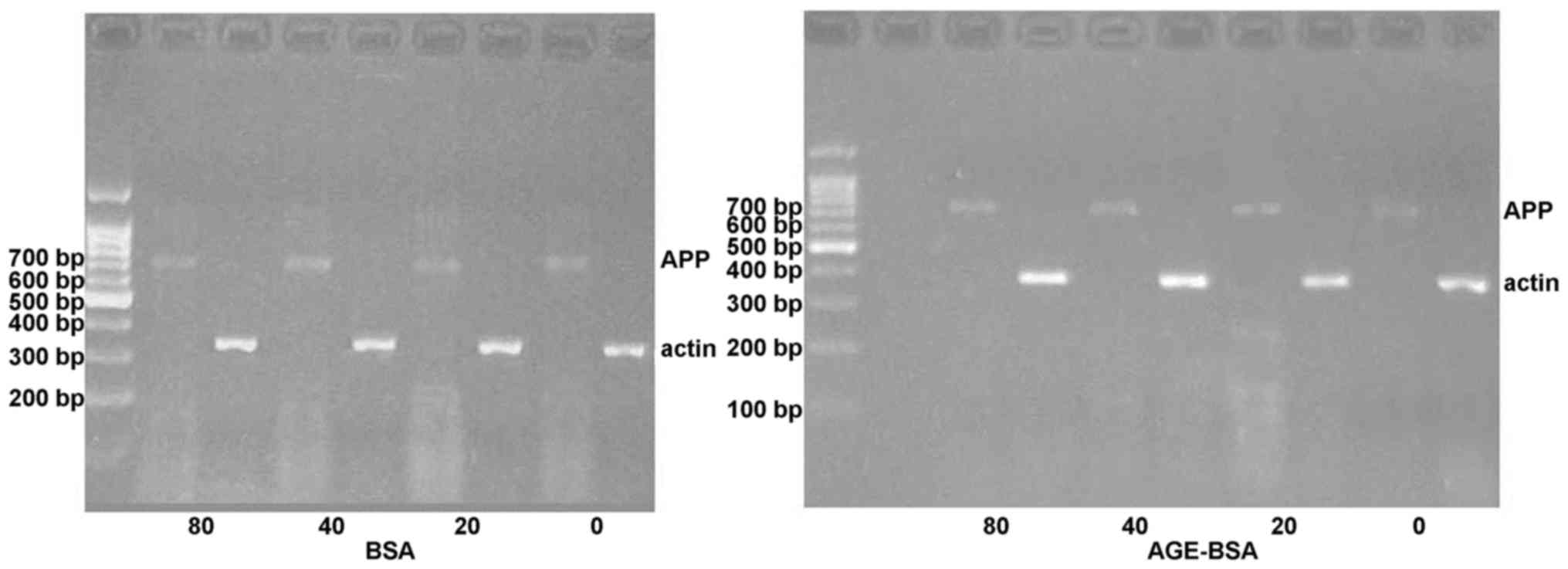
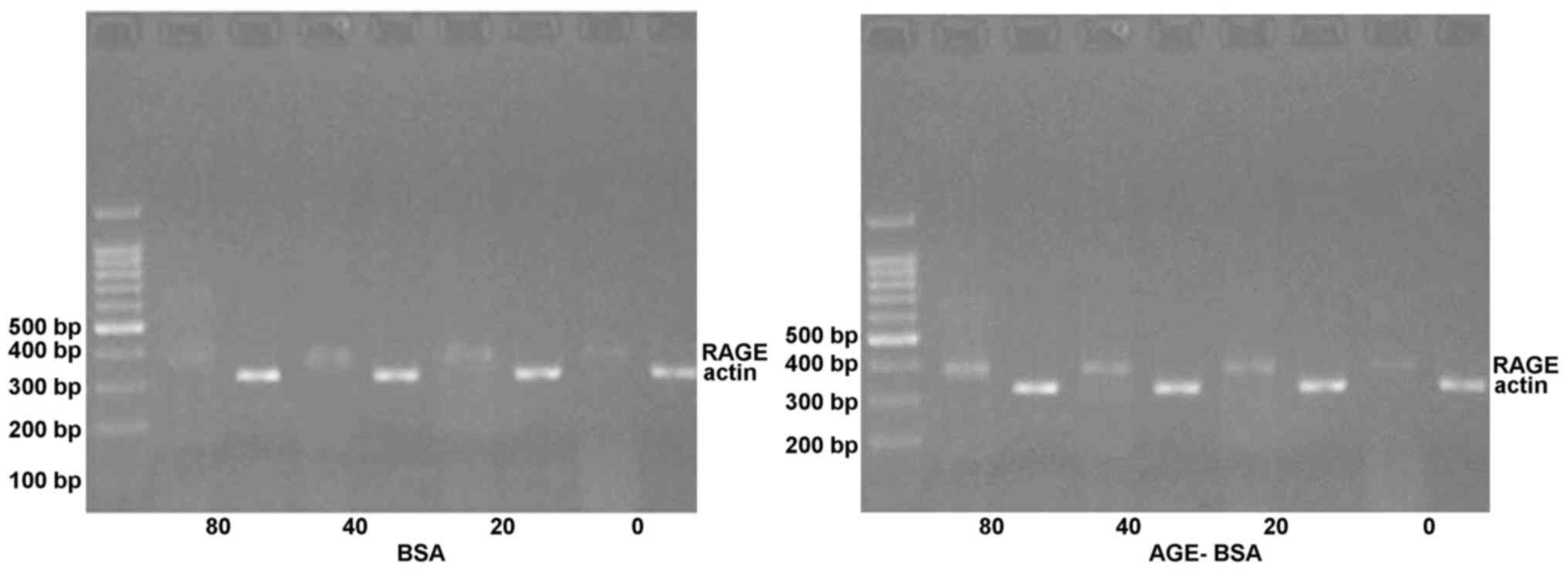
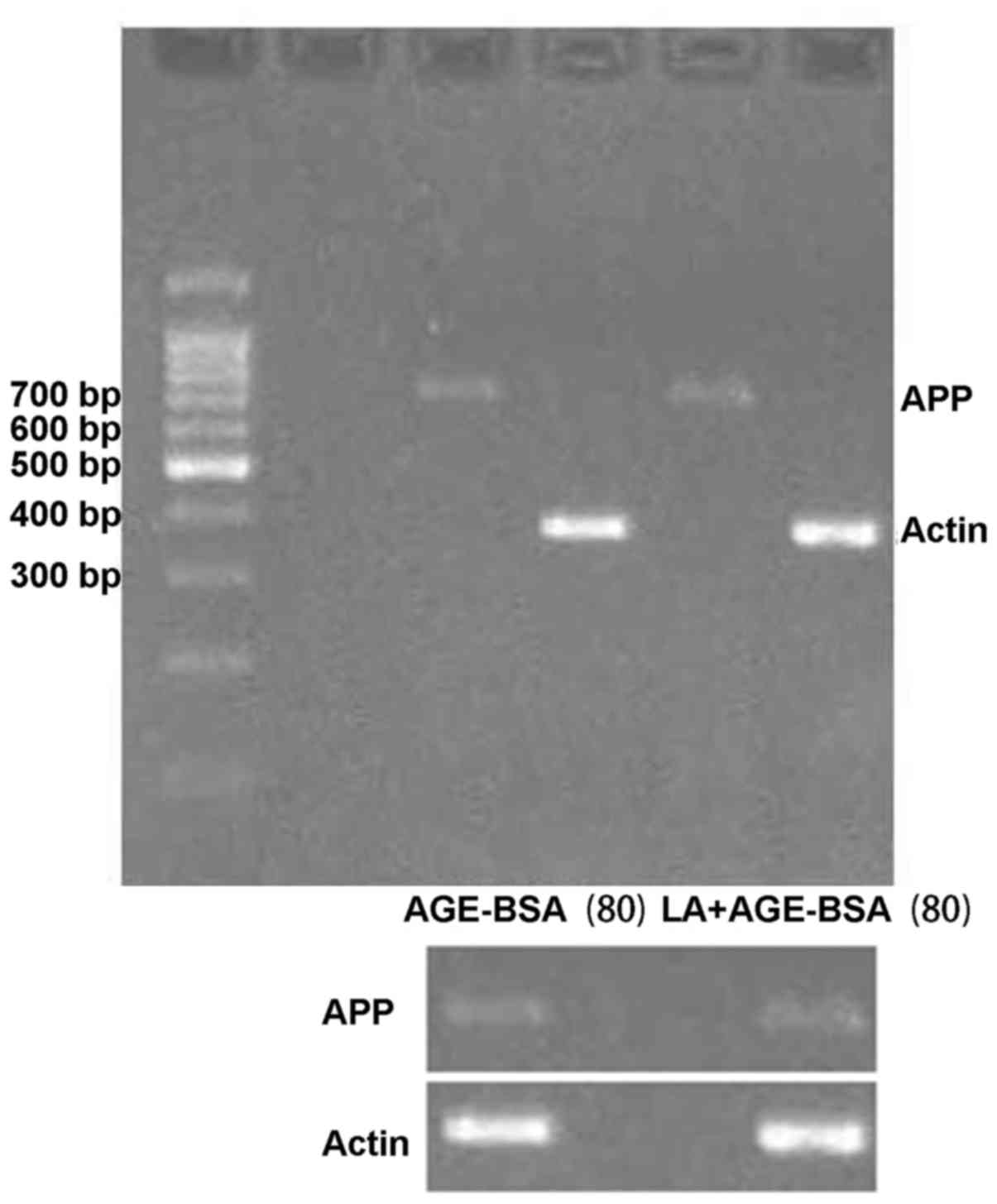
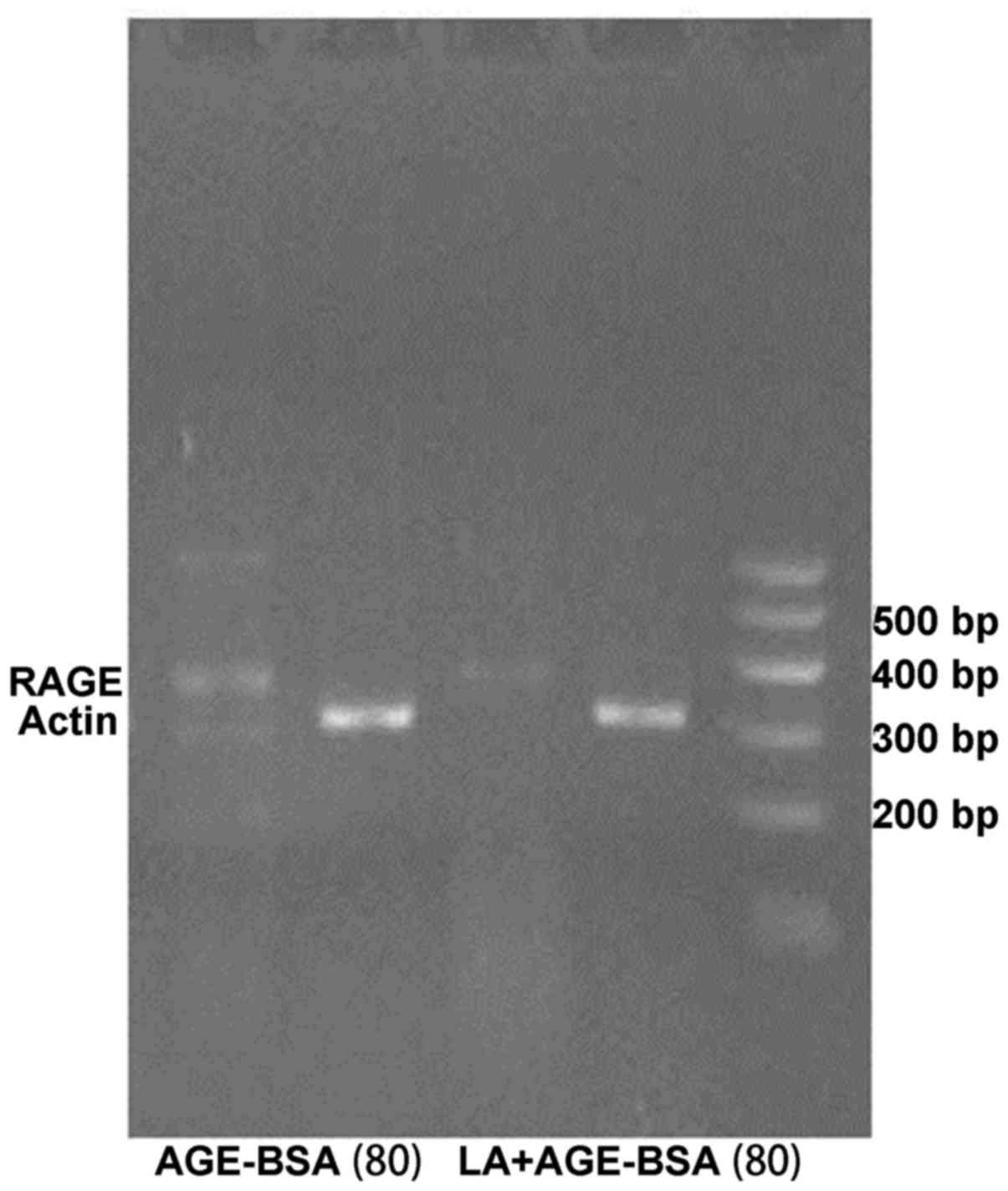
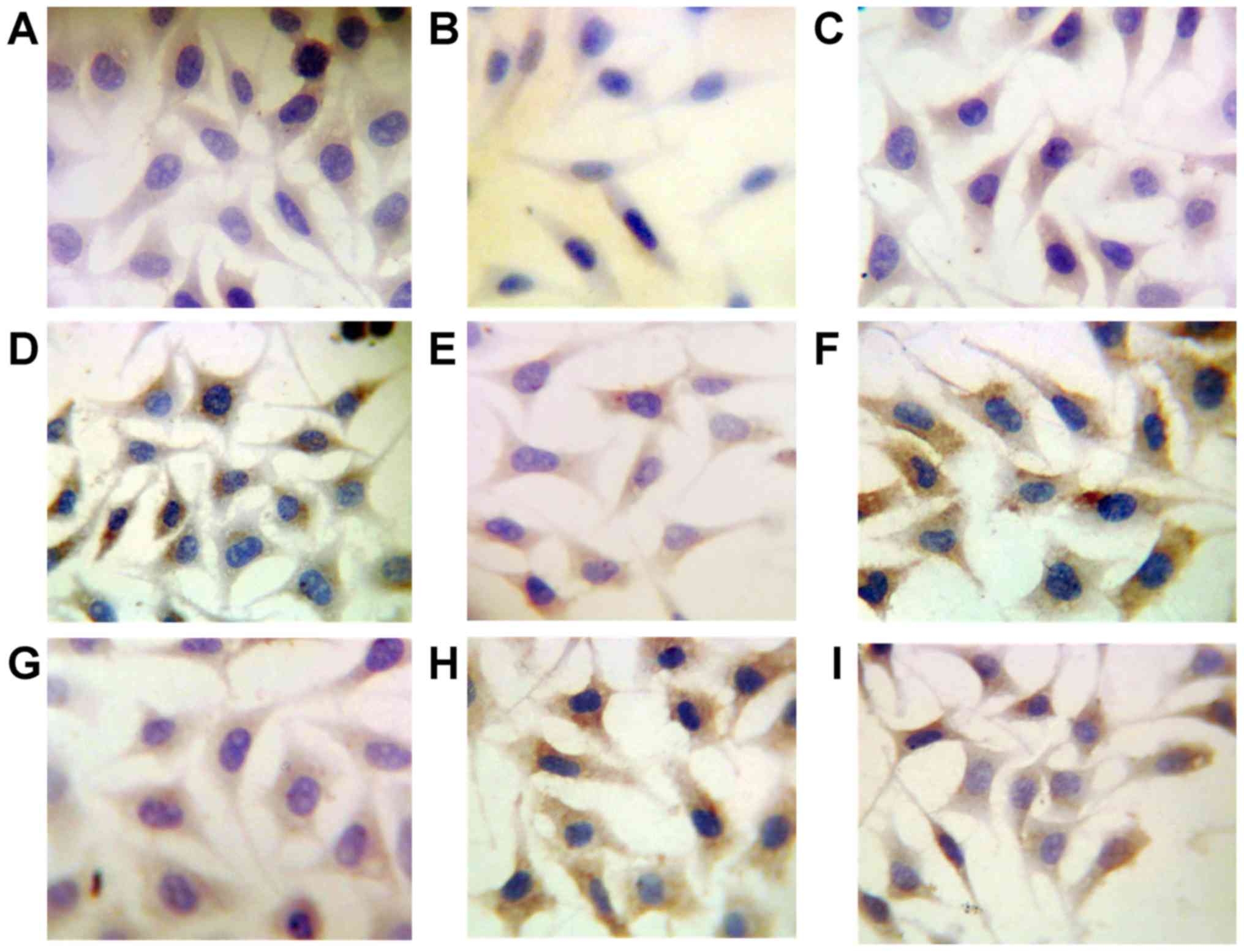
|
1
|
Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E,
Brayne C and Scheltens P: Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: A
systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 5:64–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lu FP, Lin KP and Kuo HK: Diabetes and the
risk of multi-system aging phenotypes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 4:e41442009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cukierman T, Gerstein HC and Williamson
JD: Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes-systematic overview
of prospective observational studies. Diabetologia. 48:2460–2469.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vasan S, Foiles PG and Founds HW:
Therapeutic potential of AGE inhibitors and breakers of AGE protein
cross-links. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 10:1977–1987. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gong CX, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I and Iqbal
