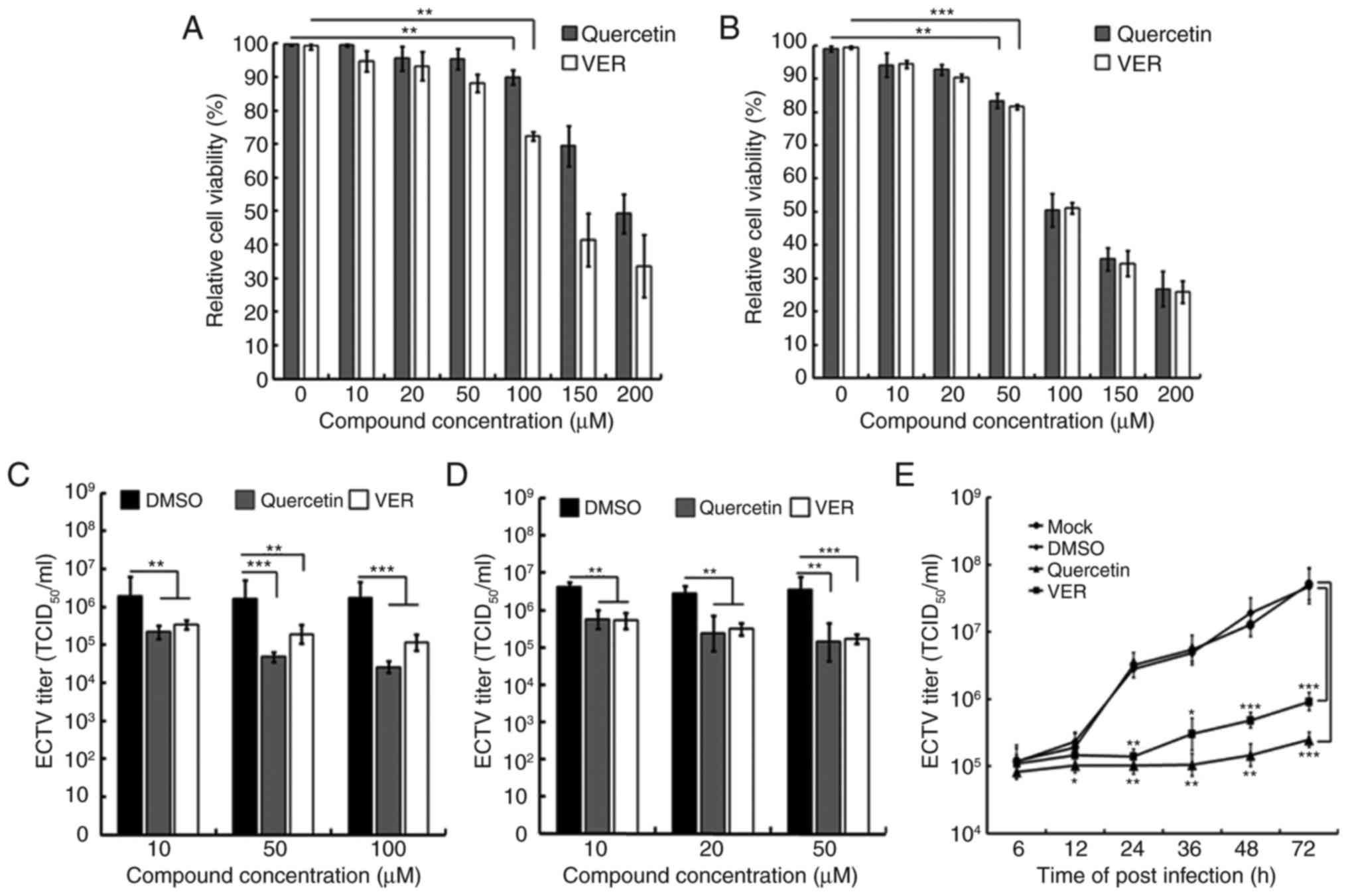
|
1
|
Puissant B and Combadière B: Keeping the
memory of smallpox virus. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:2249–2259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doellinger J, Schaade L and Nitsche A:
Comparison of the Cowpox virus and Vaccinia virus mature virion
proteome: Analysis of the species- and strain-specific proteome.
