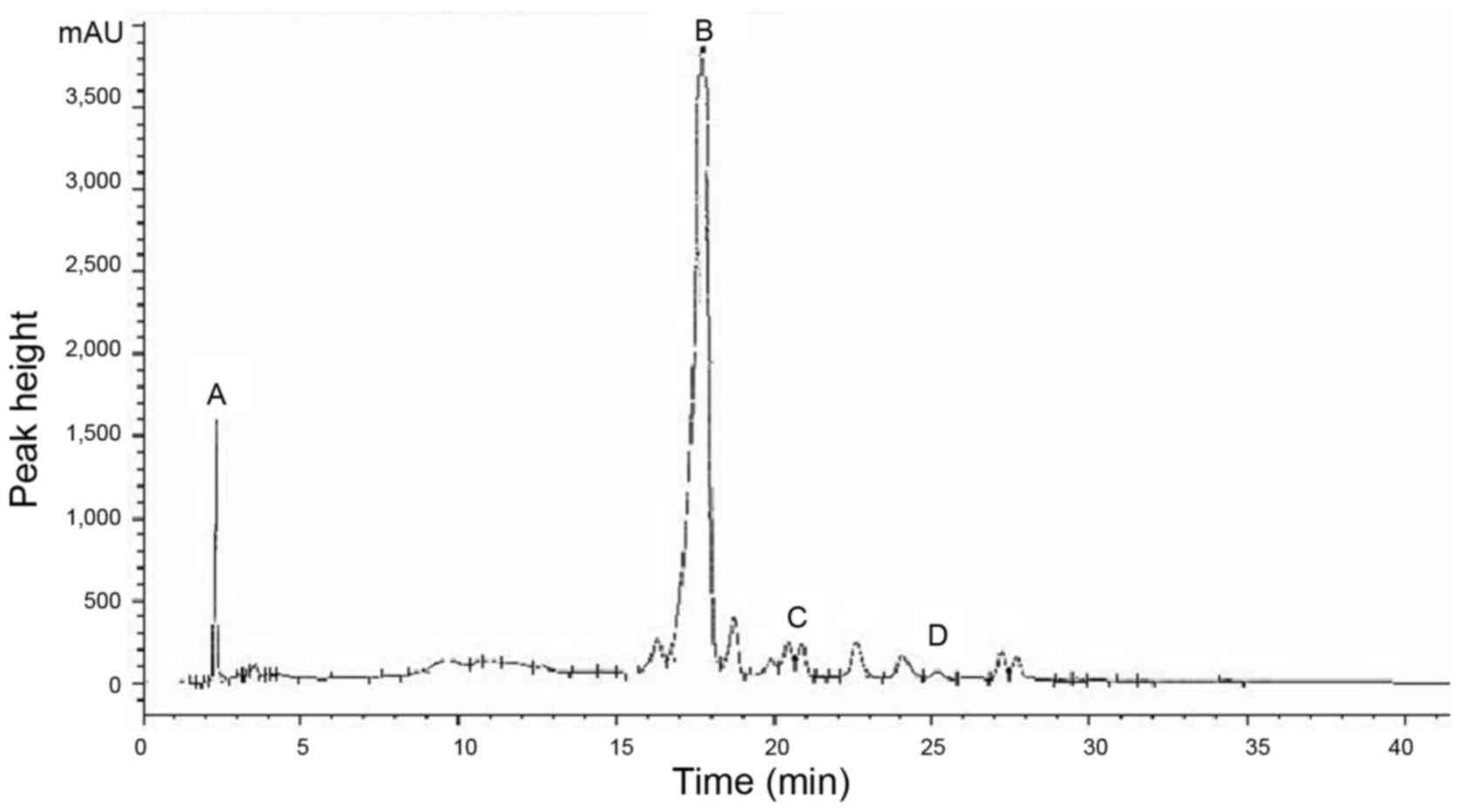
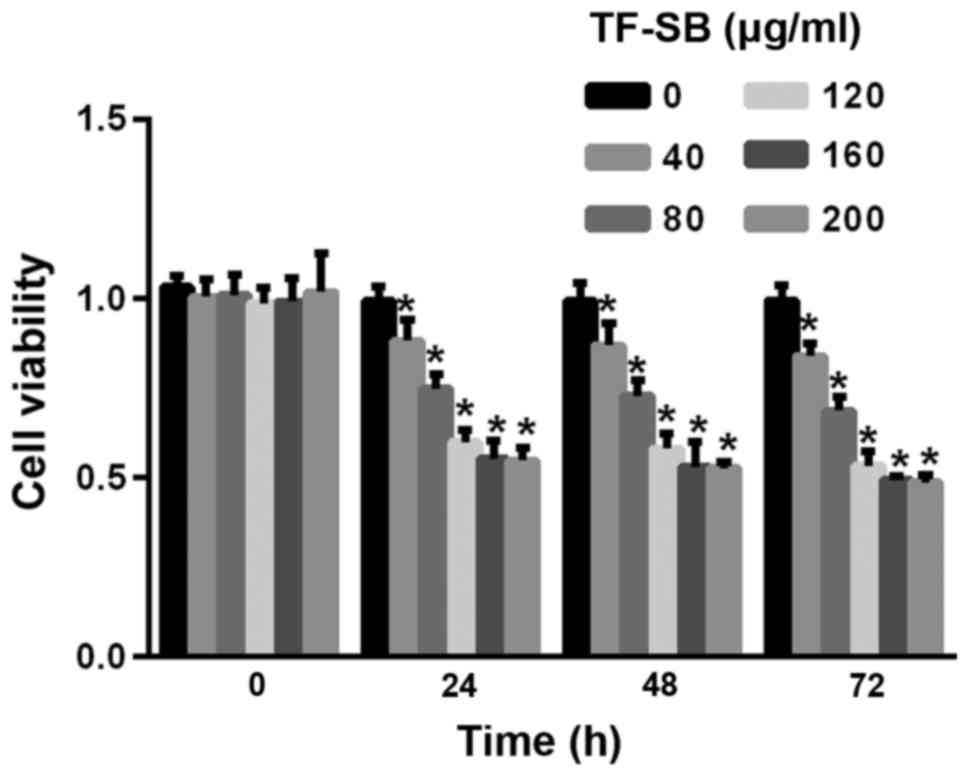
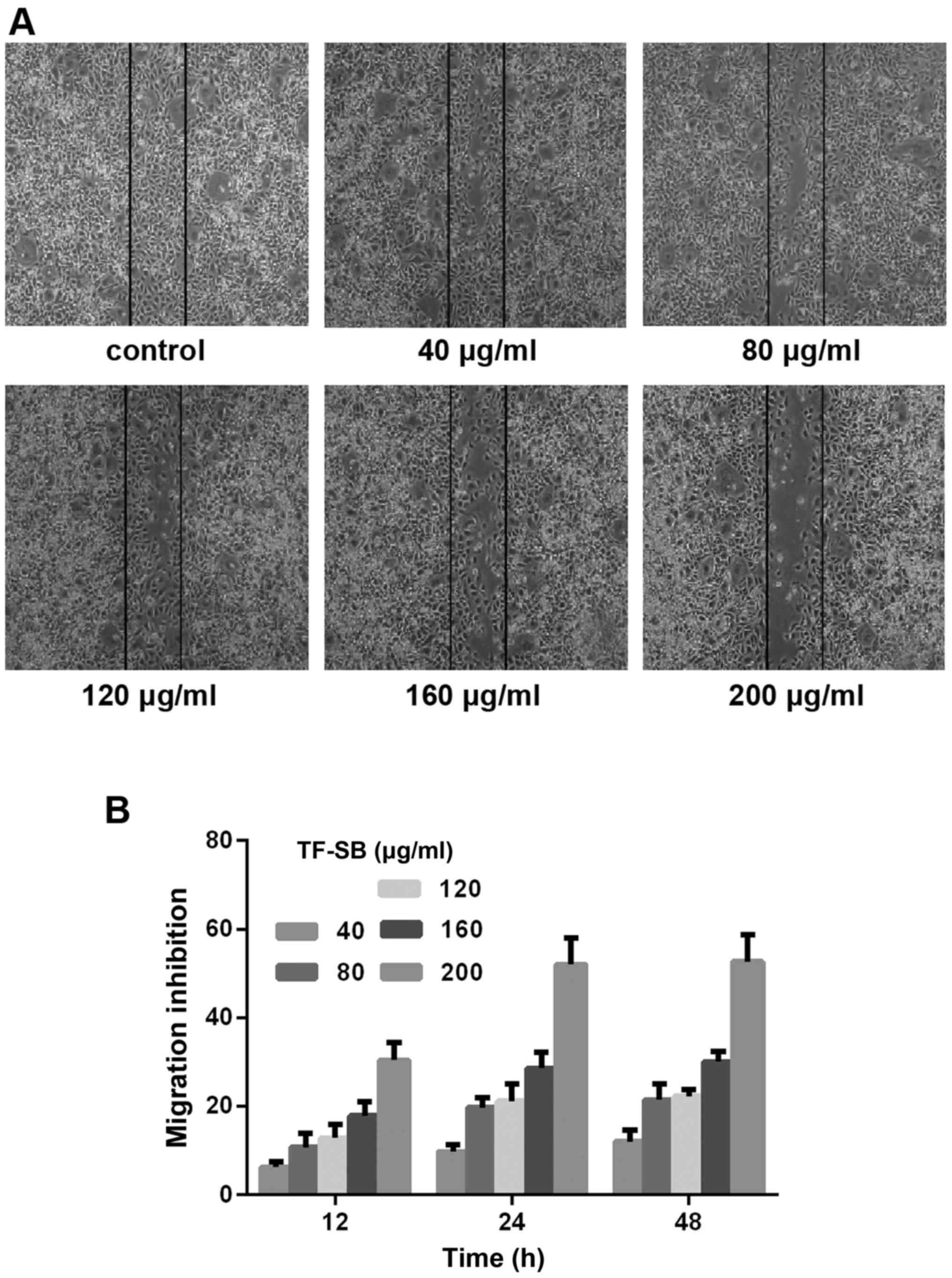
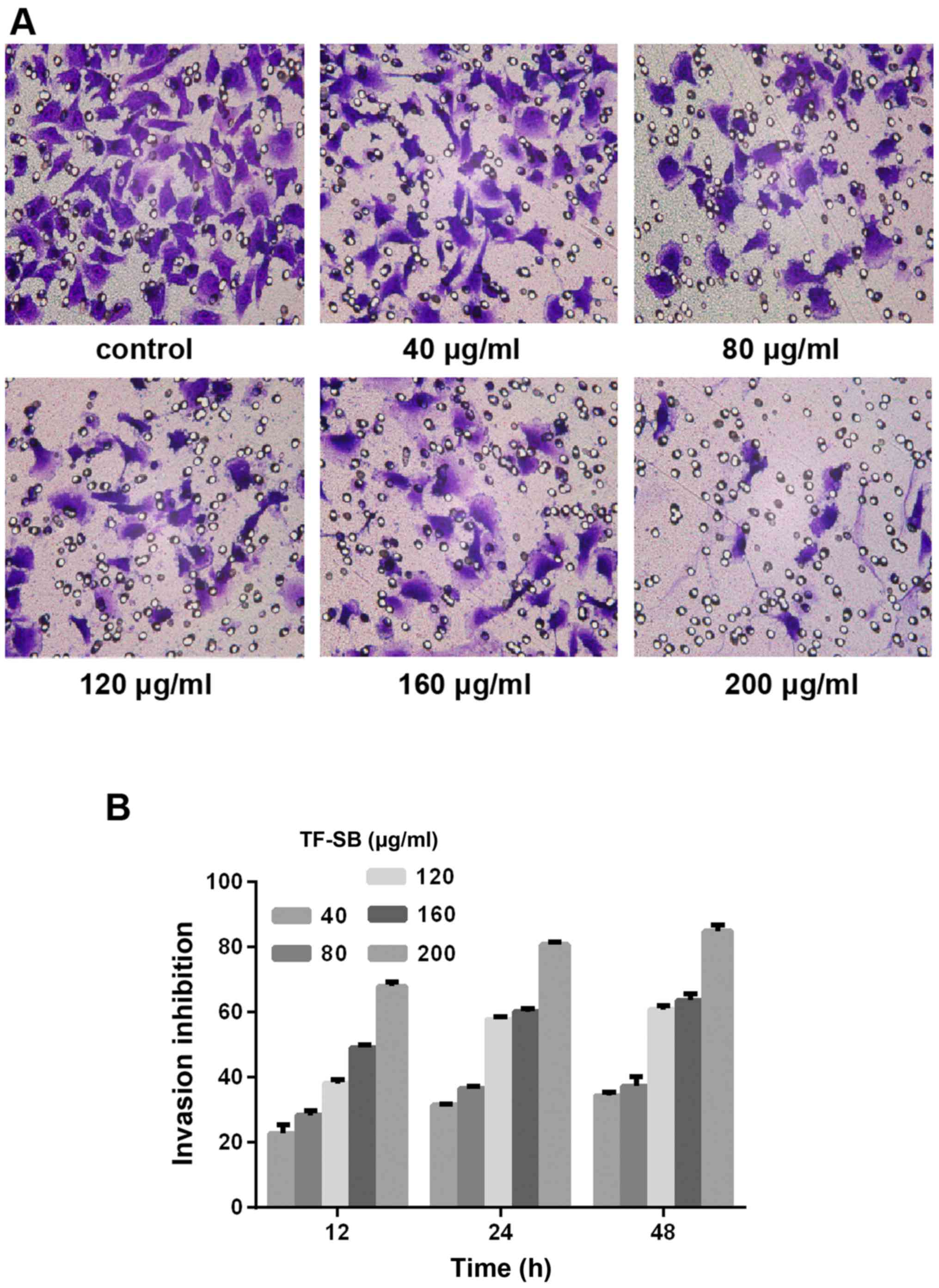
|
1
|
TA S: Genetic factors in the pathogenesis
of breast cancer: their role and relative importance. Nutr.
127(Suppl): 929–932. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Roodman GD: Mechanisms of bone metastasis.
N Engl J Med. 350:1655–1664. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet. 1:571–573. 1889.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schulman KL and Kohles J: Economic burden
of metastatic bone disease in the U.S. Cancer. 109:2334–2342. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mundy GR: Metastasis to bone: causes,
consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:584–593. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kominsky SL and Davidson NE: A 'bone' fide
predictor of metastasis? Predicting breast cancer metastasis to
bone. J Clin Oncol. 24:2227–2229. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dougall WC: Molecular pathways:
osteoclast-dependent and osteoclast-independent roles of the
RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:326–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schramek D, Sigl V and Penninger JM: RANKL
and RANK in sex hormone-induced breast cancer and breast cancer
metastasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 22:188–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang
MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO and Gelmon K: Metastatic
behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 28:3271–3277.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiechi A, Waning DL, Stayrook KR, Buijs
JT, Guise TA and Mohammad KS: Role of TGF-β in breast cancer bone
metastases. Adv Biosci Biotechnol. 4:15–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Datta NS and Abou-Samra AB: PTH and PTHrP
signaling in osteoblasts. Cell Signal. 21:1245–1254. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roelofs AJ, Coxon FP, Ebetino FH, Lundy
MW, Henneman ZJ, Nancollas GH, Sun S, Blazewska KM, Bala JL,
Kashemirov BA, et al: Fluorescent risedronate analogues reveal
bisphosphonate uptake by bone marrow monocytes and localization
around osteocytes in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 25:606–616. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Syddall SP, Ottewell PD and Holen I:
Combined therapies of bone disease with bisphosphonates. Curr Pharm
Des. 16:2988–2997. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lacey DL, Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Kostenuik
PJ, Dougall WC, Sullivan JK, San Martin J and Dansey R: Bench to
bedside: elucidation of the OPG-RANK-RANKL pathway and the
development of denosumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:401–419. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. China Medical
Science and Technology Press; Beijing: pp. 109–110. 2010
|
|
16
|
Ruan C, Xiao XH and Li GK:
Microwave-assisted extraction coupled with countercurrent
chromatography for the rapid preparation of flavonoids from
Scutellaria barbata D. Don. J Sep Sci. 37:1364–1369. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Cai Q, Wei L, Zhan Y, Shen
A, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits
colorectal cancer growth via suppression of multiple signaling
pathways. Integr Cancer Ther. 13:240–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wei L, Lin J, Wu G, Xu W, Li H, Hong Z and
Peng J: Scutellaria barbata D. Don induces G1/S arrest via
modulation of p53 and Akt pathways in human colon carcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 29:1623–1628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei L, Lin J, Xu W, Cai Q, Shen A, Hong Z
and Peng J: Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits tumor angiogenesis
via suppression of Hedgehog pathway in a mouse model of colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:9419–9430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao J, Lu WF, Dai ZJ, Lin S, Zhao Y, Li S,
Zhao NN, Wang XJ, Kang HF, Ma XB, et al: Induction of apoptosis by
total flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don in human
