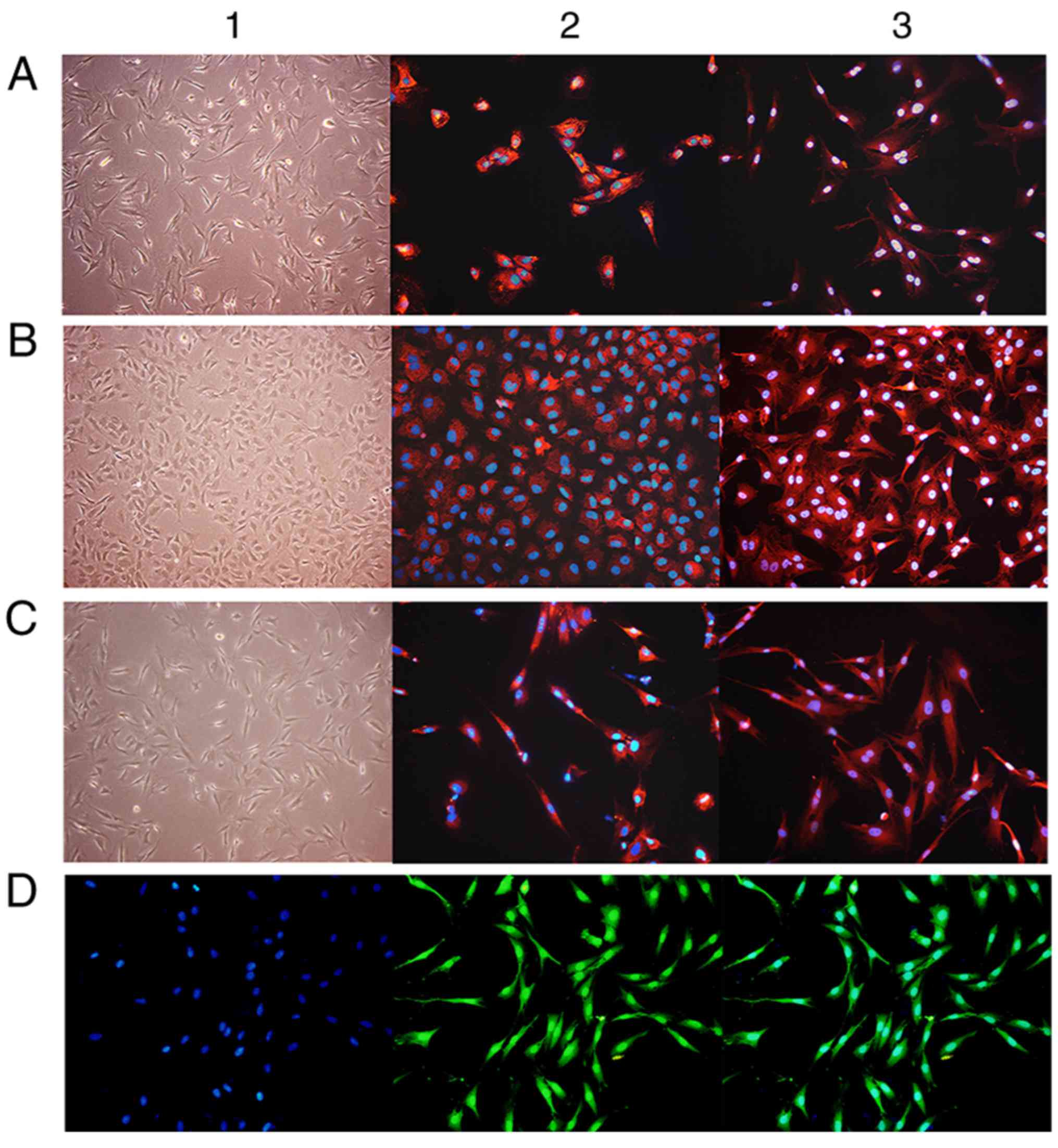
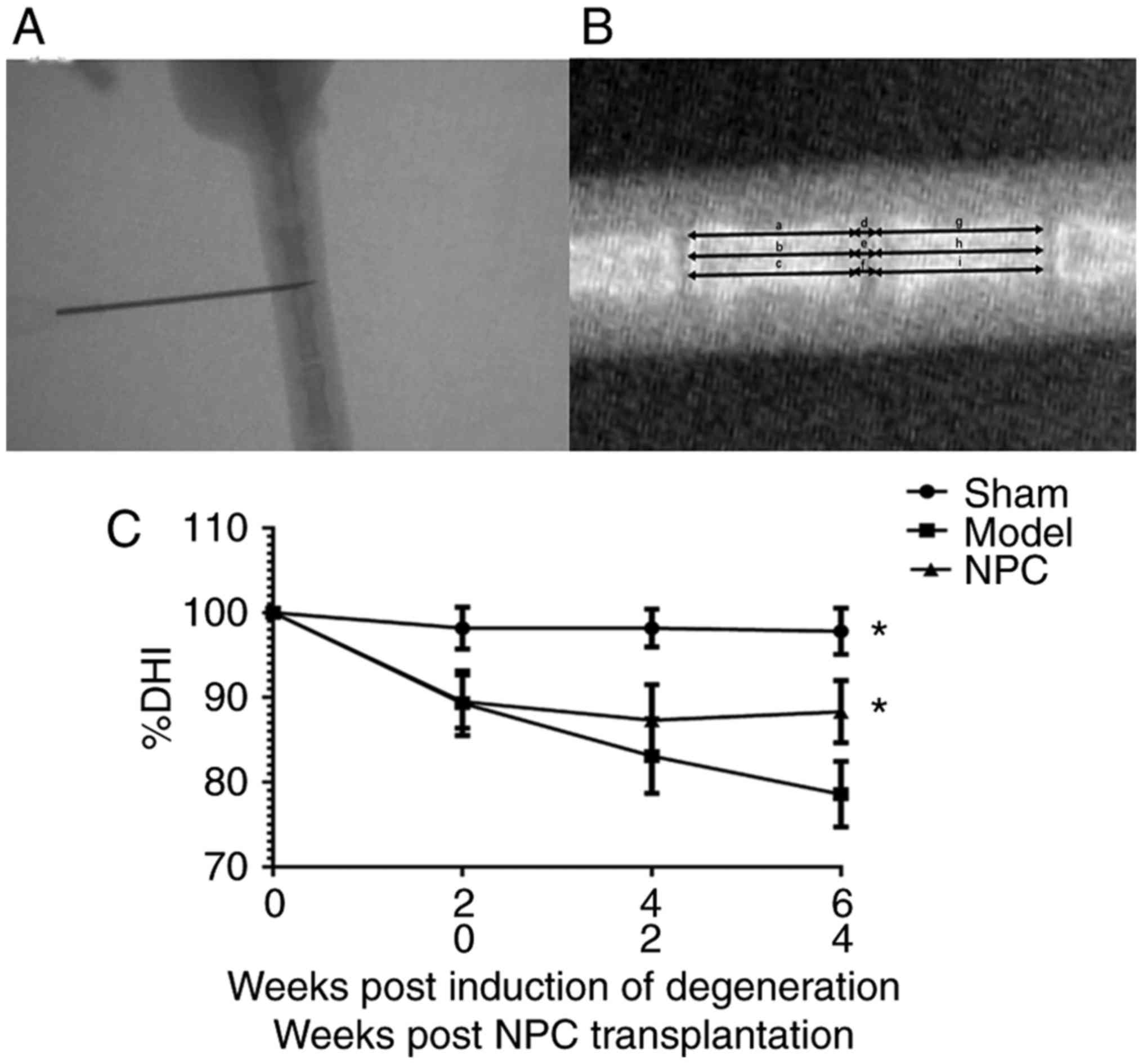
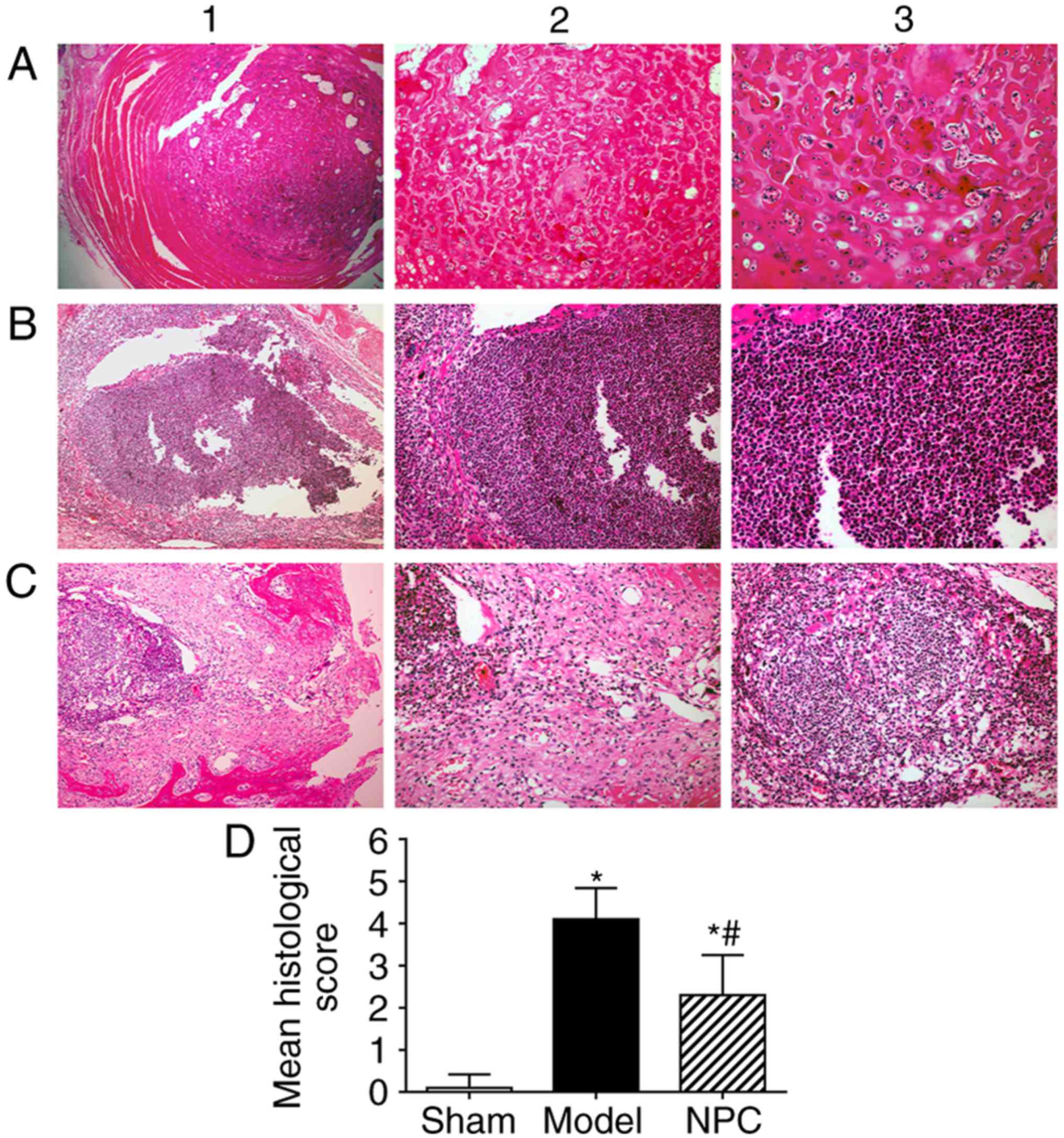
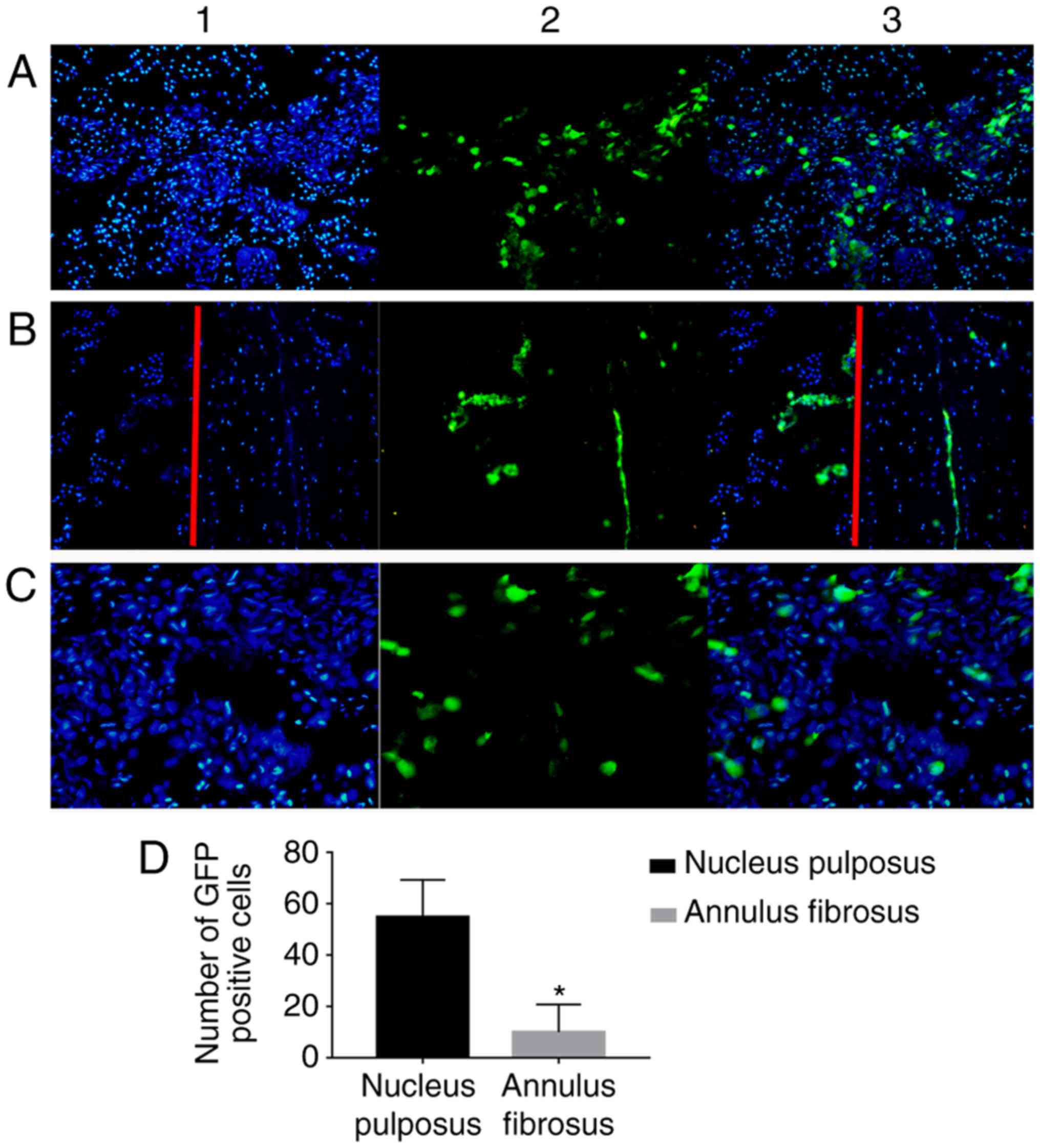
|
1
|
Ylinen J: Physical exercises and
functional rehabilitation for the management of chronic neck pain.
Eura Medicophys. 43:119–132. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salomon JA, Vos T, Hogan DR, Gagnon M,
Naghavi M, Mokdad A, Begum N, Shah R, Karyana M, Kosen S, et al:
Common values in assessing health outcomes from disease and injury:
Disability weights measurement study for the Global Burden of
disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2129–2143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raj PP: Intervertebral disc:
Anatomy-physiology-pathophysio logy treatment. Pain Pract. 8:18–44.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levin DA, Hale JJ and Bendo JA: Adjacent
segment degeneration following spinal fusion for degenerative disc
disease. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 65:29–36. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Buckwalter JA: Aging and degeneration of
the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 20:1307–1314. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lipson SJ and Muir H: 1980 Volvo award in
basic science. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc
degeneration. Spine. 6:194–210. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim KW, Lim TH, Kim JG, Jeong ST, Masuda K
and An HS: The origin of chondrocytes in the nucleus pulposus and
histologic findings associated with the transition of a notochordal
nucleus pulposus to a fibrocartilaginous nucleus pulposus in intact
rabbit intervertebral discs. Spine. 28:982–990. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishimura K and Mochida J: Percutaneous
reinsertion of the nucleus pulposus. An experimental study. Spine.
