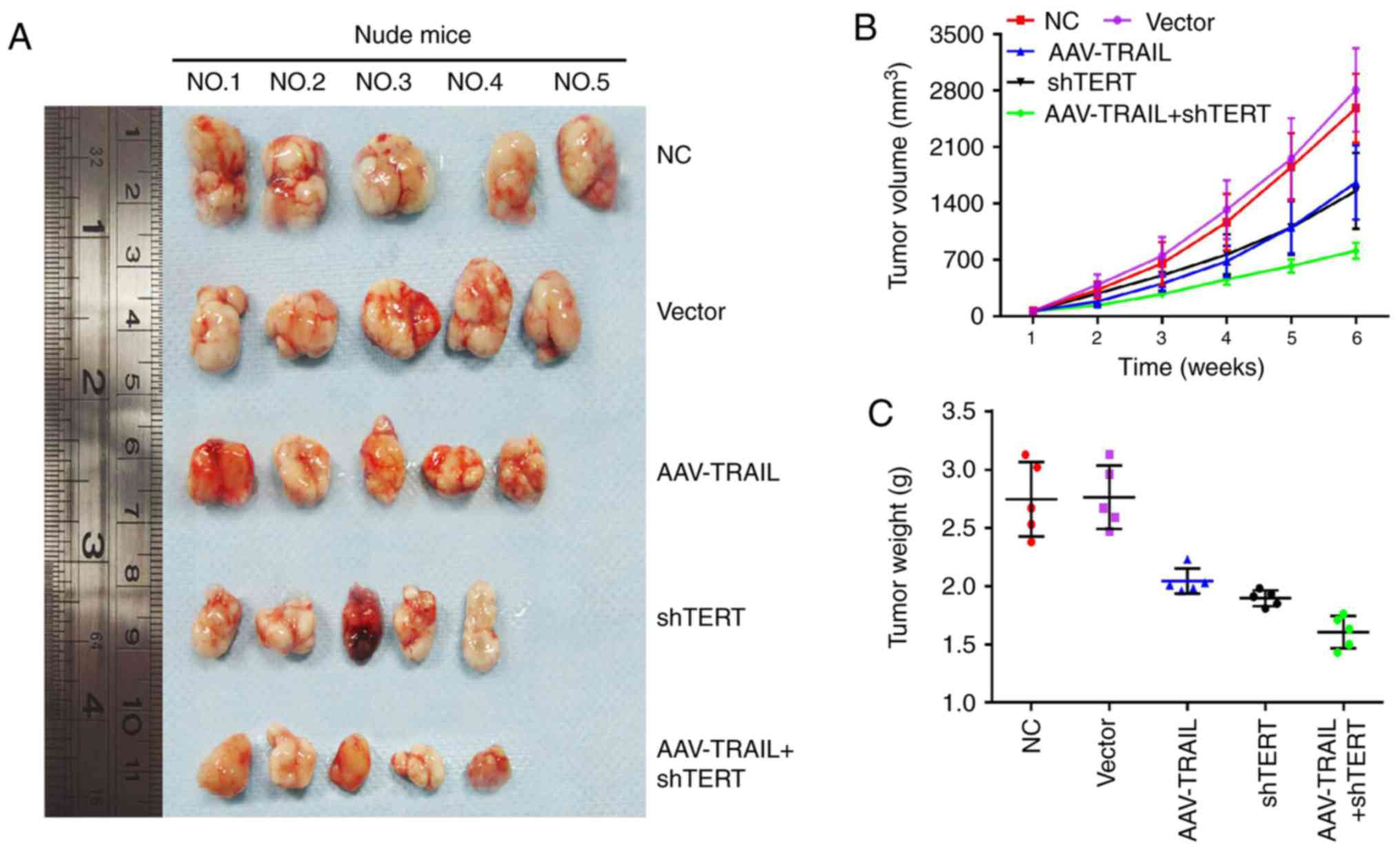
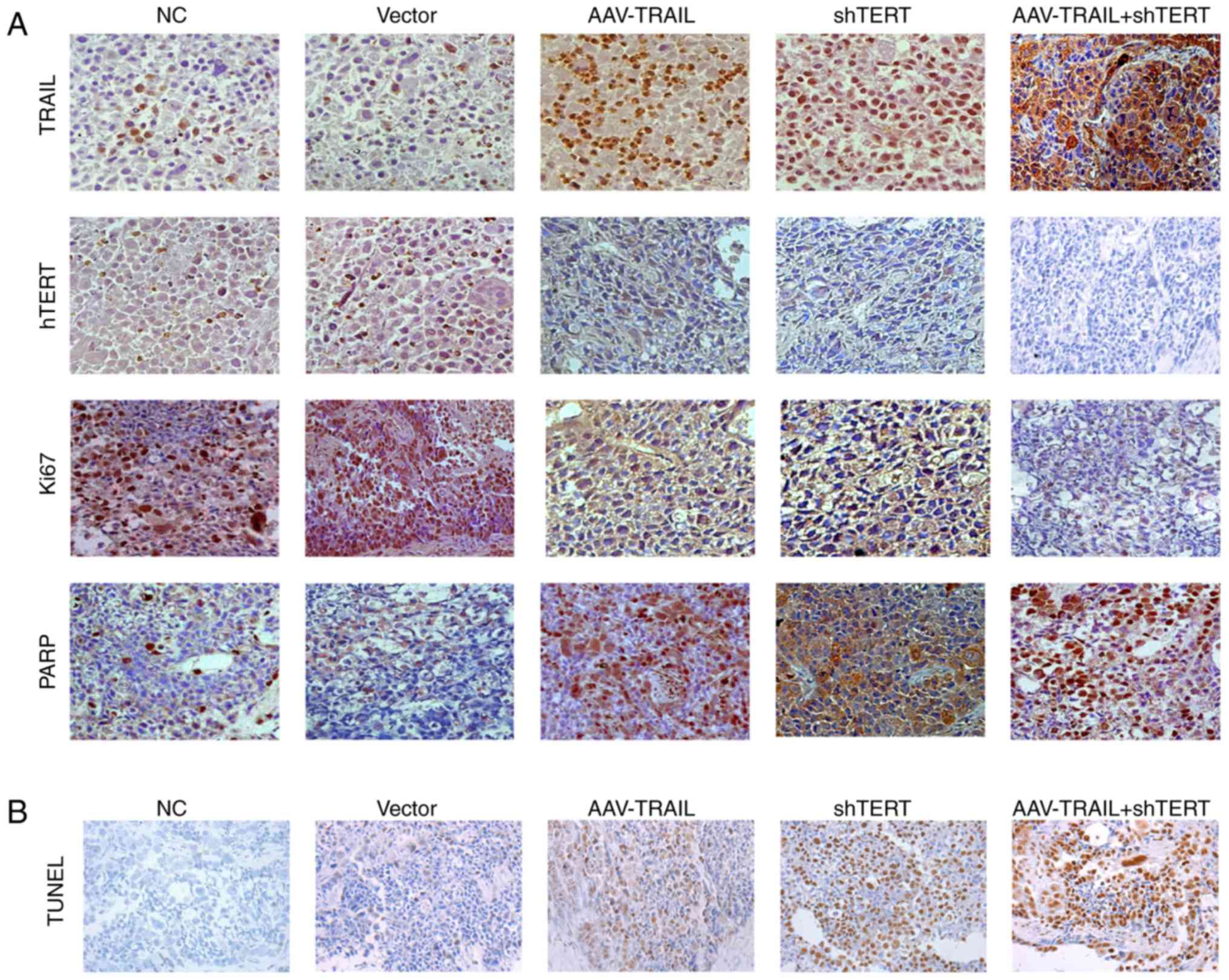
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lo Muzio L, Sartini D, Santarelli A,
Rocchetti R, Morganti S, Pozzi V, Rubini C, Bambini F and Emanuelli
M: Expression and prognostic significance of apoptotic genes in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 53:264–271. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yanamoto S, Yamada S, Takahashi H,
Yoshitomi I, Kawasaki G, Ikeda H, Minamizato T, Shiraishi T, Fujita
S, Ikeda T, et al: Clinicopathological risk factors for local
recurrence in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 41:1195–1200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhong LP, Zhang CP, Ren GX, Guo W, William
WN Jr, Sun J, Zhu HG, Tu WY, Li J, Cai YL, et al: Randomized phase
III trial of induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and
fluorouracil followed by surgery versus up-front surgery in locally
advanced resectable oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
31:744–751. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yajima T, Ochiai H, Uchiyama T, Takano N,
Shibahara T and Azuma T: Resistance to cytotoxic
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in side population cells of human
oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line Ho-1-N-1. Int J Oncol.
