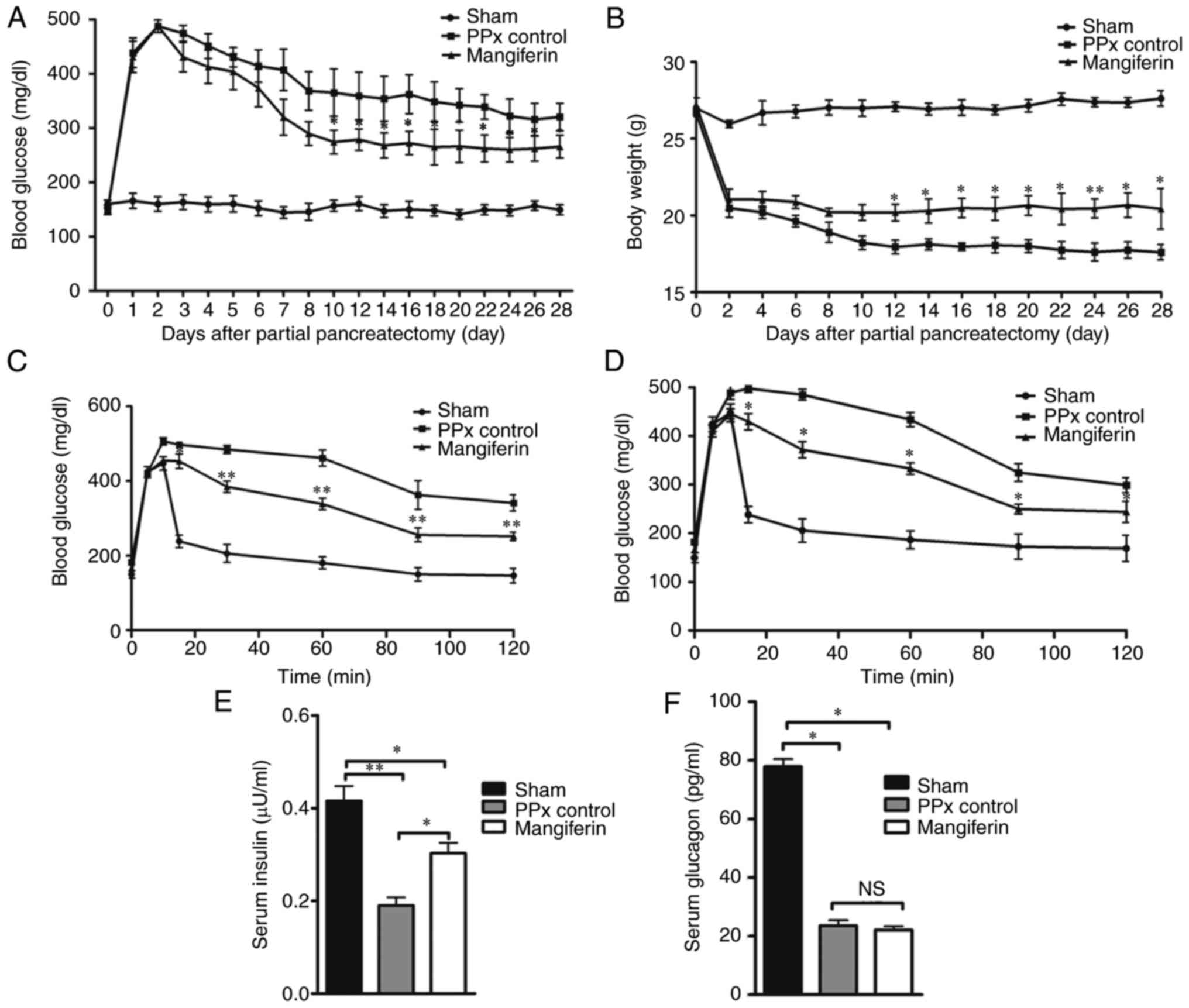
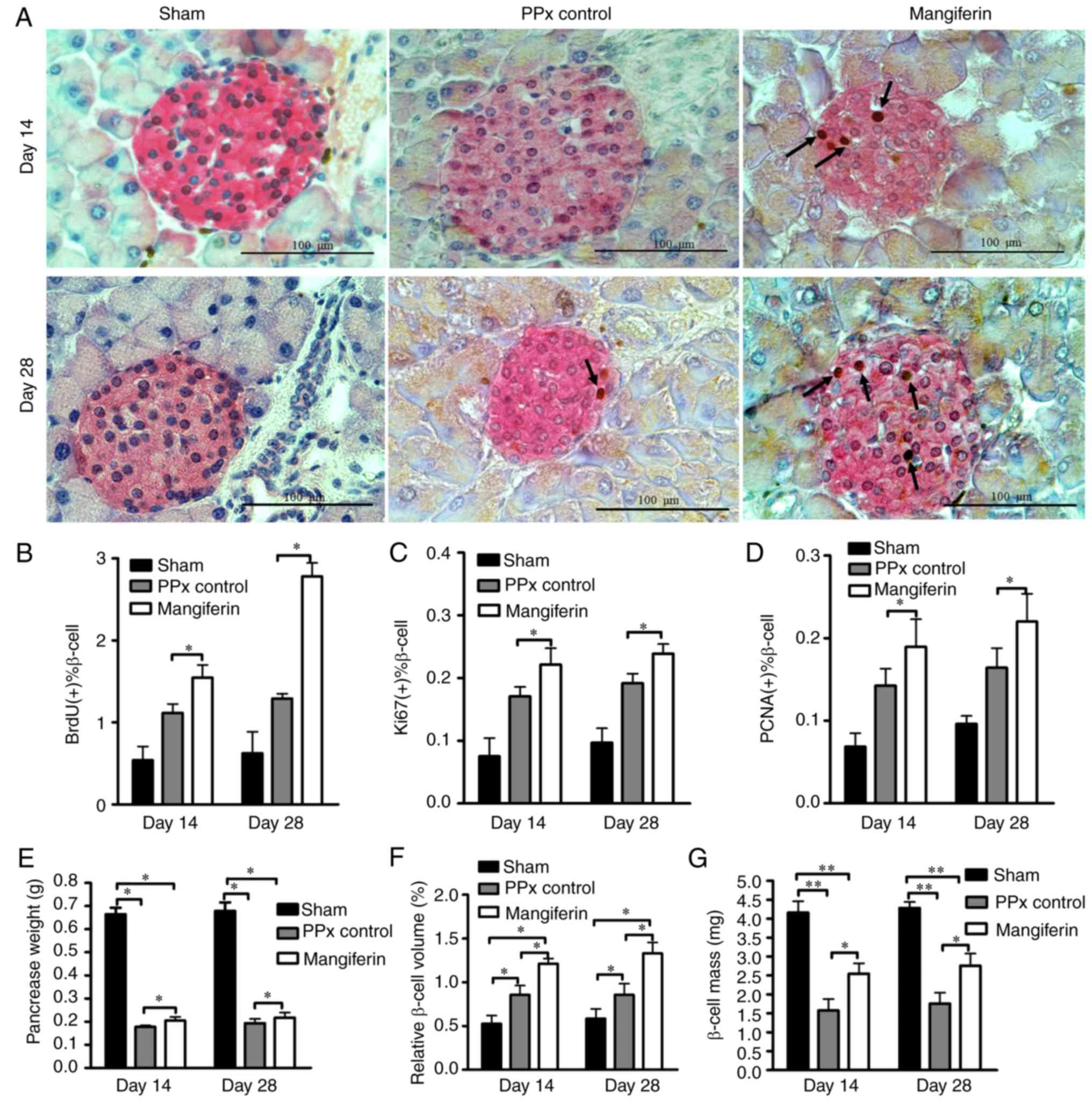
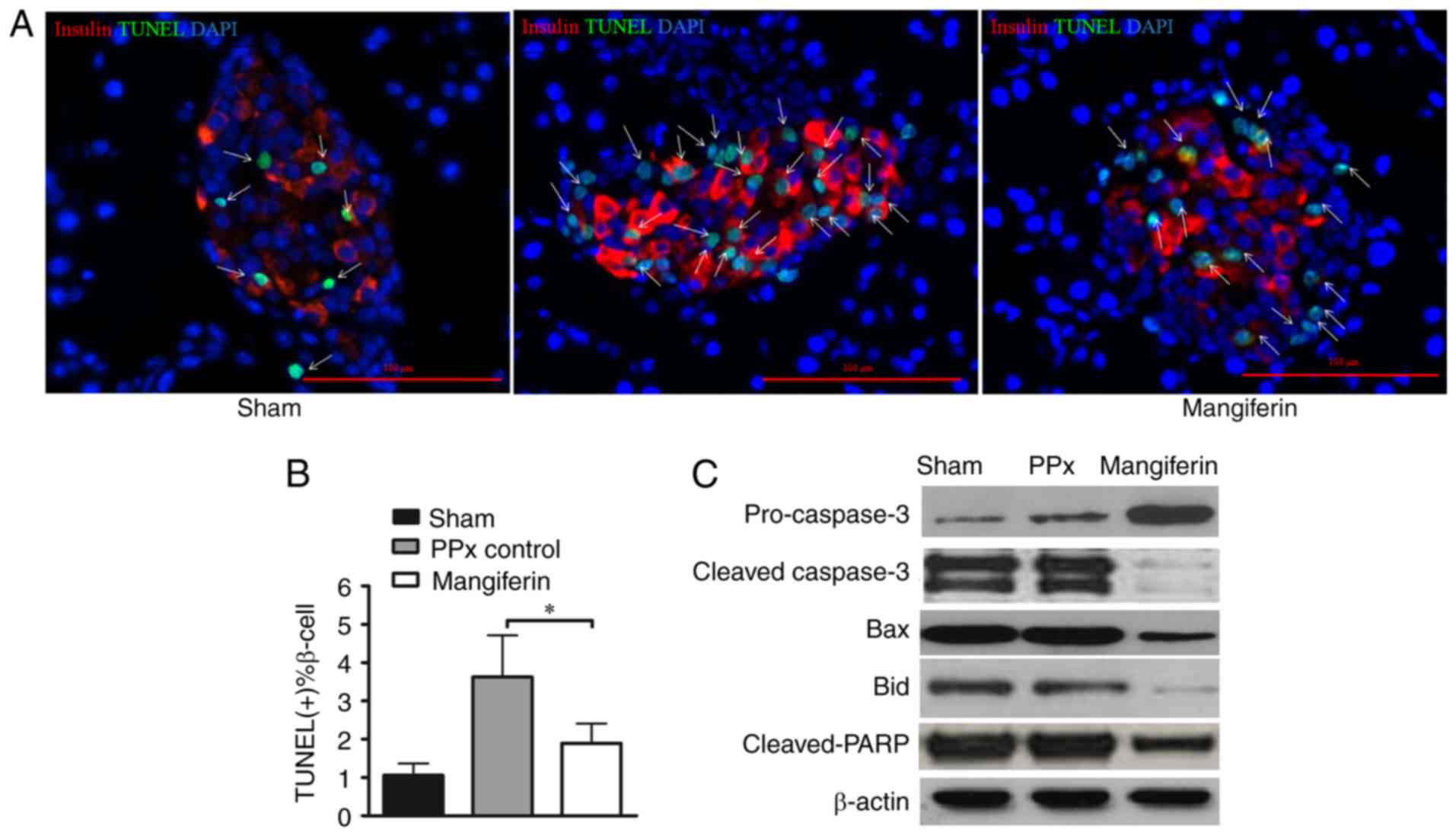
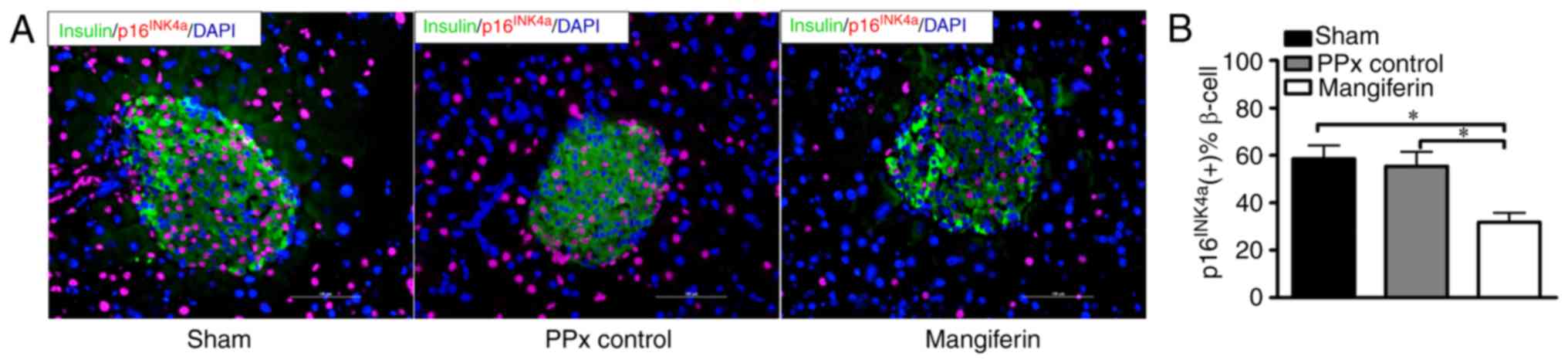
|
1
|
Dean PG, Kudva YC and Stegall MD:
Long-term benefits of pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ
Transplant. 13:85–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ,
Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, Secchi A, Brendel MD,
Berney T, Brennan DC, et al: International trial of the Edmonton
protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 355:1318–1330.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel
R, Rizza RA and Butler PC: Beta-cell deficit and increased
beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
52:102–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bock T, Pakkenberg B and Buschard K:
Increased islet volume but unchanged islet number in ob/ob mice.