K: Impaired brain glucose metabolism leads to Alzheimer
neurofibrillary degeneration through a decrease in tau
O-GlcNAcylation. J Alzheimers Dis. 9:1–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arancio O, Zhang HP, Chen X, Lin C,
Trinchese F, Puzzo D, Liu S, Hegde A, Yan SF, Stern A, Luddy JS, et
al: RAGE potentiates Abeta-induced perturbation of neuronal
function in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 23:4096–4105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lefebvre T, Ferreira S, Dupont-Wallois L,
Bussière T, Dupire MJ, Delacourte A, Michalski JC and
Caillet-Boudin ML: Evidence of a balance between phosphorylation
and O-GlcNAc glycosylation of Tau proteins-a role in nuclear
localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1619:167–176. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoyer S: Causes and consequences of
disturbances of cerebral glucose metabolism in sporadic Alzheimer
disease: Therapeutic implications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 541:135–152.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guglielmotto M, Aragno M, Tamagno E,
Vercellinatto I, Visentin S, Medana C, Catalano MG, Smith MA, Perry
G, Danni O, et al: AGEs/RAGE complex upregulates BACE1 via
NF-kappaB pathway activation. Neurobiol Aging. 33:196 e113–127.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Farr SA, Price TO, Banks WA, Ercal N and
Morley JE: Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on memory, oxidation, and
lifespan in SAMP8 mice. J Alzheimers Dis. 32:447–455.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shinto L, Quinn J, Montine T, Dodge HH,
Woodward W, Baldauf-Wagner S, Waichunas D, Bumgarner L, Bourdette
D, Silbert L, et al: A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial of
omega-3 fatty acids and alpha lipoic acid in Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimers Dis. 38:111–120. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Galasko DR, Peskind E, Clark CM, Quinn JF,
Ringman JM, Jicha GA, Cotman C, Cottrell B, Montine TJ, Thomas RG,
et al: Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study: Antioxidants for