35:273–280. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang G, Li J, Zeng Z and Xian L:
Lentivirus-mediated gene therapy by suppressing survivin in BALB/c
nude mice bearing oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:435–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang L, Wang H, Zhou L and Yu D:
Akt-FOXO3a signaling axis dysregulation in human oral squamous cell
carcinoma and potent efficacy of FOXO3a-targeted gene therapy. Oral
Oncol. 47:16–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K and Scheurich P:
TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its receptors in
tumor surveillance and cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 7:449–459. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang S: The promise of cancer therapeutics
targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL
receptor pathway. Oncogene. 27:6207–6215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McLornan DP, Barrett HL, Cummins R,
McDermott U, McDowell C, Conlon SJ, Coyle VM, Van Schaeybroeck S,
Wilson R, Kay EW, et al: Prognostic significance of TRAIL signaling
molecules in stage II and III colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:3442–3451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polanski R, Vincent J, Polanska UM,
Petreus T and Tang EK: Caspase-8 activation by TRAIL monotherapy
predicts responses to IAPi and TRAIL combination treatment in
breast cancer cell lines. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Nakagawa H, Fei P, Rustgi AK and
El-Deiry WS: Targeting Bcl-xL in esophageal squamous cancer to
sensitize to chemotherapy plus TRAIL-induced apoptosis while normal
epithelial cells are protected by blockade of caspase 9. Cell Death
Differ. 11:583–587. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen M, Wang X, Zha D, Cai F, Zhang W, He
Y, Huang Q, Zhuang H and Hua ZC: Apigenin potentiates TRAIL therapy
of non-small cell lung cancer via upregulating DR4/DR5 expression
in a p53-dependent manner. Sci Rep. 6:354682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Wen XZ, Bu ZD, Cheng XJ, Xing XF,
Wang XH, Zhang LH, Guo T, Du H, Hu Y, et al: Paclitaxel enhances
tumoricidal potential of TRAIL via inhibition of MAPK in resistant
gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 35:3009–3017. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Piras-Straub K, Khairzada K, Trippler M,
Baba HA, Kaiser GM, Paul A, Canbay A, Weber F, Gerken G and Herzer
K: TRAIL expression levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma have
implications for tumor growth, recurrence and survival. Int J
Cancer. 136:E154–E160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Holoch PA and Griffith TS: TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): A new path to anti-cancer
therapies. Eur J Pharmacol. 625:63–72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu ST, Chen L, Wang HJ, Tang XD, Fang DC
and Yang SM: hTERT promotes the invasion of telomerase-negative
tumor cells in vitro. Int J Oncol. 35:329–336. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xi L and Cech TR: Inventory of telomerase
components in human cells reveals multiple subpopulations of hTR
and hTERT. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:8565–8577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lü MH, Liao ZL, Zhao XY, Fan YH, Lin XL,
Fang DC, Guo H and Yang SM: hTERT-based therapy: A universal
anticancer approach (Review). Oncol Rep. 28:1945–1952. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu L, Yin S, Banerjee S, Sarkar F and
Reddy KB: Enhanced anticancer effect of the combination of
cisplatin and TRAIL in triple-negative breast tumor cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:550–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang WB, Zhou YL, Heng DF, Miao CH and Cao
YL: Combination of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL) and canstatin gene suppression therapy on breast
tumor xenograft growth in mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
110:283–295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
O’Neill PM, Amewu RK, Charman SA, Sabbani
S, Gnädig NF, Straimer J, Fidock DA, Shore ER, Roberts NL, Wong MH,
et al: A tetraoxane-based antimalarial drug candidate that
overcomes PfK13-C580Y dependent artemisinin resistance. Nat Commun.
8:151592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Ma H, Zhang J, Liu S, Liu Y and
Zheng D: AAV-mediated TRAIL gene expression driven by hTERT
promoter suppressed human hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice.
Life Sci. 82:1154–1161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuo WT, Lee TC, Yang HY, Chen CY, Au YC,
Lu YZ, Wu LL, Wei SC, Ni YH, Lin BR, et al: LPS receptor subunits
have antagonistic roles in epithelial apoptosis and colonic
carcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 22:1590–1604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang K, Kievit FM, Jeon M, Silber JR,
Ellenbogen RG and Zhang M: Nanoparticle-mediated target delivery of
TRAIL as gene therapy for glioblastoma. Adv Healthc Mater.
4:2719–2726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Li L, Shao N, Hu Z, Chen H, Xu L,
Wang C, Cheng Y and Xiao J: Triazine-modified dendrimer for
efficient TRAIL gene therapy in osteosarcoma. Acta Biomater.
17:115–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abe K, Kurakin A, Mohseni-Maybodi M, Kay B
and Khosravi-Far R: The complexity of TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 926:52–63. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kojima Y, Nakayama M, Nishina T, Nakano H,
Koyanagi M, Takeda K, Okumura K and Yagita H: Importin β1
protein-mediated nuclear localization of death receptor 5 (DR5)
limits DR5/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL)-induced cell death of human tumor cells. J Biol
Chem. 286:43383–43393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Valley CC, Lewis AK, Mudaliar DJ,
Perlmutter JD, Braun AR, Karim CB, Thomas DD, Brody JR and Sachs
JN: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)
induces death receptor 5 networks that are highly organized. J Biol
Chem. 287:21265–21278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vizetto-Duarte C, Custódio L, Gangadhar
KN, Lago JH, Dias C, Matos AM, Neng N, Nogueira JM, Barreira L,
Albericio F, et al: Isololiolide, a carotenoid metabolite isolated
from the brown alga Cystoseira tamariscifolia, is cytotoxic and
able to induce apoptosis in hepatocarcinoma cells through caspase-3
activation, decreased Bcl-2 levels, increased p53 expression and
PARP cleavage. Phytomedicine. 23:550–557. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu P, Cai X, Zhang W, Li Y, Qiu P, Lu D
and He X: Flavonoids of Rosa roxburghii Tratt exhibit
radioprotection and anti-apoptosis properties via the
Bcl-2(Ca(2+))/Caspase-3/PARP-1 pathway. Apoptosis. 21:1125–1143.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dudognon C, Pendino F, Hillion J, Saumet
A, Lanotte M and Ségal-Bendirdjian E: Death receptor signaling
regulatory function for telomerase: hTERT abolishes TRAIL-induced
apoptosis, independently of telomere maintenance. Oncogene.
