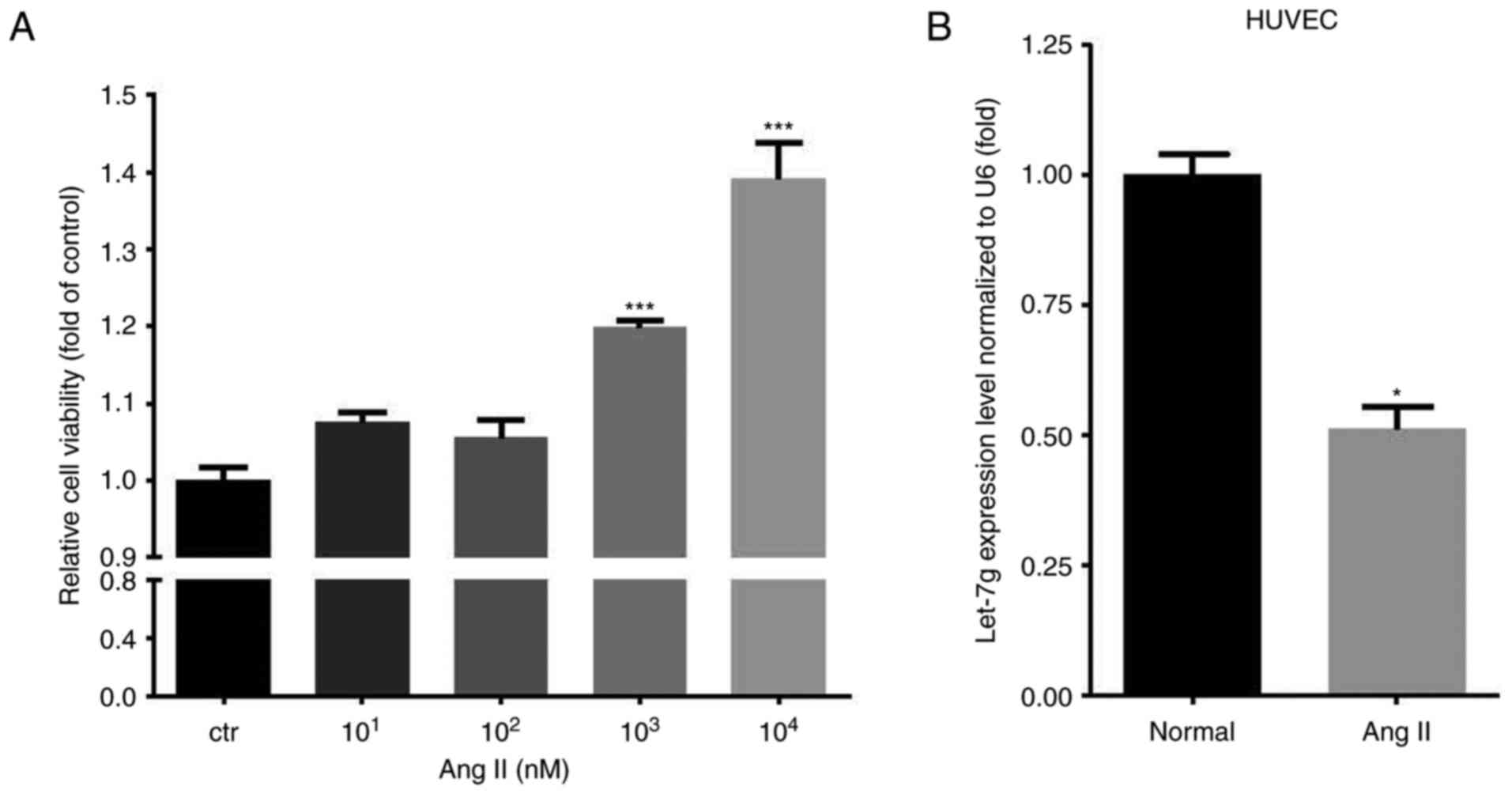
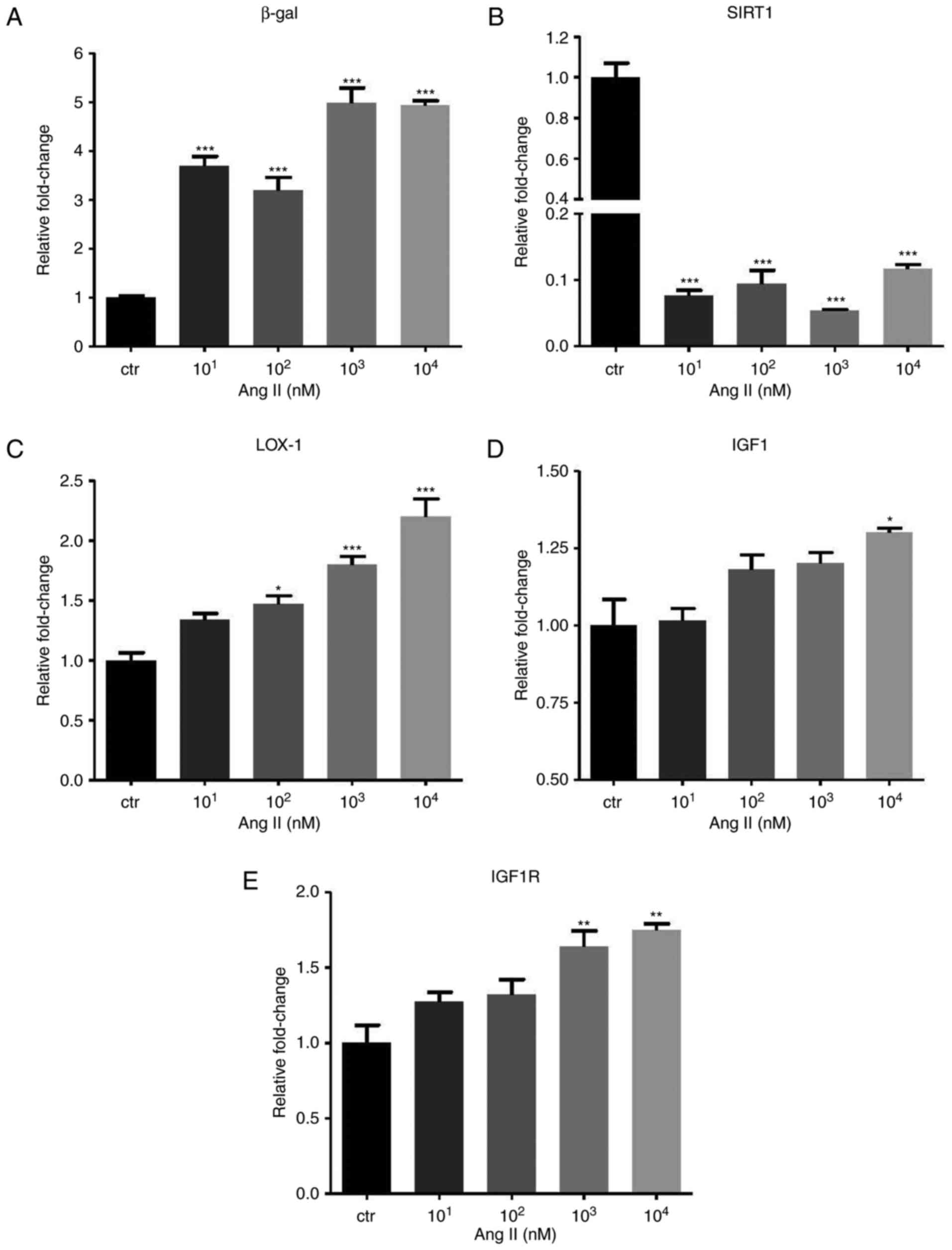
