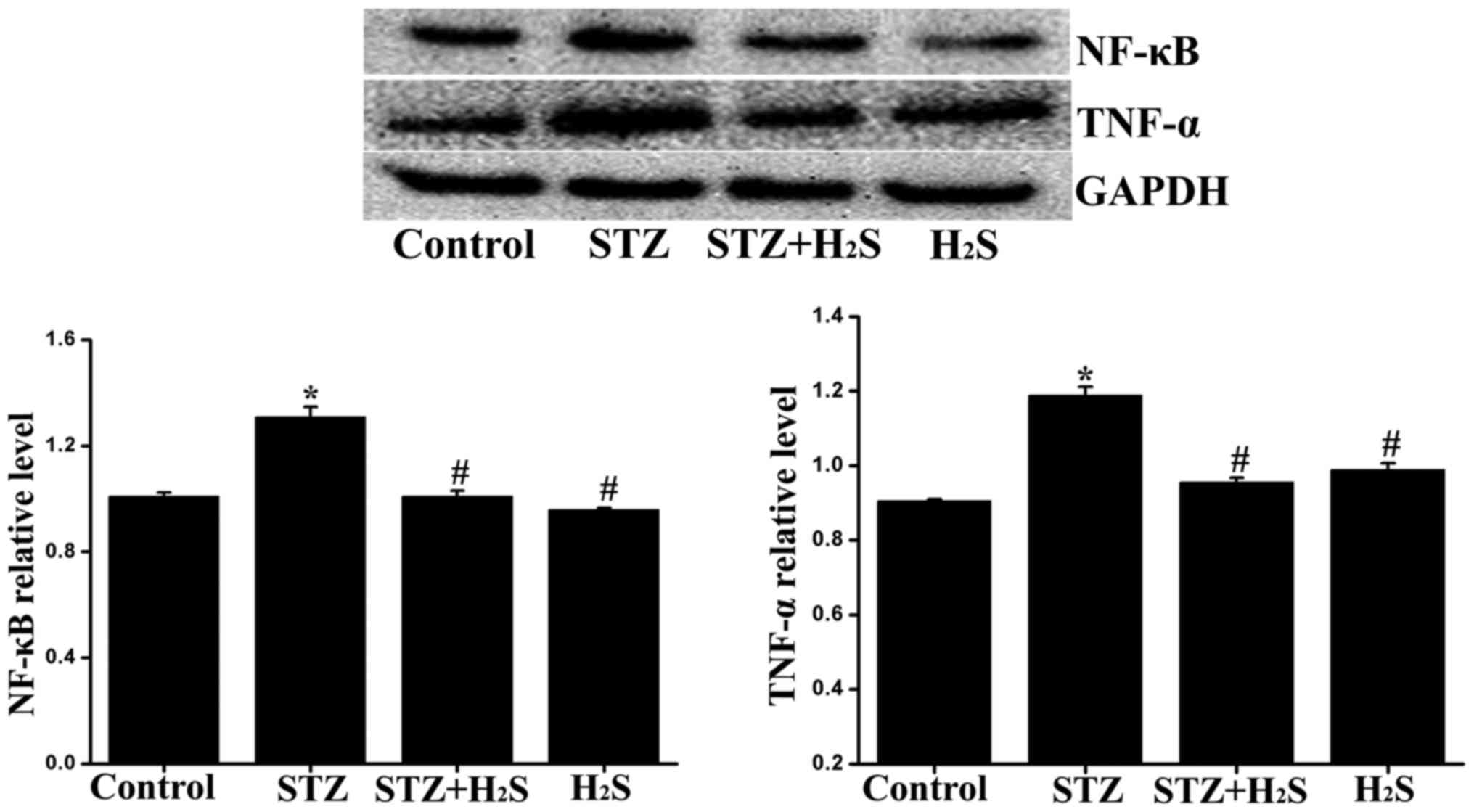
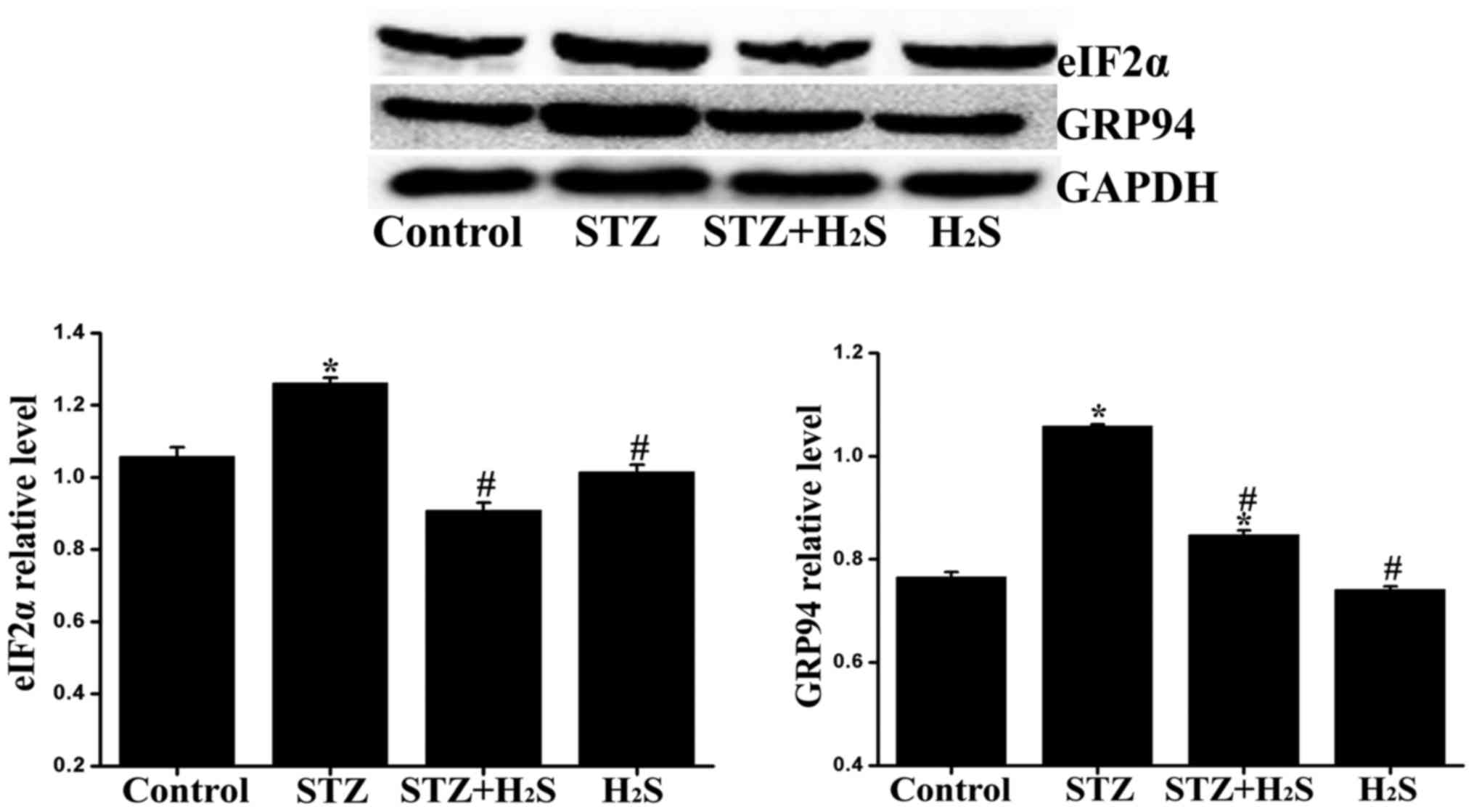
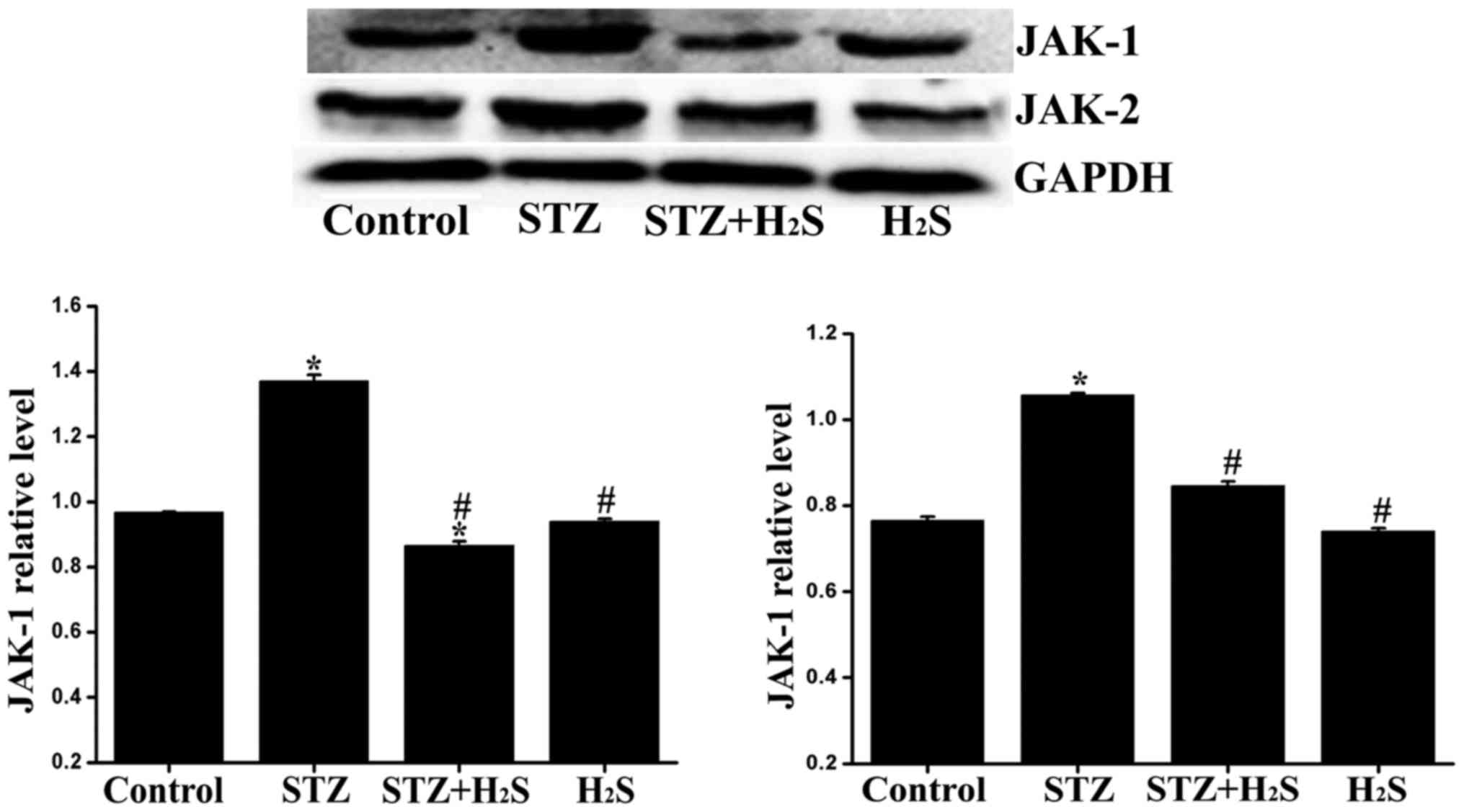
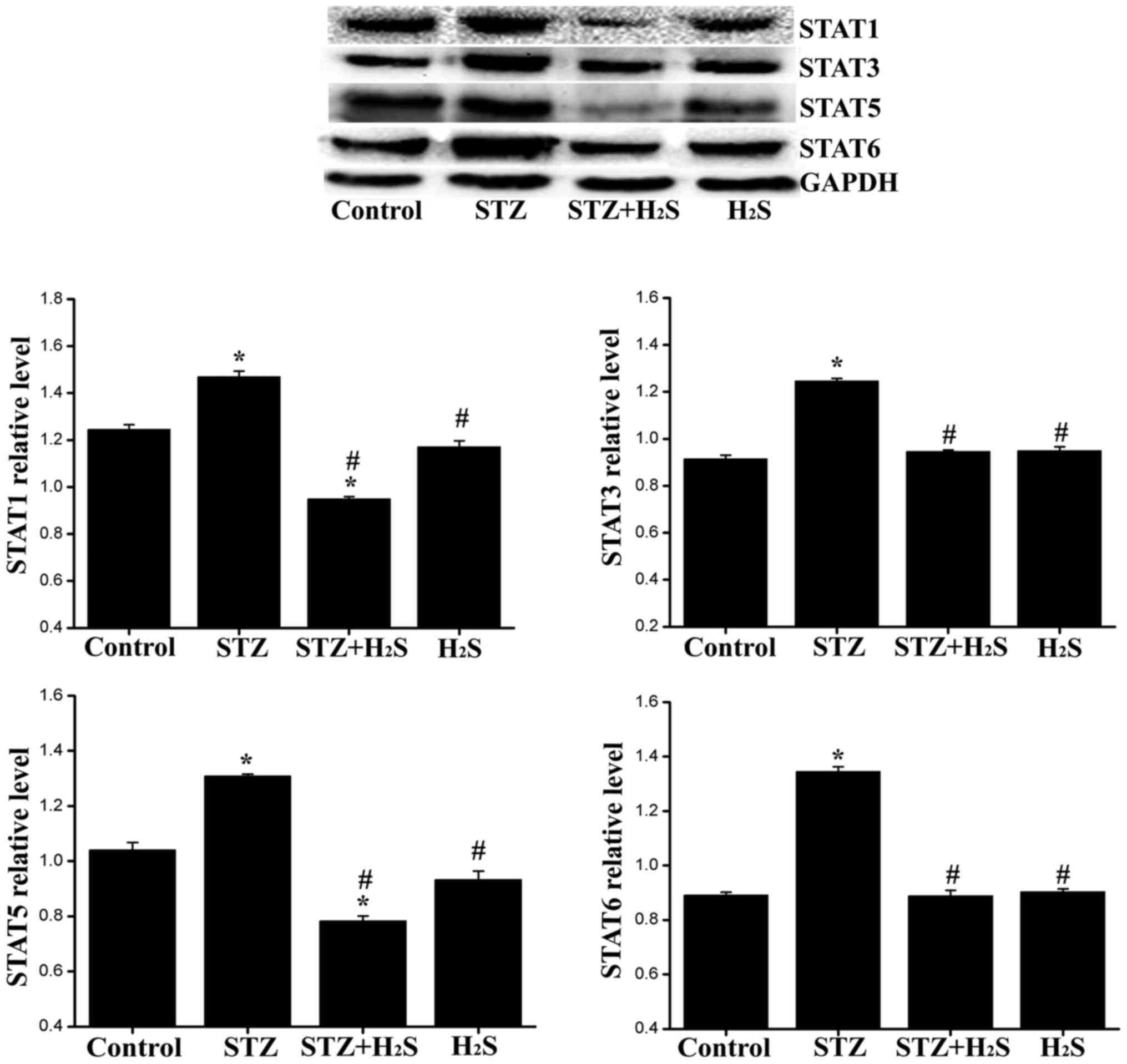
|
1
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al China National Diabetes and
Metabolic Disorders Study Group: Prevalence of diabetes among men
and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bell DS: Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes
Care. 26:2949–2951. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asbun J and Villarreal FJ: The
pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in the setting of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 47:693–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bugger H and Abel ED: Molecular mechanisms
of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 57:660–671. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thandavarayan RA, Giridharan VV, Watanabe
