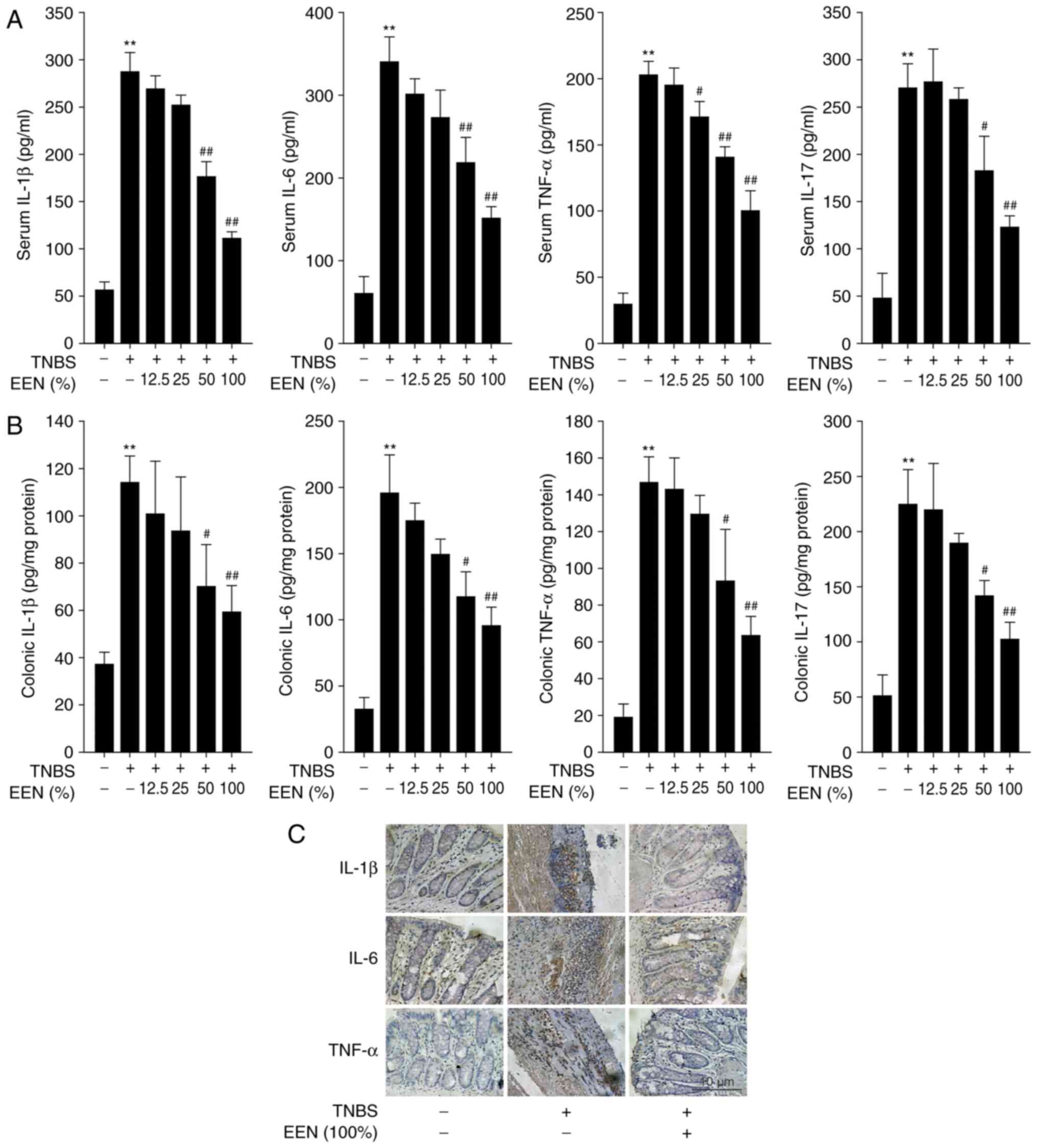
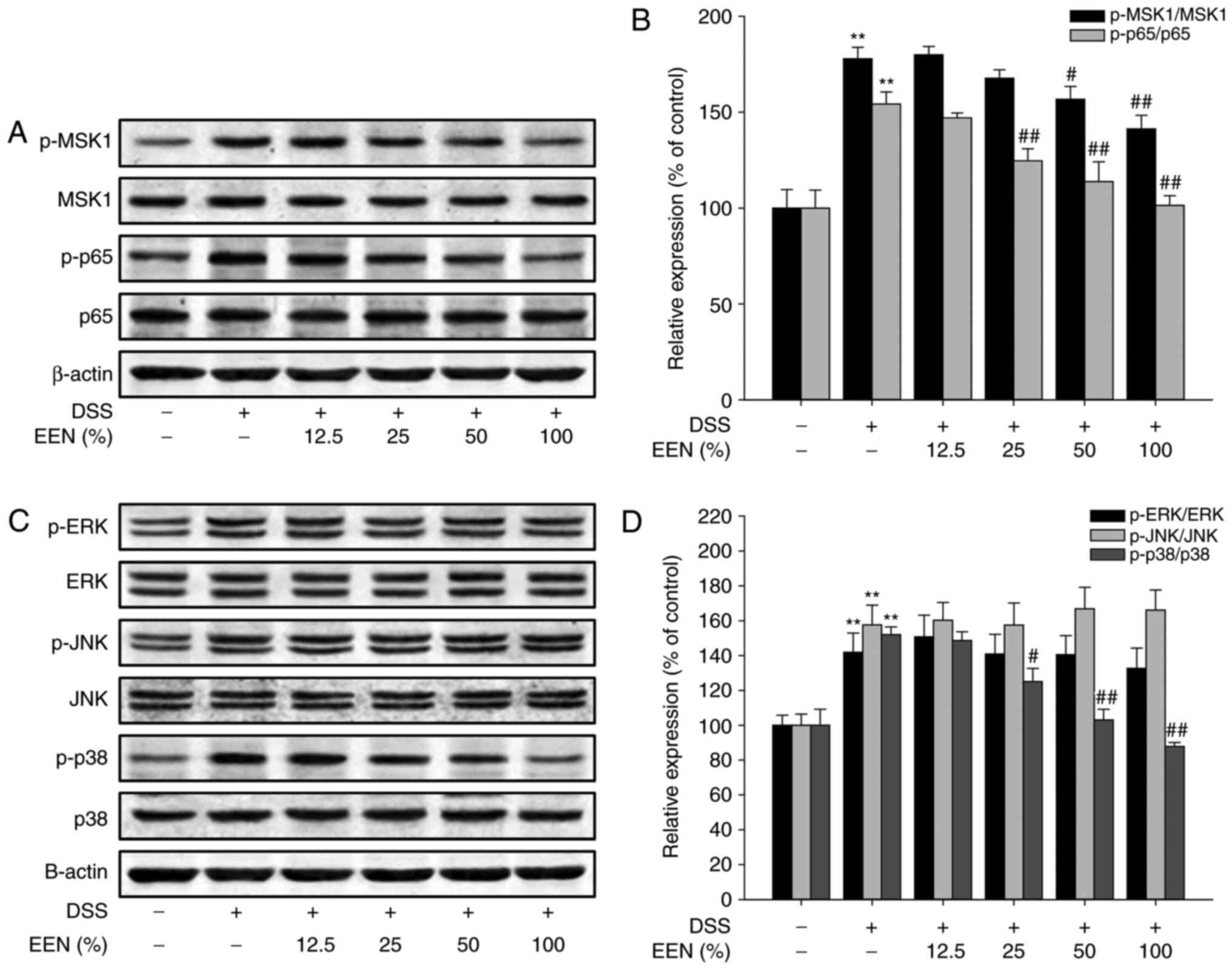
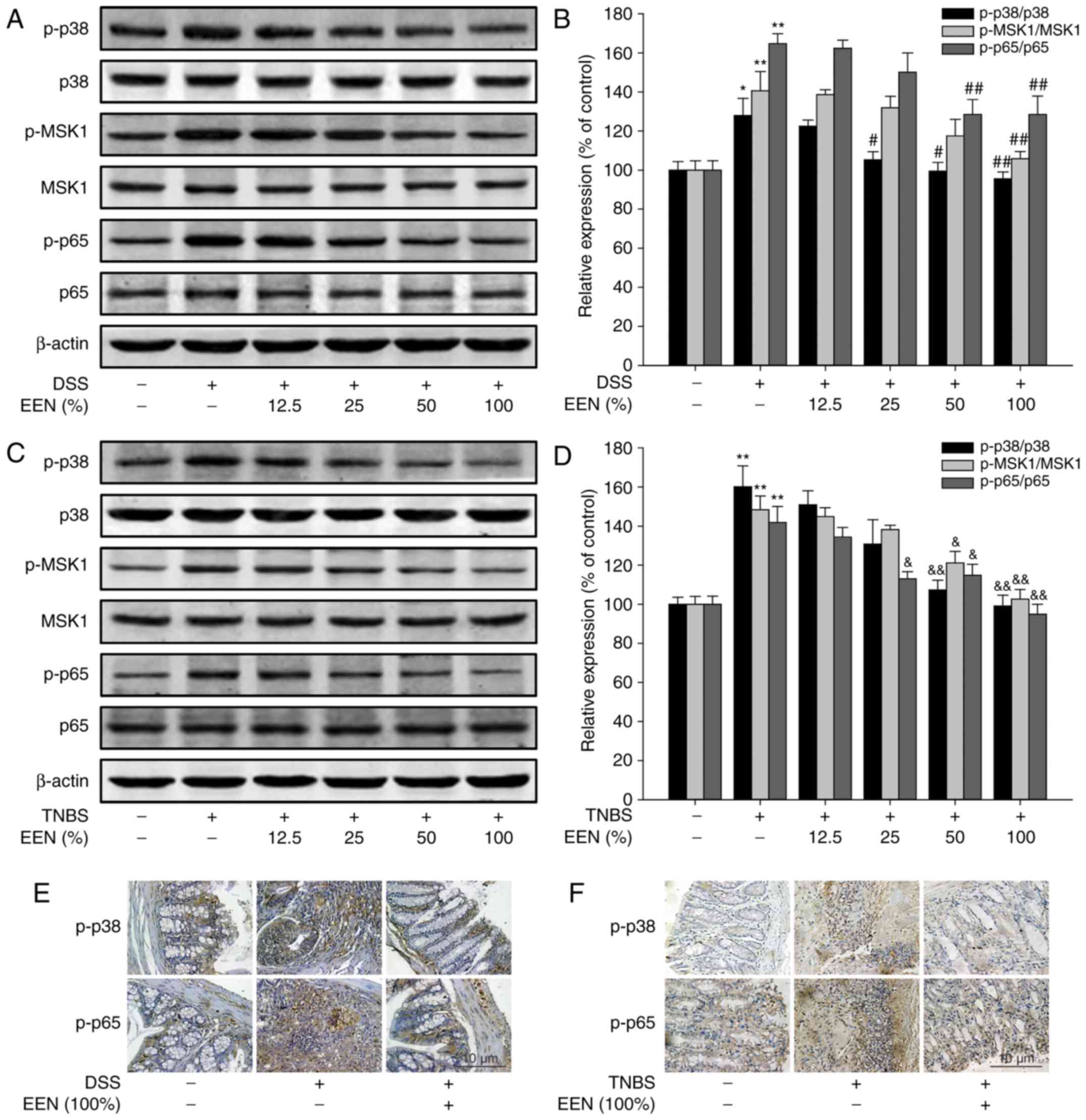
|
1
|
D’Arcangelo G and Aloi M: Inflammatory
bowel disease-unclassified in children: Diagnosis and
pharmacological management. Paediatri Drugs. 19:113–120. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mărginean CO, Meliţ LE, Mocanu S and
Mărginean MO: Inflammatory bowel diseases: a burden in pediatrics:
Case series and a review of the literature. Medicine. 96:e63292017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Francescone R, Hou V and Grivennikov SI:
Cytokines, IBD, and colitis-associated cancer. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
21:409–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Russo RA and Katsicas MM: Autoinflammatory
diseases. Medicina (B Aires). 76:166–172. 2016.In Spanish.
|
|
5
|
Striz I, Brabcova E, Kolesar L and
Sekerkova A: Cytokine networking of innate immunity cells: A
potential target of therapy. Clin Sci (Lond). 126:593–612. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Estruch M, Sanchez-Quesada JL,
Ordoñez-Llanos J and Benitez S: Inflammatory intracellular pathways
activated by electronegative LDL in monocytes. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1861.963–969. 2016.
|
|
7
|
Patel SJ, Jindal R, King KR, Tilles AW and
Yarmush ML: The inflammatory response to double stranded DNA in
endothelial cells is mediated by NFκB and TNFα. PloS One.
