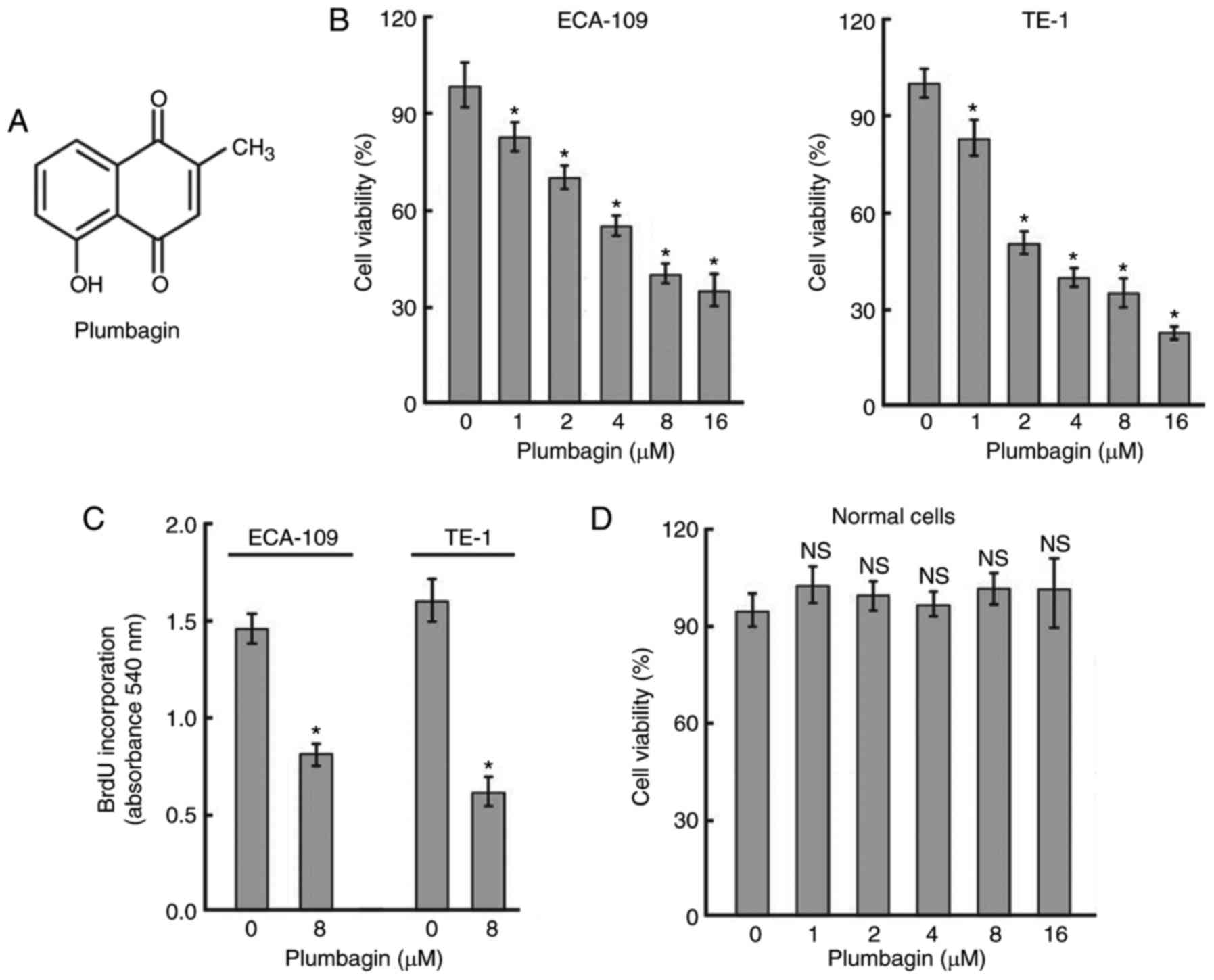
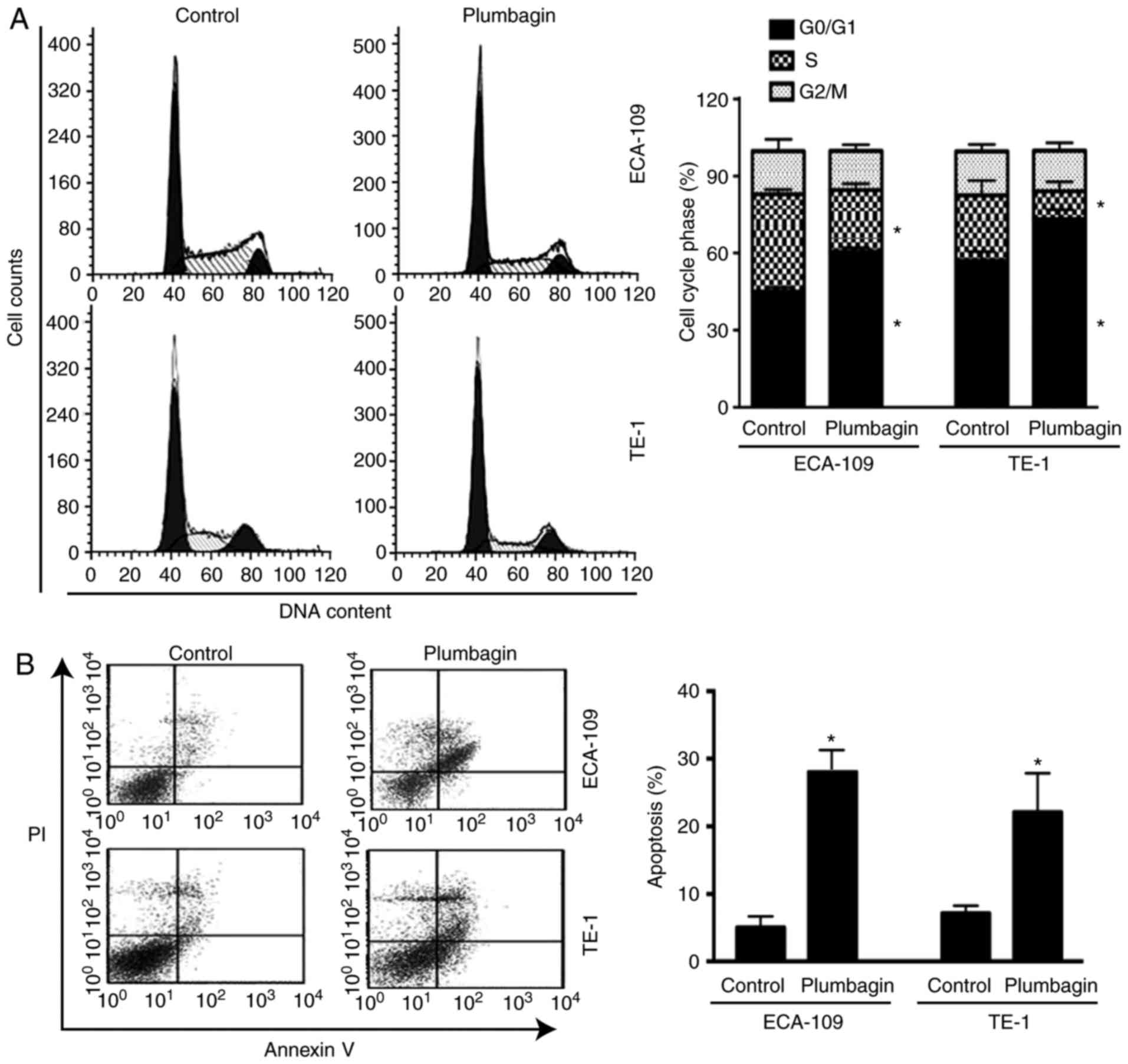
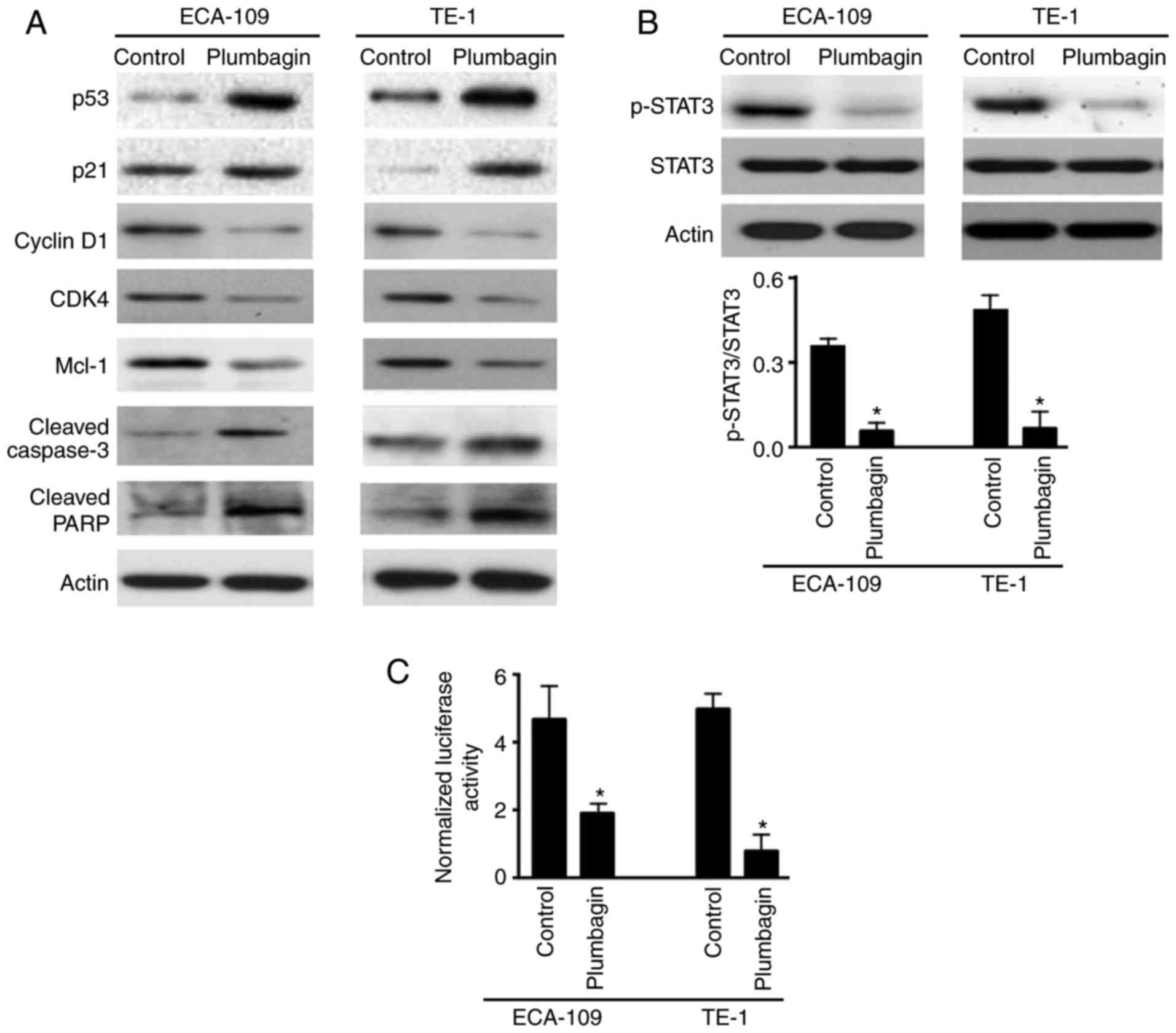
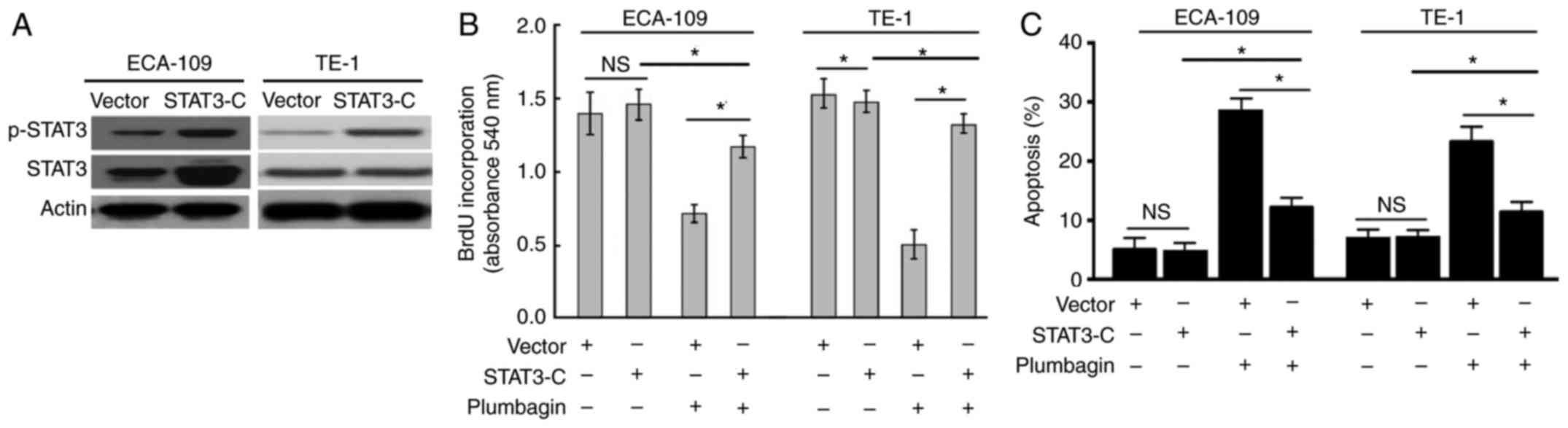
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shridhar R, Hoffe SE, Almhanna K, Weber
JM, Chuong MD, Karl RC and Meredith K: Lymph node harvest in
esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg
Oncol. 20:3038–3043. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jackie Oh S, Han S, Lee W and Lockhart AC:
