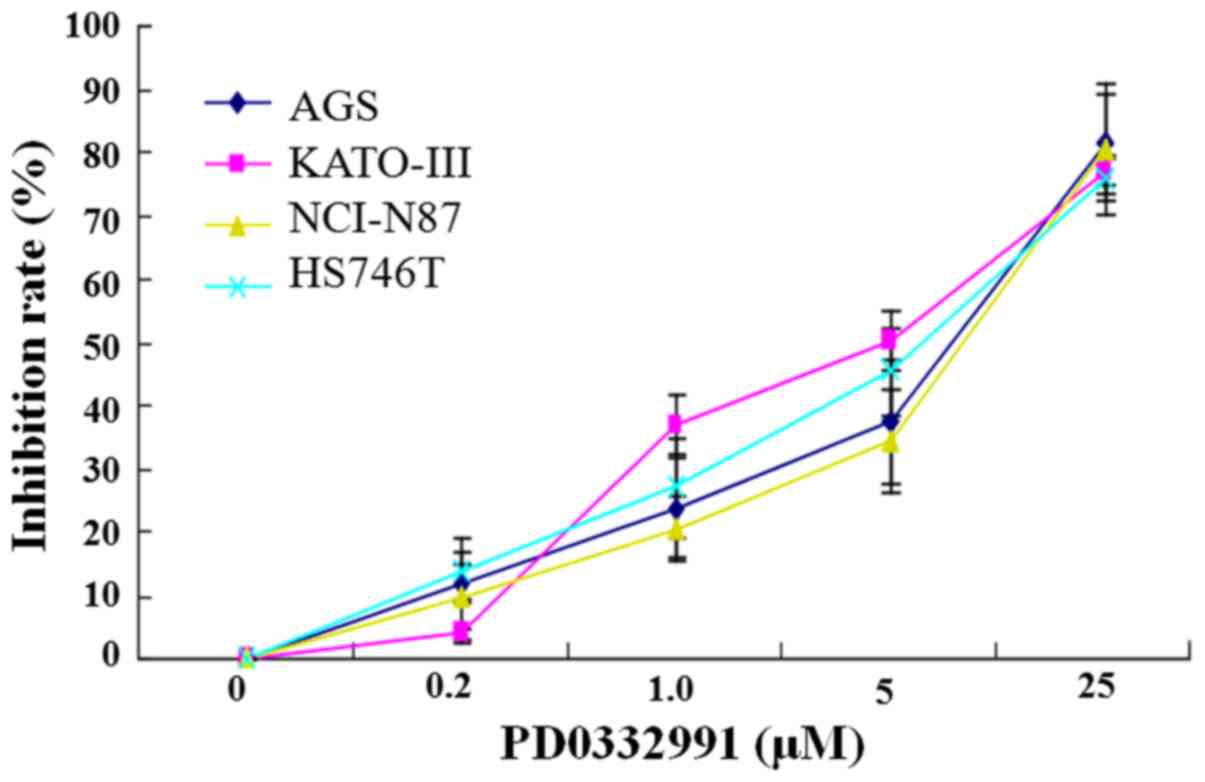
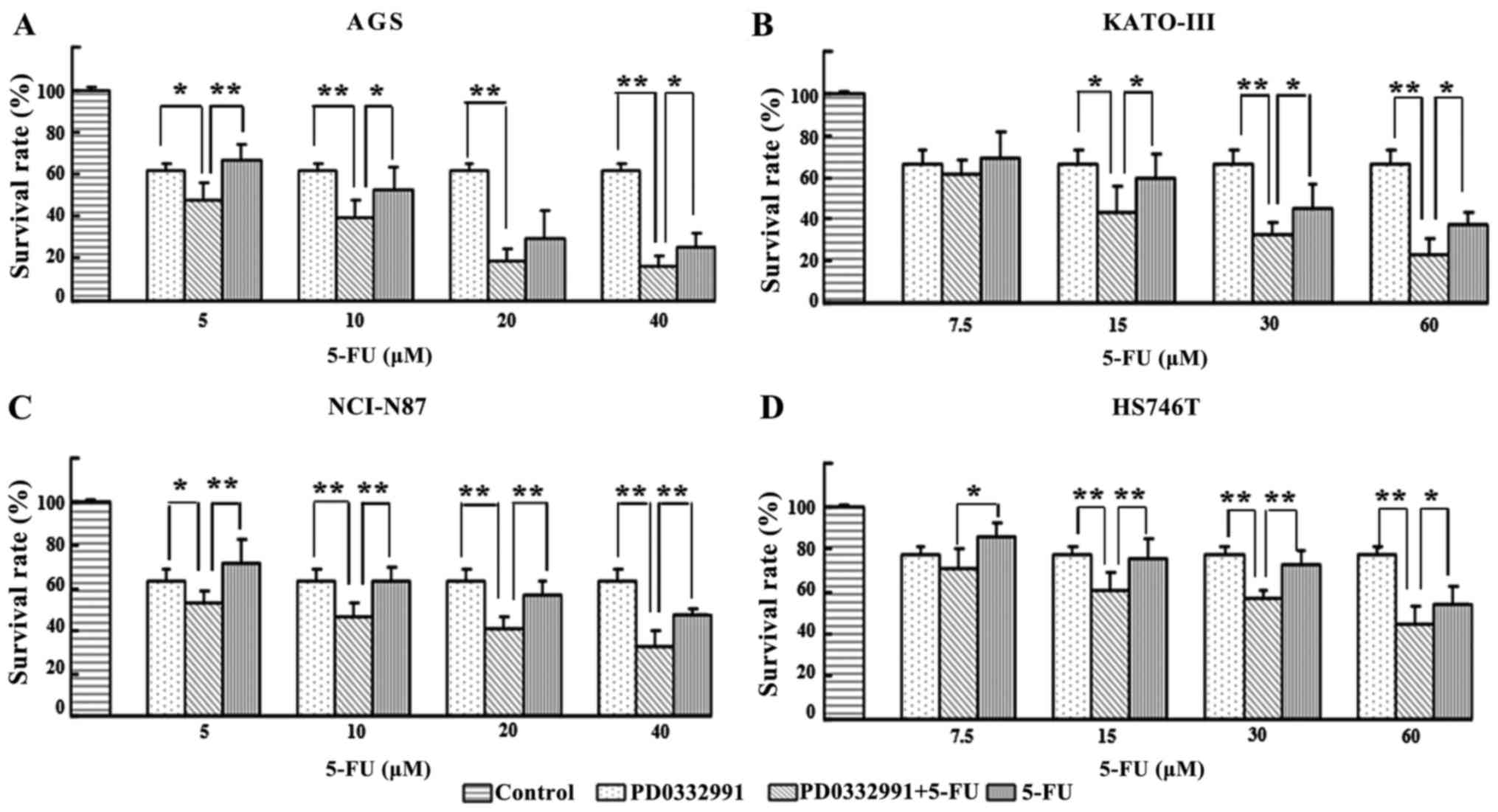
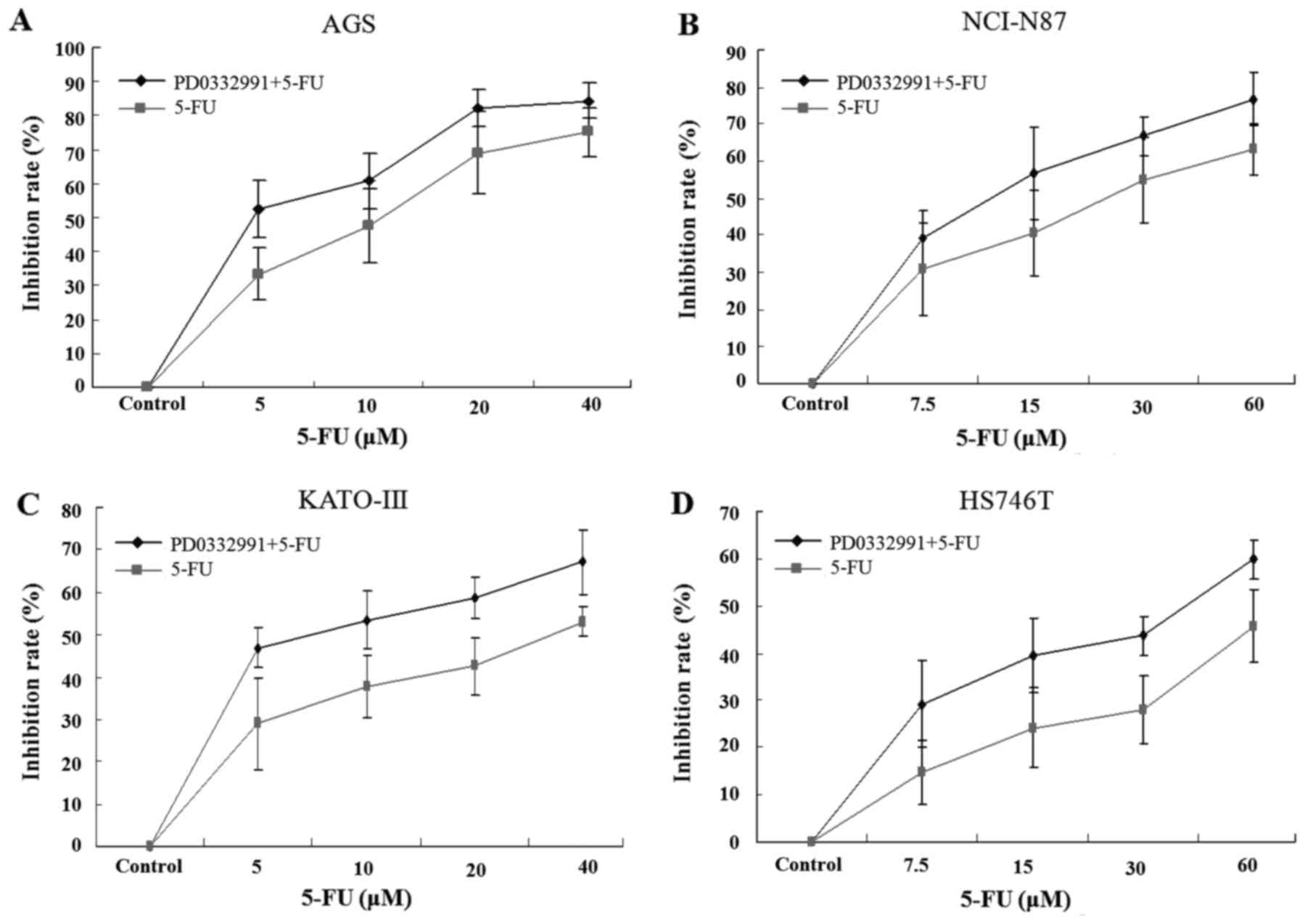