23:1531–1539. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okuma M, Mochida J, Nishimura K, Sakabe K
and Seiki K: Reinsertion of stimulated nucleus pulposus cells
retards inter-vertebral disc degeneration: An in vitro and in vivo
experimental study. J Orthop Res. 18:988–997. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cao C, Zou J, Liu X, Shapiro A, Moral M,
Luo Z, Shi Q, Liu J, Yang H and Ebraheim N: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells slow intervertebral disc degeneration through the
NF-kappaB pathway. Spine J. 15:530–538. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sakai D, Mochida J, Iwashina T, Hiyama A,
Omi H, Imai M, Nakai T, Ando K and Hotta T: Regenerative effects of
transplanting mesenchymal stem cells embedded in atelocollagen to
the degenerated intervertebral disc. Biomaterials. 27:335–345.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Murrell W, Sanford E, Anderberg L,
Cavanagh B and Mackay-Sim A: Olfactory stem cells can be induced to
express chondrogenic phenotype in a rat intervertebral disc injury
model. Spine J. 9:585–594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sivakamasundari V and Lufkin T: Stemming
the degeneration: IVD stem cells and stem cell regenerative therapy
for degenerative disc disease. Adv Stem Cells. 2013:pii: 724547.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Risbud MV, Guttapalli A, Tsai TT, Lee JY,
Danielson KG, Vaccaro AR, Albert TJ, Gazit Z, Gazit D and Shapiro
IM: Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human
intervertebral disc. Spine. 32:2537–2544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blanco JF, Graciani IF, Sanchez-Guijo FM,
Muntión S, Hernandez-Campo P, Santamaria C, Carrancio S, Barbado
MV, Cruz G, Gutierrez-Cosío S, et al: Isolation and
characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells from human
degenerated nucleus pulposus: Comparison with bone marrow
mesenchymal stromal cells from the same subjects. Spine.
35:2259–2265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hughes PC and Tanner JM: The assessment of
skeletal maturity in the growing rat. J Anat. 106:371–402.
1970.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kraus P and Lufkin T: Bovine annulus
fibrosus cell lines isolated from intervertebral discs. Genom Data.
10:83–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ganey T, Libera J, Moos V, Alasevic O,
Fritsch KG, Meisel HJ and Hutton WC: Disc chondrocyte
transplantation in a canine model: A treatment for degenerated or
damaged intervertebral disc. Spine. 28:2609–2620. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin Y, Li F, Chen W, Zeng H, Chen A and
Xiong W: Single-level lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis treated with
mini-open anterior debridement and fusion in combination with
posterior percutaneous fixation via a modified anterior lumbar
interbody fusion approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 23:747–753. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M,
Hodler J and Boos N: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 26:1873–1878. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murrell W, Féron F, Wetzig A, Cameron N,
Splatt K, Bellette B, Bianco J, Perry C, Lee G and Mackay-Sim A:
Multipotent stem cells from adult olfactory mucosa. Dev Dyn.