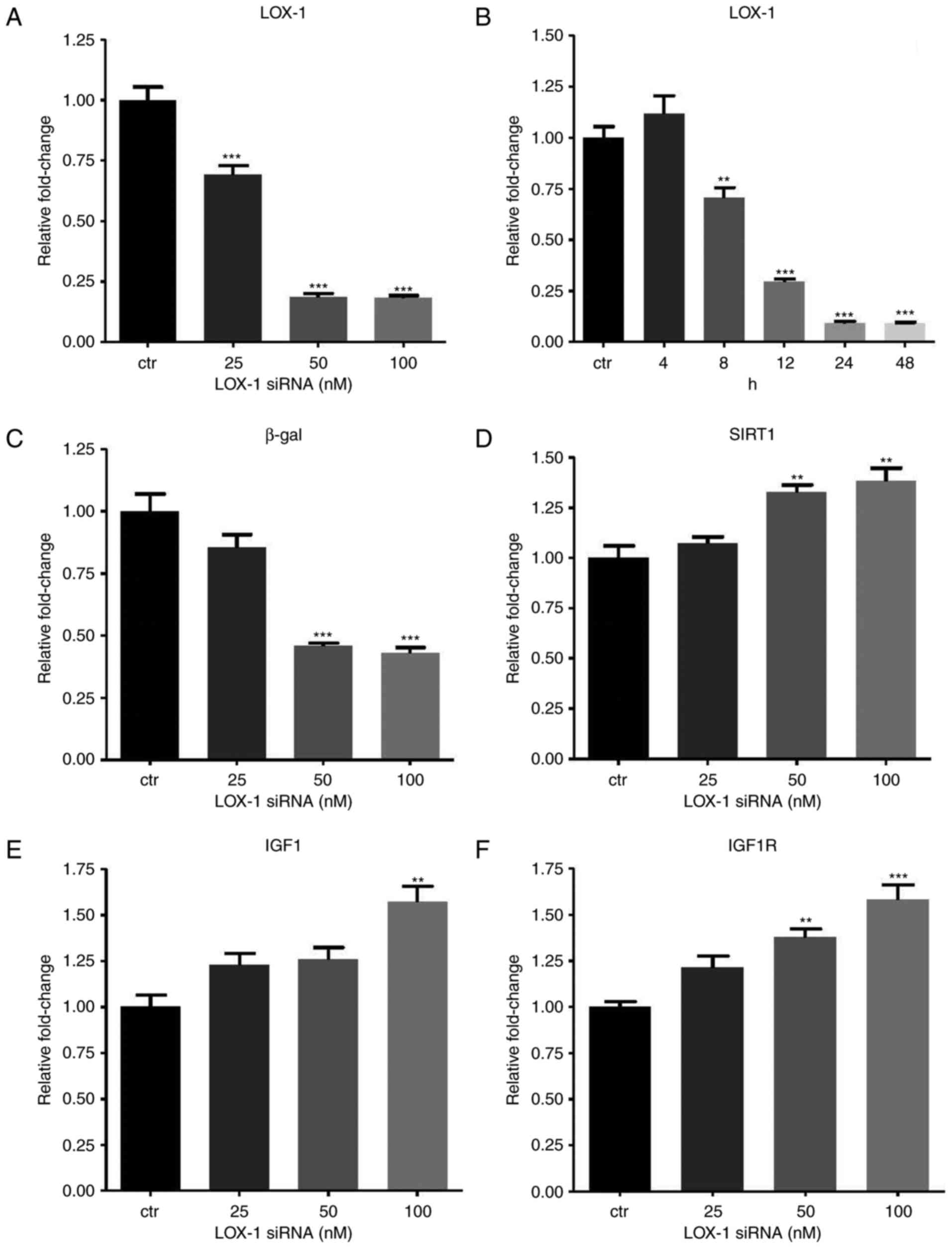
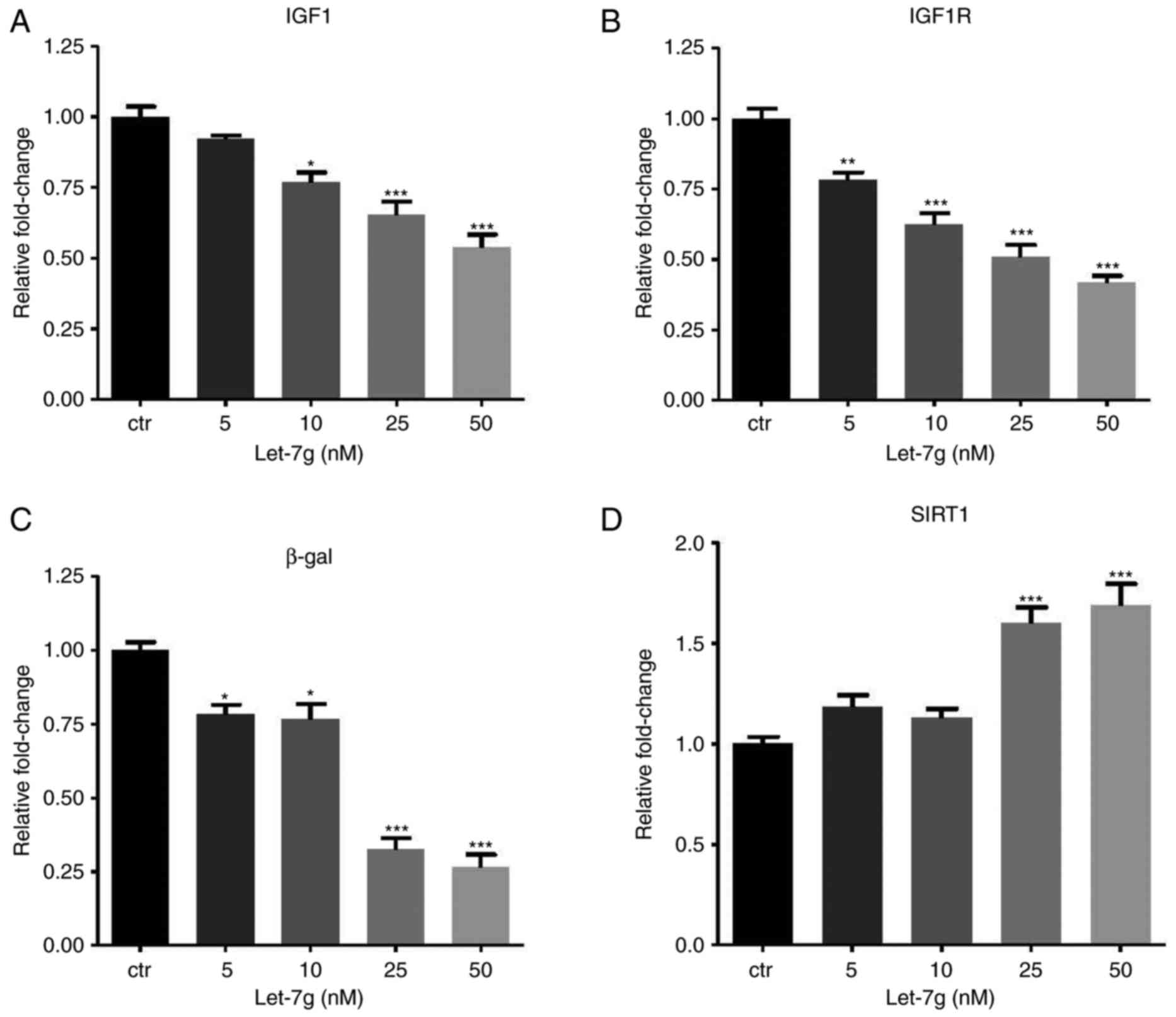
