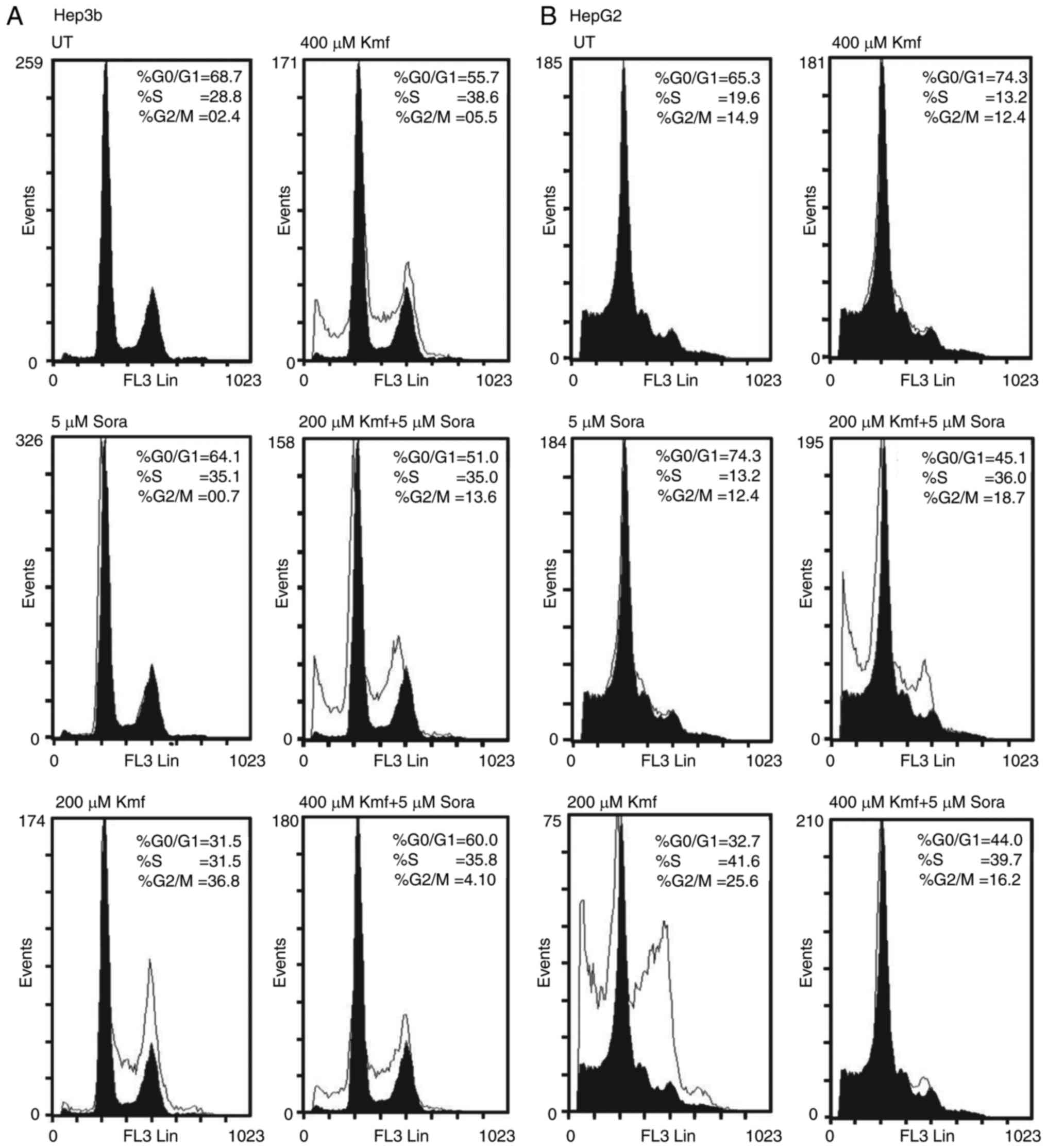
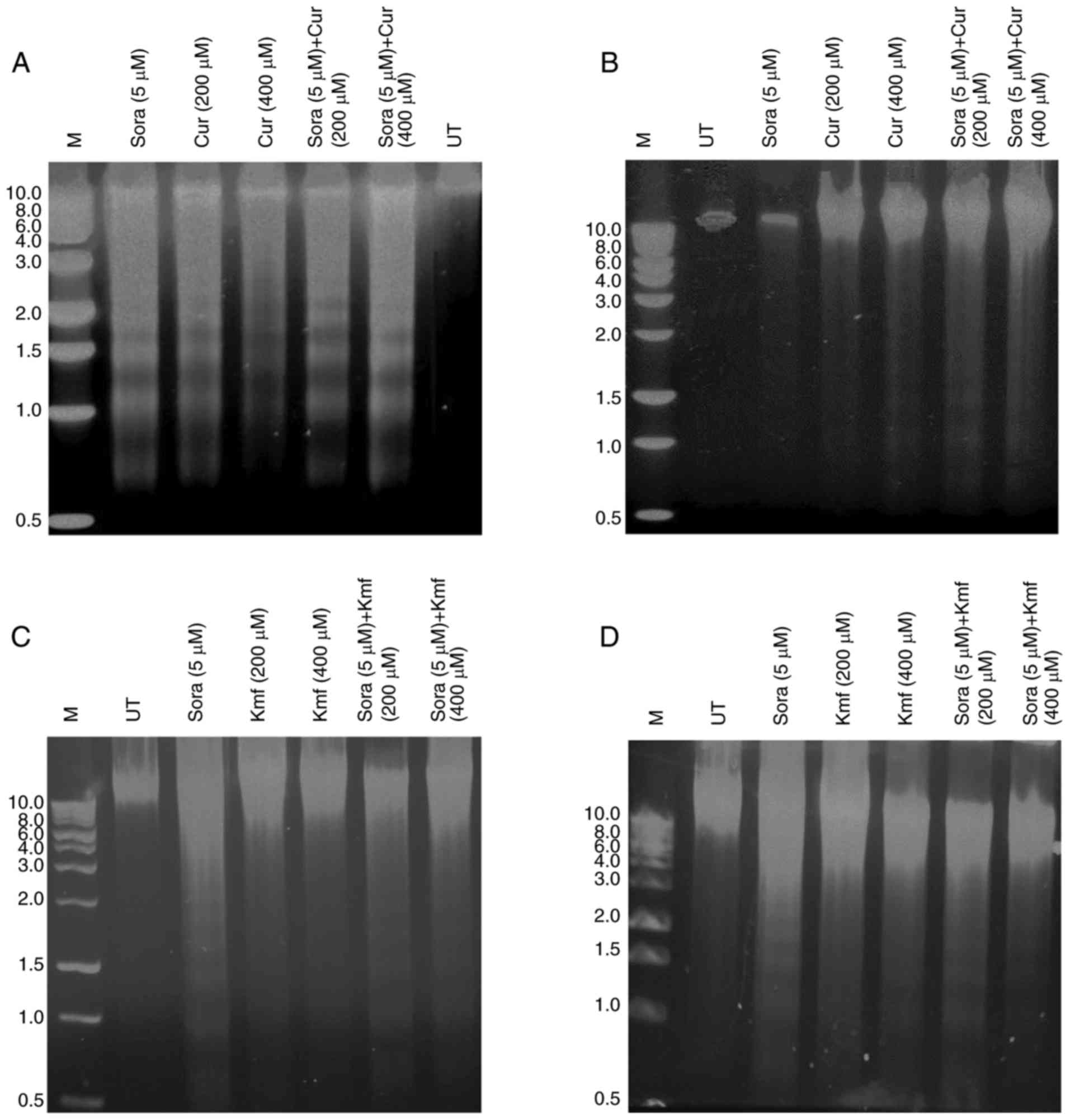
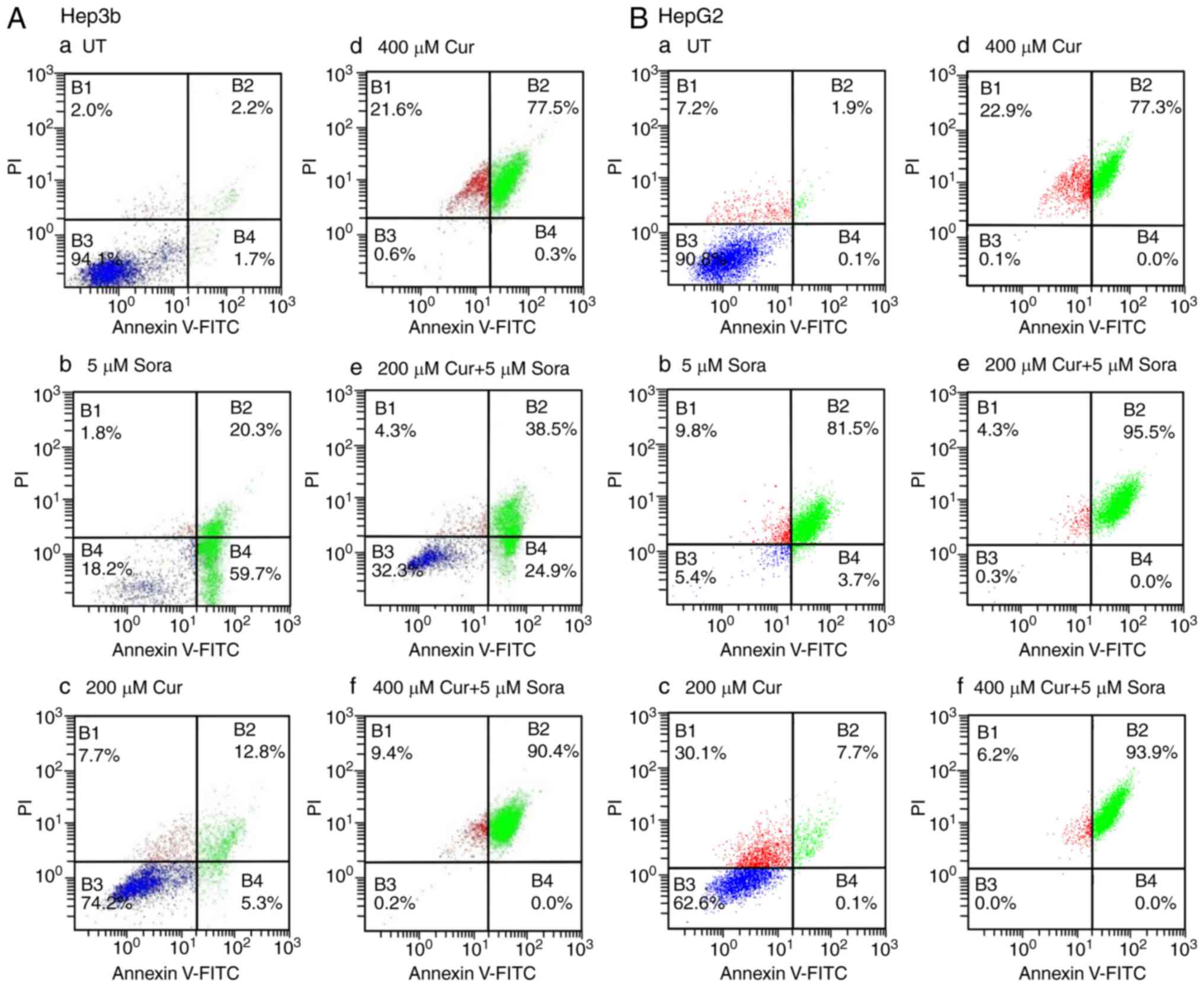
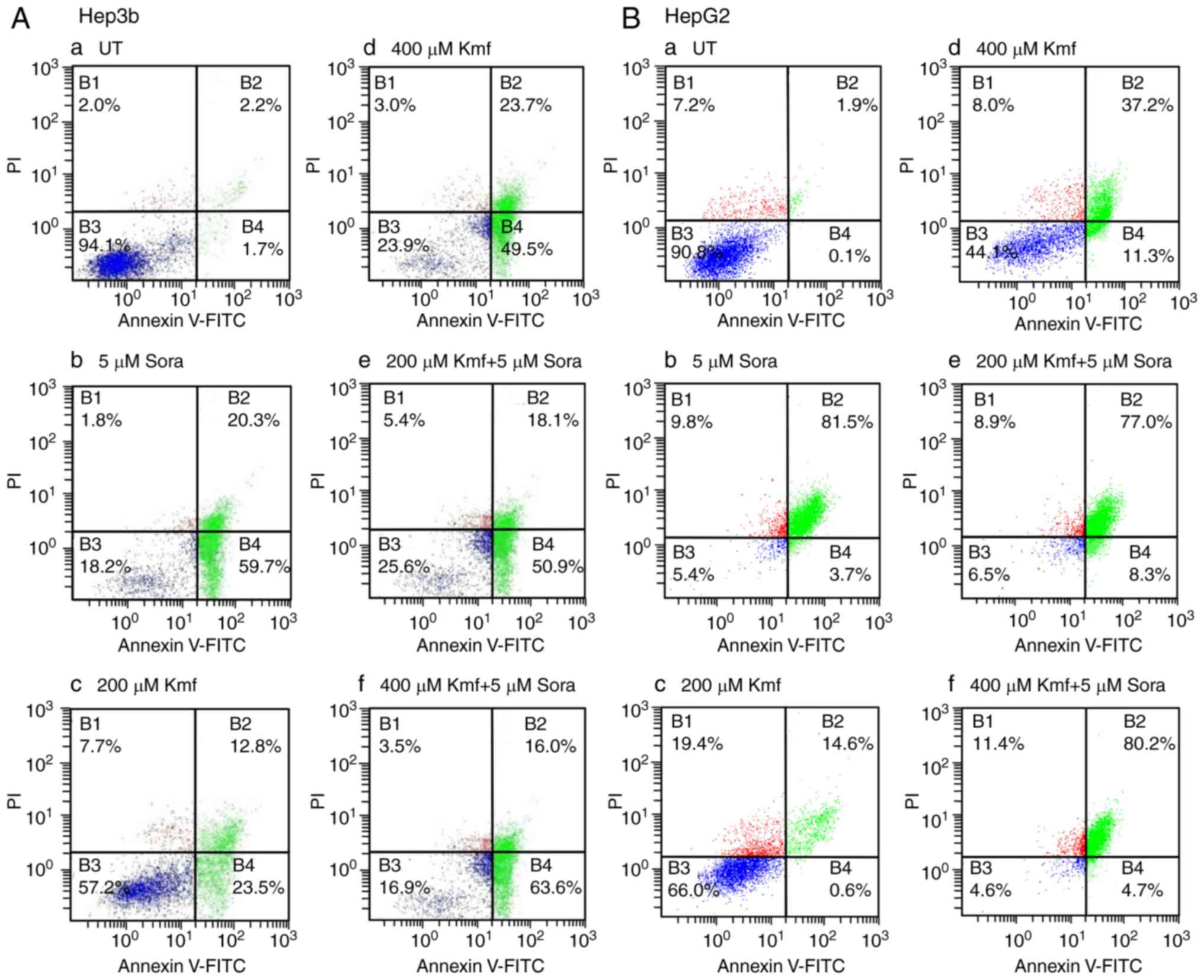
