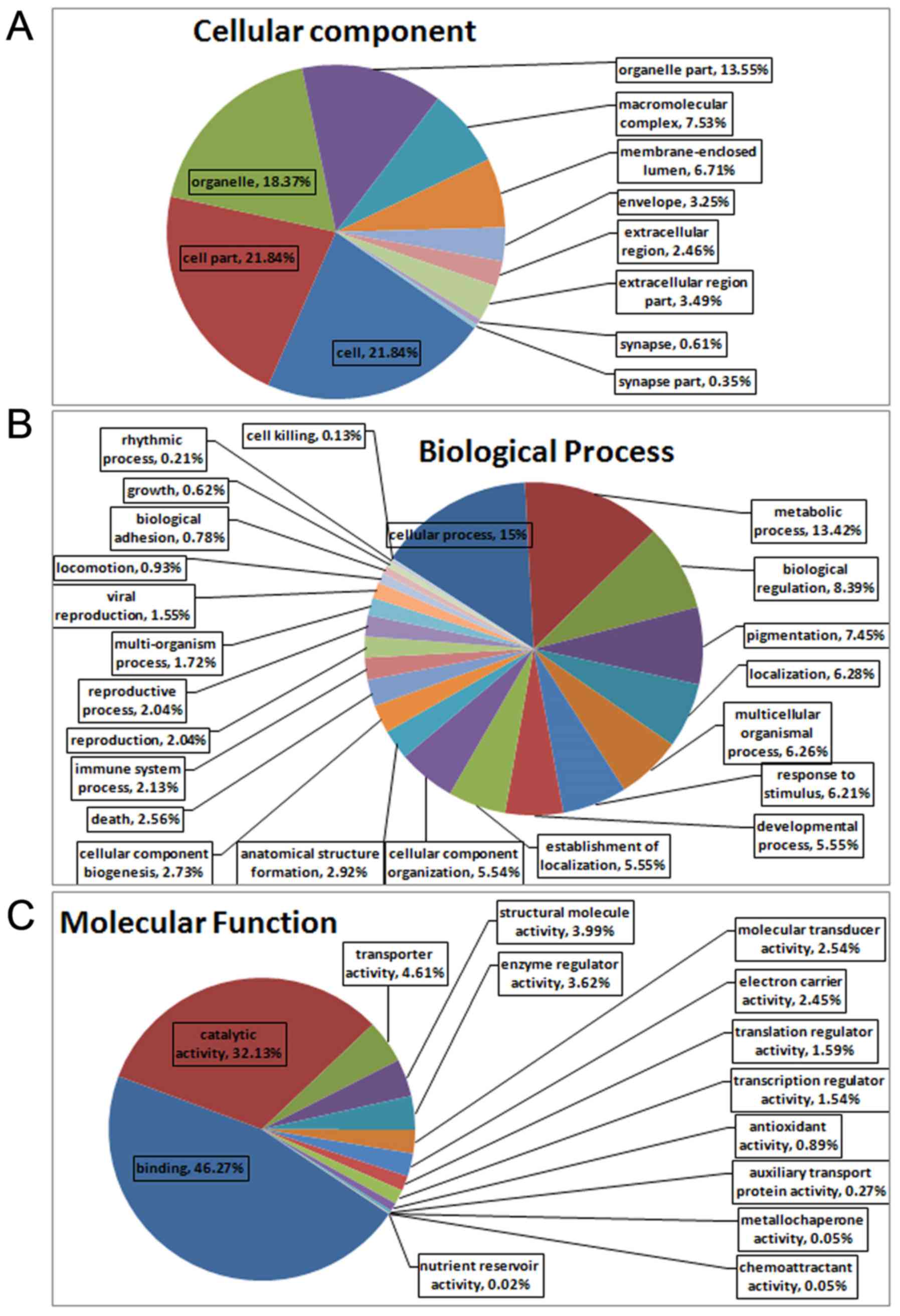
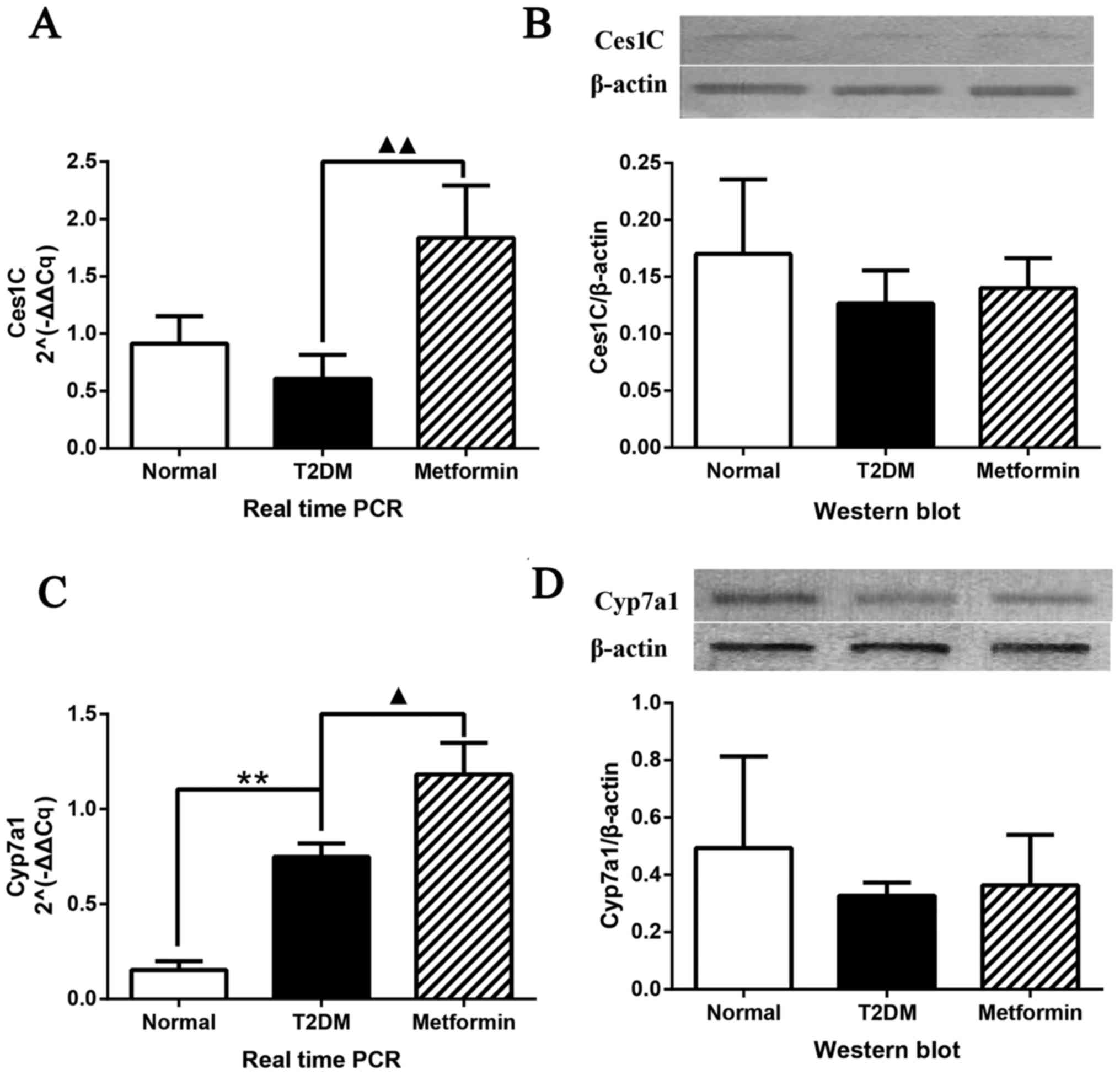
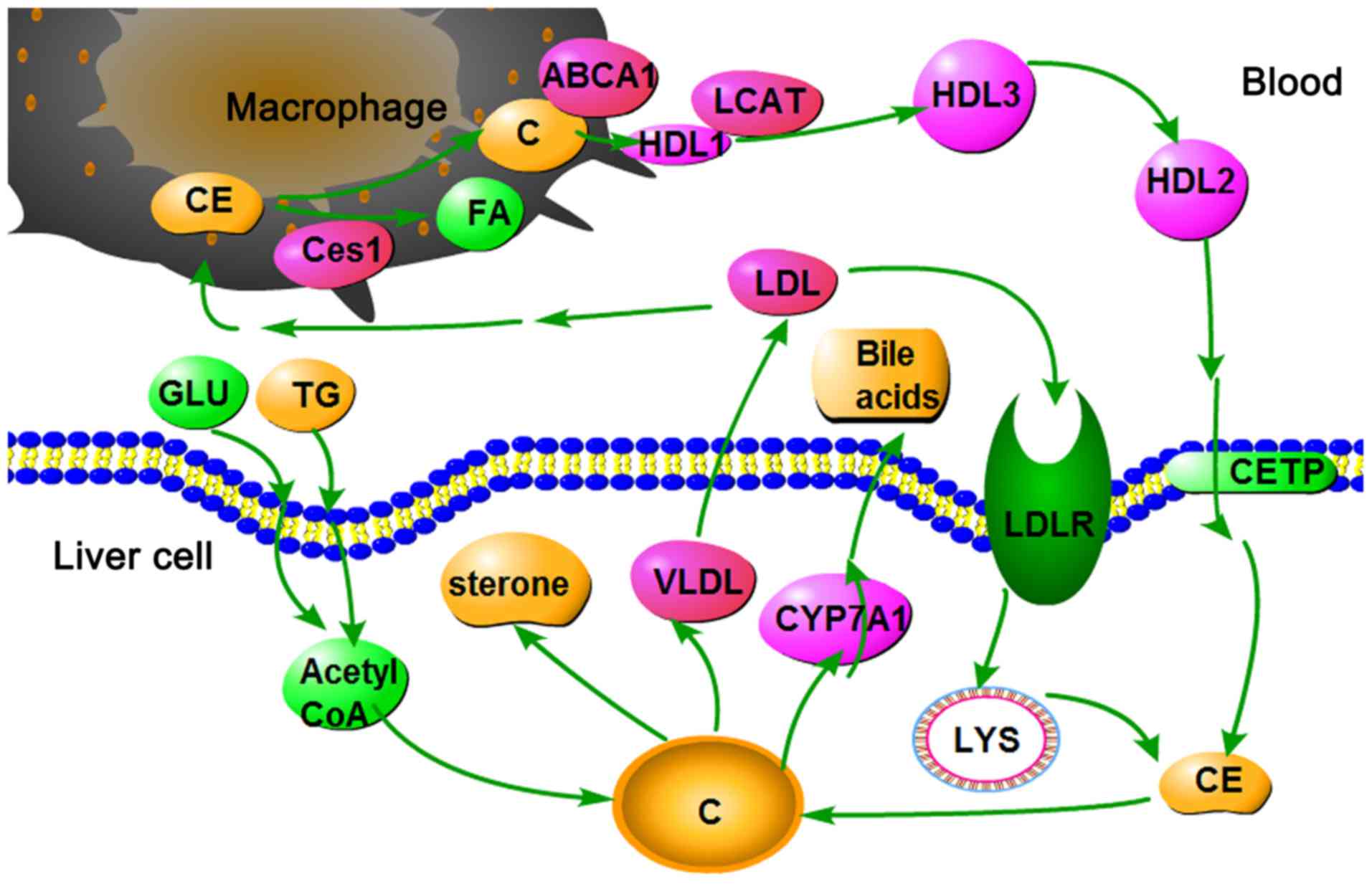
|
1
|
Wei S, Zhang M, Yu Y, Lan X, Yao F, Yan X,
Chen L and Hatch GM: Berberine attenuates development of the
hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2
diabetic mice and in palmitate-incubated HepG2 cells through
suppression of the HNF-4α miR122 pathway. PLoS One.