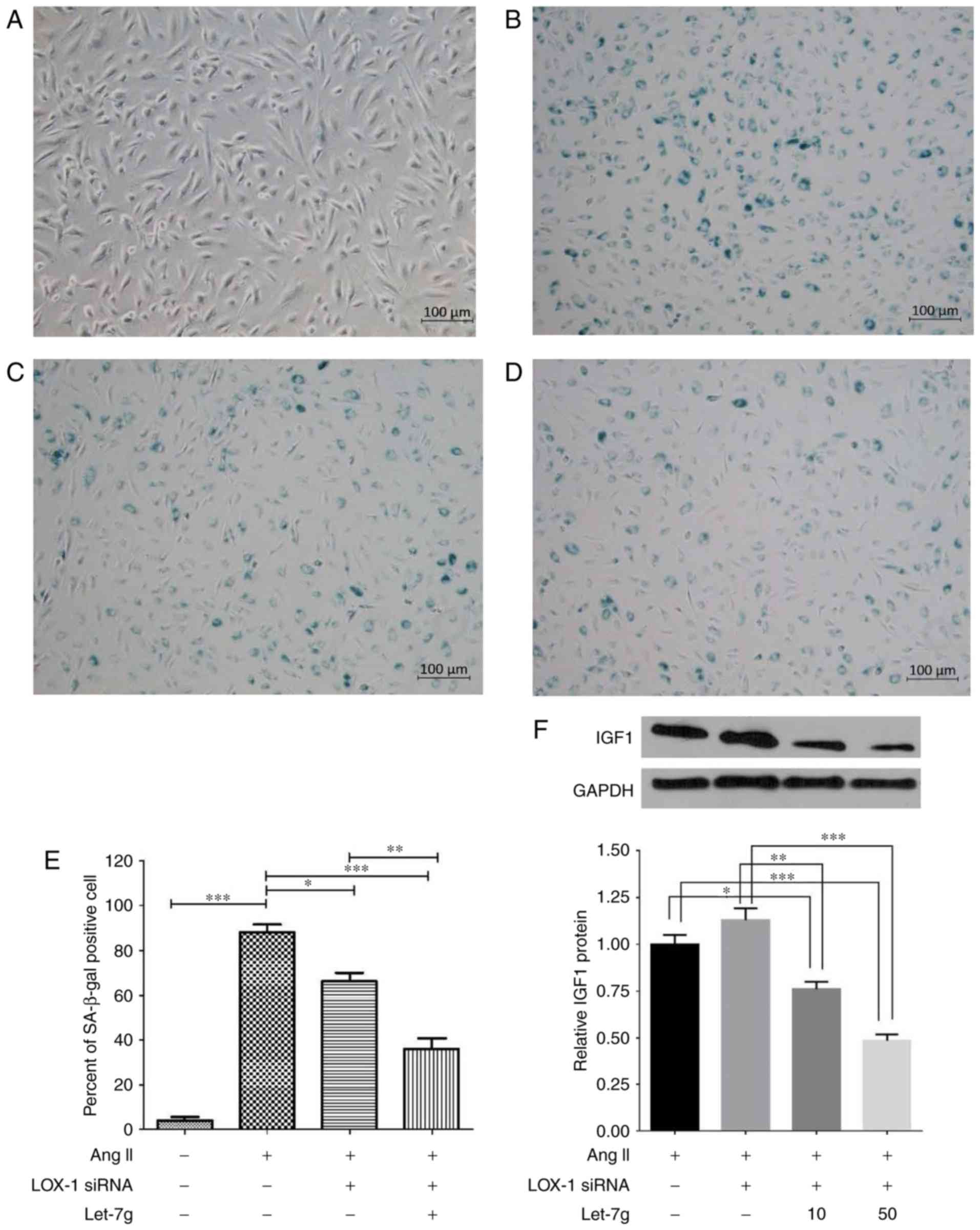
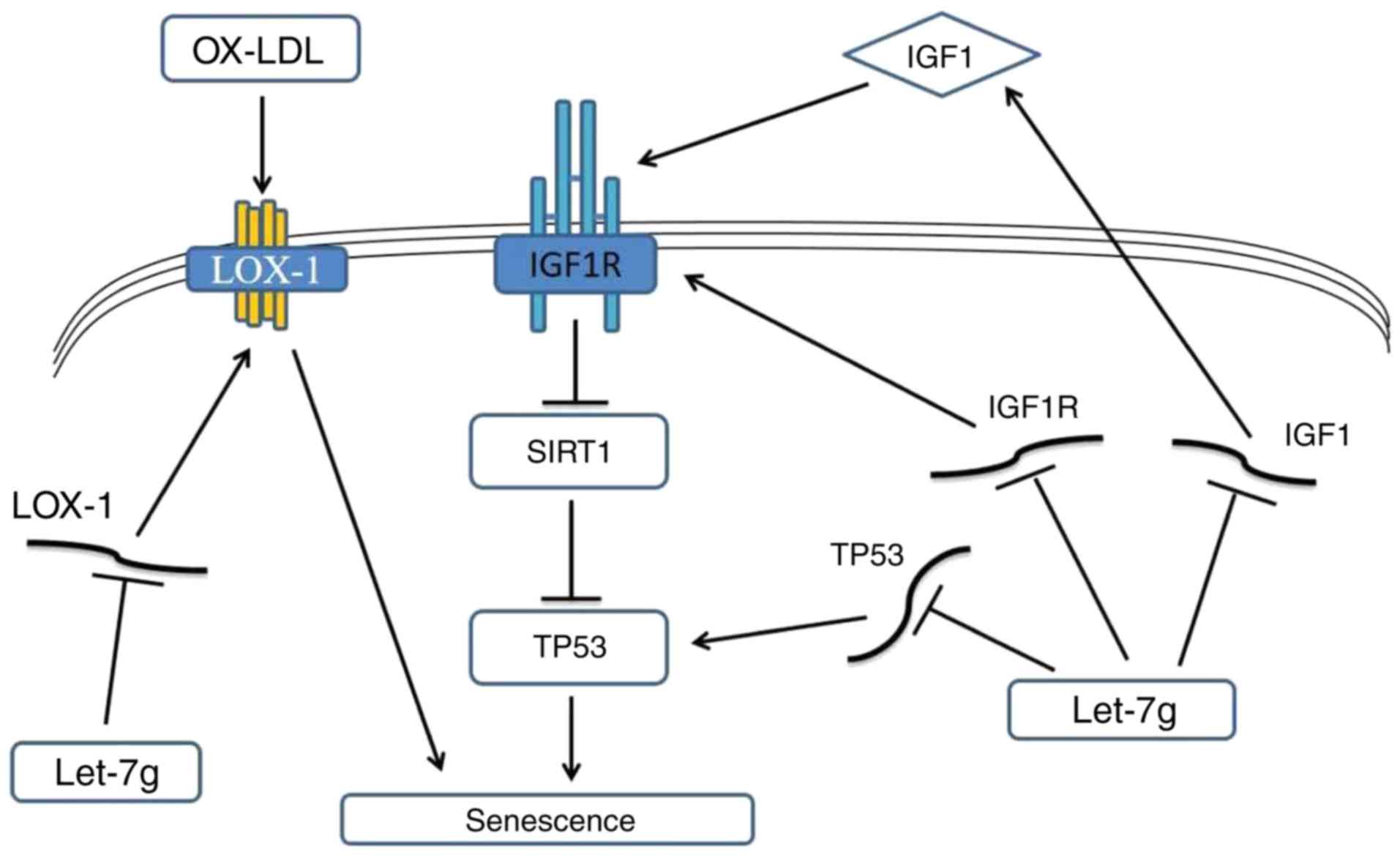
|
1
|
Campisi J: Aging, cellular senescence, and
cancer. Annu Rev Physiol. 75:685–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Félétou M and Vanhoutte PM: Endothelial
dysfunction: A multifaceted disorder (The Wiggers Award Lecture).
