda JJ, Robbins FL, Burgin
CW and Beatty RJ: The gerbil, hamster, and guinea pig as rodent
models for hyper-lipidemia. Lab Anim Sci. 43:575–578.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sima A, Stancu C, Constantinescu E,
Ologeanu L and Simionescu M: The hyperlipemic hamster-a model for
testing the anti-atherogenic effect of amlodipine. J Cell Mol Med.
5:153–162. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Ohmura H, Fukushima Y, Mizuno A, Niwa K,
Kobayashi Y, Ebina T, Kimura K, Ishibashi S and Daida H: Research
Committee on Primary Hyperlipidemia of the Ministry of Health and
Welfare of Japan: Estimated prevalence of heterozygous familial
hypercholesterolemia in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int
Heart J. 58:88–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Rosenson RS, Brewer HB Jr, Ansell BJ,
Barter P, Chapman MJ, Heinecke JW, Kontush A, Tall AR and Webb NR:
Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat
Rev Cardiol. 13:48–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Gistera A and Hansson GK: The immunology
of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:368–380. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jonsson AL and Bäckhed F: Role of gut
microbiota in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 14:79–87. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Babicek K, Cehová I, Simon RR, Harwood M
and Cox DJ: Toxicological assesment of a particulate yeast
(1,3/1,6)-beta-D-glucan in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 45:1719–1730.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Brown L, Rosner B, Willett WW and Sacks
FM: Cholesterol-lowering effects of dietary fiber: A meta-analysis.
Am J Clin Nutr. 69:30–42. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Phillips GO and Cui SW: An introduction:
Evolution and finalisation of the regulatory definition of dietary
fibre. Food Hydrocolloids. 25:139–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Slavin JL: Dietary fiber and body weight.
Nutrition. 21:4114182005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Cheung PCK: Mini-review on edible
mushrooms as source of dietary fiber: Preparation and health
benefits. Food Sci Human Wellness. 2:162–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Axelsen M,
Augustin LS and Vuksan V: Viscous and nonviscous fibres,
nonabsorbable and low glycaemic index carbohydrates, blood lipids
and coronary heart disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 11:49–56. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Gee JM, Blackburn NA and Johnson IT: The
influence of guar gum on intestinal cholesterol transport in the
rat. Br J Nutr. 50:215–224. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chau CF and Huang YL: Effects of the
insoluble fiber derived from Passiflora edulis seed on plasma and
hepatic lipids and fecal output. Mol Nutr Food Res. 49:786–790.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Cho IJ, Lee C and Ha TY: Hypolipidemic
effect of soluble fiber isolated from seeds of Cassia tora Linn. In
rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Agric Food Chem. 55:1592–1596.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zacherl C, Eisner P and Engel KH: In vitro
model to correlate viscosity and bile acid-binding capacity of
digested water-soluble and insoluble dietary fibres. Food Chem.
126:423–428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Aoki S, Iwai A, Kawata K, Muramatsu D,
Uchiyama H, Okabe M, Ikesue M, Maeda N and Uede T: Oral
administration of the Aureobasidium pullulans-derived β-glucan
effectively prevents the development of high fat diet-induced fatty
liver in mice. Sci Rep. 5:104572015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kaczmarczyk MM, Miller MJ and Freund GG:
The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of
type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer.
Metabolism. 61:1058–1066. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Drew BG, Fidge NH, Gallon-Beaumier G, Kemp
BE and Kingwell BA: High-density lipoprotein and apolipoprotein AI
increase endothelial NO synthase activity by protein association
and multisite phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:6999–7004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Roy CC, Kien CL, Bouthillier L and Levy E:
Short-chain fatty acids: Ready for prime time. Nutr Clin Pract.
21:351–366. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK,
Venema K, Reijngoud DJ and Bakker BM: The role of short-chain fatty
acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host
energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. 54:2325–2340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chan GC, Chan WK and Sze DM: The effects
of beta-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol.
