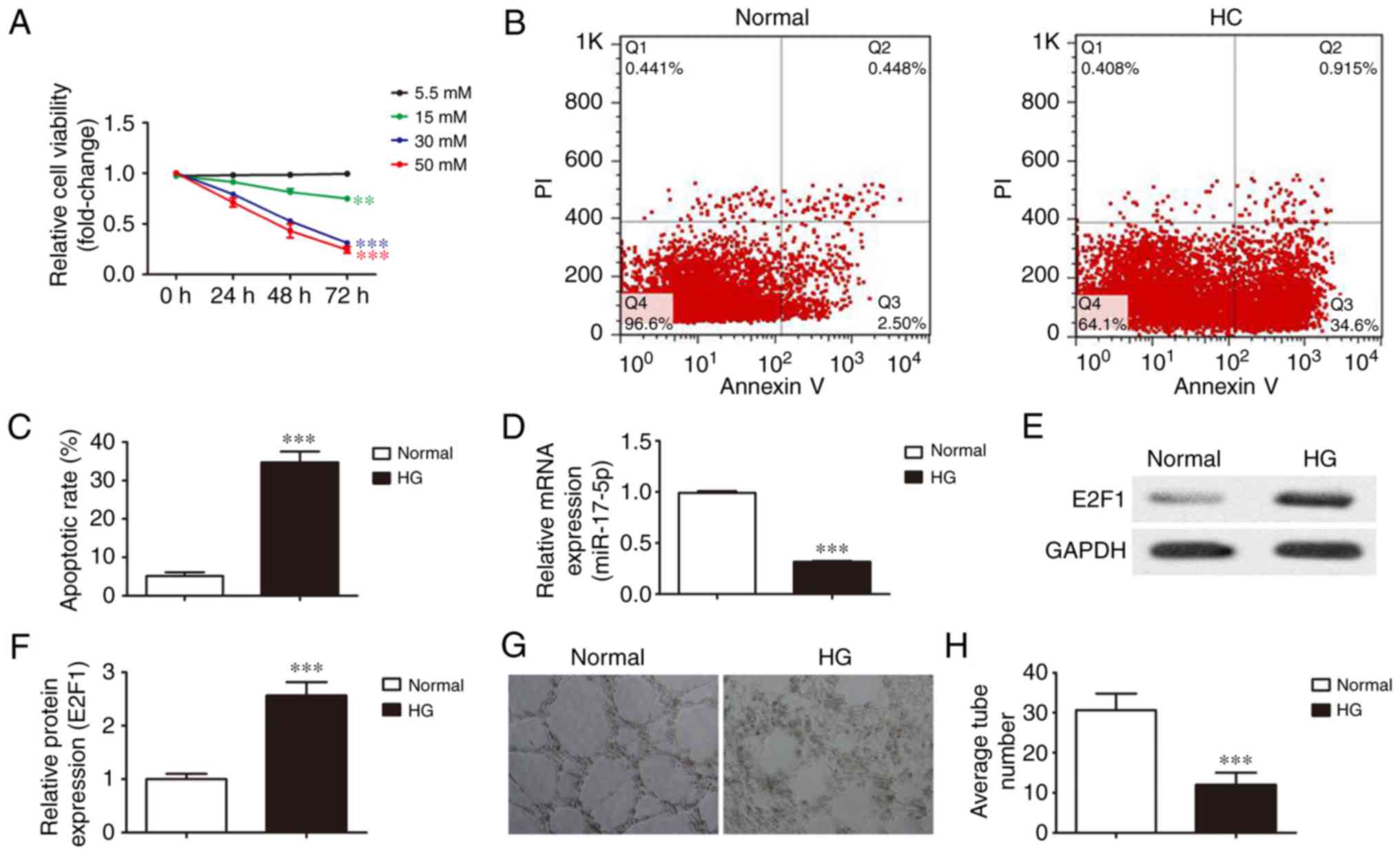
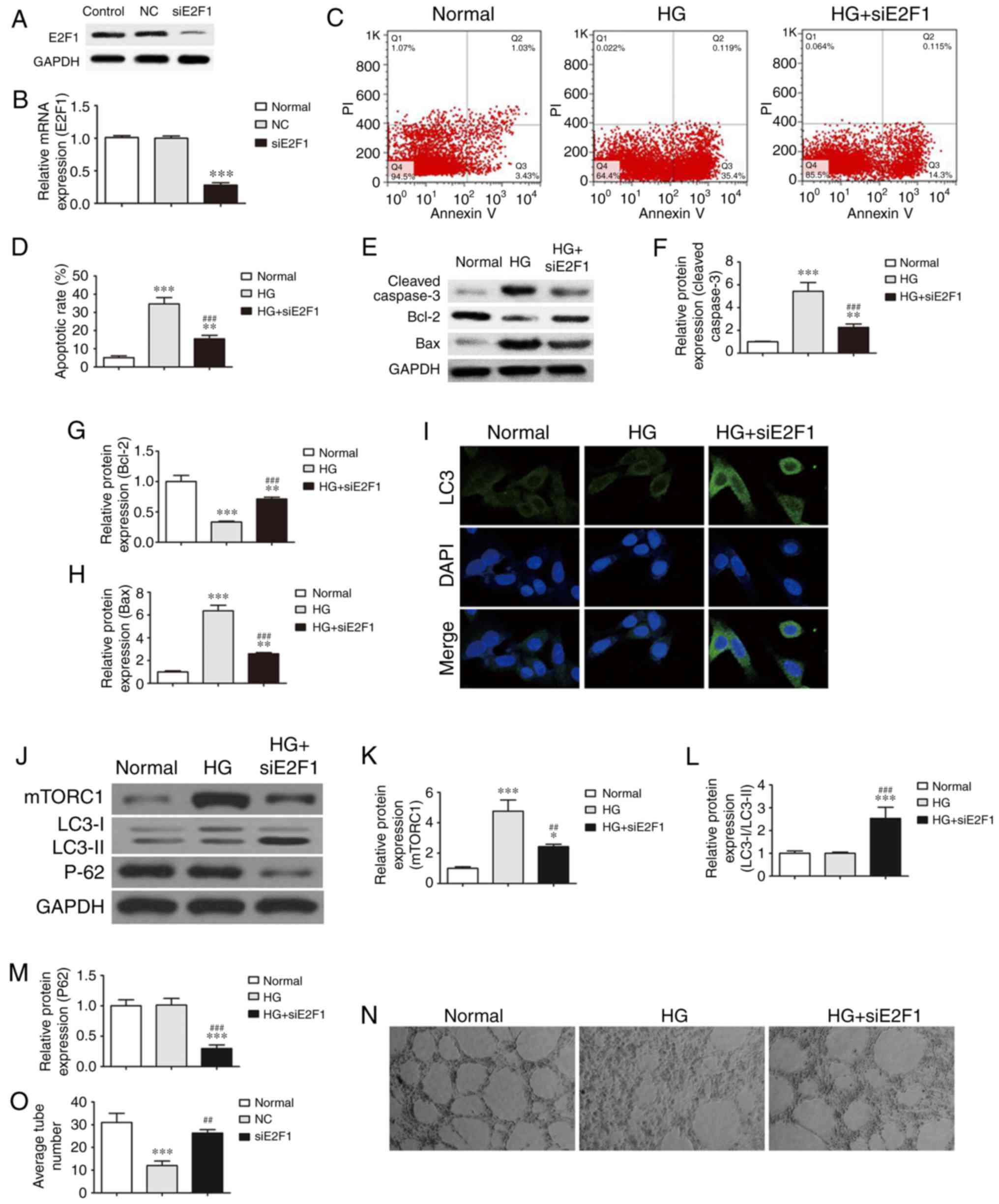
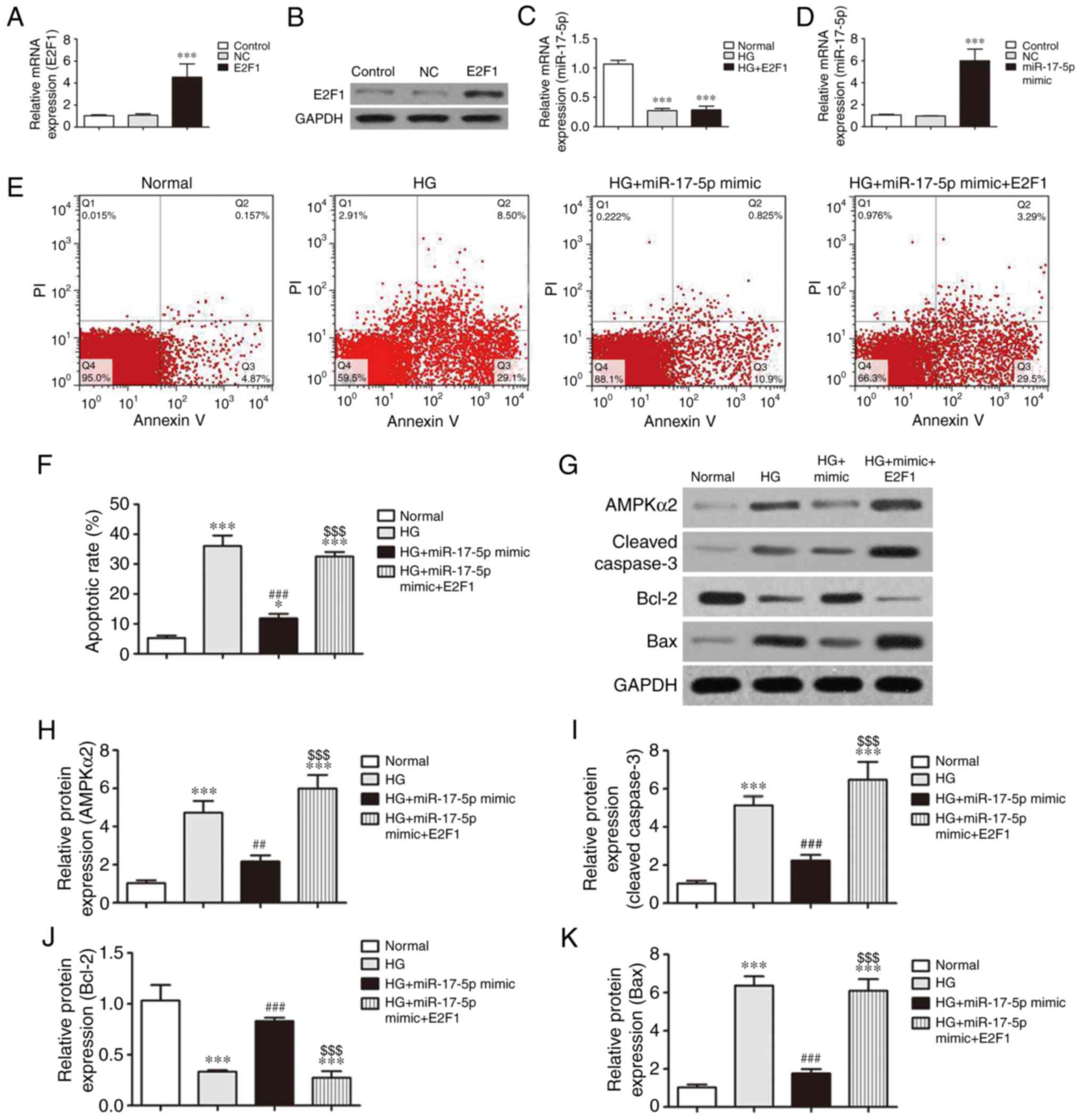
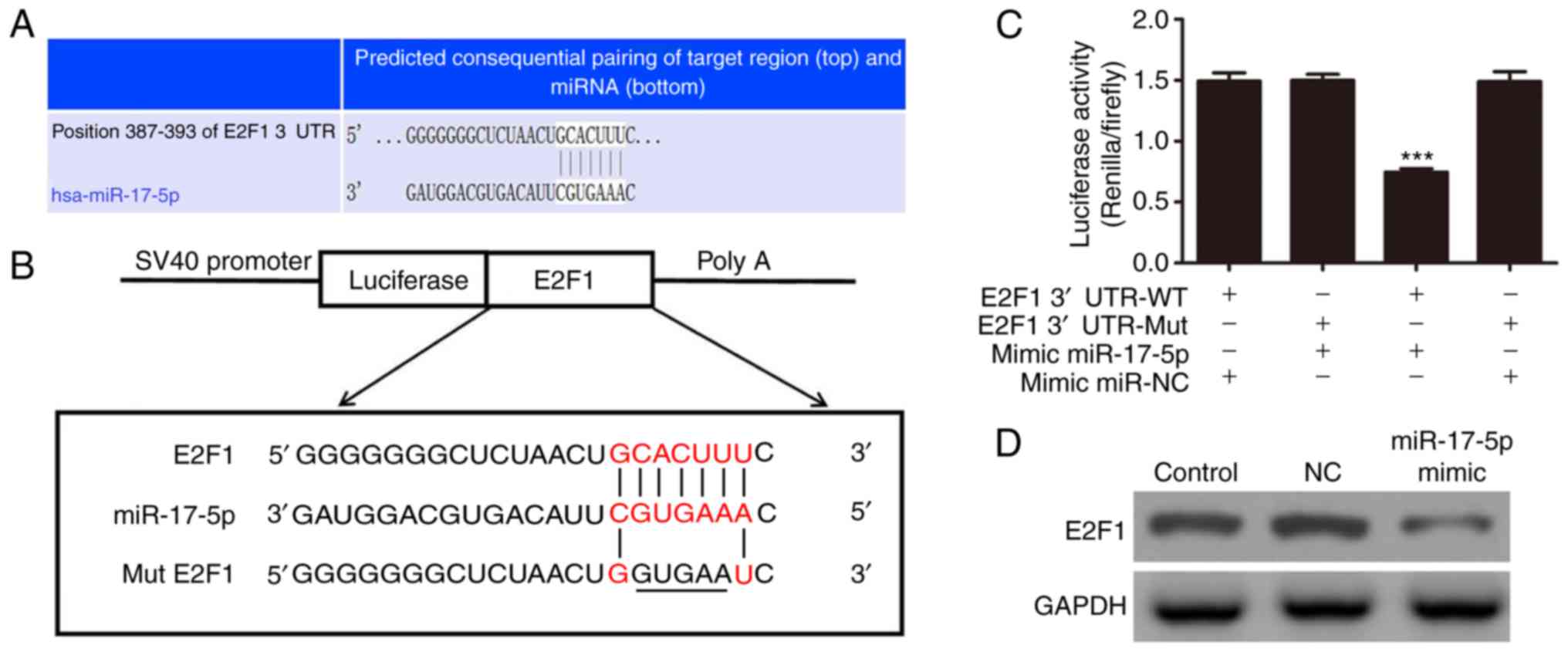
|
1
|
Chao CL, Chuang CP, Cheng YF, Lee KR,
Chang Y, Cheng SP, Chan WK and Ho FM: The protective role of
autophagy in matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cell transmigration
and cell death in high-glucose-treated endothelial cells.
Inflammation. 39:830–838. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weikel KA, Cacicedo JM, Ruderman NB and
Ido Y: Knockdown of GSK3β increases basal autophagy and AMPK
signalling in nutrient-laden human aortic endothelial cells. Biosci
Rep. 36:pii: e00382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kang H, Ma X, Liu J, Fan Y and Deng X:
High glucose-induced endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction. Diab
