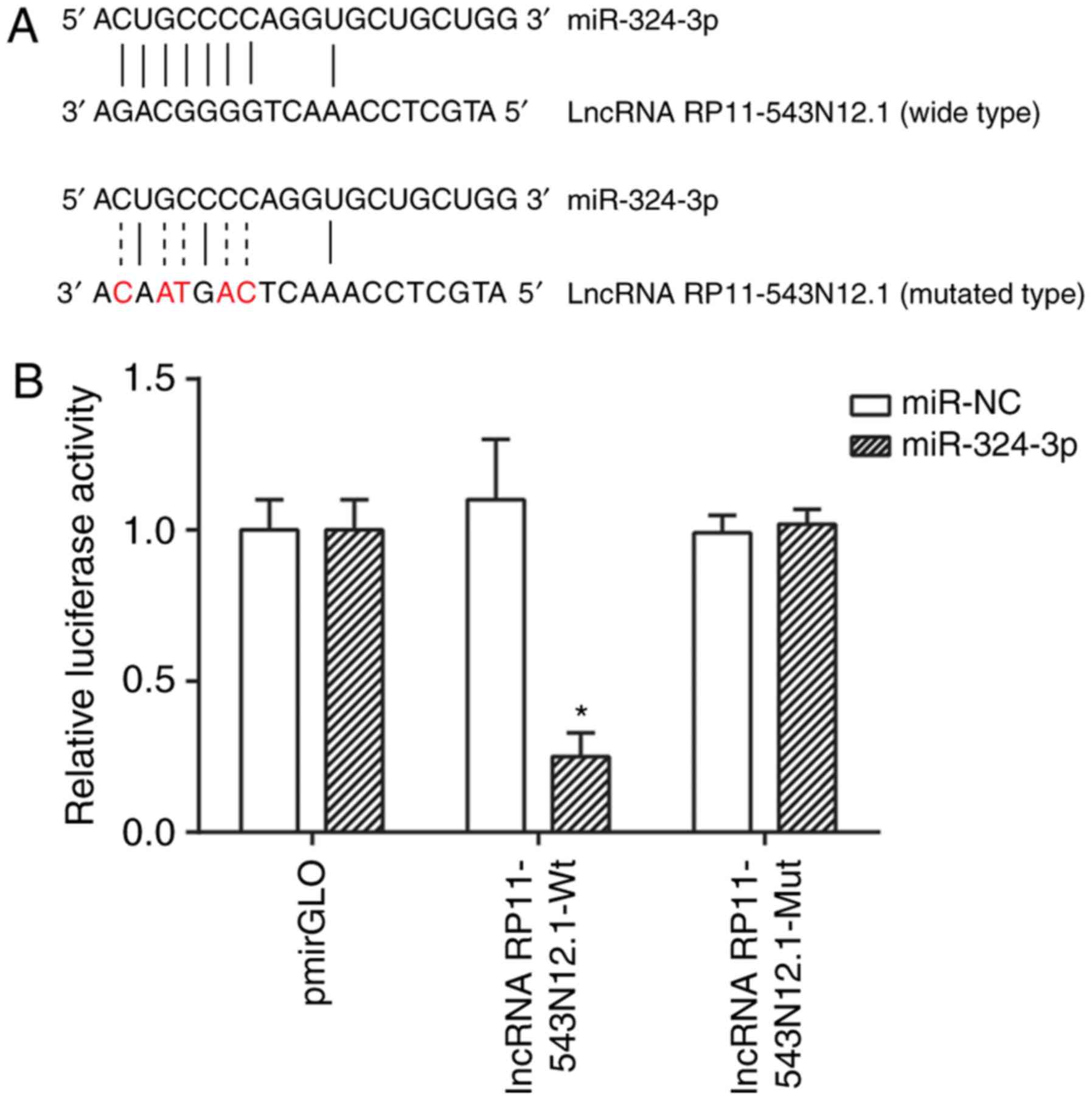
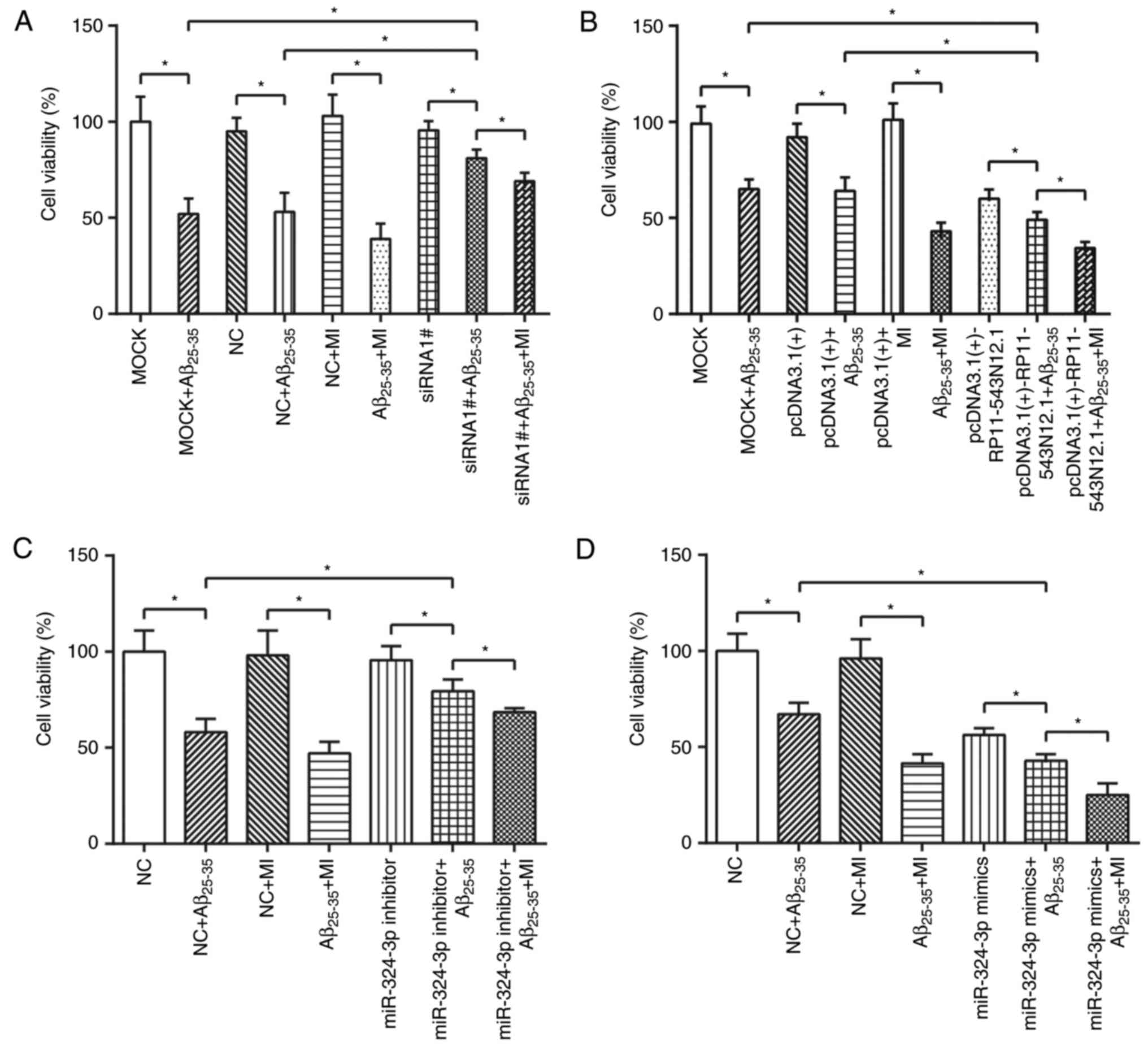
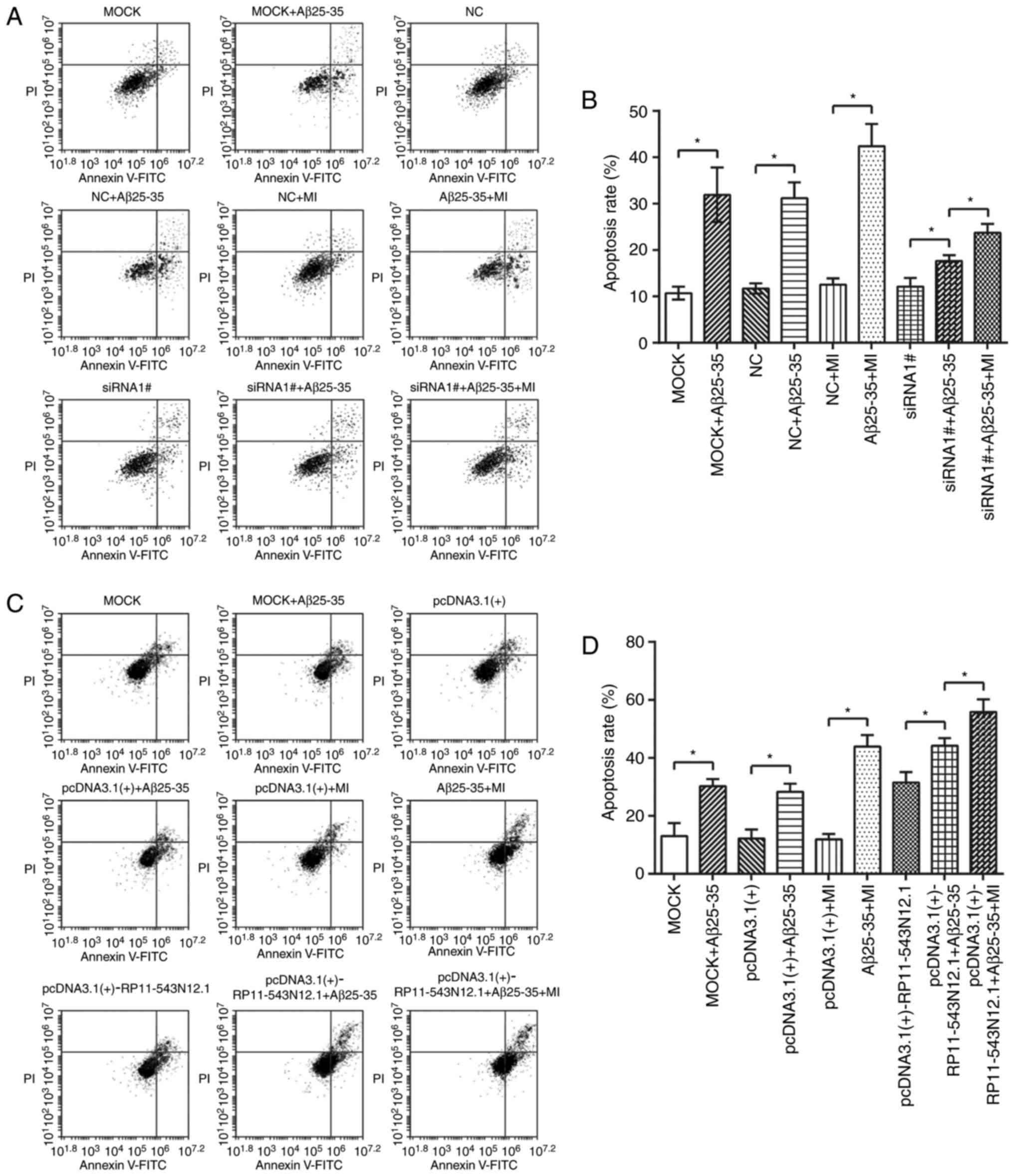
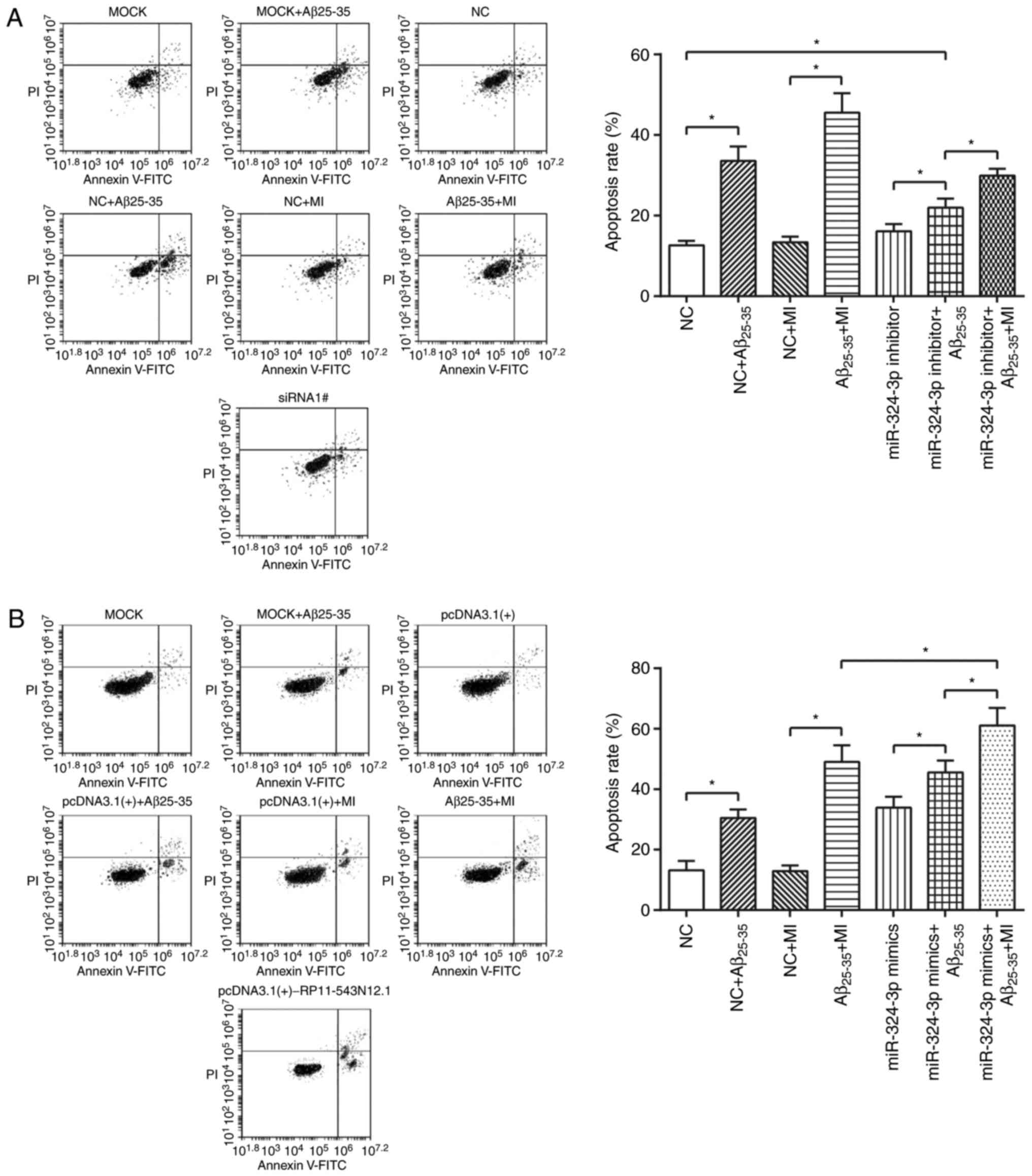
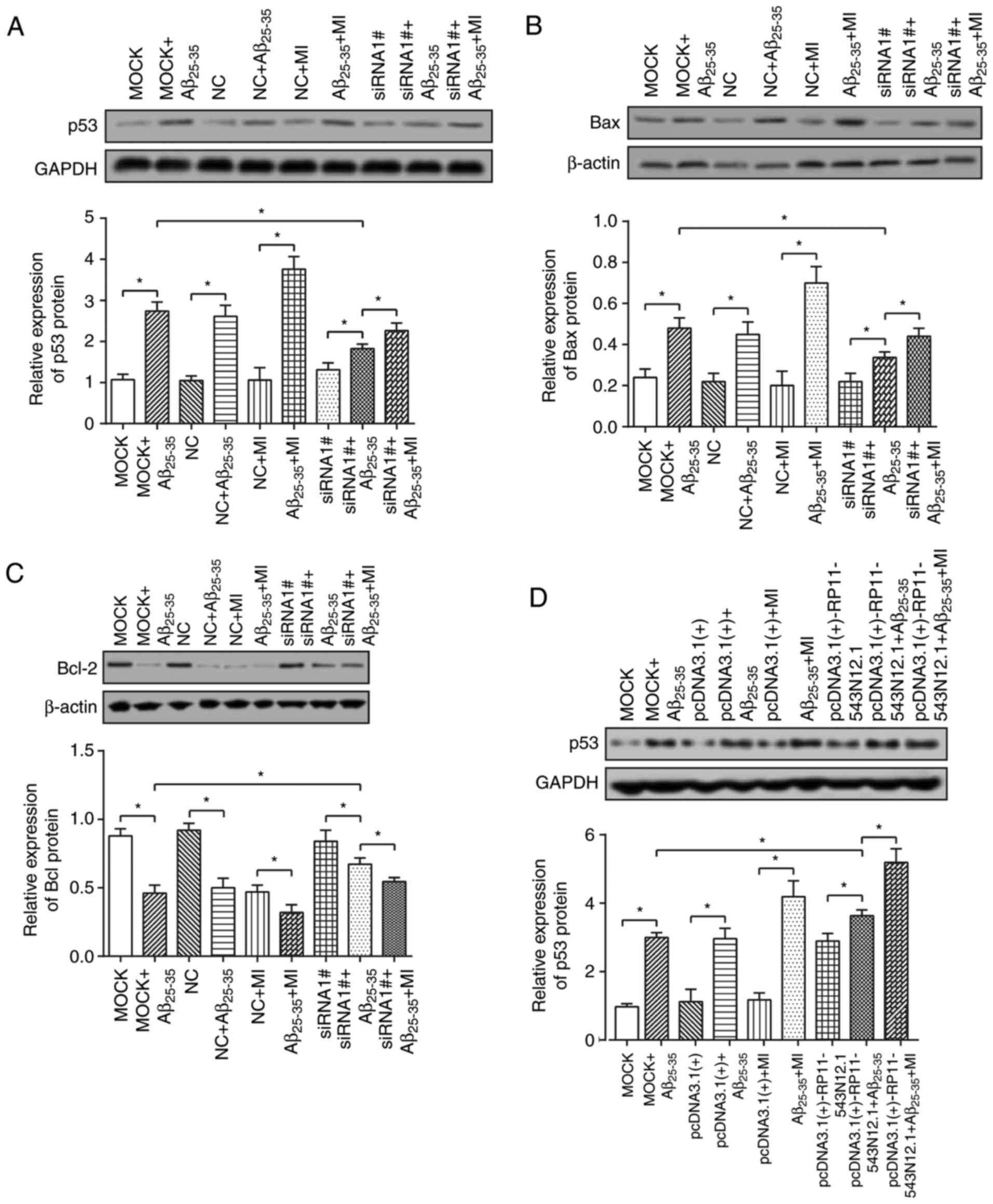
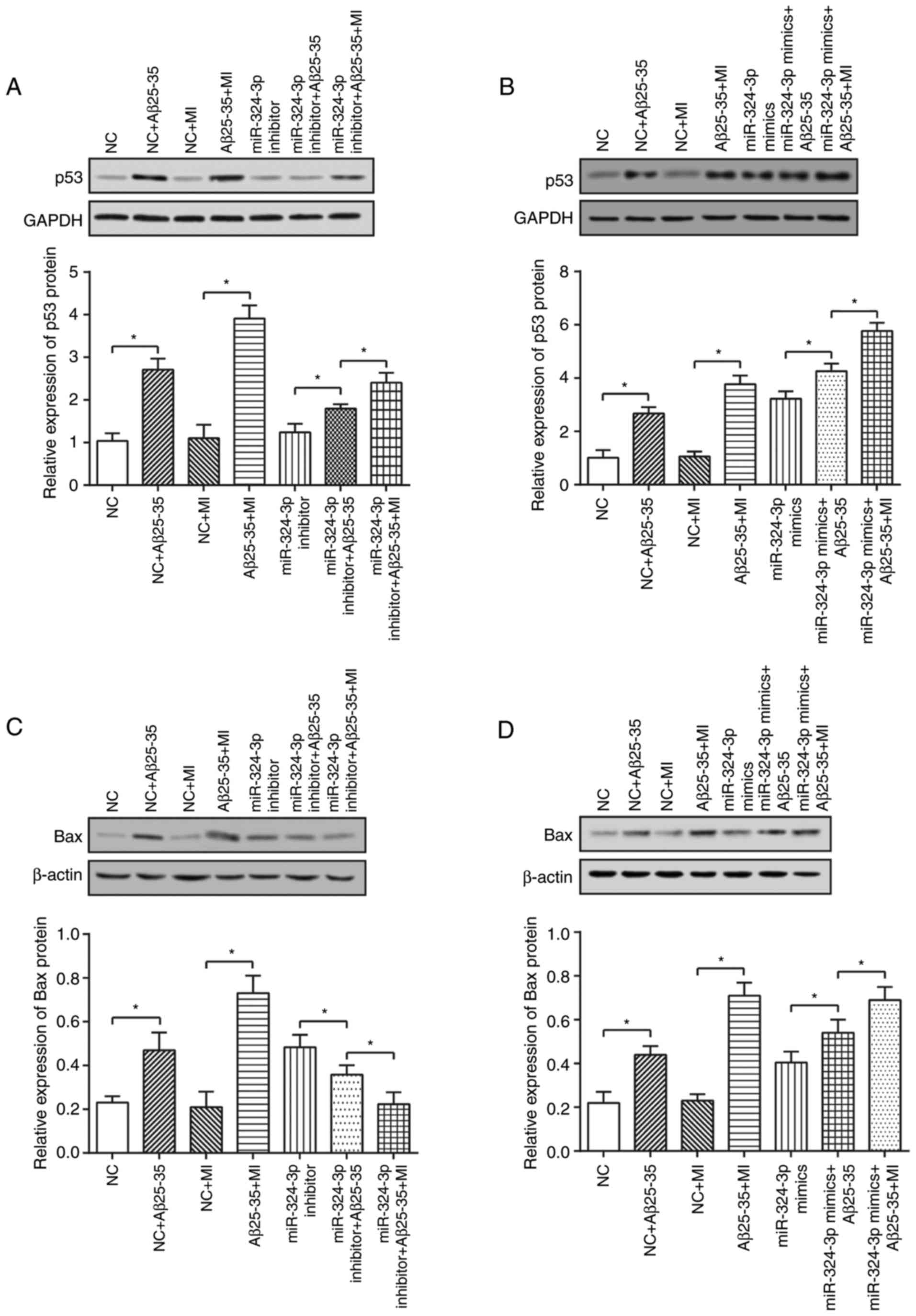
|
1
|
D'Amore JD, Kajdasz ST, McLellan ME,
Bacskai BJ, Stern EA and Hyman BT: In vivo multiphoton imaging of a
transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease reveals marked
thioflavine-S-associated alterations in neurite trajectories. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 62:137–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM,
