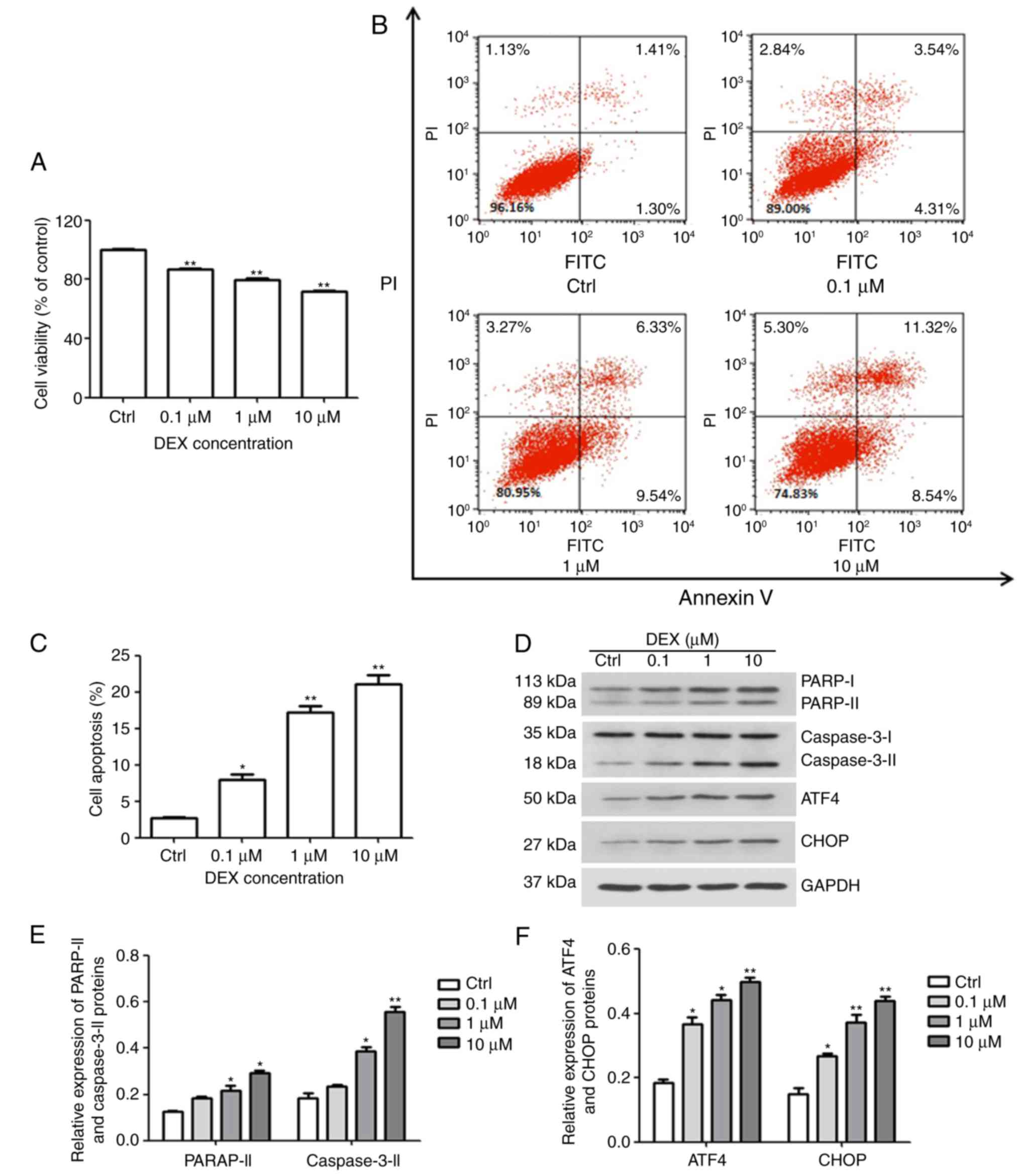
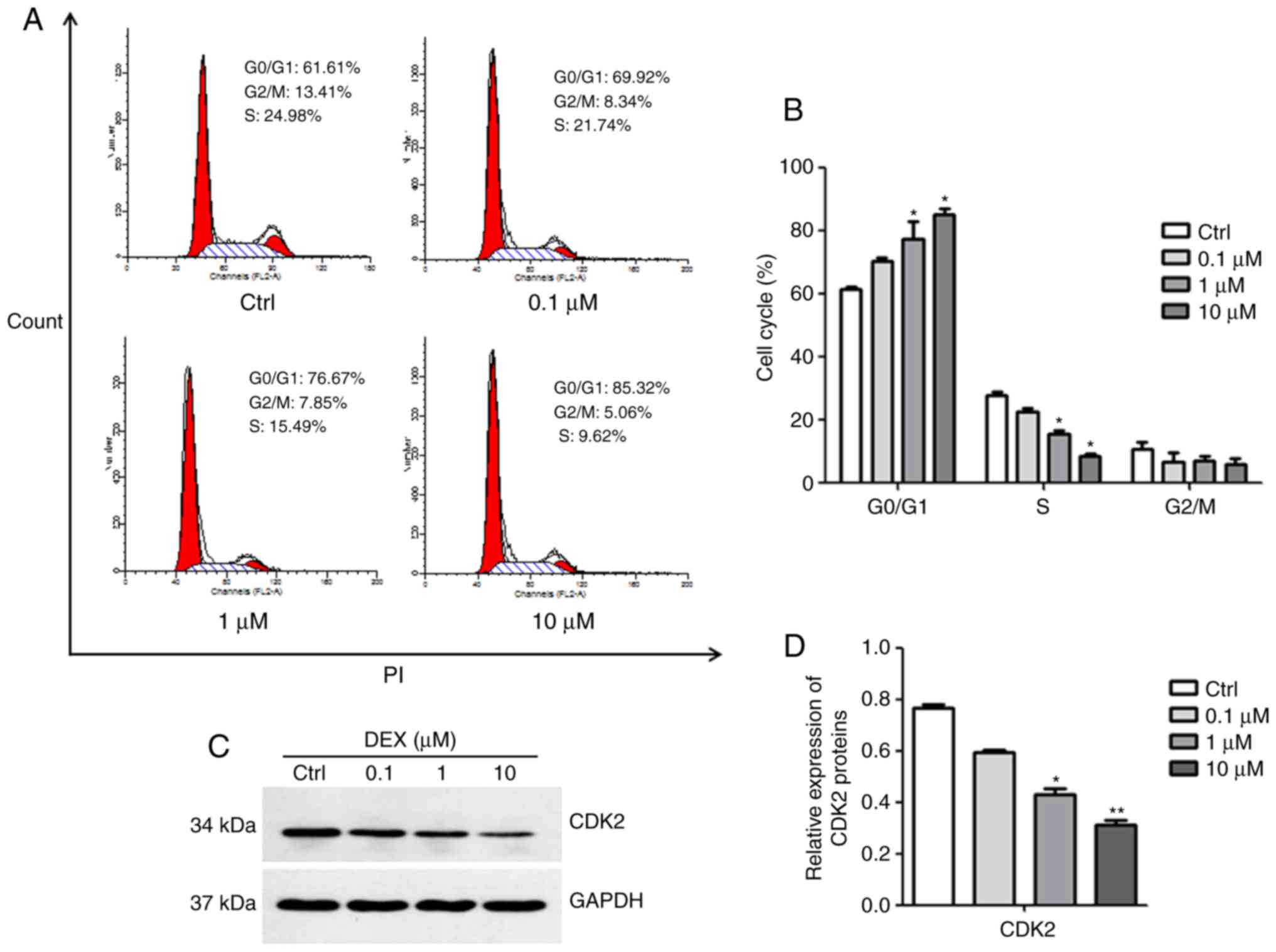
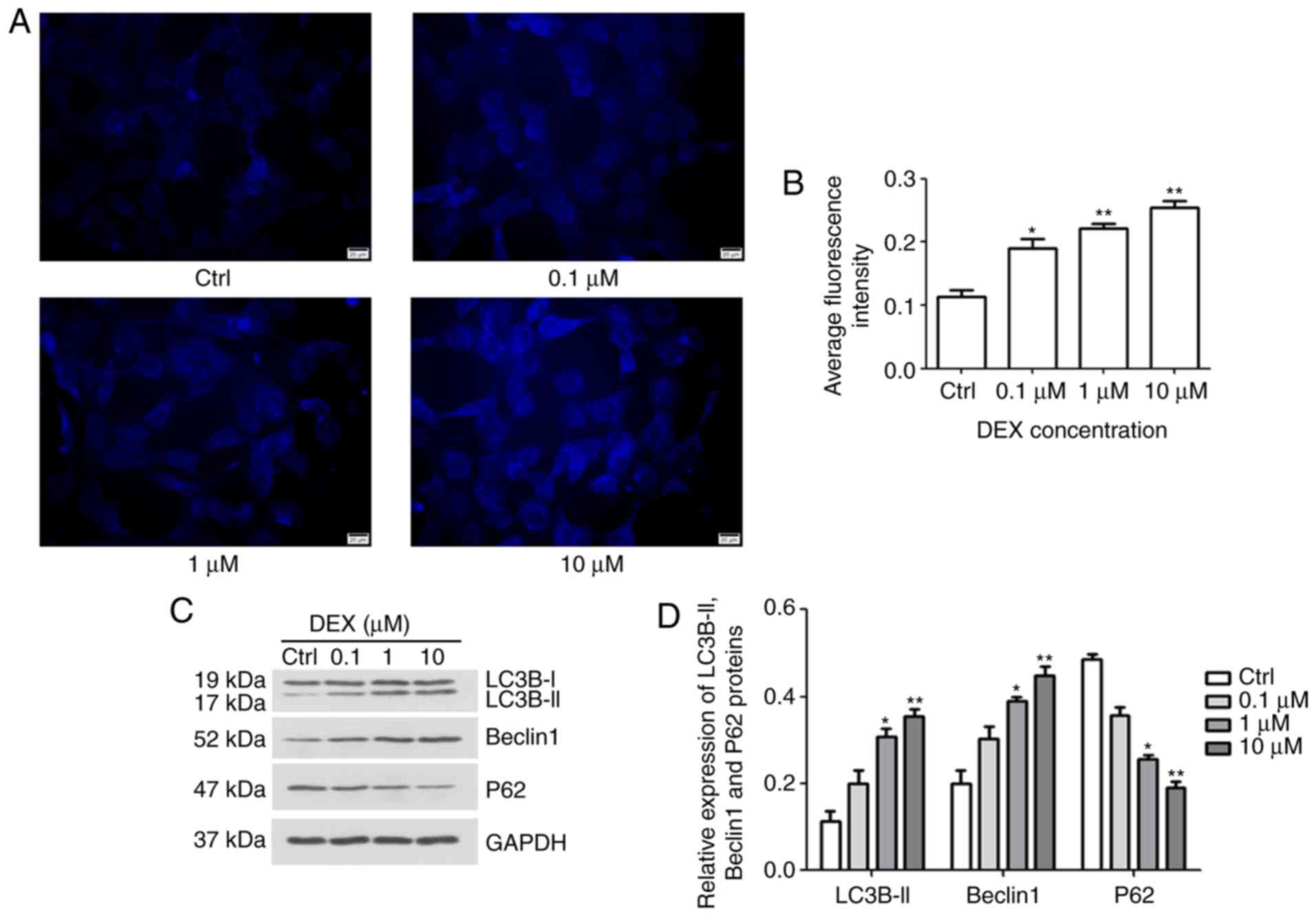
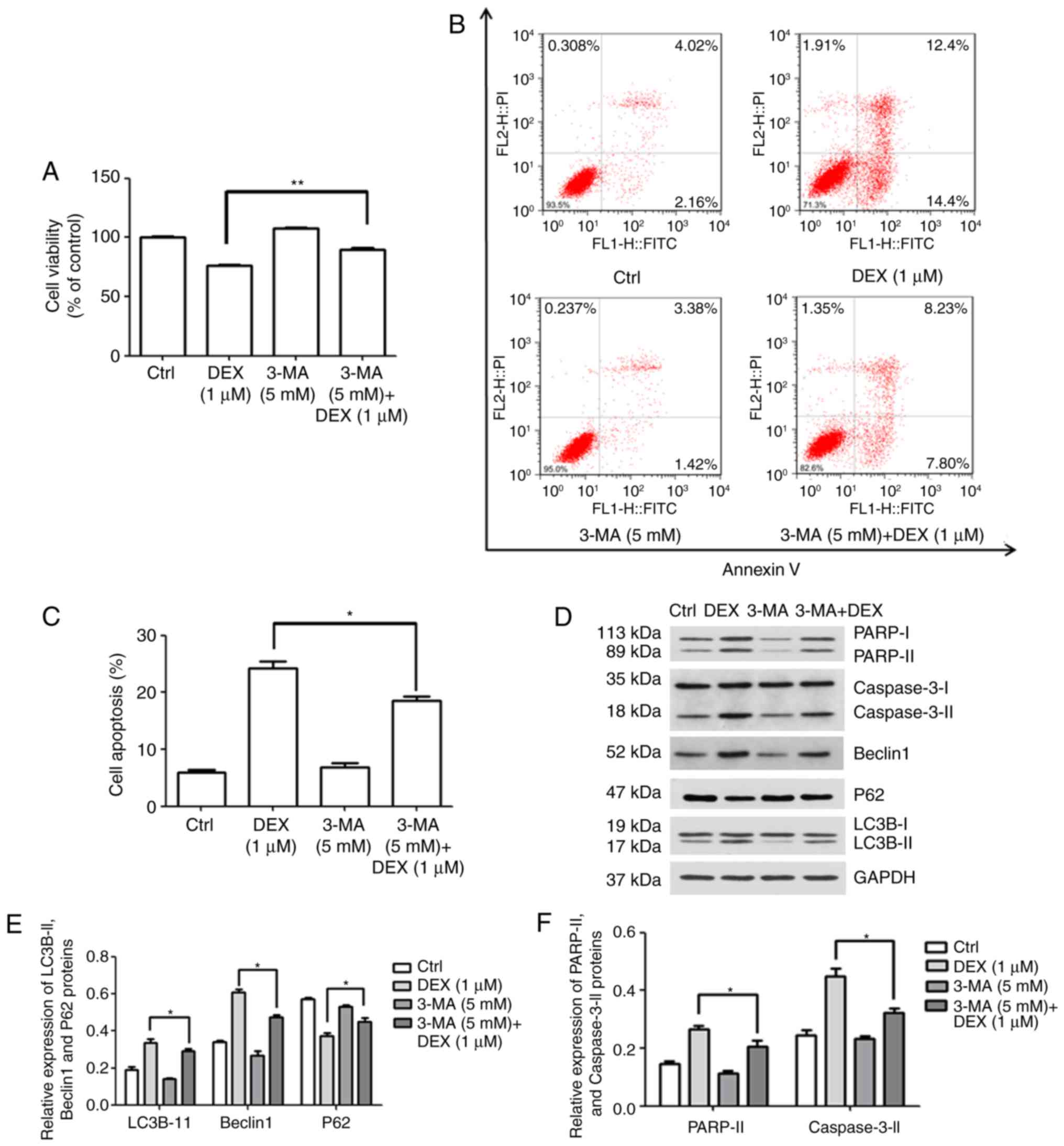
|
1
|
Kenanidis E, Potoupnis ME, Kakoulidis P,
Leonidou A, Sakellariou GT, Sayegh FE and Tsiridis E: Management of
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: Clinical data in relation to
disease demographics, bone mineral density and fracture risk.
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 14:1035–1053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bultink IE, Baden M and Lems WF:
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: An update on current
pharmacotherapy and future directions. Exp Opinion Pharmacotherapy.