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H985–H1002. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu S, Ogura S, Chen J, Little PJ, Moss J
and Liu P: LOX-1 in atherosclerosis: Biological functions and
pharmacological modifiers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:2859–2872. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Khaidakov M, Ding Z, Dai Y,
Mercanti F and Mehta JL: LOX-1 in the maintenance of cytoskeleton
and proliferation in senescent cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 60:184–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mehta PK and Griendling KK: Angiotensin II
cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the
cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C82–C97.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kambayashi Y, Bardhan S, Takahashi K,
Tsuzuki S, Inui H, Hamakubo T and Inagami T: Molecular cloning of a
novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine
phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 268:24543–24546.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sasaki K, Yamano Y, Bardhan S, Iwai N,
Murray JJ, Hasegawa M, Matsuda Y and Inagami T: Cloning and
expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal
angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 351:230–233. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Min LJ, Mogi M, Iwai M and Horiuchi M:
Signaling mechanisms of angiotensin II in regulating vascular
senescence. Ageing Res Rev. 8:113–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kunieda T, Minamino T, Nishi J, Tateno K,
Oyama T, Katsuno T, Miyauchi H, Orimo M, Okada S, Takamura M, et
al: Angiotensin II induces premature senescence of vascular smooth
muscle cells and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis via
a p21-dependent pathway. Circulation. 114:953–960. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li DY, Zhang YC, Philips MI, Sawamura T
and Mehta JL: Upregulation of endothelial receptor for oxidized
low-density lipoprotein (LOX-1) in cultured human coronary artery
endothelial cells by angiotensin II type 1 receptor activation.
Circ Res. 84:1043–1049. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feige JN and Auwerx J: Transcriptional
targets of sirtuins in the coordination of mammalian physiology.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 20:303–309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao YC, Wang YS, Guo YC, Lin WL, Chang MH
and Juo SH: Let-7g improves multiple endothelial functions through
targeting transforming growth factor-beta and SIRT-1 signaling. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 63:1685–1694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gorenne I, Kumar S, Gray K, Figg N, Yu H,
Mercer J and Bennett M: Vascular smooth muscle cell sirtuin 1
protects against DNA damage and inhibits atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 127:386–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stein S, Lohmann C, Schäfer N, Hofmann J,
Rohrer L, Besler C, Rothgiesser KM, Becher B, Hottiger MO, Borén J,
et al: SIRT1 decreases Lox-1-mediated foam cell formation in
atherogenesis. Eur Heart J. 31:2301–2309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang QJ, Wang Z, Chen HZ, Zhou S, Zheng
W, Liu G, Wei YS, Cai H, Liu DP and Liang CC: Endothelium-specific
overexpression of class III deacetylase SIRT1 decreases
atherosclerosis in apoli-poprotein E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc
Res. 80:191–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kenyon C: A conserved regulatory system
for aging. Cell. 105:165–168. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longo VD and Finch CE: Evolutionary
medicine: From dwarf model systems to healthy centenarians?