PLoS One. 10:e01415272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Panchanathan V, Chaudhri G and Karupiah G:
Correlates of protective immunity in poxvirus infection: Where does
antibody stand? Immunol Cell Biol. 86:80–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Damon IK, Damaso CR and McFadden G: Are we
there yet? The smallpox research agenda using variola virus. PLoS
Pathog. 10:e10041082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reardon S: 'Forgotten' NIH smallpox virus
languishes on death row. Nature. 514:5442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Quiner CA, Moses C, Monroe BP, Nakazawa Y,
Doty JB, Hughes CM, McCollum AM, Ibata S, Malekani J, Okitolonda E,
et al: Presumptive risk factors for monkeypox in rural communities
in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. PLoS One. 12:e01686642017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esteban DJ and Buller RM: Ectromelia
virus: The causative agent of mousepox. J Gen Virol. 86:2645–2659.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chapman JL, Nichols DK, Martinez MJ and
Raymond JW: Animal models of orthopoxvirus infection. Vet Pathol.
47:852–870. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Esteban D, Parker S, Schriewer J, Hartzler
H and Buller RM: Mousepox, a small animal model of smallpox.
Methods Mol Biol. 890:177–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sigal LJ: The pathogenesis and
immunobiology of mousepox. Adv Immunol. 129:251–276. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garver J, Weber L, Vela EM, Anderson M,
Warren R, Merchlinsky M, Houchens C and Rogers JV: Ectromelia virus
disease characterization in the BALB/c mouse: A surrogate model for
assessment of smallpox medical countermeasures. Viruses.
8:E2032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Temajo NO and Howard N: The virus-induced
HSPs regulate the apoptosis of operatus APCs that results in
autoimmunity, not in homeostasis. Autoimmun Rev. 13:1013–1019.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Makhoba XH, Burger A, Coertzen D, Zininga
T, Birkholtz LM and Shonhai A: Use of a chimeric Hsp70 to enhance
the quality of recombinant Plasmodium falciparum
s-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase protein produced in Escherichia
coli. PLoS One. 11:e01526262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burch AD and Weller SK: Nuclear
sequestration of cellular chaperone and proteasomal machinery
during herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J Virol.
78:7175–7185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manzoor R, Kuroda K, Yoshida R, Tsuda Y,
Fujikura D, Miyamoto H, Kajihara M, Kida H and Takada A: Heat shock
protein 70 modulates influenza A virus polymerase activity. J Biol
Chem. 289:7599–7614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Howe MK, Speer BL, Hughes PF, Loiselle DR,
Vasudevan S and Haystead TA: An inducible heat shock protein 70
small molecule inhibitor demonstrates anti-dengue virus activity,
validating Hsp70 as a host antiviral target. Antiviral Res.
130:81–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brown G, Rixon HW, Steel J, McDonald TP,
Pitt AR, Graham S and Sugrue RJ: Evidence for an association
between heat shock protein 70 and the respiratory syncytial virus
polymerase complex within lipid-raft membranes during virus
infection. Virology. 338:69–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mayer MP: Recruitment of Hsp70 chaperones:
A crucial part of viral survival strategies. Rev Physiol Biochem
Pharmacol. 153:1–46. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kaufer S, Coffey CM and Parker JS: The
cellular chaperone hsc70 is specifically recruited to reovirus
viral factories independently of its chaperone function. J Virol.
86:1079–1089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Cobbold C, Windsor M and Wileman T: A
virally encoded chaperone specialized for folding of the major
capsid protein of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 75:7221–7229.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alam SB and Rochon D: Evidence that Hsc70
is associated with Cucumber necrosis virus particles and plays a
role in particle disassembly. J Virol. 91:e01555–16. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Taguwa S, Maringer K, Li X, Bernal-Rubio
D, Rauch JN, Gestwicki JE, Andino R, Fernandez-Sesma A and Frydman
J: Defining Hsp70 subnetworks in Dengue virus replication reveals
key vulnerability in Flavivirus infection. Cell. 163:1108–1123.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang C, Kang K, Ning P, Peng Y, Lin Z,
Cui H, Cao Z, Wang J and Zhang Y: Heat shock protein 70 is
associated with CSFV NS5A protein and enhances viral RNA
replication. Virology. 482:9–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ye J, Chen Z, Zhang B, Miao H, Zohaib A,
Xu Q, Chen H and Cao S: Heat shock protein 70 is associated with
replicase complex of Japanese encephalitis virus and positively
regulates viral genome replication. PLoS One. 8:e751882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hirayama E, Atagi H, Hiraki A and Kim J:
Heat shock protein 70 is related to thermal inhibition of nuclear
export of the influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complex. J Virol.