Vasc Dis Res. 14:381–394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cam H and Dynlacht BD: Emerging roles for
E2F: Beyond the G1/S transition and DNA replication. Cancer Cell.
3:311–316. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin Z, Ren N, Jiang Y, Xu W, Shi Y and Liu
G: Adenovirus-mediated E2F-1 gene transfer augments
gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Clin
Lab. 61:1435–1444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Liu G, Qiu J, Zhang N, Ding J and
Hua K: E2F1-regulated long non-coding RNA RAD51-AS1 promotes cell
cycle progression, inhibits apoptosis and predicts poor prognosis
in epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 7:44692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Xiao L, Zheng S, Yan N and
Chen D: E2f1 mediates high glucose-induced neuronal death in
cultured mouse retinal explants. Cell Cycle. 16:1824–1834. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu Y, Ma S, Xia Y, Lu Y, Xiao S, Cao Y,
Zhuang S, Tan X, Fu Q, Xie L, et al: Loss of GCN5 leads to
increased neuronal apoptosis by upregulating E2F1- and
Egr-1-dependent BH3-only protein Bim. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25702017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang W, Park IJ, Yun H, Im DU, Ock S, Kim
J, Seo SM, Shin HY, Viollet B, Kang I, et al: AMP-activated protein
kinase α2 and E2F1 transcription factor mediate doxorubicin-induced
cytotoxicity by forming a positive signal loop in mouse embryonic
fibroblasts and non-carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 289:4839–4852.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abdel Malik R, Zippel N, Frömel T, Heidler
J, Zukunft S, Walzog B, Ansari N, Pampaloni F, Wingert S, Rieger
MA, et al: AMP-activated protein kinase α2 in neutrophils regulates
vascular repair via Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and a network of
proteins affecting metabolism and apoptosis. Circ Res. 120:99–109.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Liang B, Wang Q, Wu J and Zou MH:
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 alleviates
endothelial cell apoptosis by increasing the expression of
anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and survivin. J Biol Chem.
285:15346–15355. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Real S, Meo-Evoli N, Espada L and Tauler
A: E2F1 regulates cellular growth by mTORC1 signaling. PLoS One.