Alzheimer disease: A randomized clinical trial with cerebrospinal
fluid biomarker measures. Arch Neurol. 69:836–841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hager K, Marahrens A, Kenklies M, Riederer
P and Münch G: Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for
Alzheimer [corrected] type dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.
32:275–282. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Xing GQ, Barker JL, Chang Y,
Maric D, Ma W, Li BS and Rubinow DR: Alpha-lipoic acid protects rat
cortical neurons against cell death induced by amyloid and hydrogen
peroxide through the Akt signalling pathway. Neurosci Lett.
312:125–128. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ono K, Hirohata M and Yamada M:
Alpha-lipoic acid exhibits anti-amyloidogenicity for beta-amyloid
fibrils in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 341:1046–1052. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Woltjer RL, Maezawa I, Ou JJ, Montine KS
and Montine TJ: Advanced glycation endproduct precursor alters
intracellular amyloid-beta/A beta PP carboxy-terminal fragment
aggregation and cytotoxicity. J Alzheimers Dis. 5:467–476. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Takeuchi M, Bucala R, Suzuki T, Ohkubo T,
Yamazaki M, Koike T, Kameda Y and Makita Z: Neurotoxicity of
advanced glycation end-products for cultured cortical neurons. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 59:1094–1105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sasaki N, Fukatsu R, Tsuzuki K, Hayashi Y,
Yoshida T, Fujii N, Koike T, Wakayama I, Yanagihara R, Garruto R,
et al: Advanced glycation end products in Alzheimer's disease and
other neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Pathol. 153:1149–1155. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saxena P, Saxena AK, Cui XL, Obrenovich M,
Gudipaty K and Monnier VM: Transition metal-catalyzed oxidation of
ascorbate in human cataract extracts: Possible role of advanced
glycation end products. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 41:1473–1481.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh R, Barden A, Mori T and Beilin L:
Advanced glycation end-products: A review. Diabetologia.