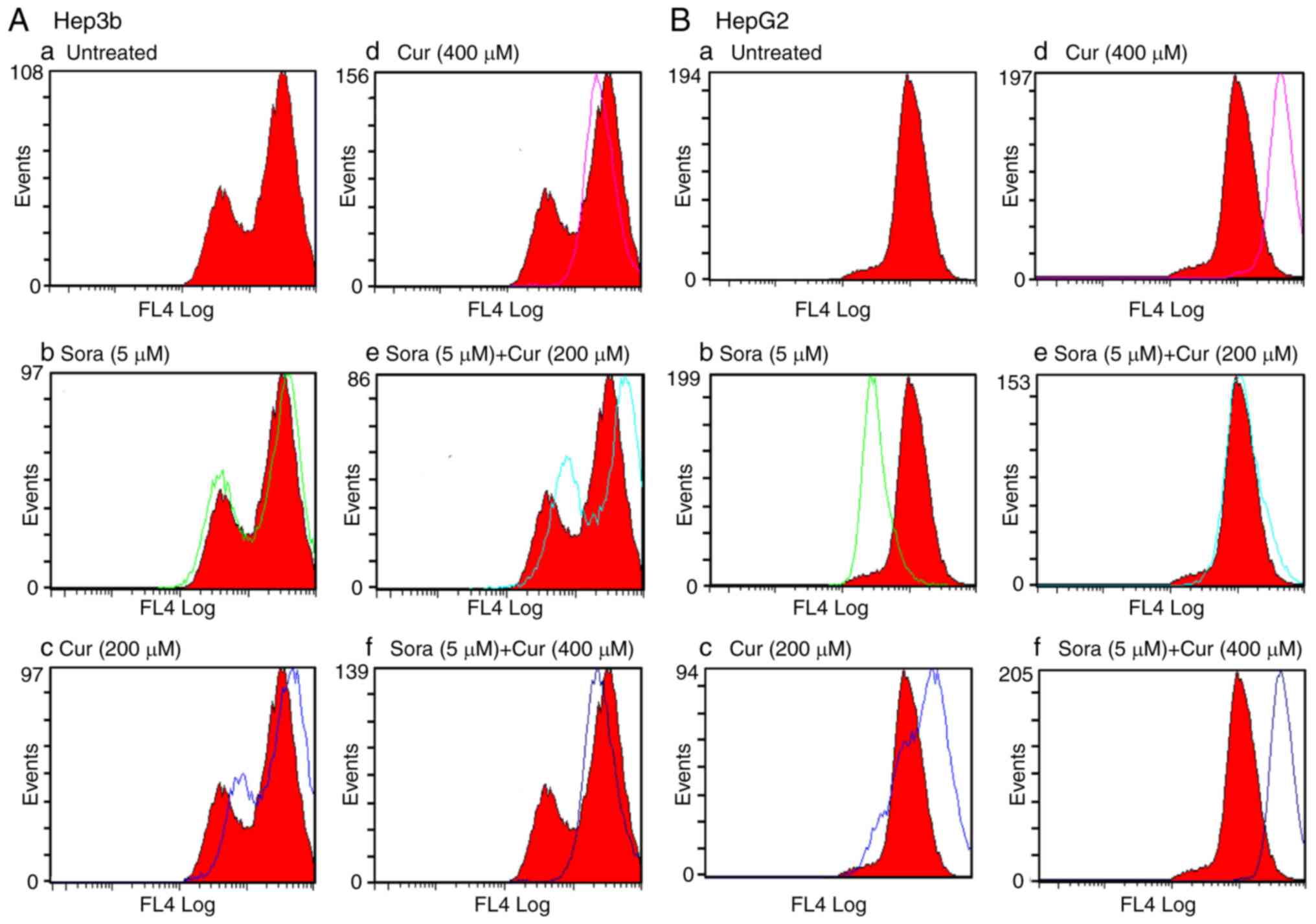
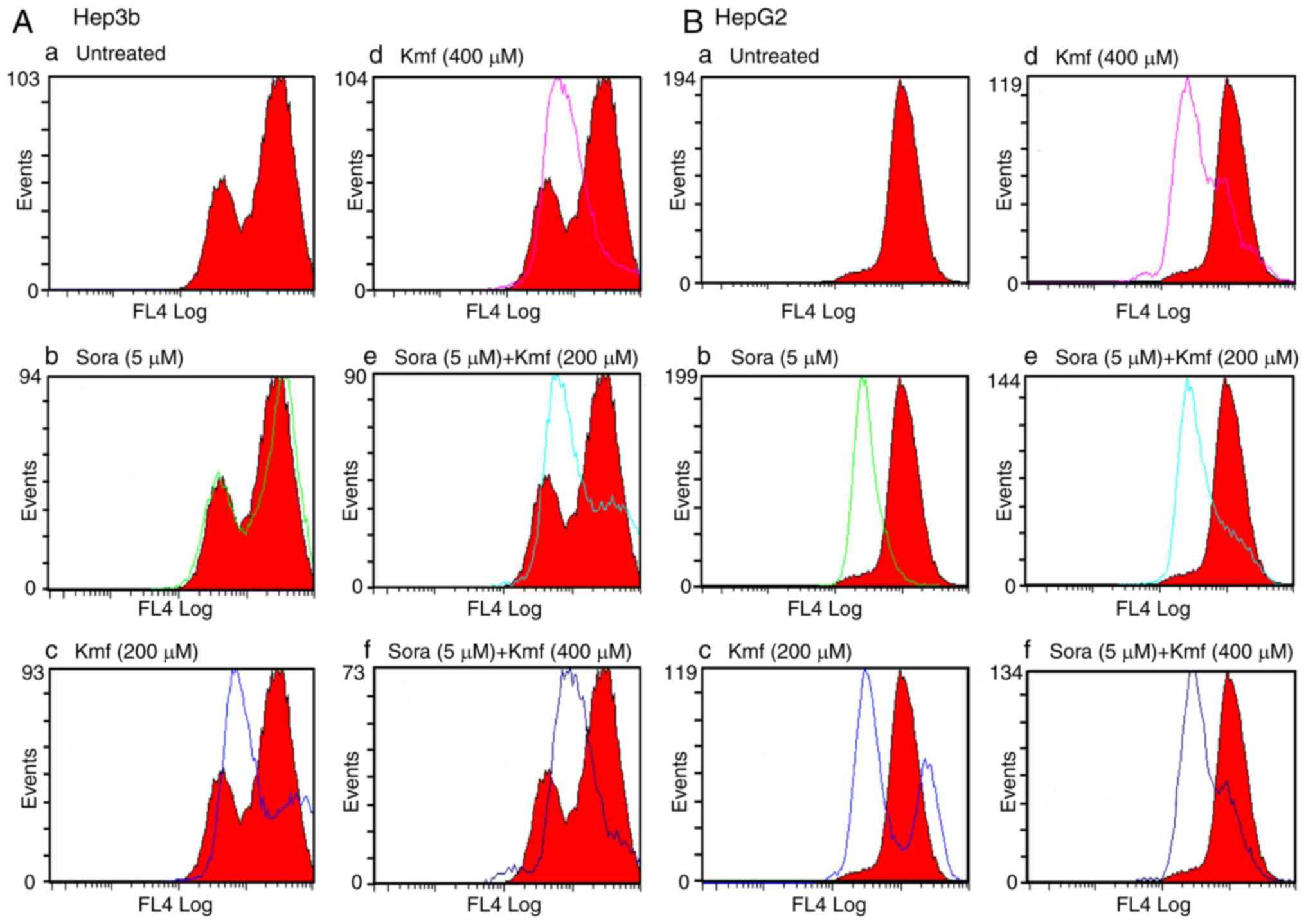
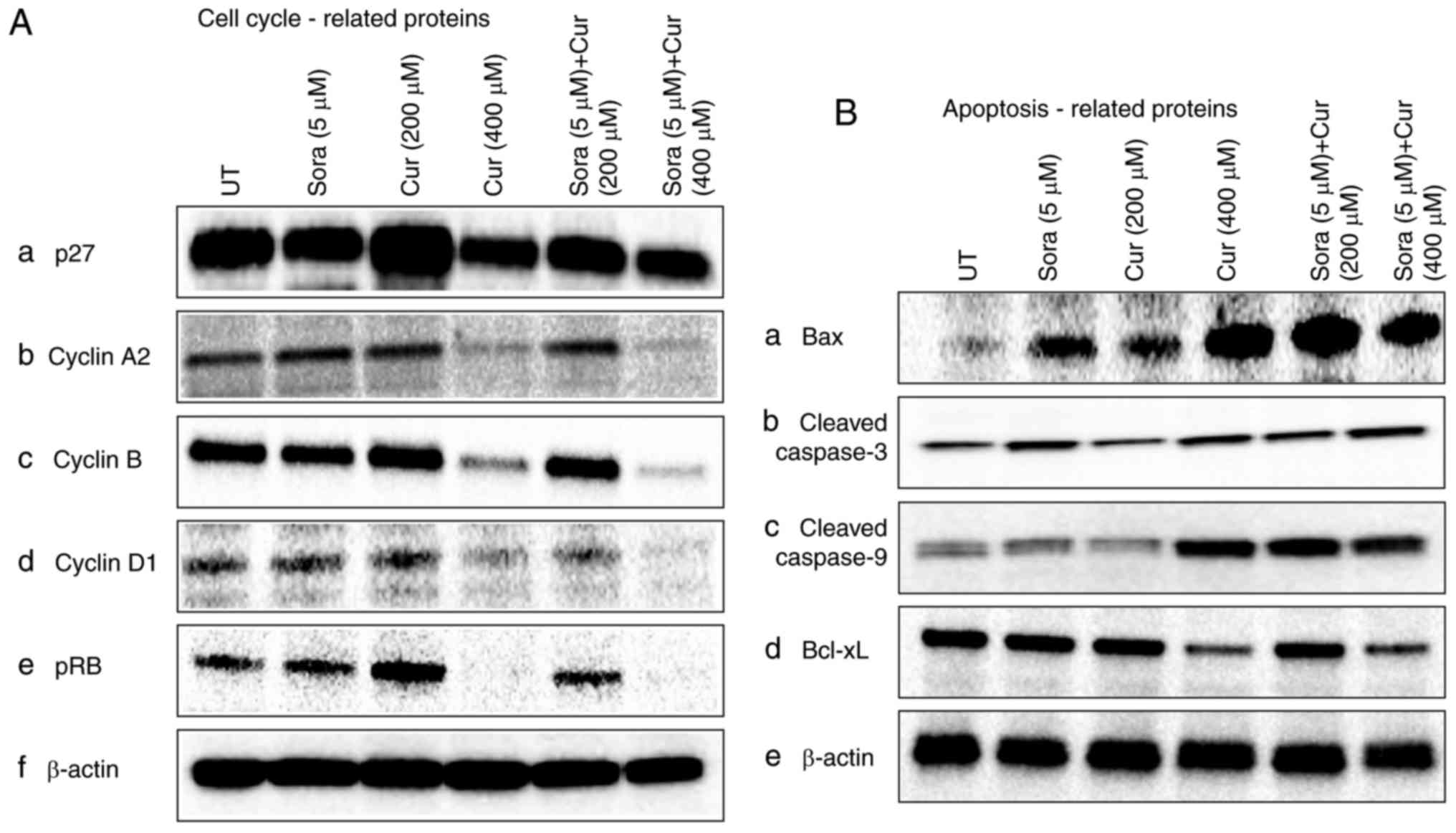
|
1
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Environmental factors
and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
127:S72–S78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127:S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
LIovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
LIovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wilhelim SM, Adnane L, Newell P,
Villanueva A, LIovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of
sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF
and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3129–3140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Furuse J: Sorafenib for the treatment of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Biologics. 2:779–788.