2:252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Al-Lahham SH, Peppelenbosch MP, Roelofsen
H, Vonk RJ and Venema K: Biological effects of propionic acid in
humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying
mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1801:1175–1183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wismar R, Brix S, Frøkiaer H and Laerke
HN: Dietary fibers as immunoregulatory compounds in health and
disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1190:70–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Vangaveti V, Shashidhar V, Jarrod G, Baune
BT and Kennedy RL: Free fatty acid receptors: Emerging targets for
treatment of diabetes and its complications. Ther Adv Endocrinol
Metab. 1:165–175. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Warnberg J, Gomez-Martinez S, Romeo J,
Diaz LE and Marcos A: Nutrition, inflammation, and cognitive
function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1153:164–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Cosola C, De Angelis M, Rocchetti MT,
Montemurno E, Maranzano V, Dalfino G, Manno C, Zito A, Gesualdo M,
Ciccone MM, et al: Beta-glucans supplementation associates with
reduction in P-Cresyl sulfate levels and improved endo-thelial
vascular reactivity in healthy individuals. PLoS One.
12:e01696352017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Mansbach CM II and Gorelick F: Development
and physiological regulation of intestinal lipid absorption. II.
Dietary lipid absorption, complex lipid synthesis, and the
intracellular packaging and secretion of chylomicrons. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G645–G650. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Black DD: Development and physiological
regulation of intestinal lipid absorption. I. Development of
intestinal lipid absorption: Cellular events in chylomicron
assembly and secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
293:G519–G524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: The SREBP
pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a
membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 89:331–340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sato R: Sterol metabolism and SREBP
activation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 501:177–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Drozdowski LA, Reimer RA, Temelli F, Bell
RC, Vasanthan T and Thomson AB: Beta-glucan extracts inhibit the in
vitro intestinal uptake of long-chain fatty acids and cholesterol
and down-regulate genes involved in lipogenesis and lipid transport
in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 21:695–701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Chen J and Huang XF: The effects of diets
enriched in beta-glucans on blood lipoprotein concentrations. J
Clin Lipidol. 3:154–158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Monteferrario F,
Klersy C, Cazzola R and Cestaro B: Beta-glucan- or rice
bran-enriched foods: A comparative crossover clinical trial on
lipidic pattern in mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Eur J Clin
Nutr. 65:864–871. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Wolever TM, Tosh SM, Gibbs AL,
Brand-Miller J, Duncan AM, Hart V, Lamarche B, Thomson BA, Duss R
and Wood PJ: Physicochemical properties of oat β-glucan influence
its ability to reduce serum LDL cholesterol in humans: A randomized
clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 92:723–732. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Johnson IT and Gee JM: Effect of
gel-forming gums on the intestinal unstirred layer and sugar
transport in vitro. Gut. 22:398–403. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Kirby RW, Anderson JW, Sieling B, Rees ED,
Chen WJ, Miller RE and Kay RM: Oat-bran intake selectively lowers
serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations of
hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 34:824–829.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fadel JG, Newman RK, Newman CW and Barnes
AE: Hypocholesterolemic effects of beta-glucans in different barley
diets fed to broiler chicks. Nutr Rep Int. 35:1049–1058. 1987.
|
|
125
|
Li J, Kaneko T, Qin LQ, Wang J, Wang Y and
Sato A: Long-term effects of high dietary fiber intake on glucose
tolerance and lipid metabolism in GK rats: Comparison among barley,
rice, and cornstarch. Metabolism. 52:1206–1210. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sima A, Bulla A and Simionescu N:
Experimental obstructive coronary atherosclerosis in the
hyperlipidemic hamster. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 22:1–16.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Lim MK, Ku SK, Choi JS and Kim JW: Effect
of polycan, a β-glucan originating from Aureobasidium, on a
high-fat diet-induced hyperlipemic hamster model. Exp Ther Med.