6:e161632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meo-Evoli N, Almacellas E, Massucci FA,
Gentilella A, Ambrosio S, Kozma SC, Thomas G and Tauler A:
V-ATPase: A master effector of E2F1-mediated lysosomal trafficking,
mTORC1 activation and autophagy. Oncotarget. 6:28057–28070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Zhang S, Wang Y, Yang M, Zhang N,
Jin Z, Ding L, Jiang W, Yang J, Sun Z, et al: Autophagy inhibits
high glucose induced cardiac microvascular endothelial cells
apoptosis by mTOR signal pathway. Apoptosis. 22:1510–1523. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu J, Wang Y, Tan X and Jing H: MicroRNAs
in autophagy and their emerging roles in crosstalk with apoptosis.
Autophagy. 8:873–882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhai H, Fesler A and Ju J: MicroRNA: A
third dimension in autophagy. Cell Cycle. 12:246–250. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Han W, Fu X, Xie J, Meng Z, Gu Y, Wang X,
Li L, Pan H and Huang W: MiR-26a enhances autophagy to protect
against ethanol-induced acute liver injury. J Mol Med.
93:1045–1055. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong D, Fu N and Yang P: MiR-17
downregulation by high glucose stabilizes Thioredoxin-interacting
protein and removes thioredoxin inhibition on ASK1 leading to
apoptosis. Toxicol Sci. 150:84–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Hajarnis S, Lakhia R, Yheskel M, Williams
D, Sorourian M, Liu X, Aboudehen K, Zhang S, Kersjes K, Galasso R,
et al: microRNA-17 family promotes polycystic kidney disease
progression through modulation of mitochondrial metabolism. Nat
Commun. 8:143952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nandakumar P, Tin A, Grove ML, Ma J,
Boerwinkle E, Coresh J and Chakravarti A: MicroRNAs in the miR-17
and miR-15 families are downregulated in chronic kidney disease
with hypertension. PLoS One. 12:e01767342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ladu S, Calvisi DF, Conner EA, Farina M,
Factor VM and Thorgeirsson SS: E2F1 inhibits c-Myc-driven apoptosis
via PIK3CA/Akt/mTOR and COX-2 in a mouse model of human liver
cancer. Gastroenterology. 135:1322–1332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rezabakhsh A, Ahmadi M, Khaksar M,
Montaseri A, Malekinejad H, Rahbarghazi R and Garjani A: Rapamycin
inhibits oxidative/nitrosative stress and enhances angiogenesis in
high glucose-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Role
of autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:885–894. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu L, Wang G, Fischbach S and Xiao X:
Suppression of microRNA-205-5p in human mesenchymal stem cells
improves their therapeutic potential in treating diabetic foot
disease. Oncotarget. 8:52294–52303. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reddy MA and Natarajan R: Targeting
miR-200c to ameliorate diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction.
Diabetes. 65:1152–1154. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kovesdi I, Reichel R and Nevins JR: E1A
transcription induction: Enhanced binding of a factor to upstream
promoter sequences. Science. 231:719–722. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Engelmann D and Pützer BM: The dark side
of E2F1: In transit beyond apoptosis. Cancer Res. 72:571–575. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang P, Long M, Zhang S, Cheng Z, Zhao X,
He F, Liu H and Ming L: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α regulates
autophagy via the p27-E2F1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:2107–2112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Korah J, Canaff L and Lebrun JJ: The
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (pRb)/E2 promoter binding
factor 1 (E2F1) pathway as a novel mediator of TGFβ-induced
autophagy. J Biol Chem. 291:2043–2054. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fox MM, Phoenix KN, Kopsiaftis SG and
Claffey KP: AMP-activated protein kinase α2 isoform suppression in
primary breast cancer alters AMPK growth control and apoptotic
signaling. Genes Cancer. 4:3–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bartolomeo R, Cinque L, De Leonibus C,
Forrester A, Salzano AC, Monfregola J, De Gennaro E, Nusco E,
Azario I, Lanzara C, et al: mTORC1 hyperactivation arrests bone
growth in lysosomal storage disorders by suppressing autophagy. J
Clin Invest. 127:3717–3729. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tan HW, Sim AY and Long YC: Glutamine
metabolism regulates autophagy-dependent mTORC1 reactivation during
amino acid starvation. Nat Commun. 8:3382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin C, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Yang K, Hu J, Si
R, Zhang G, Gao B, Li X, Xu C, et al: Helix B surface peptide
attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy via AMPK-dependent autophagy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:665–671. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang C, Hou B, Yu S, Chen Q, Zhang N and
Li H: HGF alleviates high glucose-induced injury in podocytes by
GSK3β inhibition and autophagy restoration. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2690–2699. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pickering MT, Stadler BM and Kowalik TF:
miR-17 and miR-20a temper an E2F1-induced G1 checkpoint to regulate
cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 28:140–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|