78:1263–1270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li G, Zhang J, Tong X, Liu W and Ye X:
Heat shock protein 70 inhibits the activity of Influenza A virus
ribonucleoprotein and blocks the replication of virus in vitro and
in vivo. PLoS One. 6:e165462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim MY and Oglesbee M: Virus-heat shock
protein interaction and a novel axis for innate antiviral immunity.
Cells. 1:646–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim MY, Shu Y, Carsillo T, Zhang J, Yu L,
Peterson C, Longhi S, Girod S, Niewiesk S and Oglesbee M: Hsp70 and
a novel axis of type I interferon-dependent antiviral immunity in
the measles virus-infected brain. J Virol. 87:998–1009. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Li T, He X, Jia H, Chen G, Zeng S, Fang Y,
Jin Q and Jing Z: Molecular cloning and functional characterization
of murine toll-like receptor 8. Mol Med Rep. 13:1119–1126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
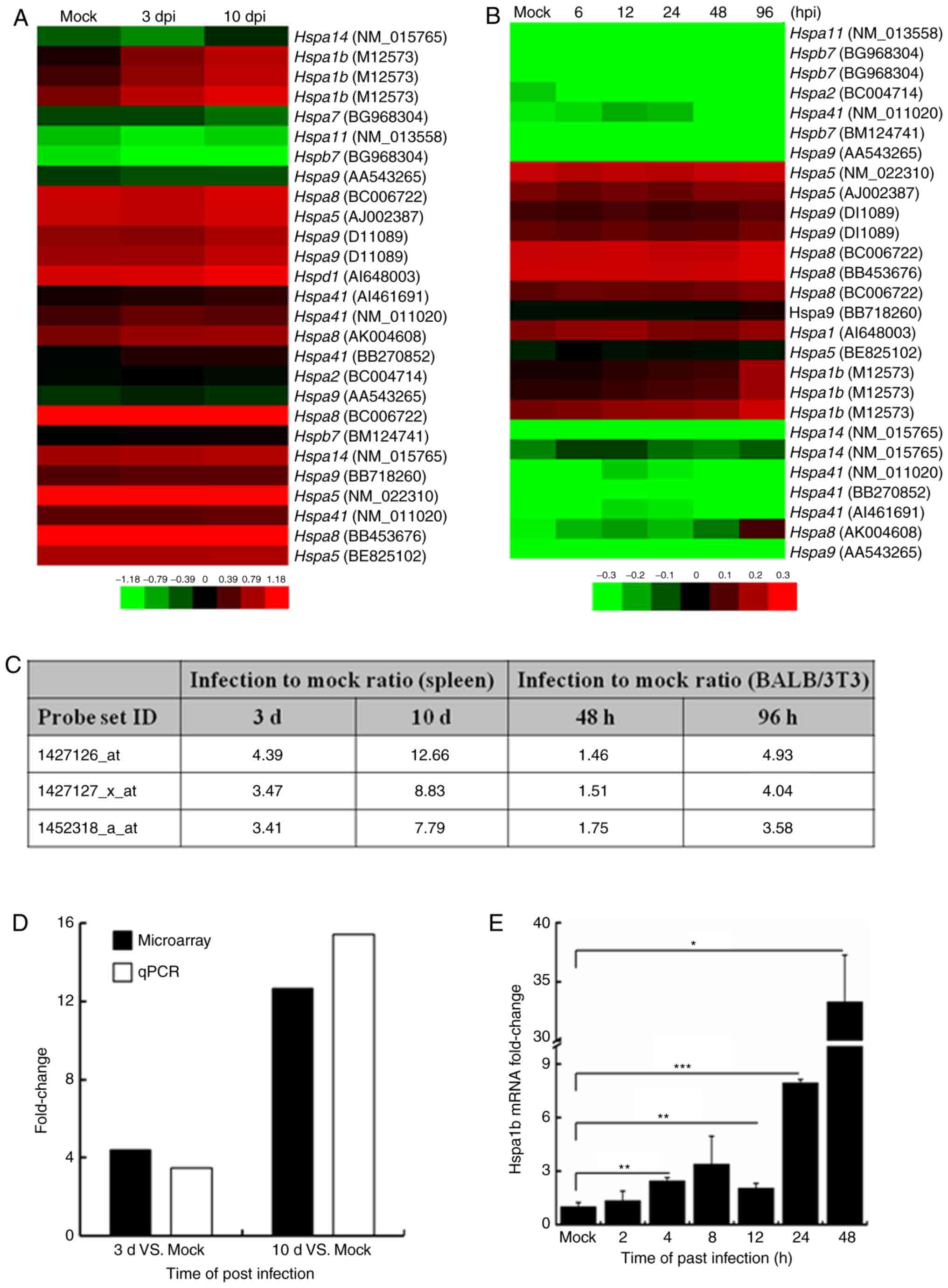
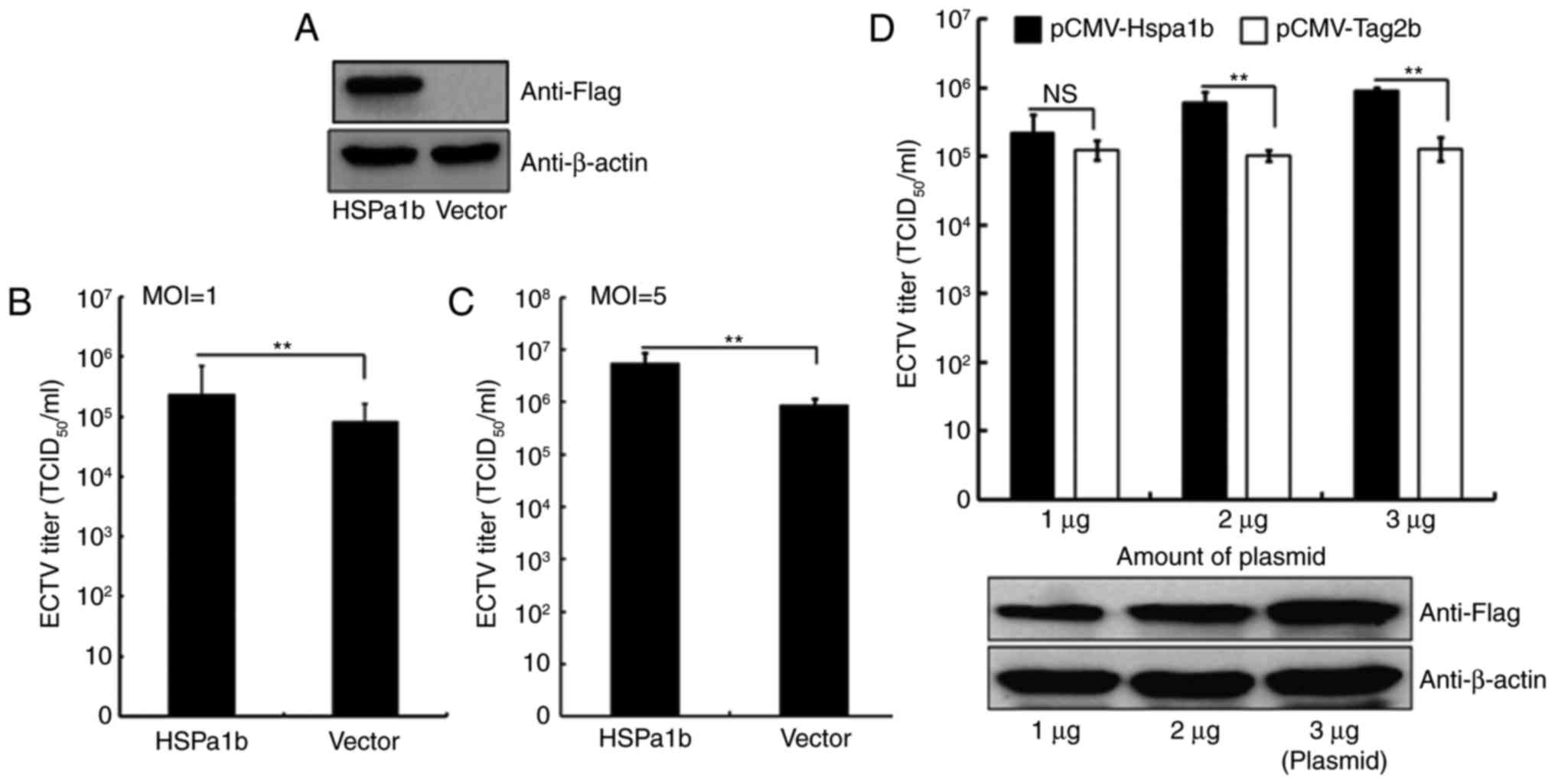
30
|
Cheng WY, Jia HJ, He XB, Chen GH, Feng Y,
Wang CY, Wang XX and Jing ZZ: Comparison of host gene expression
profiles in spleen tissues of genetically susceptible and resistant
mice during ECTV infection. Biomed Res Int. 2017:64561802017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Reed LJ and Muench H: A simple method of
estimating 50 percent endpoints. Am J Hyg. 27:493–497. 1938.