44:129–146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Münch G, Kuhla B, Lüth HJ, Arendt T and
Robinson SR: Anti-AGEing defences against Alzheimer's disease.
Biochem Soc Trans. 31:1397–1399. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maczurek A, Shanmugam K and Münch G:
Inflammation and the redox-sensitive AGE-RAGE pathway as a
therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1126:147–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Misonou H, Morishima-Kawashima M and Ihara
Y: Oxidative stress induces intracellular accumulation of amyloid
beta-protein (Abeta) in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochemistry.
39:6951–6959. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cho HJ, Son SM, Jin SM, Hong HS, Shin DH,
Kim SJ, Huh K and Mook-Jung I: RAGE regulates BACE1 and Abeta
generation via NFAT1 activation in Alzheimer's disease animal
model. FASEB J. 23:2639–2649. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Twigg SM, Chen MM, Joly AH, Chakrapani SD,
Tsubaki J, Kim HS, Oh Y and Rosenfeld RG: Advanced glycosylation
end products up-regulate connective tissue growth factor
(insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein 2) in
human fibroblasts: A potential mechanism for expansion of
extracellular matrix in diabetes mellitus. Endocrinology.
142:1760–1769. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hughes JM, Kuiper EJ, Klaassen I, Canning
P, Stitt AW, Van Bezu J, Schalkwijk CG, van Noorden CJ and
Schlingemann RO: Advanced glycation end products cause increased
CCN family and extracellular matrix gene expression in the diabetic
rodent retina. Diabetologia. 50:1089–1098. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue
B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L, Lin C, Yu J, et al:
RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain
barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med. 9:907–913. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brady MJ, Bourbonais FJ and Saltiel AR:
The activation of glycogen synthase by insulin switches from kinase
inhibition to phosphatase activation during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1
cells. J Biol Chem. 273:14063–14066. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang HY, Lee DH, D'Andrea MR, Peterson PA,
Shank RP and Reitz AB: beta-Amyloid(1–42) binds to alpha7 nicotinic
acetyl-choline receptor with high affinity. Implications for
Alzheimer's disease pathology. J Biol Chem. 275:5626–5632. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Onyango IG, Tuttle JB and Bennett JP Jr:
Altered intracellular signaling and reduced viability of
Alzheimer's disease neuronal cybrids is reproduced by beta-amyloid
peptide acting through receptor for advanced glycation end products
(RAGE). Mol Cell Neurosci. 29:333–343. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deane R, Singh I, Sagare AP, Bell RD, Ross
NT, LaRue B, Love R, Perry S, Paquette N, Deane RJ, et al: A
multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain
disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest.
122:1377–1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zlokovic BV: Neurovascular mechanisms of
Alzheimer's neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 28:202–208. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baiguera S, Fioravanzo L, Grandi C, Di
Liddo R, Parnigotto PP and Folin M: Involvement of the receptor for
advanced glycation-end products (RAGE) in β-amyloid-induced toxic
effects in rat cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells cultured in
vitro. Int J Mol Med. 24:9–15. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li M, Shang DS, Zhao WD, Tian L, Li B,
Fang WG, Zhu L, Man SM and Chen YH: Amyloid beta interaction with
receptor for advanced glycation end products up-regulates brain
endothelial CCR5 expression and promotes T cells crossing the
blood-brain barrier. J Immunol. 182:5778–5788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wong A, Lüth HJ, Deuther-Conrad W,
Dukic-Stefanovic S, Gasic-Milenkovic J, Arendt T and Münch G:
Advanced glycation endproducts co-localize with inducible nitric
oxide synthase in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 920:32–40. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boulanger E, Dequiedt P and Wautier JL:
Advanced glycosylation end products (AGE): New toxins. Nephrologie.
23:351–359. 2002.In French.
|
|
37
|
Berbaum K, Shanmugam K, Stuchbury G, Wiede
F, Körner H and Münch G: Induction of novel cytokines and
chemokines by advanced glycation endproducts determined with a
cytometric bead array. Cytokine. 41:198–203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Anzai Y, Hayashi M, Fueki N, Kurata K and
Ohya T: Protracted juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis - an
autopsy report and immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Dev.
28:462–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|