6:e199102011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kweon SM, Wang B, Rixter D, Lim JH, Koga
T, Ishinaga H, Chen LF, Jono H, Xu H and Li JD: Synergistic
activation of NF-kappaB by nontypeable H. influenzae and S.
pneumoniae is mediated by CK2, IKKbeta-IkappaBalpha, and p38 MAPK.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:368–375. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmitz ML, Mattioli I, Buss H and Kracht
M: NF-kappaB: A multifaceted transcription factor regulated at
several levels. Chembiochem. 5:1348–1358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nihira K, Ando Y, Yamaguchi T, Kagami Y,
Miki Y and Yoshida K: Pim-1 controls NF-kappaB signalling by
stabilizing RelA/p65. Cell Death Differ. 17:689–698. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Arun P, Brown MS, Ehsanian R, Chen Z and
Van Waes C: Nuclear NF-kappaB p65 phosphorylation at serine 276 by
protein kinase A contributes to the malignant phenotype of head and
neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5974–5984. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawashima T, Murata K, Akira S, Tonozuka
Y, Minoshima Y, Feng S, Kumagai H, Tsuruga H, Ikeda Y, Asano S, et
al: STAT5 induces macrophage differentiation of M1 leukemia cells
through activation of IL-6 production mediated by NF-kappaB p65. J
Immunol. 167:3652–3660. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen YM, Zhao Y, Zeng Y, Yan L, Chen BL,
Leng AM, Mu YB and Zhang GY: Inhibition of Pim-1 kinase ameliorates
dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Dig Dis Sci.
57:1822–1831. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng S, Zhang QY, Huang J, Vedantham S,
Rosario R, Ananthakrishnan R, Yan SF, Ramasamy R, DeMatteo RP,
Emond JC, et al: Opposing roles of RAGE and Myd88 signaling in
extensive liver resection. FASEB J. 26:882–893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Zhang HM, Li L, Papadopoulou N, Hodgson G,
Evans E, Galbraith M, Dear M, Vougier S, Saxton J and Shaw PE:
Mitogen-induced recruitment of ERK and MSK to SRE promoter
complexes by ternary complex factor Elk-1. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:2594–2607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Basu S, Pathak S, Pathak SK, Bhattacharyya
A, Banerjee A, Kundu M and Basu J: Mycobacterium avium-induced
matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression occurs in a
cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner and involves phosphorylation- and
acetylation-dependent chromatin modification. Cell Microbiol.
9:2804–2816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vermeulen L, De Wilde G, Van Damme P,
Vanden Berghe W and Haegeman G: Transcriptional activation of the
NF-kappaB p65 subunit by mitogen- and stress-activated protein
kinase-1 (MSK1). EMBO J. 22:1313–1324. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pan Y, Liu Y, Guo H, Jabir MS, Liu X, Cui
W and Li D: Associations between folate and vitamin B12 levels and
inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Nutrients. 9:E3822017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang F, Zhao HY, Zhang ST, Gong YZ, Zhang
HF and Zhang C: Effect of enteral nutrition on dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis in rats. J Dig Dis. 12:453–458. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park MY, Kwon HJ and Sung MK: Dietary
aloin, aloesin, or aloe-gel exerts anti-inflammatory activity in a
rat colitis model. Life Sci. 88:486–492. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Jamal N, Erdual E, Neunlist M, Koriche
D, Dubuquoy C, Maggiotto F, Chevalier J, Berrebi D, Dubuquoy L,
Boulanger E, et al: Glugacon-like peptide-2: Broad receptor
expression, limited therapeutic effect on intestinal inflammation
and novel role in liver regeneration. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 307:G274–G285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alex P, Zachos NC, Nguyen T, Gonzales L,
Chen TE, Conklin LS, Centola M and Li X: Distinct cytokine patterns
identified from multiplex profiles of murine DSS and TNBS-induced
colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 15:341–352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Yao J, Pan D, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Sun J, Wang
Y, You QD, Xi T, Guo QL and Lu N: Wogonin prevents
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in
mice via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated
attenuation of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Immunology.
143:241–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Sun Y, Ding Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Li
W, Huang S, Li Z, Kong L, Guo Q and Lu N: GL-V9, a new synthetic
flavonoid derivative, ameliorates DSS-induced colitis against
oxidative stress by up-regulating Trx-1 expression via activation
of AMPK/FOXO3a pathway. Oncotarget. 6:26291–26307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cabre E, Mañosa M, Garcia-Sanchez V,
García-Sánchez V, Gutiérrez A, Ricart E, Esteve M, Guardiola J,
Aguas M, Merino O, et al: Phenotypic concordance in familial
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Results of a nationwide IBD
Spanish database. J Crohns Colitis. 8:654–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fukuda T, Majumder K, Zhang H, Turner PV,
Matsui T and Mine Y: Adenine inhibits TNF-α signaling in intestinal
epithelial cells and reduces mucosal inflammation in a dextran
sodium sulfate-induced colitis mouse model. J Agric Food Chem.