9:1369–1378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Delaney B, Nicolosi RJ, Wilson TA, Carlson
T, Frazer S, Zheng GH, Hess R, Ostergren K, Haworth J and Knutson
N: Beta-glucan fractions from barley and oats are similarly
anti-atherogenic in hypercholesterolemic Syrian golden hamsters. J
Nutr. 133:468–475. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Wilson TA, Nicolosi RJ, Delaney B,
Chadwell K, Moolchandani V, Kotyla T, Ponduru S, Zheng GH, Hess R,
Knutson N, et al: Reduced and high molecular weight barley
beta-glucans decrease plasma total and non-HDL-cholesterol in
hypercholesterolemic Syrian golden hamsters. J Nutr. 134:2617–2622.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wu YS, Ho SY, Nan FH and Chen SN:
Ganoderma lucidum beta 1,3/1,6 glucan as an immunomodulator in
inflammation induced by a high-cholesterol diet. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 16:5002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kusmiati and Dhewantara FX:
Cholesterol-lowering effect of beta glucan extracted from
Saccharomyces cerevisiae in rats. Sci Pharm. 84:153–165. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Tong LT, Zhong K, Liu L, Zhou X, Qiu J and
Zhou S: Effects of dietary hull-less barley β-glucan on the
cholesterol metabolism of hypercholesterolemic hamsters. Food Chem.
169:344–349. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J: Physiological
effects of different types of beta-glucan. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ
Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 151:225–231. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Malkki Y: Oat fiber. Food Science and
Technology: Handbook of Dietary Fiber. Cho S and Dreher ML: M.
Dekker; New York: pp. 497–512. 2001
|
|
135
|
Veniant MM, Withycombe S and Young SG:
Lipoprotein size and atherosclerosis susceptibility in
Apoe−/− and Ldlr−/− mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 21:1567–1570. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Pendse AA, Arbones-Mainar JM, Johnson LA,
Altenburg MK and Maeda N: Apolipoprotein E knock-out and knock-in
mice: Atherosclerosis, metabolic syndrome, and beyond. J Lipid Res.
50(Suppl): S178–S182. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
137
|
Anderson JW, Story L, Sieling B, Chen WJ,
Petro MS and Story J: Hypocholesterolemic effects of oat-bran or
bean intake for hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr.
40:1146–1155. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Anderson JW and Gustafson NJ:
Hypocholesterolemic effects of oat and bean products. Am J Clin
Nutr. 48(Suppl 3): S749–S753. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Braaten JT, Wood PJ, Scott FW, Wolynetz
MS, Lowe MK, Bradley-White P and Collins MW: Oat beta-glucan
reduces blood cholesterol concentration in hypercholesterolemic
subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 48:465–474. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Newman RK, Lewis SE, Newman CW, Boik RJ
and Ramage RT: Hypocholesterolemic effect of barley foods on
healthy men. Nutr Rep Int. 39:749–760. 1989.
|
|
141
|
McIntosh GH, Whyte J, McArthur R and
Nestel PJ: Barley and wheat foods: Influence on plasma cholesterol
concentrations in hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr.
53:1205–1209. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Lupton JR, Robinson MC and Morin JL:
Cholesterol-lowering effect of barley bran flour and oil. J Am Diet
Assoc. 94:65–70. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Lia A, Hallmans G, Sandberg AS, Sundberg
B, Aman P and Anderson H: Oat beta-glucan increases bile excretion
and a fiber rich barley fracton increases cholesterol excretion in
ileostomy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 62:1245–1251. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Bell S, Goldman VM, Bistrian BR, Arnold
AH, Ostroff G and Forse RA: Effect of beta-glucan from oats and
yeast on serum lipids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 39:189–202. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Li J, Kaneko T, Qin LQ, Wang J and Wang Y:
Effects of barley intake on glucose tolerance, lipid metabolism,
and bowel function in women. Nutrition. 19:926–929. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Behall KM, Scholfield DJ and Hallfrisch J:
Diets containing barley significantly reduce lipids in mildly
hypercholesterolemic men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 80:1185–1193.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Behall KM, Scholfield DJ and Hallfrisch J:
Lipids significantly reduced by diets containing barley in
moderately hypercholes-terolemic men. J Am Coll Nutr. 23:55–62.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Keenan JM, Goulson M, Shamliyan T, Knutson
N, Kolberg L and Curry L: The effects of concentrated barley
beta-glucan on blood lipids in a population of
hypercholesterolaemic men and women. Br J Nutr. 97:1162–1168. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Shimizu C, Kihara M, Aoe S, Araki S, Ito
K, Hayashi K, Watari J, Sakata Y and Ikegami S: Effect of high
beta-glucan barley on serum cholesterol concentrations and visceral
fat area in Japanese men-a randomized, double-blinded,
placebo-controlled trial. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 63:21–25. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Sundberg B: Cholesterol lowering effects
of a barley fibre flake product. Agro Food Industry Hi-Tech.
