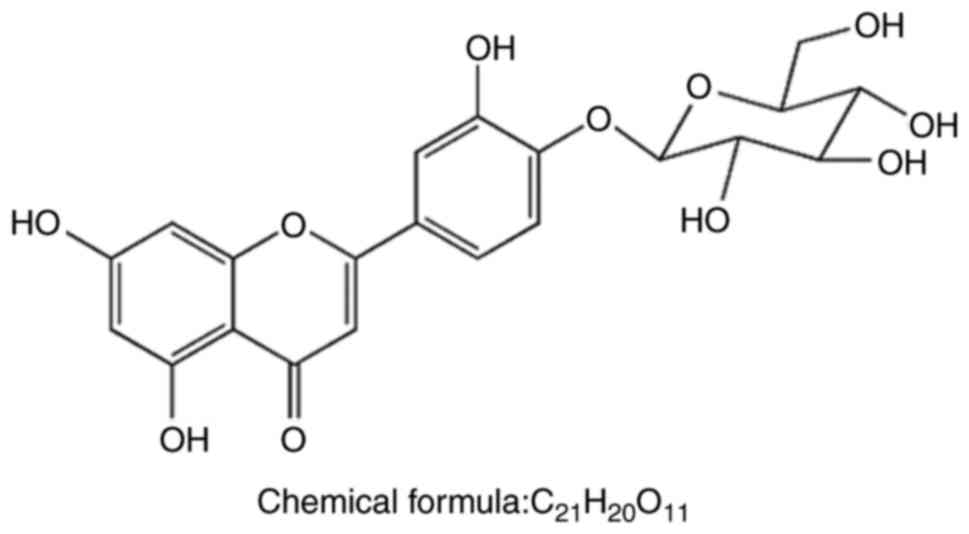
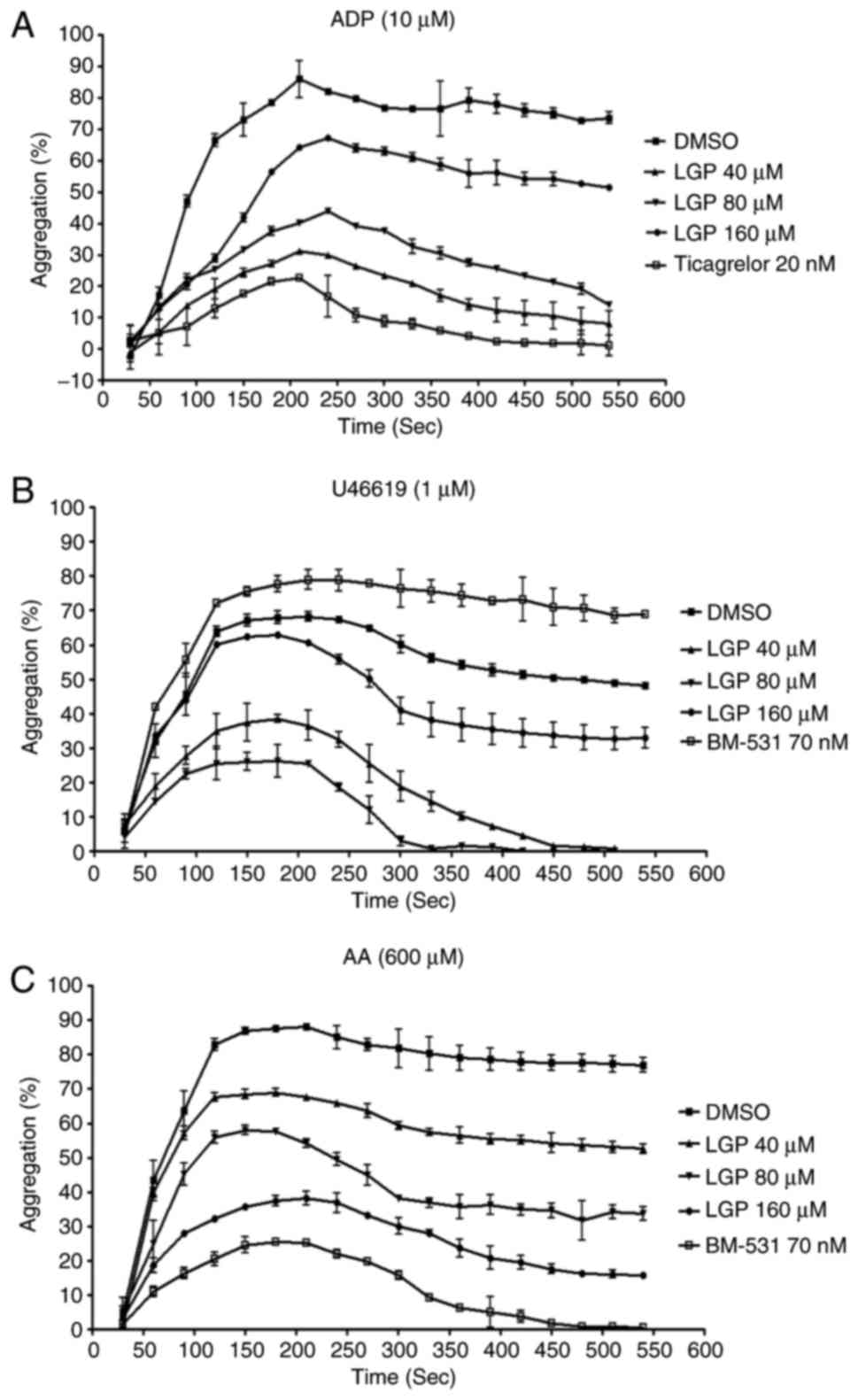
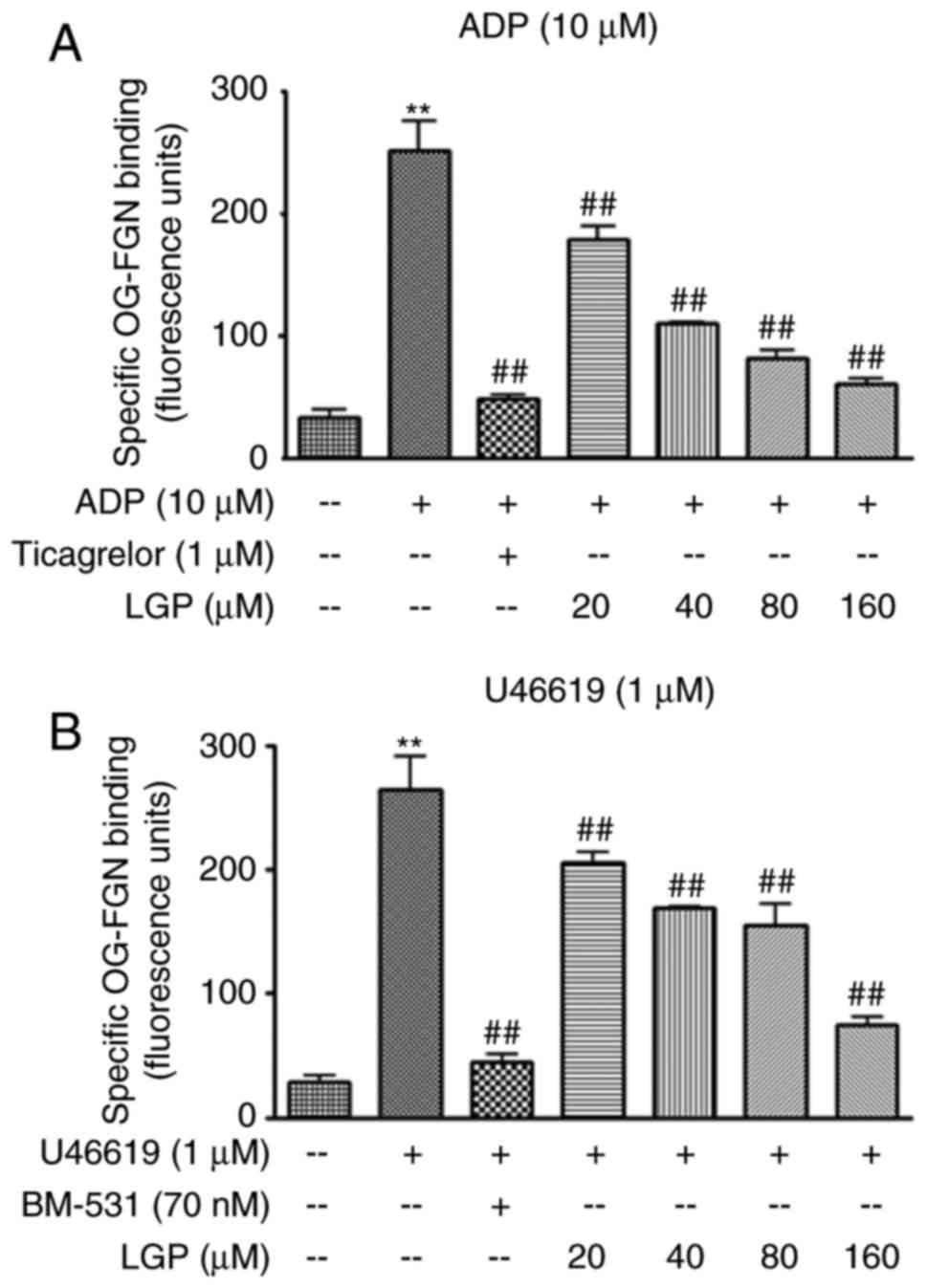
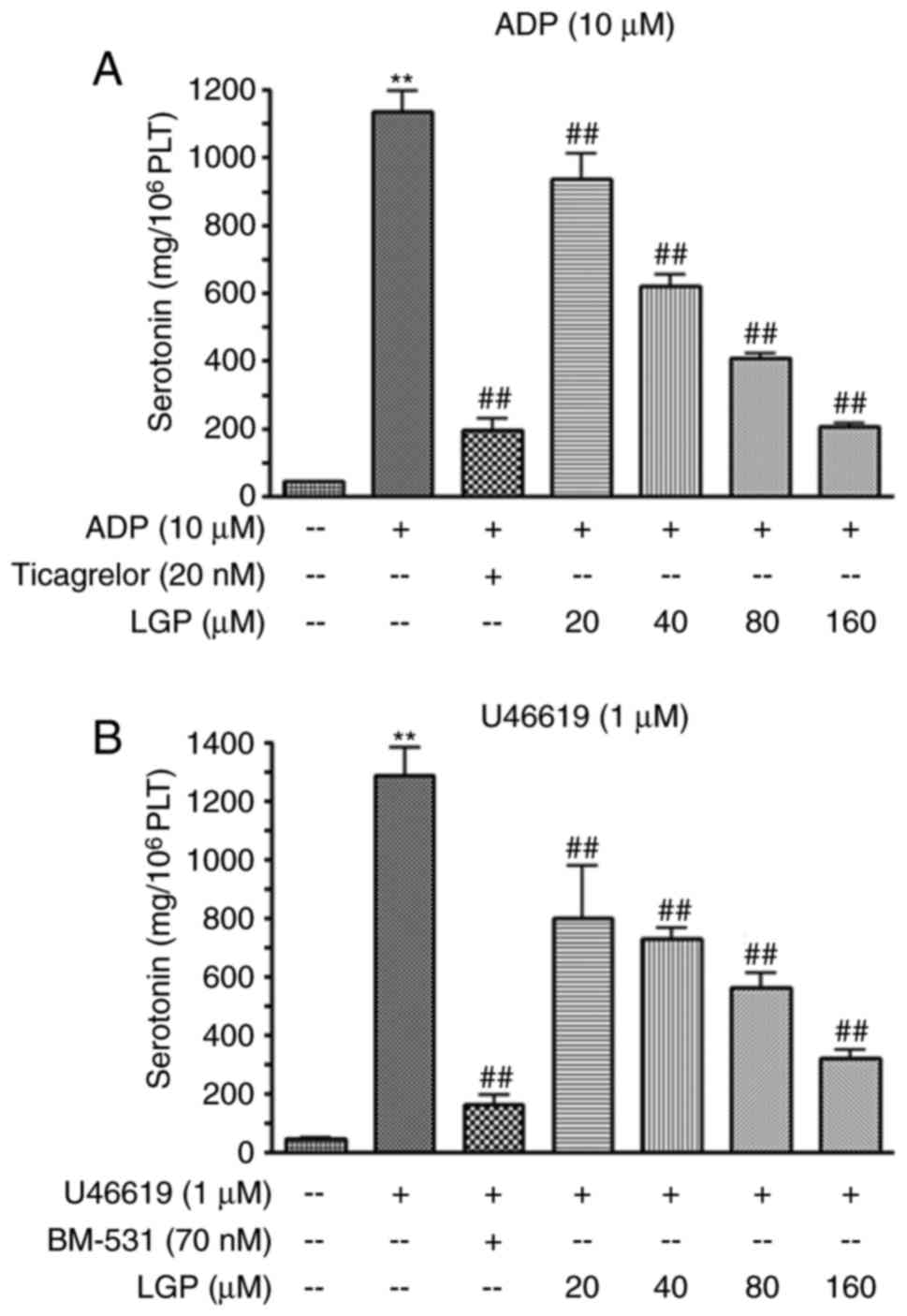
|
1
|
Harrison P: Platelet function analysis.
Blood Rev. 19:111–123. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ghoshal K and Bhattacharyya M: Overview of
platelet physiology: Its hemostatic and nonhemostatic role in
disease pathogenesis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:7818572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weyrich AS: Platelets: More than a sack of
glue. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014:400–403.