233:496–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Stanton TR, Latimer J, Maher CG and
Hancock M: Definitions of recurrence of an episode of low back
pain: A systematic review. Spine. 34:E316–E322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chou R and Huffman LH; American Pain
Society; American College of Physicians: Medications for acute and
chronic low back pain: A review of the evidence for an American
Pain Society/American College of Physicians clinical practice
guideline. Ann Intern Med. 147:505–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwon B and Kim DH: Lateral lumbar
interbody fusion: Indications, outcomes, and complications. J Am
Acad Orthop Surg. 24:96–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rajaee SS, Bae HW, Kanim LE and Delamarter
RB: Spinal fusion in the United States: Analysis of trends from
1998 to 2008. Spine. 37:67–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Rajaee SS, Kanim LE and Bae HW: National
trends in revision spinal fusion in the USA: Patient
characteristics and complications. Bone Joint J. 96-B:807–816.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stich S, Stolk M, Girod PP, Thomé C,
Sittinger M, Ringe J, Seifert M and Hegewald AA: Regenerative and
immunogenic characteristics of cultured nucleus pulposus cells from
human cervical intervertebral discs. PLoS One. 10:e01269542015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Feng G, Zhao X, Liu H, Zhang H, Chen X,
Shi R, Liu X, Zhao X, Zhang W and Wang B: Transplantation of
mesenchymal stem cells and nucleus pulposus cells in a degenerative
disc model in rabbits: A comparison of 2 cell types as potential
candidates for disc regeneration. J Neurosurg Spine. 14:322–329.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ishihara H, Warensjo K, Roberts S and
Urban JP: Proteoglycan synthesis in the intervertebral disk
nucleus: The role of extracellular osmolality. Am J Physiol.
272:C1499–C1506. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van Dijk B, Potier E and Ito K: Culturing
bovine nucleus pulposus explants by balancing medium osmolarity.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 17:1089–1096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wuertz K, Godburn K, Neidlinger-Wilke C,
Urban J and Iatridis JC: Behavior of mesenchymal stem cells in the
chemical microenvironment of the intervertebral disc. Spine.
33:1843–1849. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vadalà G, Sowa G, Hubert M, Gilbertson LG,
Denaro V and Kang JD: Mesenchymal stem cells injection in
degenerated inter-vertebral disc: Cell leakage may induce
osteophyte formation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 6:348–355. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fields AJ, Liebenberg EC and Lotz JC:
Innervation of pathologies in the lumbar vertebral end plate and
intervertebral disc. Spine J. 14:513–521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liang CZ, Li H, Tao YQ, Peng LH, Gao JQ,
Wu JJ, Li FC, Hua JM and Chen QX: Dual release of dexamethasone and
TGF-beta3 from polymeric microspheres for stem cell matrix
accumulation in a rat disc degeneration model. Acta Biomater.
9:9423–9433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chik TK, Ma XY, Choy TH, Li YY, Diao HJ,
Teng WK, Han SJ, Cheung KM and Chan BP: Photochemically crosslinked
collagen annulus plug: A potential solution solving the leakage
problem of cell-based therapies for disc degeneration. Acta
Biomater. 9:8128–8139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carragee EJ, Don AS, Hurwitz EL, Cuellar
JM, Carrino JA and Herzog R: 2009 ISSLS Prize Winner: Does
discography cause accelerated progression of degeneration changes
in the lumbar disc: A ten-year matched cohort study. Spine.
34:2338–2345. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schmidt MB, Mow VC, Chun LE and Eyre DR:
Effects of proteo-glycan extraction on the tensile behavior of
articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 8:353–363. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lotz JC, Colliou OK, Chin JR, Duncan NA
and Liebenberg E: Compression-induced degeneration of the
intervertebral disc: An in vivo mouse model and finite-element
study. Spine. 23:2493–2506. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Holm S, Holm AK, Ekström L, Karladani A
and Hansson T: Experimental disc degeneration due to endplate
injury. J Spinal Disord Tech. 17:64–71. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mitchell PG, Magna HA, Reeves LM,
Lopresti-Morrow LL, Yocum SA, Rosner PJ, Geoghegan KF and Hambor
JE: Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of
matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. J
Clin Invest. 97:761–768. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matrisian LM: Metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 6:121–125. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gruber HE, Johnson TL, Leslie K, Ingram
JA, Martin D, Hoelscher G, Banks D, Phieffer L, Coldham G and
Hanley EN Jr: Autologous intervertebral disc cell implantation: A
model using Psammomys obesus, the sand rat. Spine. 27:1626–1633.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang W, Zhang X, Hao J, Shen J, Fang J,
Dong W, Wang D, Zhang X, Shui W, Luo Y, et al: SIRT1 protects
against apoptosis by promoting autophagy in degenerative human disc
nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep. 4:74562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|