11:e01520972016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Reboldi G, Gentile G, Angeli F, Ambrosio
G, Mancia G and Verdecchia P: Effects of intensive blood pressure
reduction on myocardial infarction and stroke in diabetes: A
meta-analysis in 73,913 patients. J Hypertens. 29:1253–1269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Q, Xiao X, Li M, Li W, Yu M, Zhang
H, Ping F, Wang Z and Zheng J: Berberine moderates glucose
metabolism through the GnRH-GLP-1 and MAPK pathways in the
intestine. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:1882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Correia S, Carvalho C, Santos MS, Seiça R,
Oliveira CR and Moreira PI: Mechanisms of action of metformin in
type 2 diabetes and associated complications: An overview. Mini Rev
Med Chem. 8:1343–1354. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
No authors listed. Intensive blood-glucose
control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional
treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2
diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group.
Lancet. 352:837–853. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
No authors listed. Effect of intensive
blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight
patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes
Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 352:854–865. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tian S, Li Y, Li D, Xu X, Wang J, Zhang Q
and Hou T: Modeling compound-target interaction network of
traditional Chinese medicines for type II diabetes mellitus:
Insight for polypharmacology and drug design. J Chem Inf Model.
53:1787–1803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kirpichnikov D, McFarlane SI and Sowers
JR: Metformin: An update. Ann Intern Med. 137:25–33. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bailey CJ and Turner RC: Metformin. N Engl
J Med. 334:574–579. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cusi K and DeFronzo RA: Metformin: A
review of its metabolic effects. Diabetes Res. 6:89–131. 1998.
|
|
11
|
Stumvoll M, Nurjhan N, Perriello G, Dailey
G and Gerich JE: Metabolic effects of metformin in
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 333:550–554.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Epstein S: Role of metformin in type II
diabetes. Cleve Clin J Med. 62:278–279. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH,
Bardeesy N, Depinho RA, Montminy M and Cantley LC: The kinase LKB1
mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of
metformin. Science. 310:1642–1646. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim J, Shon E, Kim CS and Kim JS: Renal
podocyte injury in a rat model of type 2 diabetes is prevented by
metformin. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:2108212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hopkins AL: Network pharmacology. Nat
Biotechnol. 25:1110–1111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hopkins AL: Network pharmacology: The next
paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 4:682–690. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang GB, Li QY, Chen QL and Su SB:
Network pharmacology: A new approach for chinese herbal medicine
research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:621423.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: China National Diabetes and
Metabolic Disorders Study Group: Prevalence of diabetes among men
and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T,
Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, et al: 2010 China Noncommunicable
Disease Surveillance Group: Prevalence and control of diabetes in
Chinese adults. JAMA. 310:948–959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ and van Haeften
TW: Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Res. 32:19–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hundal RS, Krssak M, Dufour S, Laurent D,
Lebon V, Chandramouli V, Inzucchi SE, Schumann WC, Petersen KF,
Landau BR, et al: Mechanism by which metformin reduces glucose
production in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 49:2063–2069. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reed MJ, Meszaros K, Entes LJ, Claypool
MD, Pinkett JG, Gadbois TM and Reaven GM: A new rat model of type 2
diabetes: The fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism.
49:1390–1394. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharif S, van der Graaf Y, Nathoe HM, de
Valk HW, Visseren FL and Westerink J; SMART Study Group: HDL
cholesterol as a residual risk factor for vascular events and
all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes
Care. 39:1424–1430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morton J, Zoungas S, Li Q, Patel AA,
Chalmers J, Woodward M, Celermajer DS, Beulens JW, Stolk RP,
Glasziou P, et al: ADVANCE Collaborative Group: Low HDL cholesterol
and the risk of diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy: Results of
the ADVANCE study. Diabetes Care. 35:2201–2206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 36(Suppl
1): S67–S74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagashima S, Yagyu H, Takahashi N,
Kurashina T, Takahashi M, Tsuchita T, Tazoe F, Wang XL, Bayasgalan
T, Sato N, et al: Depot-specific expression of lipolytic genes in
human adipose tissues - association among CES1 expression,
triglyceride lipase activity and adiposity. J Atheroscler Thromb.
