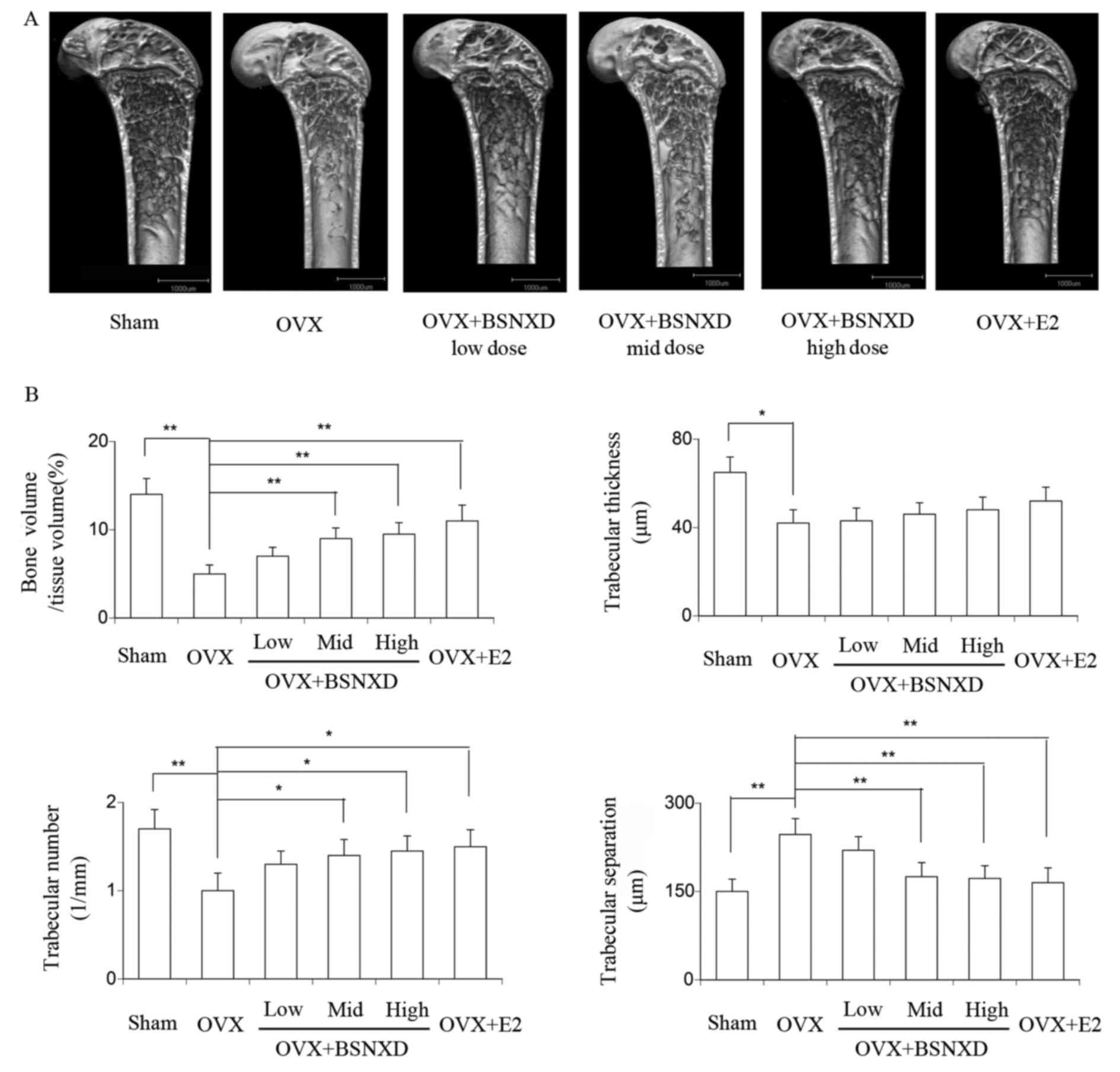
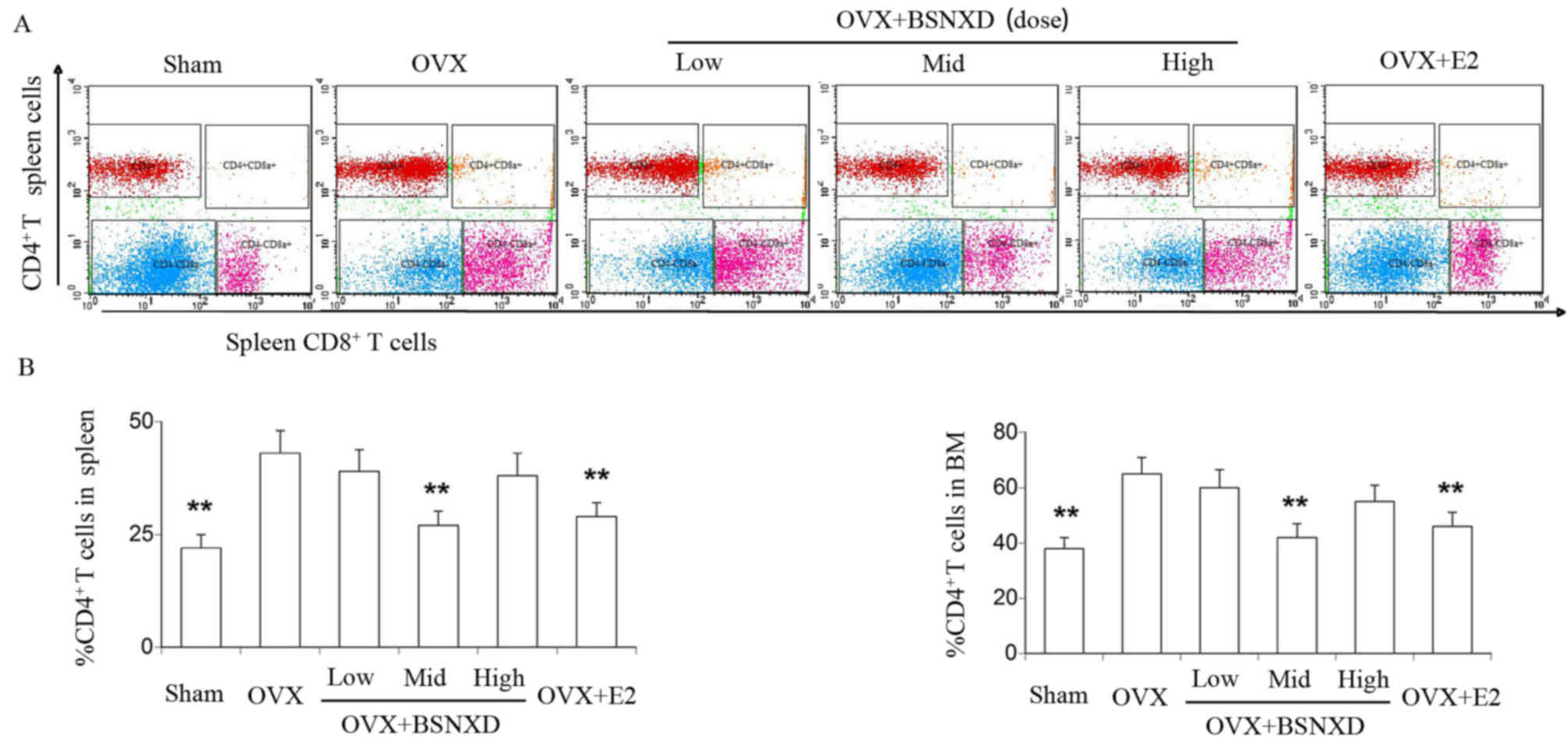
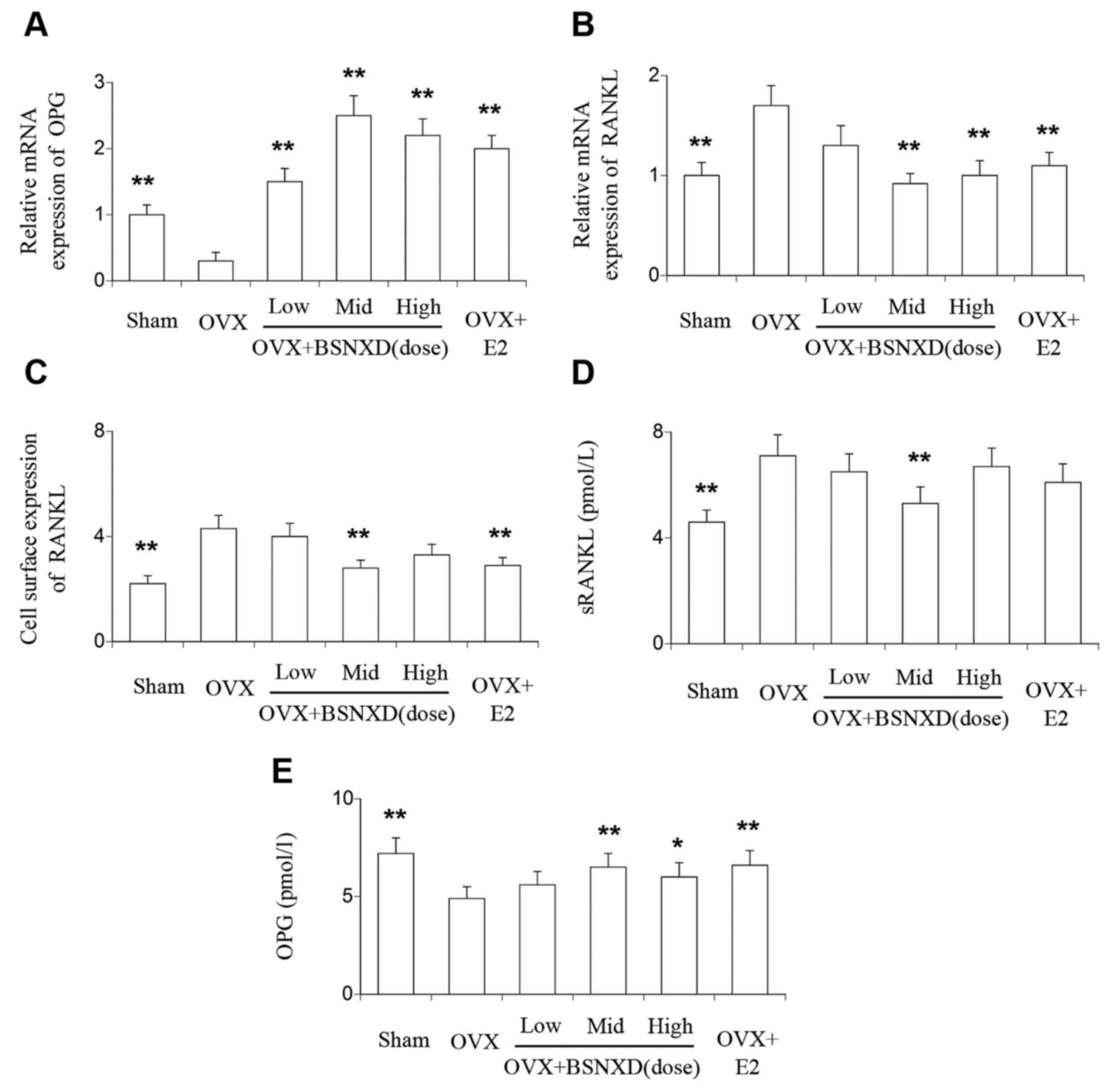
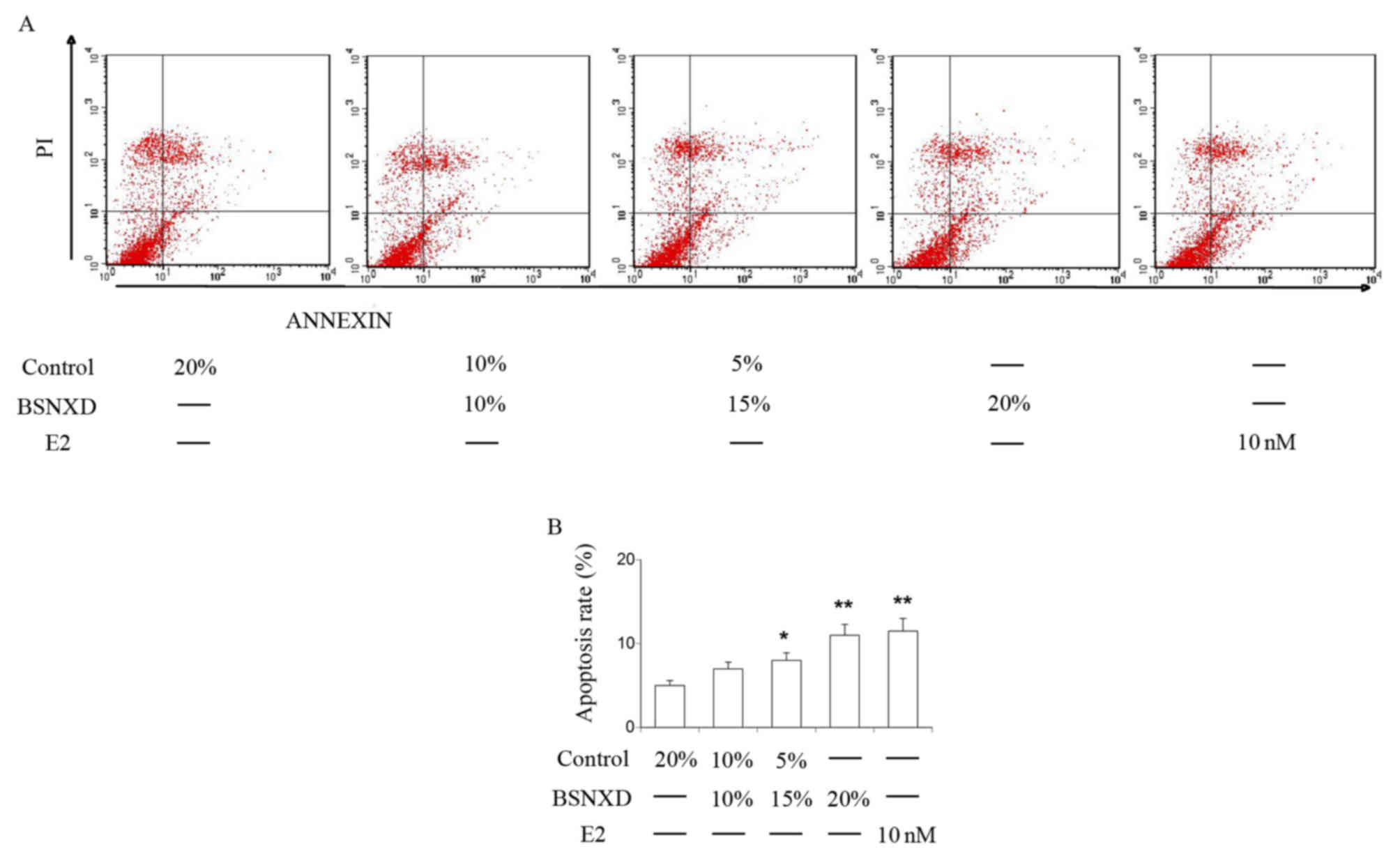
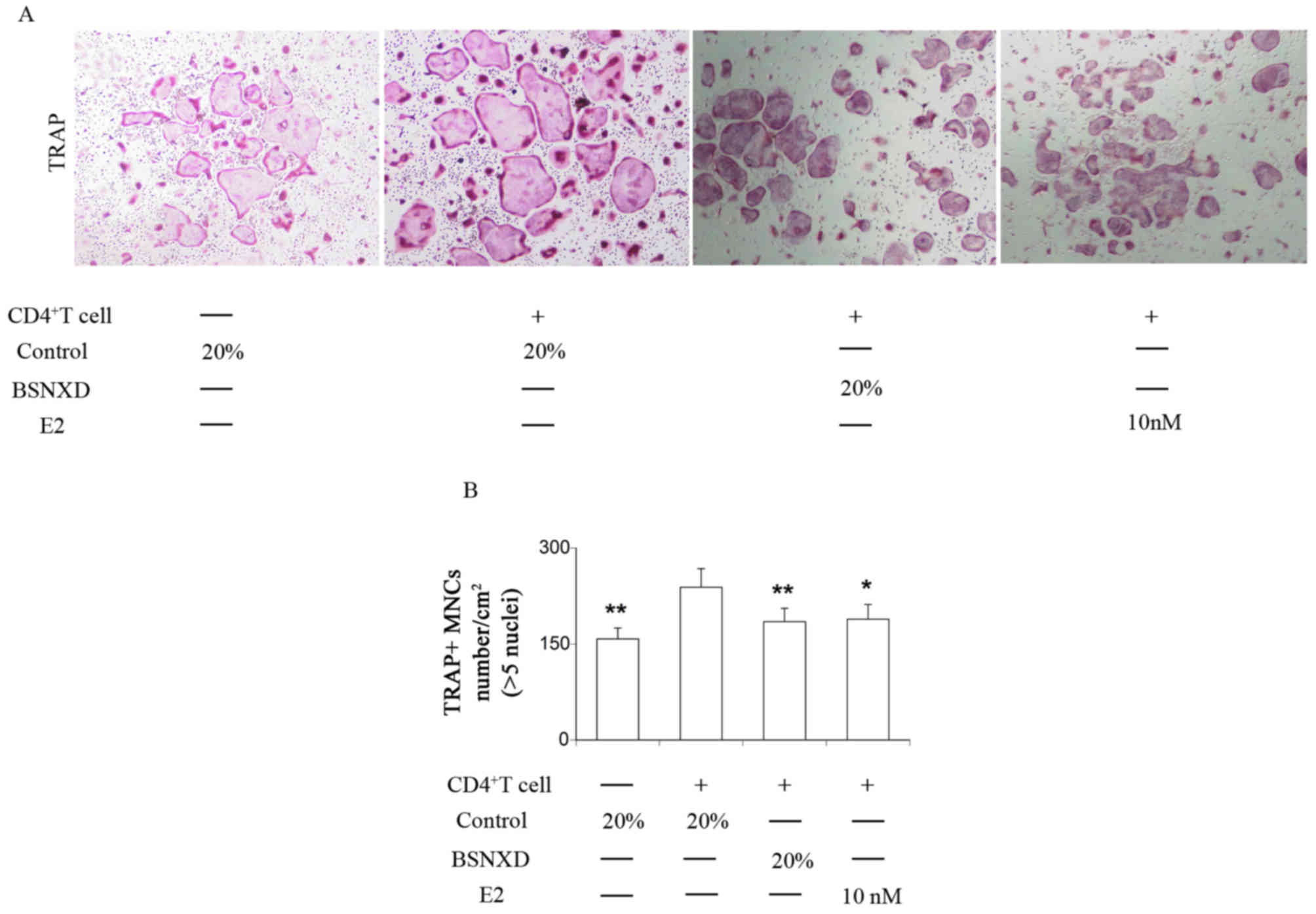