Diabetes. 52:1716–1722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bonner-Weir S: Islet growth and
development in the adult. J Mol Endocrinol. 24:297–302. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonner-Weir S and Sharma A: Are there
pancreatic progenitor cells from which new islets form after birth?
Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2:240–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tschen SI, Dhawan S, Gurlo T and Bhushan
A: Age-dependent decline in beta-cell proliferation restricts the
capacity of beta-cell regeneration in mice. Diabetes. 58:1312–1320.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rankin MM and Kushner JA: Adaptive
beta-cell proliferation is severely restricted with advanced age.
Diabetes. 58:1365–1372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krishnamurthy J, Ramsey MR, Ligon KL,
Torrice C, Koh A, Bonner-Weir S and Sharpless NE:
p16INK4a induces an age-dependent decline in islet
regenerative potential. Nature. 443:453–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krishnamurthy J, Torrice C, Ramsey MR,
Kovalev GI, Al-Regaiey K, Su L and Sharpless NE: Ink4a/Arf
expression is a biomarker of aging. J Clin Invest. 114:1299–1307.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi W, Deng J, Tong R, Yang Y, He X, Lv J,
Wang H, Deng S, Qi P, Zhang D and Wang Y: Molecular mechanisms
underlying mangiferin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:3423–3432. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guha S, Ghosal S and Chattopadhyay U:
Antitumor, immunomodulatory and anti-HIV effect of mangiferin, a
naturally occurring glucosylxanthone. Chemotherapy. 42:443–451.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dar A, Faizi S, Naqvi S, Roome T,
Zikr-ur-Rehman S, Ali M, Firdous S and Moin ST: Analgesic and
antioxidant activity of mangiferin and its derivatives: The
structure activity relationship. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:596–600. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prabhu S, Narayan S and Devi CS: Mechanism
of protective action of mangiferin on suppression of inflammatory
response and lysosomal instability in rat model of myocardial
infarction. Phytother Res. 23:756–760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Muruganandan S, Srinivasan K, Gupta S,
Gupta PK and Lal J: Effect of mangiferin on hyperglycemia and
atherogenicity in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
97:497–501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miura T, Ichiki H, Hashimoto I, Iwamoto N,
Kato M, Kubo M, Ishihara E, Komatsu Y, Okada M, Ishida T and
Tanigawa K: Antidiabetic activity of a xanthone compound,
mangiferin. Phytomedicine. 8:85–87. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miura T, Iwamoto N, Kato M, Ichiki H, Kubo
M, Komatsu Y, Ishida T, Okada M and Tanigawa K: The suppressive
effect of mangiferin with exercise on blood lipids in type 2
diabetes. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:1091–1092. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Cui X, Sun X, Li X, Zhu Q and Li W:
Mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytother Res. 24:893–899.
2010.
|
|
19
|
Liu YW, Zhu X, Zhang L, Lu Q, Wang JY,
Zhang F, Guo H, Yin JL and Yin XX: Up-regulation of glyoxalase 1 by
mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 721:355–364.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bwititi P, Musabayane CT and Nhachi CF:
Effects of Opuntia megacantha on blood glucose and kidney function
in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 69:247–252.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang HL, Li CY, Zhang B, Liu YD, Lu BM,
Shi Z, An N, Zhao LK, Zhang JJ, Bao JK and Wang Y: Mangiferin
facilitates islet regeneration and β-cell proliferation through
upregulation of cell cycle and β-cell regeneration regulators. Int
J Mol Sci. 15:9016–9035. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miura T, Ichiki H, Iwamoto N, Kato M, Kubo
M, Sasaki H, Okada M, Ishida T, Seino Y and Tanigawa K:
Antidiabetic activity of the rhizoma of Anemarrhena asphodeloides
and active components, mangiferin and its glucoside. Biol Pharm
Bull. 24:1009–1011. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang H, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Agaricus bisporus lectins mediates islet β-cell proliferation
through regulation of cell cycle proteins. Exp Biol Med.
237:287–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li C, Chen J, Lu B, Shi Z, Wang H, Zhang
B, Zhao K, Qi W, Bao J and Wang Y: Molecular switch role of Akt in
Polygonatum odoratum lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in
human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. PLoS One.