|
|
33
|
Cheng W, He X, Jia H, Chen G, Wang C,
Zhang J and Jing Z: Development of a SYBR Green I real-time PCR for
detection and quantitation of orthopoxvirus by using Ectromelia
virus. Mol Cell Probes. 38:45–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gonzalez O, Fontanes V, Raychaudhuri S,
Loo R, Loo J, Arumugaswami V, Sun R, Dasgupta A and French SW: The
heat shock protein inhibitor quercetin attenuates hepatitis C virus
production. Hepatology. 50:1756–1764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Bai J, Zhang L, Jiang Z, Wang X, Li
Y and Jiang P: Hsp70 positively regulates porcine circovirus type 2
replication in vitro. Virology. 447:52–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Surtees R, Dowall SD, Shaw A, Armstrong S,
Hewson R, Carroll MW, Mankouri J, Edwards TA, Hiscox JA and Barr
JN: Heat shock protein 70 family members interact with
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus and Hazara virus nucleocapsid
proteins and perform a functional role in the nairo-virus
replication cycle. J Virol. 90:9305–9316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanguy Le Gac N and Boehmer PE: Activation
of the herpes simplex virus type-1 origin-binding protein (UL9) by
heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. 277:5660–5666. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pogany J, Stork J, Li Z and Nagy PD: In
vitro assembly of the Tomato bushy stunt virus replicase requires
the host Heat shock protein 70. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:19956–19961. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baquero-Pérez B and Whitehouse A: Hsp70
isoforms are essential for the formation of Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus replication and transcription
compartments. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10052742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Smee DF: Orthopoxvirus inhibitors that are
active in animal models: An update from 2008 to 2012. Future Virol.
8:891–901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Parker S, Crump R, Foster S, Hartzler H,
Hembrador E, Lanier ER, Painter G, Schriewer J, Trost LC and Buller
RM: Co-administration of the broad-spectrum antiviral,
brincidofovir (CMX001), with smallpox vaccine does not compromise
vaccine protection in mice challenged with ectromelia virus.
Antiviral Res. 111:42–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mercer J, Snijder B, Sacher R, Burkard C,
Bleck CK, Stahlberg H, Pelkmans L and Helenius A: RNAi screening
reveals protea-some- and Cullin3-dependent stages in vaccinia virus
infection. Cell Rep. 2:1036–1047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bourquain D, Dabrowski PW and Nitsche A:
Comparison of host cell gene expression in cowpox, monkeypox or
vaccinia virus-infected cells reveals virus-specific regulation of
immune response genes. Virol J. 10:612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Filone CM, Caballero IS, Dower K, Mendillo
ML, Cowley GS, Santagata S, Rozelle DK, Yen J, Rubins KH, Hacohen
N, et al: The master regulator of the cellular stress response
(HSF1) is critical for orthopoxvirus infection. PLoS Pathog.
10:e10039042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Frydman J: Folding of newly translated
proteins in vivo: The role of molecular chaperones. Annu Rev
Biochem. 70:603–647. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu A, Li P, Tang T, Wang J, Chen Y and Liu
L: Roles of Hsp70s in stress responses of microorganisms, plants,
and animals. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5103192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim MY, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Shu Y and
Oglesbee M: hsp70-dependent antiviral immunity against cytopathic
neuronal infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Viro.
187:10668–10678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hung JJ, Chung CS and Chang W: Molecular
chaperone Hsp90 is important for vaccinia virus growth in cells. J
Virol. 76:1379–1390. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Khachatoorian R, Ganapathy E, Ahmadieh Y,
Wheatley N, Sundberg C, Jung CL, Arumugaswami V, Raychaudhuri S,
Dasgupta A and French SW: The NS5A-binding heat shock proteins
HSC70 and HSP70 play distinct roles in the hepatitis C viral life
cycle. Virology. 454–455:118–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|