K and Konishi T: Diabetic cardiomyopathy and oxidative stress: role
of antioxidants. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 9:225–230.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumar S, Prasad S and Sitasawad SL:
Multiple antioxidants improve cardiac complications and inhibit
cardiac cell death in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. PLoS
One. 8:e670092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Varga ZV, Giricz Z, Liaudet L, Haskó G,
Ferdinandy P and Pacher P: Interplay of oxidative,
nitrosative/nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and
autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:232–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kiu H and Nicholson SE: Biology and
significance of the JAK/STAT signalling pathways. Growth Factors.
30:88–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kimura H: Production and physiological
effects of hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:783–793.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Lavu M, Bhushan S and Lefer DJ: Hydrogen
sulfide-mediated cardioprotection: mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 120:219–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R and
King H: Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000
and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 27:1047–1053. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Du J, Zhao YT, Zhang L, Lv G,
Zhuang S, Qin G and Zhao TC: Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
improves myocardial function and prevents cardiac remodeling in
diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Falcão-Pires I and Leite-Moreira AF:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: understanding the molecular and cellular
basis to progress in diagnosis and treatment. Heart Fail Rev.
17:325–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Zhao D, Ren J and Yang J:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and protein quality control in
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:209–218. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jia G, DeMarco VG and Sowers JR: Insulin
resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 12:144–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Sun X, Chen RC, Yang ZH, Sun GB, Wang M,
Ma XJ, Yang LJ and Sun XB: Taxifolin prevents diabetic
cardiomyopathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibition of oxidative
stress and cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 63:221–232. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao Y, Zhang L, Qiao Y, Zhou X, Wu G,
Wang L, Peng Y, Dong X, Huang H and Si L: Heme oxygenase-1 prevents
cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin-diabetic mice by reducing
inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and enhancing autophagy.