Emerging immuno therapy for the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 25:667–677. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Omosa LK, Midiwo JO, Mbaveng AT, Tankeo
SB, Seukep JA, Voukeng IK, Dzotam JK, Isemeki J, Derese S, Omolle
RA, et al: Antibacterial activities and structure-activity
relationships of a panel of 48 compounds from Kenyan plants against
multidrug resistant phenotypes. Springerplus. 5:9012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sumsakul W, Chaijaroenkul W and
Na-Bangchang K: In vitro inhibitory effects of plumbagin, the
promising antimalarial candidate, on human cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:914–918. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pile JE, Navalta JW, Davis CD and Sharma
NC: Interventional effects of plumbagin on experimental ulcerative
colitis in mice. J Nat Prod. 76:1001–1006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan W, Tu B, Liu YY, Wang TY, Qiao H, Zhai
ZJ, Li HW and Tang TT: Suppressive effects of plumbagin on invasion
and migration of breast cancer cells via the inhibition of STAT3
signaling and down-regulation of inflammatory cytokine expressions.
Bone Res. 1:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hafeez BB, Jamal MS, Fischer JW, Mustafa A
and Verma AK: Plumbagin, a plant derived natural agent inhibits the
growth of pancreatic cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo via
targeting EGFR, Stat3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Cancer.