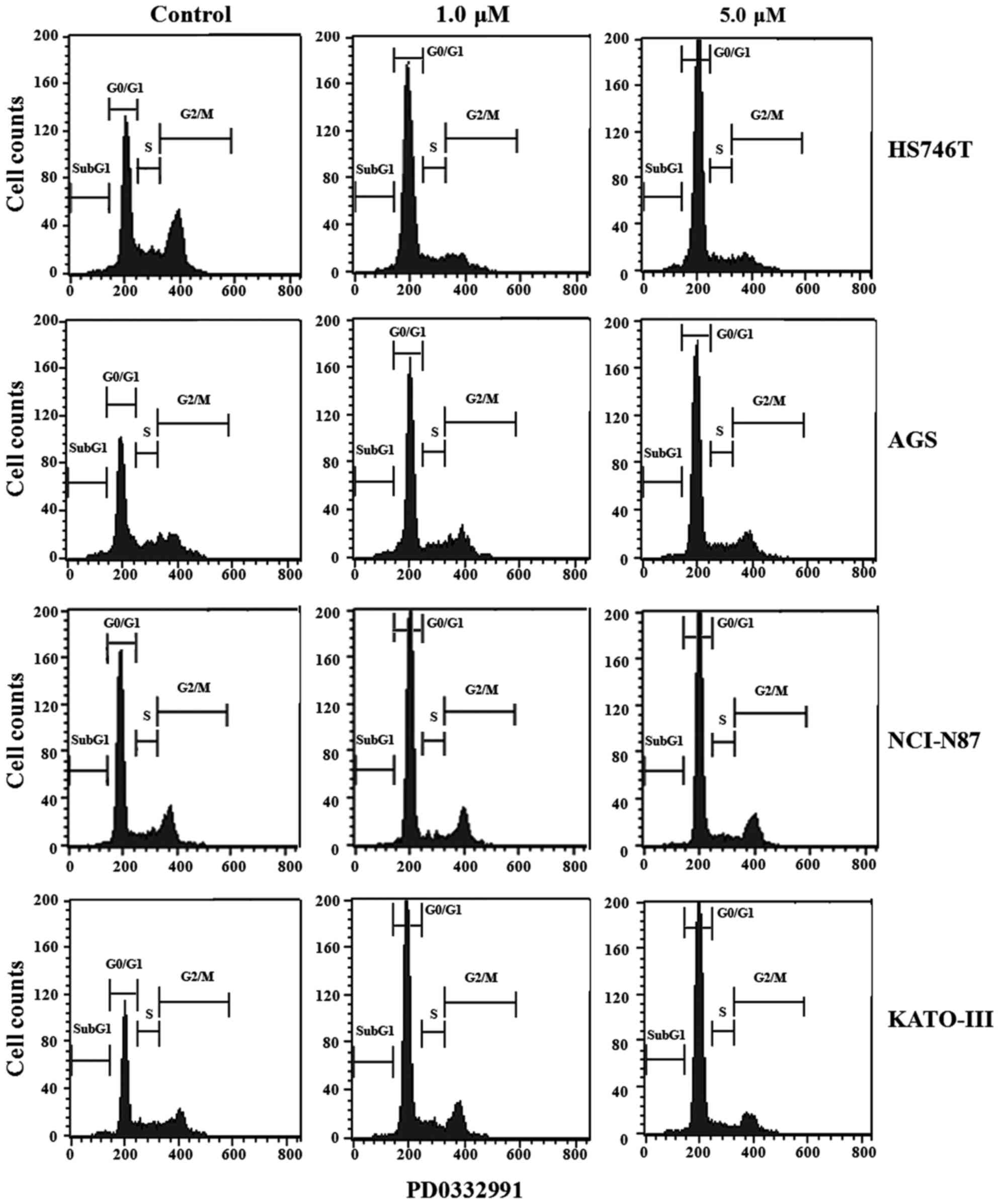
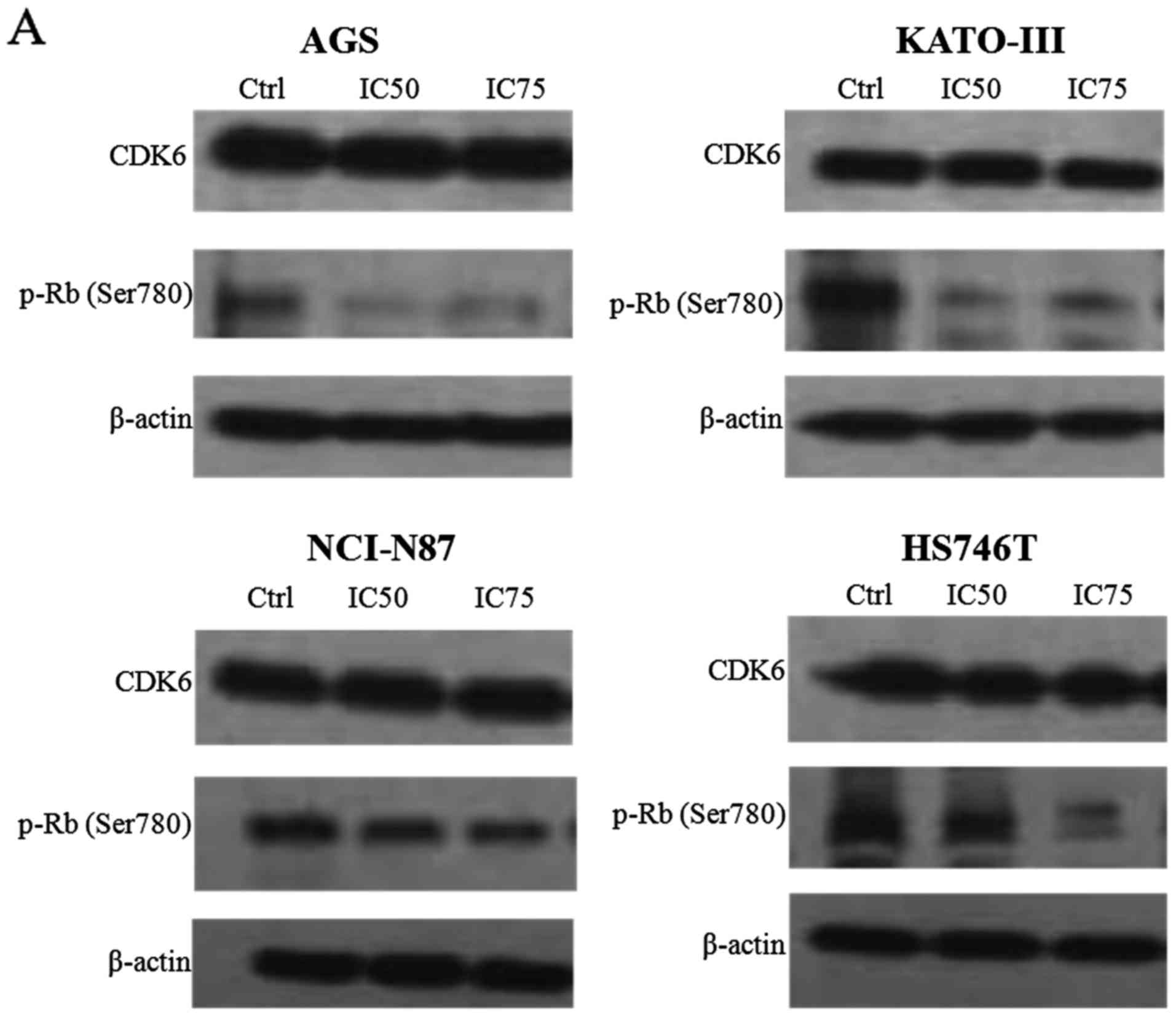