Science. 299:1342–1346. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lai CH, Ho TJ, Kuo WW, Day CH, Pai PY,
Chung LC, Liao PH, Lin FH, Wu ET and Huang CY: Exercise training
enhanced SIRT1 longevity signaling replaces the IGF1 survival
pathway to attenuate aging-induced rat heart apoptosis. Age
(Dordr). 36:97062014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua
KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, et
al: Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by
the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 303:2011–2015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cohen HY, Miller C, Bitterman KJ, Wall NR,
Hekking B, Kessler B, Howitz KT, Gorospe M, de Cabo R and Sinclair
DA: Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by
inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 305:390–392. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tissenbaum HA and Guarente L: Increased
dosage of a sir-2 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Nature. 410:227–230. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bao MH, Feng X, Zhang YW, Lou XY, Cheng Y
and Zhou HH: Let-7 in cardiovascular diseases, heart development
and cardiovascular differentiation from stem cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:23086–23102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chiu SC, Chung HY, Cho DY, Chan TM, Liu
MC, Huang HM, Li TY, Lin JY, Chou PC, Fu RH, et al: Therapeutic
potential of microRNA let-7: Tumor suppression or impeding normal
stemness. Cell Transplant. 23:459–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen KC, Hsieh IC, His E, Wang YS, Dai CY,
Chou WW and Juo SH: Negative feedback regulation between microRNA
let-7g and the oxLDL receptor LOX-1. J Cell Sci. 124:4115–4124.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsu PY, His E, Wang TM, Lin RT, Liao YC
and Juo SH: MicroRNA let-7g possesses a therapeutic potential for
peripheral artery disease. J Cell Mol Med. 21:519–529. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang LL, Li DY, Zhang YB, Zhu MY, Chen D
and Xu TD: Salvianolic acid A inhibits angiotensin II-induced
proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by
attenuating the production of ROS. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:41–48.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choo KB, Soon YL, Nguyen PN, Hiew MS and
Huang CJ: MicroRNA-5p and -3p co-expression and cross-targeting in
colon cancer cells. J Biomed Sci. 21:952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Yao W, Liu K, Wen Q, Wu W, Liu H
and Li Q: MicroRNA let-7g regulates mouse granulosa cell autophagy
by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 78:130–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shan H, Bai X and Chen X: Angiotensin II
induces endothelial cell senescence via the activation of
mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cell Biochem Funct. 26:459–466.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Huang XR, Wei LH, Chung AC, Yu CM
and Lan HY: miR-29b as a therapeutic agent for angiotensin
II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting TGF-β/Smad3 signaling. Mol
Ther. 22:974–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu Z, Klein JD, Mitch WE, Zhang L,
Martinez I and Wang XH: MicroRNA-29 induces cellular senescence in
aging muscle through multiple signaling pathways. Aging (Albany
NY). 6:160–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Xu Z, Zhang L, Fei X, Yi X, Li W and Wang
Q: The miR-29b-Sirt1 axis regulates self-renewal of mouse embryonic
stem cells in response to reactive oxygen species. Cell Signal.
26:1500–1505. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pirillo A, Norata GD and Catapano AL:
LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:1527862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Morawietz H, Rueckschloss U, Niemann B,
Duerrschmidt N, Galle J, Hakim K, Zerkowski HR, Sawamura T and
Holtz J: Angiotensin II induces LOX-1, the human endothelial
receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Circulation.
100:899–902. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez-Perez AI, Borrajo A, Diaz-Ruiz
C, Garrido-Gil P and Labandeira-Garcia JL: Crosstalk between
insulin-like growth factor-1 and angiotensin-II in dopaminergic
neurons and glial cells: Role in neuroinflammation and aging.
Oncotarget. 7:30049–30067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Suh Y, Atzmon G, Cho MO, Hwang D, Liu B,
Leahy DJ, Barzilai N and Cohen P: Functionally significant
insulin-like growth factor I receptor mutations in centenarians.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3438–3442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dubinsky AN, Dastidar SG, Hsu CL, Zahra R,
Djakovic SN, Duarte S, Esau CC, Spencer B, Ashe TD, Fischer KM, et
al: Let-7 coordinately suppresses components of the amino acid
sensing pathway to repress mTORC1 and induce autophagy. Cell Metab.
20:626–638. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu H, Shyh-Chang N, Segrè AV, Shinoda G,
Shah SP, Einhorn WS, Takeuchi A, Engreitz JM, Hagan JP, Kharas MG,
et al: The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism. Cell.
147:81–94. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|