19:14–17. 2008.
|
|
151
|
Zhu X, Sun X, Wang M, Zhang C, Cao Y, Mo
G, Liang J and Zhu S: Quantitative assessment of the effects of
beta-glucan consumption on serum lipid profile and glucose level in
hypercholesterolemic subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
25:714–723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Keogh GF, Cooper GJ, Mulvey TB, McArdle
BH, Coles GD, Monro JA and Poppitt SD: Randomized controlled
crossover study of the effect of a highly beta-glucan-enriched
barley on cardiovascular disease risk factors in mildly
hypercholesterol-emic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 78:711–718. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Biörklund M, van Rees A, Mensink RP and
Onning G: Changes in serum lipids and postprandial glucose and
insulin concentrations after consumption of beverages with
beta-glucans from oats or barley: A randomised dose-controlled
trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 5. 9:1272–1281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Ibrügger S, Kristensen M, Poulsen MW,
Mikkelsen MS, Ejsing J, Jespersen BM, Dragsted LO, Engelsen SB and
Bügel S: Extracted oat and barley β-glucans do not affect
cholesterol metabolism in young healthy adults. J Nutr.
143:1579–1585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Talati R, Baker WL, Pabilonia MS, White CM
and Coleman CI: The effects of barley-derived soluble fiber on
serum lipids. Ann Fam Med. 7:157–163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
AbuMweis SS, Jew S and Ames NP: β-glucan
from barley and its lipid-lowering capacity: A meta-analysis of
randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. 64:1472–1480. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Anderson TJ, Grégoire J, Hegele RA,
Couture P, Mancini GB, McPherson R, Francis GA, Poirier P, Lau DC,
Grover S, et al: 2012 update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society
guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia for the
prevention of cardiovascular disease in the adult. Can J Cardiol.
29:151–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Newman RK and Newman CW: Barley for food
and health: Science, technology, and products. Genetics and
Nutrient Composition. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ: pp.
56–94. 2008
|
|
159
|
Ho HV, Sievenpiper JL, Zurbau A, Blanco
Mejia S, Jovanovski E, Au-Yeung F, Jenkins AL and Vuksan V: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
of the effect of barley β-glucan on LDL-C, non-HDL-C and apoB for
cardiovascular disease risk reductioni-iv. Eur J Clin Nutr.
70:13402016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Mori K, Kobayashi C, Tomita T, Inatomi S
and Ikeda M: Antiatherosclerotic effect of the edible mushrooms
Pleurotus eryngii (Eringi), Grifola frondosa (Maitake), and
Hypsizygus marmoreus (Bunashimeji) in apolipoprotein E-deficient
mice. Nutr Res. 28:335–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Sun JE, Ao ZH, Lu ZM, Xu HY, Zhang XM, Dou
WF and Xu ZH: Antihyperglycemic and antilipidperoxidative effects
of dry matter of culture broth of Inonotus obliquus in submerged
culture on normal and alloxan-diabetes mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
118:7–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Bays HE, Evans JL, Maki KC, Evans M,
Maquet V, Cooper R and Anderson JW: Chitin-glucan fiber effects on
oxidized low-density lipoprotein: A randomized controlled trial.
Eur J Clin Nutr. 67:2–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
163
|
Serra-Majem L, Roman B and Estruch R:
Scientific evidence of interventions using the Mediterranean diet:
A systematic review. Nutr Rev. 64(Suppl): S27–S47. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Wang Y, Harding SV, Eck P, Thandapilly SJ,
Gamel TH, Abdel-Aal el-SM, Crow GH, Tosh SM, Jones PJ and Ames NP:
High-molecular-weight β-glucan decreases serum cholesterol
differentially based on the CYP7A1 rs3808607 polymorphism in mildly
hypercholesterolemic adults. J Nutr. 146:720–727. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|