131:2175–2186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Du XL, Wang CJ, Lin DC, Ruan X,
Feng YB, Huo YQ, Peng H, Cui JL, Zhang TT, et al: Reciprocal
activation between PLK1 and Stat3 contributes to survival and
proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
142:521–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Timme S, Ihde S, Fichter CD, Waehle V,
Bogatyreva L, Atanasov K, Kohler I, Schöpflin A, Geddert H, Faller
G, et al: STAT3 expression, activity and functional consequences of
STAT3 inhibition in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and
Barrett's adenocarcinomas. Oncogene. 33:3256–3266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Niu M, Cai W, Liu H, Chong Y, Hu W, Gao S,
Shi Q, Zhou X, Liu X and Yu R: Plumbagin inhibits growth of gliomas
in vivo via suppression of FOXM1 expression. J Pharmacol Sci.
128:131–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Radestock Y, Hoang-Vu C and
Hombach-Klonisch S: Relaxin reduces xenograft tumour growth of
human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res.
10:R712008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sinha S, Pal K, Elkhanany A, Dutta S, Cao
Y, Mondal G, Iyer S, Somasundaram V, Couch FJ, Shridhar V, et al:
Plumbagin inhibits tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer
cells in vivo. Int J Cancer. 132:1201–1212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Dai LH, Dou DQ, Ma LQ and Sun YX: A
natural food sweetener with anti-pancreatic cancer properties.
Oncogenesis. 5:e2172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hafeez BB, Fischer JW, Singh A, Zhong W,
Mustafa A, Meske L, Sheikhani MO and Verma AK: Plumbagin inhibits
prostate carcinogenesis in intact and castrated PTEN knockout mice
via targeting PKCε, Stat3, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
markers. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 8:375–386. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Joo MK, Park JJ, Kim SH, Yoo HS, Lee BJ,
Chun HJ, Lee SW and Bak YT: Antitumorigenic effect of plumbagin by
induction of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 in human
gastric cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:2380–2388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gowda R, Sharma A and Robertson GP:
Synergistic inhibitory effects of Celecoxib and Plumbagin on
melanoma tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 385:243–250. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Coqueret O: New roles for p21 and p27
cell-cycle inhibitors: A function for each cell compartment? Trends
Cell Biol. 13:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vousden KH and Lu X: Live or let die: The
cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:594–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morciano G, Pedriali G, Sbano L, Iannitti
T, Giorgi C and Pinton P: Intersection of mitochondrial fission and
fusion machinery with apoptotic pathways: Role of Mcl-1. Biol Cell.
108:279–293. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang XQ, Yang CY, Rao XF and Xiong JP:
Plumbagin shows anti-cancer activity in human breast cancer cells
by the up regulation of p53 and p21 and suppression of G1 cell
cycle regulators. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 37:30–35. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Eldhose B, Gunawan M, Rahman M, Latha MS
and Notario V: Plumbagin reduces human colon cancer cell survival
by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Int J Oncol. 45:1913–1920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hsu YL, Cho CY, Kuo PL, Huang YT and Lin
CC: Plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 cells through p53
accumulation via c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated phosphorylation
at serine 15 in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
318:484–494. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hafeez BB, Zhong W, Fischer JW, Mustafa A,
Shi X, Meske L, Hong H, Cai W, Havighurst T, Kim K and Verma AK:
Plumbagin, a medicinal plant (Plumbago zeylanica)-derived
1,4-naphthoquinone, inhibits growth and metastasis of human
prostate cancer PC-3M-luciferase cells in an orthotopic xenograft
mouse model. Mol Oncol. 7:428–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leslie K, Lang C, Devgan G, Azare J,
Berishaj M, Gerald W, Kim YB, Paz K, Darnell JE, Albanese C, et al:
Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for
transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3. Cancer Res. 66:2544–2552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhattacharya S, Ray RM and Johnson LR:
STAT3-mediated transcription of Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and c-IAP2 prevents
apoptosis in polyamine-depleted cells. Biochem J. 392:335–344.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|