2008.
|
|
7
|
Hartmann JT, Haap M, Kopp HG and Lipp HP:
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors-a review on pharmacology, metabolism and
side effects. Curr Drug Metab. 10:470–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shen YC, Ou DL, Hsu C, Lin KL, Chang CY,
Lin C, Liu SH and Cheng AL: Activating oxidative phosphorylation by
a pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor overcomes sorafenib
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:72–81.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Pezzuto JM: Plant-derived anticancer
agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 53:121–133. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Holbeck S and
Sausville EA: Natural products and derivatives as leads to cell
cycle pathway targets in cancer chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 2:279–308. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sak K: Chemotherapy and dietary
phytochemical agents. Chemother Res Pract. 2012:2825702012.
|
|
12
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase
activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt
and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr.
136:2715–2721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qiu GH, Xie X, Xu F, Shi X, Wang Y and
Deng L: Distinctive pharmacological differences between liver
cancer cell lines HepG2 and Hep3B. Cytotechnology. 67:1–12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: HepG2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Abaza MS, Al-Saffar A, Al-Sawan S and
Al-Attiyah R: c-myc antisense oligonucleotides sensitize human
colorectal cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Tumor Biol.
29:287–303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chan W, Wu C and Yu J: Curcumin inhibits
UV irradiation-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic biochemical
changes in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biochem.
90:327–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee J, Park S, Kim S, Um S and Moon E:
Curcumin hampers the antitumor effect of vinblastine via the
inhibition of microtubule dynamics and mitochondrial membrane
potential in Hela cervical cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 23:705–713.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ruby AJ, Kuttan G, Babu KD, Rajasekharan
KN and Kuttan R: Antitumor and antioxidant activity of natural
curcuminoids. Cancer Lett. 94:79–83. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Strumberg D: Preclinical and clinical
development of the oral multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in cancer
treatment. Drugs Today (Barc). 41:773–784. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shen C, Qiu Z and Luo Q: Sorafenib in the
treatment of radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer:
A meta-analysis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:253–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wilhelm S and Chien DS: Bay 43-9006:
Preclinical data. Curr Pharm Des. 8:2255–2257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
Bay 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK/pathway and receptor kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Panka DJ, Wang W, Atkins MB and Mier JW:
The Raf inhibitor Bay 43-9006 (Sorafenib) induces
caspase-independent apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cancer Res.
66:1611–1619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T,
Dumas J, Smith RA, Schwartz B, Simantov R and Kelley S: Discovery
and development of sorafenib: A multikinase inhibitor for treating
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:835–844. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jakubowicz-Gil J, Langner E and Rzeski W:
Kinetic studies of the effects of Temodal and quercetin on
astrocytoma cells. Pharmacol Rep. 63:403–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jakubowicz-Gil J, Langner E, Bądziul D,
Wertel I and Rzeski W: Apoptosis induction in human glioblastoma
multiform T98G cells upon temozolomide and quercetin treatment.
Tumour Biol. 34:2367–2378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Zhou J, Fan J, Qiu SJ, Yu Y, Huang
XW and Tang ZY: Effect of rapamycin alone and in combination with
sorafenib in an orthotopic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:5124–5130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clark JW, Eder JP, Ryan D, Lathia C and
Lenz HJ: Safety and pharmacokinetics of the dual action Raf kinase
and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor, BAY
43-9006, in patients with advanced, refractory solid tumors. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:5472–5480. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pal HC, Baxter RD, Hunt KM, Agarwal J,
Elmets CA, Athar M and Afaq F: Fisetin, a phytochemical,
potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis and abrogates tumor growth
in athymic nude mice implanted with BRAF-mutated melanoma cells.
Oncotarget. 6:28296–28311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rausch V, Liu L, Kallifatidis G, Baumann
B, Mattern J, Gladkich J, Wirth T, Schemmer P, Büchler MW, Zöller
M, et al: Synergistic activity of sorafenib and sulforaphane
abolishes pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics. Cancer Res.
70:5004–5013. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jakubowicz-Gil J, Langner E, Bądziul D,
Wertel I and Rzeski W: Quercetin and sorafenib as a novel and
effective couple in programmed cell death induction in human
gliomas. Neurotox Res. 26:64–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Hu B, Sun D, Sun C, Sun YF, Sun HX, Zhu
QF, Yang XR, Gao YB, Tang WG, Fan J, et al: A polymeric
nanoparticle formulation of curcumin in combination with sorafenib
synergistically inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in an
orthotopic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 468:525–532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao H, Wang Y, He X, Zhang Z, Yin Q, Chen
Y, Yu H, Huang Y, Chen L, Xu M, et al: Codelivery of sorafenib and
curcumin by directed self-assembled nanoparticles enhances
therapeutic effect on hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Pharm.