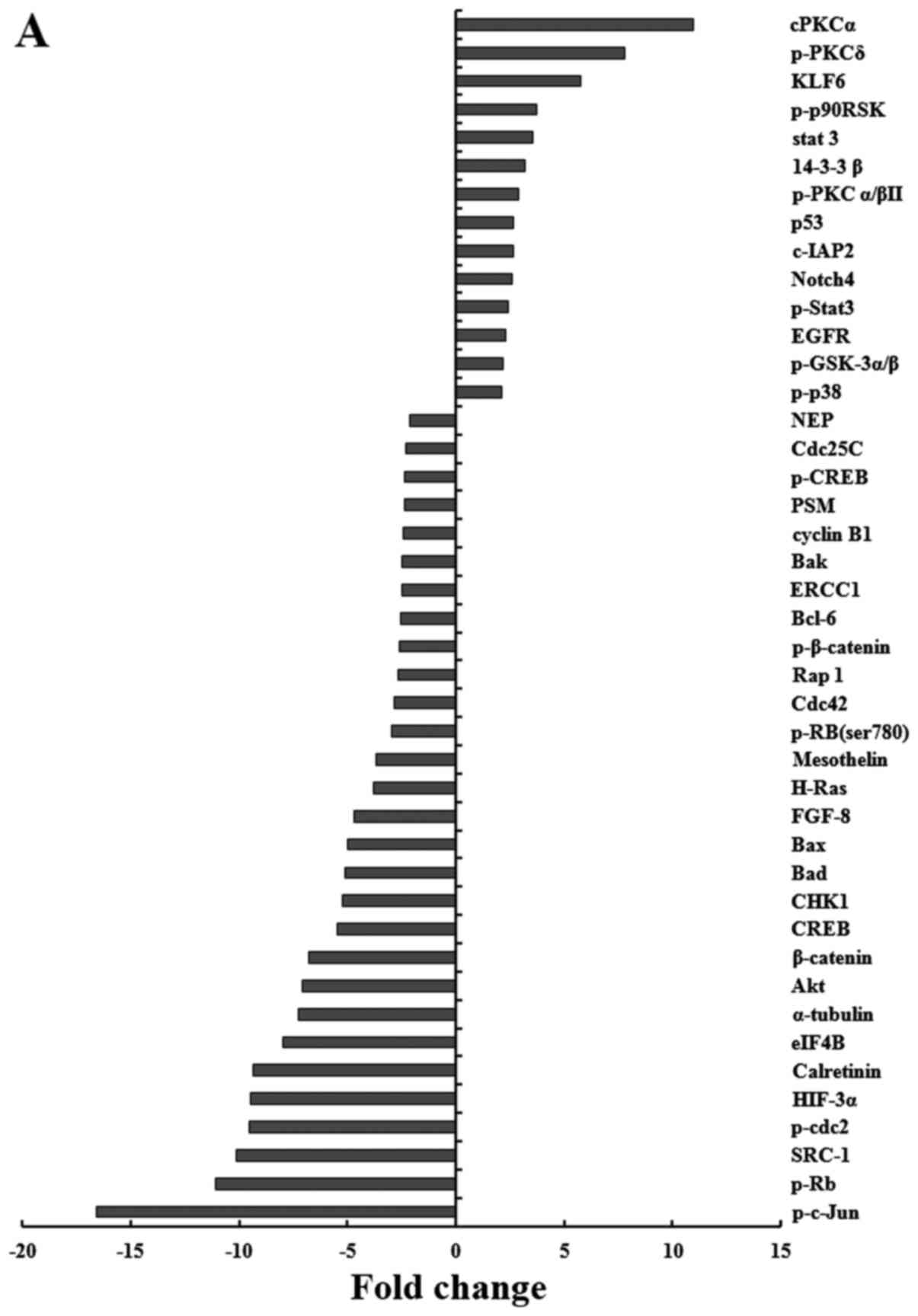
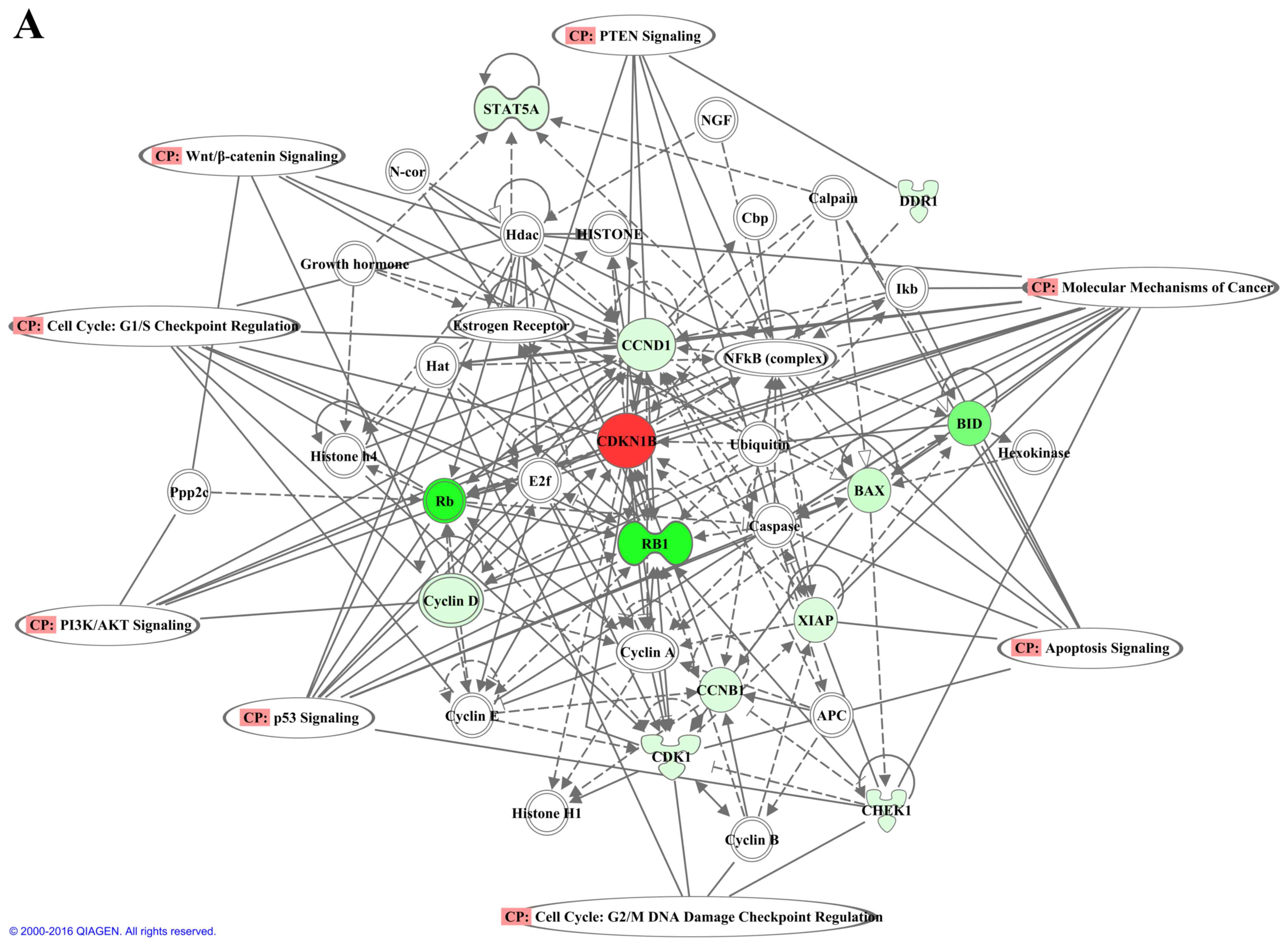
|
1
|
Carcas LP: Gastric cancer review. J
Carcinog. 13:142014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thiel A and Ristimäki A: Targeted therapy
in gastric cancer. APMIS. 123:365–372. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hohenberger P and Gretschel S: Gastric
cancer. Lancet. 362:305–315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
May P and May E: Twenty years of p53
research: Structural and functional aspects of the p53 protein.