14:185–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weinstein RS: Clinical practice.
Glucocorticoid-induced bone disease. N Engl J Med. 365:62–70. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weinstein RS: Glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
41:595–611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim J, Lee H, Kang KS, Chun KH and Hwang
GS: Protective effect of Korean Red Ginseng against
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in vitro and in vivo. J Ginseng
Res. 39:46–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yun SI, Yoon HY, Jeong SY and Chung YS:
Glucocorticoid induces apoptosis of osteoblast cells through the
activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Bone Miner Metab.
27:140–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gu G, Hentunen TA, Nars M, Härkönen PL and
Väänänen HK: Estrogen protects primary osteocytes against
glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 10:583–595. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arai M, Shibata Y, Pugdee K, Abiko Y and
Ogata Y: Effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on antioxidant
system and osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. IUBMB
Life. 59:27–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schröder K: NADPH oxidases in bone
homeostasis and osteoporosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:25–38. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Filaire E and Toumi H: Reactive oxygen
species and exercise on bone metabolism: Friend or enemy. Joint
Bone Spine. 79:341–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, Guicheux
J and Wittrant Y: Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease.
Trends Mol Med. 15:468–477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chu CC, Chua BH, Chen Z, Landy C and Hamdy
RC: Dexamethasone induces caspase activation in murine osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1642:79–85. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Biederbick A, Kern HF and Elsässer HP:
Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for
autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol. 66:3–14. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eruslanov E and Kusmartsev S:
Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry.