12:922–931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kong J, Kong F, Gao J, Zhang Q, Dong S, Gu
F, Ke S, Pan B, Shen Q, Sun H, et al: YC-1 enhances the anti-tumor
activity of sorafenib through inhibition of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mol Cancer. 13:7–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wild AT, Gandhi N, Chettiar ST, Aziz K,
Gajula RP, Williams RD, Kumar R, Taparra K, Zeng J, Cades JA, et
al: Concurrent versus sequential sorafenib therapy in combination
with radiation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e657262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen G, Nicula D, Renko K and Derwahl M:
Synergistic anti-proliferative effect of metformin and sorafenib on
growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells and their stem cells.
Oncol Rep. 33:1994–2000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ling S, Feng T, Ke Q, Fan N, Li L, Li Z,
Dong C, Wang C, Xu F, Li Y and Wang L: Metformin inhibits
proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Oncol Rep. 31:2611–2618. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brooks G and La Thangue NB: The cell cycle
and drug discovery: The promise and the hope. Drug Discov Today.
4:455–464. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chiruvella KK and Raghavan SC: A natural
compound, methyl angolensate, induces mitochondrial pathway of
apoptosis in Daudi cells. Invest New Drugs. 29:583–592. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, Chen R, Liu X, Li
Y, Lee NP, Lee WH, Ariyaratne PN, Tennakoon C, et al: Genome-wide
survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Nat Genet. 44:765–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Taylor WR and Stark GR: Regulation of the
G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene. 20:1803–1815. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li J, Cheung HY, Zhang Z, Chan GK and Fong
W: Andrographolide induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and cell
death in HepG2 cells via alteration of reactive oxygen species. Eur
J Pharmacol. 568:31–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hadfield JA, Ducki S, Hirst N and McGown
AT: Tubulin and microtubules as targets for anticancer drugs. Prog
Cell Cycle Res. 5:309–325. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kasibhatla S and Tseng B: Why target
apoptosis in cancer treatment. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:573–580.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Locatelli SL, Giacomini A, Guidetti A,
Cleris L, Mortarini R, Anichini A, Gianni AM and Carlo-Stella C:
Perifosine and sorafenib combination induces mitochondrial cell
death and antitumor effects in NOD/SCID mice with Hodgkin lymphoma
cell line xenografts. Leukemia. 27:1677–1687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dai W, Wang F, Lu J, Xia Y, He L, Chen K,
Li J, Li S, Liu T, Zheng Y, et al: By reducing hexokinase 2,
resveratrol induces apoptosis in HCC cells addicted to aerobic
glycolysis and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Oncotarget.
6:13703–13717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yuen JS, Sim MY, Sim HG, Chong TW, Lau WK,
Cheng CW and Huynh H: Inhibition of angiogenic and non-angiogenic
targets by sorafenib in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in a RCC
xenograft model. Br J Cancer. 104:941–947. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tomizawa M, Shinozaki F, Sugiyama T,
Yamamoto S, Sueishi M and Yoshida T: Sorafenib suppresses the cell
cycle and induces the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell
lines in serum-free media. Exp Ther Med. 1:863–866. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim YB, Jeung HC, Jeong I, Lee K, Rha SY,
Chung HC and Kim GE: Mechanism of enhancement of radiation-induced
cytotoxicity by sorafenib in colorectal cancer. J Radiat Res.
54:52–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: How do BCL-2
proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
Trends Cell Biol. 18:157–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao X, Tian C, Puszyk WM, Ogunwobi OO,
Cao M, Wang T, Cabrera R, Nelson DR and Liu C: OPA1 downregulation
is involved in sorafenib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Lab Invest. 93:8–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ramirez-Labrada A, López-Royuela N,
Jarauta V, Galán-Malo P, Azaceta G, Palomera L, Pardo J, Anel A,
Marzo I and Naval J: Two death pathways induced by sorafenib in
myeloma cells: Puma-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis. Clin Trans
Oncol. 17:121–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cervello M, Bachvarov D, Lampiasi N,
Cusimano A, Azzolina A, McCubrey JA and Montalto G: Molecular
mechanisms of sorafenib action in liver cancer cells. Cell Cycle.
11:2843–2855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|