64:4227–4234. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morin C, Blier PU and Fortin S: MAG-EPA
reduces severity of DSS-induced colitis in rats. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 310:G808–G821. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shah KH, Shi P, Giani JF, Janjulia T,
Bernstein EA, Li Y, Zhao T, Harrison DG, Bernstein KE and Shen XZ:
Myeloid Suppressor cells accumulate and regulate blood pressure in
hypertension. Circ Res. 117:858–869. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reber L, Vermeulen L, Haegeman G and
Frossard N: Ser276 phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 by MSK1 controls
SCF expression in inflammation. PloS One. 4:e43932009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Schiller M, Bohm M, Dennler S, Ehrchen JM
and Mauviel A: Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 is
critical for interleukin-1-induced, CREB-mediated, c-fos gene
expression in keratinocytes. Oncogene. 25:4449–4457. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deak M, Clifton AD, Lucocq LM and Alessi
DR: Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1) is
directly activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may mediate
activation of CREB. EMBO J. 17:4426–4441. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Burisch J: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative
colitis. Occurrence, course and prognosis during the first year of
disease in a European population-based inception cohort. Dan Med J.
61:B47782014.
|
|
33
|
McDermott F, Hughes ES and Pihl E:
Mortality and morbidity of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
in Australia. Med J Aust. 1:534–536. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grimm IS and Friedman LS: Inflammatory
bowel disease in the elderly. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
19:361–389. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reich K, Leonardi C, Langley RG, Warren
RB, Bachelez H, Romiti R, Ohtsuki M, Xu W, Acharya N, Solotkin K,
et al: Inflammatory bowel disease among patients with psoriasis
treated with ixekizumab: A presentation of adjudicated data from an
integrated database of 7 randomized controlled and uncontrolled
trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 76:441–448e2. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Archer R, Tappenden P, Ren S, Martyn-St
James M, Harvey R, Basarir H, Stevens J, Carroll C, Cantrell A,
Lobo A and Hoque S: Infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab for
treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis after the
failure of conventional therapy (including a review of TA140 and
TA262): Clinical effectiveness systematic review and economic
model. Health Technol Assess. 20:1–326. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Perdikis DA and Basson MD: Basal nutrition
promotes human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) proliferation, brush
border enzyme activity, and motility. Crit Care Med. 25:159–165.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zaiss MM, Rapin A, Lebon L, Dubey LK,
Mosconi I, Sarter K, Piersigilli A, Menin L, Walker AW, Rougemont
J, et al: The intestinal microbiota contributes to the ability of
helminths to modulate allergic inflammation. Immunity. 43:998–1010.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vitetta L, Saltzman ET, Nikov T, Ibrahim I
and Hall S: Modulating the gut micro-environment in the treatment
of intestinal parasites. J Clin Med. 5:E1022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
No authors listed. Inflammatory bowel
disease. Prog Drug Res. 71:117–122. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C,
Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M and Nageshwar Reddy D: Role of the normal gut
microbiota. World J Gastroenterol. 21:8787–8803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dae Park D, Yum HW, Zhong X, Kim SH, Kim
SH, Kim DH, Kim SJ, Na HK, Sato A, Miura T and Surh YJ: Perilla
frutescens extracts protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced
murine colitis: NF-κB, STAT3, and Nrf2 as putative targets. Front
Pharmacol. 8:4822017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kono H, Fujii H, Ogiku M, Tsuchiya M,
Ishii K and Hara M: Enteral diets enriched with medium-chain
triglycerides and N-3 fatty acids prevent chemically induced
experimental colitis in rats. Transl Res. 156:282–291. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kawahara R, Yasuda M, Hashimura H, Amagase
K, Kato S and Takeuchi K: Activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptors ameliorates indomethacin-induced small intestinal
ulceration in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 650:411–417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hata K, Andoh A, Shimada M, Fujino S,
Bamba S, Araki Y, Okuno T, Fujiyama Y and Bamba T: IL-17 stimulates
inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways in
human colonic myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 282:G1035–G1044. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rivera-Serrano EE and Sherry B: NF-κB
activation is cell type-specific in the heart. Virology.
502:133–143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lim H, Lee H, Noh K and Lee SJ:
IKK/NF-κB-dependent satellite glia activation induces spinal cord
microglia activation and neuropathic pain after nerve injury. Pain.
158:1666–1677. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Durand JK and Baldwin AS: Targeting IKK
and NF-κB for therapy. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 107:77–115.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Rinkenbaugh AL, Cogswell PC, Calamini B,
Dunn DE, Persson AI, Weiss WA, Lo DC and Baldwin AS: IKK/NF-κB
signaling contributes to glioblastoma stem cell maintenance.
Oncotarget. 7:69173–69187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|