2014.
|
|
4
|
Clemetson KJ: Platelets and primary
haemostasis. Thromb Res. 129:220–224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yun SH, Sim EH, Goh RY, Park JI and Han
JY: Platelet Activation: The mechanisms and potential biomarkers.
Biomed Res Int. 2016:90601432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bye AP, Unsworth AJ and Gibbins JM:
Platelet signaling: A complex interplay between inhibitory and
activatory networks. J Thromb Haemost. 14:918–930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Michelson AD: Antiplatelet therapies for
the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
9:154–169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jackson SP and Schoenwaelder SM:
Antiplatelet therapy: In search of the ‘magic bullet’. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 2:775–789. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sigalov AB: Novel mechanistic concept of
platelet inhibition. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:677–692. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Varon D and Spectre G: Antiplatelet
agents. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 267–272.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pei J and Chen SL: Flora of China.
Beijing: Science Press; 1982
|
|
12
|
Zhou Z, Wei X, Fu H and Luo Y: Chemical
constituents of Callicarpa nudiflora and their anti-platelet
aggregation activity. Fitoterapia. 88:91–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo YH, Ma SC, Hu SR, Fu HZ, Zhou ZQ and
Chen WK: Chemical constituents from callicarpa nudiflora. Zhong Yao
Cai. 38:2306–2310. 2015.In Chinese.
|
|
14
|
Del Turco S, Sartini S, Cigni G, Sentieri
C, Sbrana S, Battaglia D, Papa A, Da Settimo F, La Motta C and
Basta G: Synthetic analogues of flavonoids with improved activity
against platelet activation and aggregation as novel prototypes of
food supplements. Food Chem. 175:494–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Armstrong PC, Truss NJ, Ali FY, Dhanji AA,
Vojnovic I, Zain ZN, Bishop-Bailey D, Paul-Clark MJ, Tucker AT,
Mitchell JA and Warner TD: Aspirin and the in vitro linear
relationship between thromboxane A2-mediated platelet
aggregation and platelet production of thromboxane A2. J
Thromb Haemost. 6:1933–1943. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schoenwaelder SM, Ono A, Sturgeon S, Chan
SM, Mangin P, Maxwell MJ, Turnbull S, Mulchandani M, Anderson K,
Kauffenstein G, et al: Identification of a unique co-operative
phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling mechanism regulating integrin
alpha IIb beta 3 adhesive function in platelets. J Biol Chem.
282:28648–28658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao J and Shattil SJ: An enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay to identify inhibitors of activation of
platelet integrin alpha IIb beta 3. J Immunol Methods. 181:55–64.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gratacap MP, Payrastre B, Nieswandt B and
Offermanns S: Differential regulation of Rho and Rac through
heterotrimeric G-proteins and cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem.
276:47906–47913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Angiolillo DJ, Ueno M and Goto S: Basic
principles of platelet biology and clinical implications. Circ J.
74:597–607. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yousuf O and Bhatt DL: The evolution of
antiplatelet therapy in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol.
8:547–559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gachet C: Antiplatelet drugs: Which
targets for which treatments? J Thromb Haemost. 13(Suppl 1):
S313–S322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Meyer SF, Vanhoorelbeke K, Broos K,
Salles II and Deckmyn H: Antiplatelet drugs. Br J Haematol.
142:515–528. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shifrin MM and Widmar SB: Platelet
inhibitors. Nurs Clin North Am. 51:29–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakahata N: Thromboxane A2:
Physiology/pathophysiology, cellular signal transduction and
pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther. 118:18–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stegner D and Nieswandt B: Platelet
receptor signaling in thrombus formation. J Mol Med. 89:109–121.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Goggs R and Poole AW: Platelet signaling–a
primer. J Vet Emerg Crit Care. 22:5–29. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Gurbel PA, Kuliopulos A and Tantry US:
G-protein-coupled receptors signaling pathways in new antiplatelet
drug development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:500–512. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Von Kügelgen I and Hoffmann K:
Pharmacology and structure of P2Y receptors. Neuropharmacology.
104:50–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cattaneo M: P2Y12 receptors: Structure and
function. J Thromb Haemost. 13(Suppl 1): S10–S16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang JS, Ramamurthy SK, Lin X and Le
Breton GC: Cell signalling through thromboxane A2
receptors. Cell Signal. 16:521–533. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goggs R, Williams CM, Mellor H and Poole
AW: Platelet Rho GTPases-a focus on novel players, roles and
relationships. Biochem J. 466:431–442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang JS, Dong L, Kozasa T and Le Breton
GC: Signaling through Gα13 switch region I is essential
for protease-activated receptor 1-mediated human platelet shape
change, aggregation, and secretion. J Biol Chem. 282:10210–10222.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|