Methods Mol Biol. 594:57–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heckmann BL, Yang X, Zhang X and Liu J:
The autophagic inhibitor 3-methyladenine potently stimulates
PKA-dependent lipolysis in adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 168:163–171.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
de Quervain D, Schwabe L and Roozendaal B:
Stress, gluco-corticoids and memory: Implications for treating
fear-related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 18:7–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fowler TW, Acevedo C, Mazur CM, Hall-Glenn
F, Fields AJ, Bale HA, Ritchie RO, Lotz JC, Vail TP and Alliston T:
Glucocorticoid suppression of osteocyte perilacunar remodeling is
associated with subchondral bone degeneration in osteonecrosis. Sci
Rep. 7:446182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Woolf AD: An update on
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
19:370–375. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Henneicke H, Gasparini SJ,
Brennan-Speranza TC, Zhou H and Seibel MJ: Glucocorticoids and
bone: Local effects and systemic implications. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 25:197–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qian Li H, Weng WX, Wu Z, Li H, Zhuang Q,
Feng B and Bian Y: Glucocorticoid receptor and sequential P53
activation by dexamethasone mediates apoptosis and cell cycle
arrest of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. PLoS One. 7:e370302012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin H, Wei B, Li G, Zheng J, Sun J, Chu J,
Zeng R and Niu Y: Sulforaphane reverses glucocorticoid-induced
apoptosis in osteoblastic cells through regulation of the Nrf2
pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:973–982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin H, Gao X, Chen G, Sun J, Chu J, Jing
K, Li P, Zeng R and Wei B: Indole-3-carbinol as inhibitors of
glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblastic cells through
blocking ROS-mediated Nrf2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
460:422–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mcilwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 7(pii): a0086562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li J, He C, Tong W, Zou Y, Li D, Zhang C
and Xu W: Tanshinone IIA blocks dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in
osteoblasts through inhibiting Nox4-derived ROS production. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13695–13706. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Oakes V, Wang W, Harrington B, Lee WJ,
Beamish H, Chia KM, Pinder A, Goto H, Inagaki M, Pavey S and
Gabrielli B: Cyclin A/Cdk2 regulates Cdh1 and claspin during late
S/G2 phase of the cell cycle. Cell Cycle. 13:3302–3311. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iurlaro R and Muñoz-Pinedo C: Cell death
induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 283:2640–2652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bánhegyi G, Baumeister P, Benedetti A,
Dong D, Fu Y, Lee AS, Li J, Mao C, Margittai E, Ni M, et al:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1113:58–71. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Wu Q, Lv J and Nie H: 4-Phenyl
butyric acid prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoblast apoptosis
by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Bone Miner Metab.
35:366–374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sato AY, Tu X, McAndrews KA, Plotkin LI
and Bellido T: Prevention of glucocorticoid induced-apoptosis of
osteoblasts and osteocytes by protecting against endoplasmic
reticulum (ER) stress in vitro and in vivo in Female Mice. Bone.
73:60–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sui Y, Yao H, Li S, Jin L, Shi P, Li Z,
Wang G, Lin S, Wu Y, Li Y, et al: Delicaflavone induces autophagic
cell death in lung cancer via Akt/mTOR/70S6K signaling pathway. J
Mol Med. 95:311–322. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang M, Wang B, Miao L, Xu X and He X:
Autophagy is involved in aldosterone-induced mesangial cell
proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 14:4638–4642. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pattingre S, Espert L, Biard-Piechaczyk M
and Codogno P: Regulation of macroautophagy by mTOR and Beclin 1
complexes. Biochimie. 90:313–323. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pawlowska E, Wysokiński D, Tokarz P,
Piastowska-Ciesielska A, Szczepanska J and Blasiak J: Dexamethasone
and 1,25-dihy-droxyvitamin D3 reduce oxidative stress-related DNA
damage in differentiating osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci.
15:16649–16664. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang Y, Su Y, Wang D, Chen Y, Wu T, Li G,
Sun X and Cui L: Tanshinol attenuates the deleterious effects of
oxidative stress on osteoblastic differentiation via Wnt/FoxO3a
signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:3518952013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang S, Li D, Yang JY and Yan TB:
Plumbagin protects against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
through Nrf-2 pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones. 20:621–629. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ryter SW, Mizumura K and Choi AM: The
impact of autophagy on cell death modalities. Int J Cell Biol.
2014:5026762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li M, Gao P and Zhang J: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis: Potential and emerging therapeutic targets
for cardiac diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 17:3322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Z, Zheng L, Zhao Z, Shi J, Wang X
and Huang J: Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit
H2O2-induced osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cell
apoptosis via ameliorating H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.
J Toxicol Sci. 39:803–813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Suh KS, Choi EM, Lee YS and Kim YS:
Protective effect of albiflorin against oxidative-stress-mediated
toxicity in osteo-blast-like MC3T3-E1 cells. Fitoterapia. 89:33–41.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li L, Tan J, Miao Y, Lei P and Zhang Q:
ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and molecular regulatory
mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:615–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|