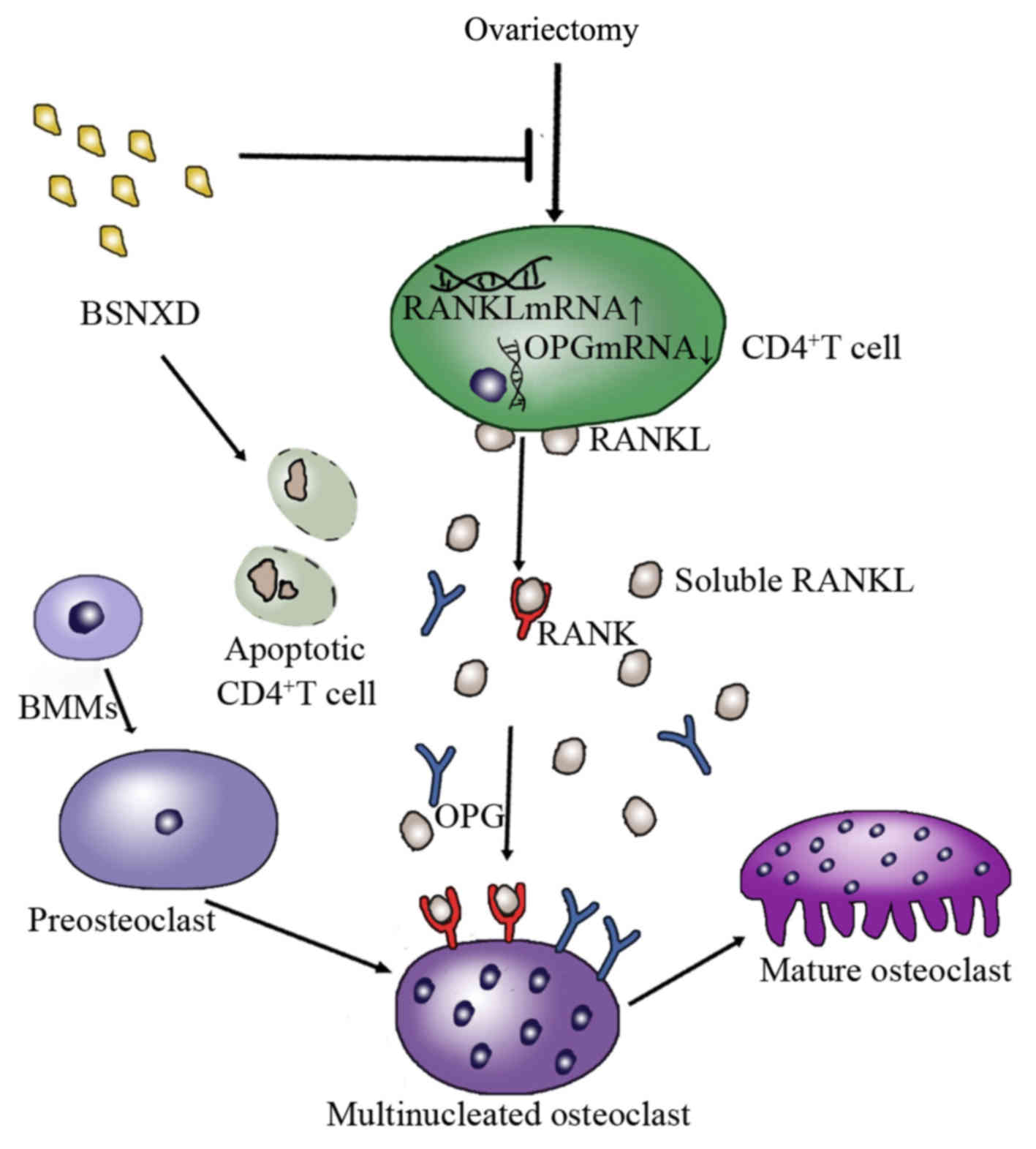
|
1
|
Geusens P: New insights into treatment of
osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. RMD open. 1:e0000512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Recker R, Lappe J, Davies KM and Heaney R:
Bone remodeling increases substantially in the years after
menopause and remains increased in older osteoporosis patients. J
Bone Miner Res. 19:1628–1633. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bernabei R, Martone AM, Ortolani E, Landi
F and Marzetti E: Screening, diagnosis and treatment of
osteoporosis: a brief review. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab.
11:201–207. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Danks L and Takayanagi H: Immunology and
bone. J Biochem. 154:29–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wada T, Nakashima T, Hiroshi N and
Penninger JM: RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone
disease. Trends Mol Med. 12:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Leibbrandt A and Penninger JM: RANK(L) as
a key target for controlling bone loss. Adv Exp Med Biol.