PLoS One. 8:e759272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taye A, Abouzied MM and Mohafez OM: Tempol
ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats: role of oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 386:1071–1080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malfitano C, Alba Loureiro TC, Rodrigues
B, Sirvente R, Salemi VM, Rabechi NB, Lacchini S, Curi R and
Irigoyen MC: Hyperglycaemia protects the heart after myocardial
infarction: aspects of programmed cell survival and cell death. Eur
J Heart Fail. 12:659–667. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Van Linthout S, Riad A, Dhayat N,
Spillmann F, Du J, Dhayat S, Westermann D, Hilfiker-Kleiner D,
Noutsias M, Laufs U, et al: Anti-inflammatory effects of
atorvastatin improve left ventricular function in experimental
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 50:1977–1986. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Westermann D, Walther T, Savvatis K,
Escher F, Sobirey M, Riad A, Bader M, Schultheiss HP and Tschöpe C:
Gene deletion of the kinin receptor B1 attenuates cardiac
inflammation and fibrosis during the development of experimental
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes. 58:1373–1381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Westermann D, Van Linthout S, Dhayat S,
Dhayat N, Schmidt A, Noutsias M, Song XY, Spillmann F, Riad A,
Schultheiss HP, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonism
protects from myocardial inflammation and fibrosis in experimental
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol. 102:500–507. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu W, Zha W, Guo S, Cheng H, Wu J and Liu
C: Flos Puerariae extract prevents myocardial apoptosis via
attenuation oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
mice. PLoS One. 9:e980442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–1070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C,
Jakoniuk I, Leri A, Maseri A, Nadal-Ginard B and Anversa P:
Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res. 87:1123–1132.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yaras N, Sariahmetoglu M, Bilginoglu A,
Aydemir-Koksoy A, Onay-Besikci A, Turan B and Schulz R: Protective
action of doxycycline against diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Br J
Pharmacol. 155:1174–1184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, Morioka M,
Gotoh T, Hamada JI, Ushio Y and Mori M: Ischemia-induced neuronal
cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway
involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ. 11:403–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Williams JA, Hou Y, Ni HM and Ding WX:
Role of intracellular calcium in proteasome inhibitor-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and cell death. Pharm Res.
30:2279–2289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang C, Koulajian K, Schuiki I, Zhang L,
Desai T, Ivovic A, Wang P, Robson-Doucette C, Wheeler MB, Minassian
B, et al: Glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction in vivo in rats:
link between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Diabetologia. 55:1366–1379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miki T, Miura T, Hotta H, Tanno M, Yano T,
Sato T, Terashima Y, Takada A, Ishikawa S and Shimamoto K:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic hearts abolishes
erythropoietin-induced myocardial protection by impairment of
phospho-glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-mediated suppression of
mitochondrial permeability transition. Diabetes. 58:2863–2872.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo R, Liu W, Liu B, Zhang B, Li W and Xu
Y: SIRT1 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy: An insight into endoplasmic reticulum stress
response mechanism. Int J Cardiol. 191:36–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeglinski MR, Roche P, Hnatowich M, Jassal
DS, Wigle JT, Czubryt MP and Dixon IM: TGFβ1 regulates Scleraxis
expression in primary cardiac myofibroblasts by a Smad-independent
mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H239–H249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu Y and Zhang J: Nox2 contributes to
cardiac fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy in a transforming
growth factor-β dependent manner. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10908–10914. 2015.
|
|
34
|
Duhé RJ: Redox regulation of Janus kinase:
the elephant in the room. JAKSTAT. 2:e261412013.
|
|
35
|
Shi K, Jiang J, Ma T, Xie J, Duan L, Chen
R, Song P, Yu Z, Liu C, Zhu Q, et al: Dexamethasone attenuates
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice through TGF-β, Smad3 and
JAK-STAT pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:2645–2650. 2014.
|
|
36
|
Matsui F and Meldrum KK: The role of the
Janus kinase family/signal transducer and activator of
transcription signaling pathway in fibrotic renal disease. J Surg
Res. 178:339–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Du C, Zhao S, Qi
Z, Zhang Q and Duan H: Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 reduces
high glucose-induced TGF-beta1 and fibronectin synthesis in human
mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 582:3484–3488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boengler K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Drexler H,
Heusch G and Schulz R: The myocardial JAK/STAT pathway: from
protection to failure. Pharmacol Ther. 120:172–185. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Calvert JW, Coetzee WA and Lefer DJ: Novel
insights into hydrogen sulfide - mediated cytoprotection. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1203–1217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Xu W, Chen J, Lin J, Liu D, Mo L, Pan W,
Feng J, Wu W and Zheng D: Exogenous H2S protects H9c2
cardiac cells against high glucose-induced injury and inflammation
by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and IL-1β pathways. Int J
Mol Med. 35:177–186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xiao T, Luo J, Wu Z, Li F, Zeng O and Yang
J: Effects of hydrogen sulfide on myocardial fibrosis and
PI3K/AKT1-regulated autophagy in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep.
13:1765–1773. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhou X and Lu X: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
high-glucose-induced apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 238:370–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|