hepatocarcinoma MHCC97-H cells via the mitochondrial pathway.
Tumour Biol. 35:2549–2559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tang PM, Chan JY, Zhang DM, Au SW, Fong
WP, Kong SK, Tsui SK, Waye MM, Mak TC and Fung KP: Pheophorbide a,
an active component in Scutellaria barbata, reverses
P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance on a human hepatoma
cell line R-HepG2. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:504–509. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin X, Zhou J, Jie C, Xing D and Zhang Y:
Anticancer activity and mechanism of Scutellaria barbata extract on
human lung cancer cell line A549. Life Sci. 75:2233–2244. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi Y, Zhou ZY, Cheng LJ and Lin MB: The
effects of scutellarin in barbated skullcup herb on galactophore
cancer MCF-7 cell proliferation and invasion potentia. Acta
Academiae Medicinae Jiangxi. 49:12–14. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
24
|
Fong S, Shoemaker M, Cadaoas J, Lo A, Liao
W, Tagliaferri M, Cohen I and Shtivelman E: Molecular mechanisms
underlying selective cytotoxic activity of BZL101, an extract of
Scutellaria barbata, towards breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
7:577–586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bustin SA and Mueller R: Real-time reverse
transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical
diagnosis. Clin Sci (Lond). 109:365–379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA and McCauley LK:
Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:411–425.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kearns AE, Khosla S and Kostenuik PJ:
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and
osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and
disease. Endocr Rev. 29:155–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Blanco MA and Kang Y: Signaling pathways
in breast cancer metastasis - novel insights from functional
genomics. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin JJ, Selander K, Chirgwin JM, Dallas M,
Grubbs BG, Wieser R, Massagué J, Mundy GR and Guise TA: TGF-beta
signaling blockade inhibits PTHrP secretion by breast cancer cells
and bone metastases development. J Clin Invest. 103:197–206. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hastings RH, Burton DW, Nefzi A, Montgrain
PR, Quintana R and Deftos LJ: Combinatorial library discovery of
small molecule inhibitors of lung cancer proliferation and
parathyroid hormone-related protein expression. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:1067–1075. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soki FN, Park SI and McCauley LK: The
multifaceted actions of PTHrP in skeletal metastasis. Future Oncol.
8:803–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|