647:130–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao P, Li J, Li Y, Tian Y, Wang Y and
Zheng C: Systems pharmacology-based approach for dissecting the
active ingredients and potential targets of the Chinese herbal
Bufei Jianpi formula for the treatment of COPD. Int J Chron
Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 10:2633–2656. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Penno H, Silfverswärd CJ, Frost A,
Brändström H, Nilsson O and Ljunggren O: Osteoprotegerin secretion
from prostate cancer is stimulated by cytokines, in vitro. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 293:451–455. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greenblatt MB and Shim JH:
Osteoimmunology: A brief introduction. Immune Netw. 13:111–115.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Faienza MF, Ventura A, Marzano F and
Cavallo L: Postmenopausal osteoporosis: The role of immune system
cells. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:5759362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pacifici R: Estrogen deficiency, T cells
and bone loss. Cell Immunol. 252:68–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao R: Immune regulation of osteoclast
function in postmenopausal osteoporosis: A critical
interdisciplinary perspective. Int J Med Sci. 9:825–832. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cenci S, Weitzmann MN, Roggia C, Namba N,
Novack D, Woodring J and Pacifici R: Estrogen deficiency induces
bone loss by enhancing T-cell production of TNF-alpha. J Clin
Invest. 106:1229–1237. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
D'Amelio P, Grimaldi A, Di Bella S,
Brianza SZ, Cristofaro MA, Tamone C, Giribaldi G, Ulliers D,
Pescarmona GP and Isaia G: Estrogen deficiency increases
osteoclastogenesis up-regulating T cells activity: A key mechanism
in osteoporosis. Bone. 43:92–100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sato K and Takayanagi H: Osteoclasts,
rheumatoid arthritis and osteoimmunology. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
18:419–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kong YY, Feige U, Sarosi I, Bolon B,
Tafuri A, Morony S, Capparelli C, Li J, Elliott R, McCabe S, et al:
Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in
adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature.
402:304–309. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Horwood NJ, Kartsogiannis V, Quinn JM,
Romas E, Martin TJ and Gillespie MT: Activated T lymphocytes
support osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
265:144–150. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Hakoda M, Mogi M,
Yano K, Tsuda E, Takahashi K, Furuya T, Ishiyama S, Kim KJ, et al:
Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from
human monocytes: Possible role of T cells in bone destruction in
rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1003–1012. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Rifas L, Haug J,
Dipersio J and Pacifici R: T cell activation induces human
osteoclast formation via receptor activator of nuclear factor
kappaB ligand-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Bone Miner
Res. 16:328–337. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang R, Zhang L, Zhang X, Moreno J,
Celluzzi C, Tondravi M and Shi Y: Regulation of activation-induced
receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) expression in T
cells. Eur J Immunol. 32:1090–1098. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maki PM: Critical window hypothesis of
hormone therapy and cognition: a scientific update on clinical
studies. Menopause. 20:695–709. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hodis HN and Mack WJ: Hormone replacement
therapy and the association with coronary heart disease and overall
mortality: Clinical application of the timing hypothesis. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 142:68–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
López-Grueso R, Gambini J, Abdelaziz KM,
Monleón D, Díaz A, El Alami M, Bonet-Costa V, Borrás C, Viña J, et
al: Early, but not late onset estrogen replacement therapy prevents
oxidative stress and metabolic alterations caused by ovariectomy.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:236–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Russell RG, Watts NB, Ebetino FH and
Rogers MJ: Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities
and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy.
Osteoporos Int. 19:733–759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et
al: Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women
with osteoporosis. New Engl J Med. 361:756–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Oden A, et al:
Denosumab reduces the risk of osteoporotic fractures in
postmenopausal women, particularly in those with moderate to high
fracture risk as assessed with FRAX. J Bone Min Res. 27:1480–1486.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Andreopoulou P and Bockman RS: Management
of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Annu Rev Med. 66:329–342. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Qiu XM, Hao Q and Li DJ:
Anti-inflammatory effects of a Chinese herbal medicine in
atherosclerosis via estrogen receptor β mediating nitric oxide
production and NF-κB suppression in endothelial cells. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e5512013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y,
Yan XJ, Xu F, Wang BS, Mao JH, Shen ZX, et al: Dissection of
mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as
an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:4826–4831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Qiu XM, Gui YY, Xu YP, Gober HJ
and Li DJ: Bu-Shen-Ning-Xin Decoction ameliorated the osteoporotic
phenotype of ovariectomized mice without affecting the serum
estrogen concentration or uterus. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:5019–5031.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gui Y, Qiu X, Xu Y, Li D and Wang L:
Bu-Shen-Ning-Xin decoction suppresses osteoclastogenesis via
increasing dehydroepiandrosterone to prevent postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Biosci Trends. 9:169–181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nguyen K, Sparks J and Omoruyi FO:
Investigation of the cytotoxicity, antioxidative and
immune-modulatory effects of Ligusticum porteri (Osha) root extract
on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Integr Med. 14:465–472.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han BH, Lee YJ, Yoon JJ, Choi ES, Namgung
S, Jin XJ, Jeong DH, Kang DG and Lee HS: Hwangryunhaedoktang exerts
anti- inflammation on LPS-induced NO production by suppressing MAPK
and NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Integr Med.