9:e1015262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Antihyperglycemic effect of ginsenoside Rh2 by inducing islet
β-cell regeneration in mice. Horm Metab Res. 44:33–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang G, Lv J, Li T, Huai G, Li X, Xiang
S, Wang L, Qin Z, Pang J, Zou B and Wang Y: Notoginsenoside R1
ameliorates podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by
activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
38:1179–1189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB,
Song KH, Yoo SJ, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, et al: Selective
beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88:2300–2308.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Porter AG and Janicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Nichols A, Eskes
R, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Maundrell K, Antonsson B and Martinou
JC: Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for
mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
144:891–901. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Shimoda M, Chen J, Matsumoto S and
Grayburn PA: Transient overexpression of cyclin D2/CDK4/GLP1 genes
induces proliferation and differentiation of adult pancreatic
progenitors and mediates islet regeneration. Cell Cycle.
11:695–705. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fiaschi-Taesch N, Bigatel TA, Sicari B,
Takane KK, Salim F, Velazquez-Garcia S, Harb G, Selk K,
Cozar-Castellano I and Stewart AF: Survey of the human pancreatic
beta-cell G1/S proteome reveals a potential therapeutic role for
cdk-6 and cyclin D1 in enhancing human beta-cell replication and
function in vivo. Diabetes. 58:882–893. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takasawa S, Ikeda T and Akiyama T: Cyclin
D1 activation through ATF-2 in Reg-induced pancreatic beta-cell
regeneration. FEBS letters. 580:585–591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Narita M, Nunez S, Heard E, Narita M, Lin
AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ and Lowe SW: Rb-mediated
hetero-chromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during
cellular senescence. Cell. 113:703–716. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI and Melton DA:
Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather
than stem-cell differentiation. Nature. 429:41–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Teta M, Rankin MM, Long SY, Stein GM and
Kushner JA: Growth and regeneration of adult beta cells does not
involve specialized progenitors. Dev Cell. 12:817–826. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kee N, Sivalingam S, Boonstra R and
Wojtowicz JM: The utility of Ki-67 and BrdU as proliferative
markers of adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci Methods. 115:97–105.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Muskhelishvili L, Latendresse JR, Kodell
RL and Henderson EB: Evaluation of cell proliferation in rat
tissues with BrdU, PCNA, Ki-67(MIB-5) immunohistochemistry and in
situ hybridization for histone mRNA. J Histochem Cytochem.
51:1681–1688. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Golias CH, Charalabopoulos A and
Charalabopoulos K: Cell proliferation and cell cycle control: A
mini review. Int J Clin Pract. 58:1134–1141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Butler AE, Janson J, Soeller WC and Butler
PC: Increased beta-cell apoptosis prevents adaptive increase in
beta-cell mass in mouse model of type 2 diabetes: Evidence for role
of islet amyloid formation rather than direct action of amyloid.
Diabetes. 52:2304–2314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hanley SC, Austin E, Assouline-Thomas B,
Kapeluto J, Blaichman J, Moosavi M, Petropavlovskaia M and
Rosenberg L: {beta}-Cell mass dynamics and islet cell plasticity in
human type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology. 151:1462–1472. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen H, Gu X, Su IH, Bottino R, Contreras
JL, Tarakhovsky A and Kim SK: Polycomb protein Ezh2 regulates
pancreatic β-cell Ink4a/Arf expression and regeneration in diabetes
mellitus. Genes Dev. 23:975–985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fehsel K, Kolb-Bachofen V and Kröncke KD:
Necrosis is the predominant type of islet cell death during
development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in BB rats. Lab
Invest. 83:549–559. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hoorens A, Stangé G, Pavlovic D and
Pipeleers D: Distinction between interleukin-1-induced necrosis and
apoptosis of islet cells. Diabetes. 50:551–557. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maedler K, Schumann DM, Schulthess F,
Oberholzer J, Bosco D, Berney T and Donath MY: Aging correlates
with decreased beta-cell proliferative capacity and enhanced
sensitivity to apoptosis: A potential role for Fas and pancreatic
duodenal homeobox-1. Diabetes. 55:2455–2462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Donath MY, Gross DJ, Cerasi E and Kaiser
N: Hyperglycemia-induced beta-cell apoptosis in pancreatic islets
of Psammomys obesus during development of diabetes. Diabetes.
48:738–744. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu X, D'Hoker J, Stangé G, Bonné S, De Leu
N, Xiao X, Van de Casteele M, Mellitzer G, Ling Z, Pipeleers D, et
al: Beta cells can be generated from endogenous progenitors in
injured adult mouse pancreas. Cell. 132:197–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|