23:7469–7474. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luiten RM, Pene J, Yssel H and Spits H:
Ectopic hTERT expression extends the life span of human CD4+ helper
and regulatory T-cell clones and confers resistance to oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis. Blood. 101:4512–4519. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dômont J, Pawlik TM, Boige V, Rose M,
Weber JC, Hoff PM, Brown TD, Zorzi D, Morat L, Pignon JP, et al:
Catalytic subunit of human telomerase reverse transcriptase is an
independent predictor of survival in patients undergoing curative
resection of hepatic colorectal metastases: A multicenter analysis.
J Clin Oncol. 23:3086–3093. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Z, Li Q, Li K, Chen L, Li W, Hou M,
Liu T, Yang J, Lindvall C, Björkholm M, et al: Telomerase reverse
transcriptase promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem
cell-like traits in cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:4203–4213. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhao T, Hu F, Qiao B, Chen Z and Tao Q:
Telomerase reverse transcriptase potentially promotes the
progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma through induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 46:2205–2215. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi MJ, Cho KH, Lee S, Bae YJ, Jeong KJ,
Rha SY, Choi EJ, Park JH, Kim JM, Lee JS, et al: hTERT mediates
norepinephrine-induced Slug expression and ovarian cancer
aggressiveness. Oncogene. 34:3402–3412. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Qin YZ, Xie XC, Liu HZ, Lai H, Qiu H and
Ge LY: Screening and preliminary validation of miRNAs with the
regulation of hTERT in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:2728–2736.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wennerberg E, Sarhan D, Carlsten M,
Kaminskyy VO, D’Arcy P, Zhivotovsky B, Childs R and Lundqvist A:
Doxorubicin sensitizes human tumor cells to NK cell- and
T-cell-mediated killing by augmented TRAIL receptor signaling. Int
J Cancer. 133:1643–1652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kahana S, Finniss S, Cazacu S, Xiang C,
Lee HK, Brodie S, Goldstein RS, Roitman V, Slavin S, Mikkelsen T
and Brodie C: Proteasome inhibitors sensitize glioma cells and
glioma stem cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by
PKCepsilon-dependent downregulation of AKT and XIAP expressions.
Cell Signal. 23:1348–1357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dhandapani L, Yue P, Ramalingam SS, Khuri
FR and Sun SY: Retinoic acid enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
cancer cells by upregulating TRAIL receptor 1 expression. Cancer
Res. 71:5245–5254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA,
Xiong M, Curley SA, Yu Y, Hunt KK and Fang B: Long-term tumor-free
survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed
from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
21:8020–8028. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jacob D, Bahra M, Schumacher G, Neuhaus P
and Fang B: Gene therapy in colon cancer cells with a
fiber-modified adenovector expressing the TRAIL gene driven by the
hTERT promoter. Anticancer Res. 24:3075–3079. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang RG, Zhao JJ, Yang LQ, Yang SM, Wang
RQ, Chen WS, Peng GY and Fang DC: RNA interference-mediated hTERT
inhibition enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in resistant
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 23:1013–1019.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen L, Lü MH, Zhang D, Hao NB, Fan YH, Wu
YY, Wang SM, Xie R, Fang DC, Zhang H, et al: miR-1207 5p and
miR-1266 suppress gastric cancer growth and invasion by targeting
telomerase reverse transcriptase. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10342014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zang G, Miao L, Mu Y, Qiao C, Liu J, Ke X,
Zheng C and Sun H: Adenoviral mediated transduction of adenoid
cystic carcinoma by human TRAIL gene driven with hTERT tumor
specific promoter induces apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:966–972.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wirth T, Kühnel F, Fleischmann-Mundt B,
Woller N, Djojosubroto M, Rudolph KL, Manns M, Zender L and Kubicka
S: Telomerase-dependent virotherapy overcomes resistance of
hepatocellular carcinomas against chemotherapy and tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand by elimination of Mcl-1.
Cancer Res. 65:7393–7402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|