15:326–336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Qiu XM, Gui YY, Xu YP, Gober HJ
and Li DJ: Bu-Shen-Ning-Xin decoction: Inhibition of
osteoclastogenesis by abrogation of the RANKL-induced NFATc1 and
NF-κB signaling pathways via selective estrogen receptor α. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 9:3755–3766. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Cui K, Zhao H, Li D, Wang W and
Zhu Y: Bushen Ningxin Decoction pharmacological serum promotes the
proliferation and suppresses the apoptosis of murine osteoblasts
through MAPK pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 122:221–226. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Wang YD, Wang WJ and Li DJ:
Differential regulation of dehydroepiandrosterone and estrogen on
bone and uterus in ovariectomized mice. Osteoporos Int. 20:79–92.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tyagi AM, Srivastava K, Kureel J, Kumar A,
Raghuvanshi A, Yadav D, Maurya R, Goel A and Singh D: Premature T
cell senescence in Ovx mice is inhibited by repletion of estrogen
and medicarpin: a possible mechanism for alleviating bone loss.
Osteoporos Int. 23:1151–1161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Utermöhlen O, Tárnok A, Bönig L and
Lehmann-Grube F: T lymphocyte-mediated antiviral immune responses
in mice are diminished by treatment with monoclonal antibody
directed against the interleukin-2 receptor. Eur J Immunol.
24:3093–3099. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Walsh NC, Alexander KA, Manning CA,
Karmakar S, Wang JF, Weyand CM, Pettit AR and Gravallese EM:
Activated human T cells express alternative mRNA transcripts
encoding a secreted form of RANKL. Genes Immun. 14:336–345. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Senthilkumar R and Lee HW: CD137L- and
RANKL-mediated reverse signals inhibit osteoclastogenesis and T
lymphocyte proliferation. Immunobiology. 214:153–161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li JY, Tawfeek H, Bedi B, Yang X, Adams J,
Gao KY, Zayzafoon M, Weitzmann MN and Pacifici R: Ovariectomy
disregulates osteoblast and osteoclast formation through the T-cell
receptor CD40 ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:768–773. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Jilka RL, Hangoc G, Girasole G, Passeri G,
Williams DC, Abrams JS, Boyce B, Broxmeyer H and Manolagas SC:
Increased osteoclast development after estrogen loss: Mediation by
interleukin-6. Science. 257:88–91. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jilka RL, Takahashi K, Munshi M, Williams
DC, Roberson PK and Manolagas SC: Loss of estrogen upregulates
osteoblastogenesis in the murine bone marrow. Evidence for autonomy
from factors released during bone resorption. J Clin Invest.
101:1942–1950. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim HR, Kim KW, Kim BM, Jung HG, Cho ML
and Lee SH: Reciprocal activation of CD4+ T cells and synovial
fibroblasts by stromal cell-derived factor 1 promotes RANKL
expression and osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:538–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stein NC, Kreutzmann C, Zimmermann SP,
Niebergall U, Hellmeyer L, Goettsch C, Schoppet M and Hofbauer LCl:
Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 stimulate the osteoclast inhibitor
osteoprotegerin by human endothelial cells through the STAT6
pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 23:750–758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Khosla S: Minireview: The OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|