Oncogene. 18:7621–7636. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL,
Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, et
al: Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD0332991
and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol
Cancer Ther. 3:1427–1438. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toogood PL, Harvey PJ, Repine JT, Sheehan
DJ, VanderWel SN, Zhou H, Keller PR, McNamara DJ, Sherry D, Zhu T,
et al: Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor of
cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. J Med Chem. 48:2388–2406. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
VanderWel SN, Harvey PJ, McNamara DJ,
Repine JT, Keller PR, Quin J III, Booth RJ, Elliott WL, Dobrusin
EM, Fry DW, et al: Pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-ones as specific
inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4. J Med Chem. 48:2371–2387.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Foo M and Leong T: Adjuvant therapy for
gastric cancer: Current and future directions. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:13718–13727. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kanat O and O'Neil BH: Metastatic gastric
cancer treatment: A little slow but worthy progress. Med Oncol.
30:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SR, Shin JW, Kim HO, Son BH, Yoo CH
and Shin JH: Determining the effect of transforming growth
factor-β1 on cdk4 and p27 in gastric cancer and cholangiocarcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 5:694–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Motohashi M, Wakui S, Muto T, Suzuki Y,
Shirai M, Takahashi H and Hano H: Cyclin D1/cdk4, estrogen
receptors α and β, in N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced
rat gastric carcinogenesis: Immunohistochemical study. J Toxicol
Sci. 36:373–378. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takano Y, Kato Y, van Diest PJ, Masuda M,
Mitomi H and Okayasu I: Cyclin D2 overexpression and lack of p27
correlate positively and cyclin E inversely with a poor prognosis
in gastric cancer cases. Am J Pathol. 156:585–594. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dhillon S: Palbociclib: First global
approval. Drugs. 75:543–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carey LA and Perou CM: Palbociclib -
taking breast-cancer cells out of gear. N Engl J Med. 373:273–274.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dukelow T, Kishan D, Khasraw M and Murphy
CG: CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs.
26:797–806. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morikawa A and Henry L: Palbociclib for
the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative
metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3591–3596. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Young MR, Li JJ, Rincón M, Flavell RA,
Sathyanarayana BK, Hunziker R and Colburn N: Transgenic mice
demonstrate AP-1 (activator protein-1) transactivation is required
for tumor promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:9827–9832. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eferl R, Ricci R, Kenner L, Zenz R, David
JP, Rath M and Wagner EF: Liver tumor development. c-Jun
antagonizes the proapoptotic activity of p53. Cell. 112:181–192.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Behrens A, Sibilia M, David JP,
Möhle-Steinlein U, Tronche F, Schütz G and Wagner EF: Impaired
postnatal hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration in mice
lacking c-jun in the liver. EMBO J. 21:1782–1790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schreiber M, Kolbus A, Piu F, Szabowski A,
Möhle-Steinlein U, Tian J, Karin M, Angel P and Wagner EF: Control
of cell cycle progression by c-Jun is p53 dependent. Genes Dev.
13:607–619. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wisdom R, Johnson RS and Moore C: c-Jun
regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct
mechanisms. EMBO J. 18:188–197. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Behrens A, Sibilia M and Wagner EF:
Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced
apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 21:326–329. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mechta F, Lallemand D, Pfarr CM and Yaniv
M: Transformation by ras modifies AP1 composition and activity.
Oncogene. 14:837–847. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Amelio I and Melino G: The p53 family and
the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs): Determinants of cancer
progression. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:425–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baker SJ, Markowitz S, Fearon ER, Willson
JK and Vogelstein B: Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell
growth by wild-type p53. Science. 249:912–915. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diller L, Kassel J, Nelson CE, Gryka MA,
Litwak G, Gebhardt M, Bressac B, Ozturk M, Baker SJ and Vogelstein
B: p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas.
Mol Cell Biol. 10:5772–5781. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martinez J, Georgoff I, Martinez J and
Levine AJ: Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a
temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 5:151–159. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Steelman LS, Stadelman KM, Chappell WH,
Horn S, Bäsecke J, Cervello M, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Stivala F,
Martelli AM, et al: Akt as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 12:1139–1165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fraser M, Leung BM, Yan X, Dan HC, Cheng
JQ and Tsang BK: p53 is a determinant of X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein/Akt-mediated chemoresistance in human ovarian
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:7081–7088. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|