18:190–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Marrades MP, González-Muniesa P, Martínez
JA and Moreno-Aliaga MJ: A dysregulation in CES1, APOE and other
lipid metabolism-related genes is associated to cardiovascular risk
factors linked to obesity. Obes Facts. 3:312–318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jernås M, Olsson B, Arner P, Jacobson P,
Sjöström L, Walley A, Froguel P, McTernan PG, Hoffstedt J and
Carlsson LM: Regulation of carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) in human
adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 383:63–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shin DJ, Plateroti M, Samarut J and
Osborne TF: Two uniquely arranged thyroid hormone response elements
in the far upstream 5′ flanking region confer direct thyroid
hormone regulation to the murine cholesterol 7α hydroxylase gene.
Nucleic Acids Res. 34:3853–3861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Noshiro M, Usui E, Kawamoto T, Kubo H,
Fujimoto K, Furukawa M, Honma S, Makishima M, Honma K and Kato Y:
Multiple mechanisms regulate circadian expression of the gene for
cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7a), a key enzyme in hepatic bile
acid biosynthesis. J Biol Rhythms. 22:299–311. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li T, Owsley E, Matozel M, Hsu P, Novak CM
and Chiang JY: Transgenic expression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase
in the liver prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin
resistance in mice. Hepatology. 52:678–690. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fukami T, Nakajima M, Maruichi T,
Takahashi S, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, McLeod HL and Yokoi T: Structure
and characterization of human carboxylesterase 1A1, 1A2, and 1A3
genes. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 18:911–920. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yoshimura M, Kimura T, Ishii M, Ishii K,
Matsuura T, Geshi E, Hosokawa M and Muramatsu M: Functional
polymorphisms in carboxylesterase1A2 (CES1A2) gene involves
specific protein 1 (Sp1) binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
369:939–942. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu S, Cao B, Sun R, Tang Y, Paletta JL, Wu
X, Liu L, Zha W, Zhao C, Li Y, et al: A metabolomic and
pharmacokinetic study on the mechanism underlying the
lipid-lowering effect of orally administered berberine. Mol
Biosyst. 11:463–474. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Murphy C, Parini P, Wang J, Björkhem I,
Eggertsen G and Gåfvels M: Cholic acid as key regulator of
cholesterol synthesis, intestinal absorption and hepatic storage in
mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1735:167–175. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li T and Chiang JY: Bile Acid signaling in
liver metabolism and diseases. J Lipids. 2011:7540672012.
|
|
39
|
Ferrier Denise R: Biochemistry. 6th
edition. Peking University Medical Press; pp. 219–224. 2013
|
|
40
|
Memişoğullari R and Bakan E: Levels of
ceruloplasmin, transferrin, and lipid peroxidation in the serum of
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications.
18:193–197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Logie L, Harthill J, Patel K, Bacon S,
Hamilton DL, Macrae K, McDougall G, Wang HH, Xue L, Jiang H, et al:
Cellular responses to the metal-binding properties of metformin.
Diabetes. 61:1423–1433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schoonjans K, Watanabe M, Suzuki H,
Mahfoudi A, Krey G, Wahli W, Grimaldi P, Staels B, Yamamoto T and
Auwerx J: Induction of the acyl-coenzyme A synthetase gene by
fibrates and fatty acids is mediated by a peroxisome proliferator
response element in the C promoter. J Biol Chem. 270:19269–19276.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Suzuki H, Kawarabayasi Y, Kondo J, Abe T,
Nishikawa K, Kimura S, Hashimoto T and Yamamoto T: Structure and
regulation of rat long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. J Biol Chem.
265:8681–8685. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang Z, Zhang W, Wan C, Xu G, Nie X, Zhu
X, Xia N, Zhao Y, Wang S, Cui S, et al: TRAM1 protect HepG2 cells
from palmitate induced insulin resistance through ER stress-JNK
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:578–584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|