Iwata N, Saido TC, Maeda J, Suhara T, Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM:
Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S
tauopathy mouse model. Neuron. 53:337–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lemere CA, Maier M, Jiang L, Peng Y and
Seabrook TJ: Amyloid-beta immunotherapy for the prevention and
treatment of Alzheimer disease: Lessons from mice, monkeys, and
humans. Rejuvenation Res. 9:77–84. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galimberti D and Scarpini E: Progress in
Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol. 259:201–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alzheimer's Association: 2010 Alzheimer's
disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 6:158–194. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Millan MJ: Linking deregulation of
non-coding RNA to the core pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease:
An integrative review. Prog Neurobiol. 156:1–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qi X, Shao M, Sun H, Shen Y, Meng D and
Huo W: Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 promotes microglia activation by
regulating miR-145-5p/PLA2G4A in cerebral infarction. Neuroscience.
348:98–106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin ST, Heng MY, Ptáček LJ and Fu YH:
Regulation of myelination in the central nervous system by nuclear
lamin B1 and non-coding RNAs. Transl Neurodegener. 3:42014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Hou L, Huang W, Gao Y, Lv X and
Tang J: The mechanism of long non-coding RNA MEG3 for neurons
apoptosis caused by hypoxia: Mediated by miR-181b-12/15-LOX
signaling pathway. Front Cell Neuroscie. 10:2012016.
|
|
10
|
Ko CY, Chu YY, Narumiya S, Chi JY,
Furuyashiki T, Aoki T, Wang SM, Chang WC and Wang JM:
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta/miR135a/thrombospondin 1 axis
mediates PGE2-induced angiogenesis in Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 36:1356–1368. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Bhattacharjee S, Jones BM, Dua P,
Alexandrov PN, Hill JM and Lukiw WJ: Regulation of TREM2 expression
by an NF-κB-sensitive miRNA-34a. Neuroreport. 24:318–323. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jayadev S, Case A, Alajajian B, Eastman
AJ, Möller T and Garden GA: Presenilin 2 influences miR146 level
and activity in microglia. J Neurochem. 127:592–599. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dharap A, Pokrzywa C, Murali S, Pandi G
and Vemuganti R: MicroRNA miR-324-3p induces promoter-mediated
expression of RelA gene. PLoS One. 8:e794672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gutierrez H, O'Keeffe GW, Gavaldà N,
Gallagher D and Davies AM: Nuclear factor kappa B signaling either
stimulates or inhibits neurite growth depending on the
phosphorylation status of p65/RelA. J Neurosci. 28:8246–8256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng Y, Gallagher SF, Landmann R, Haines K
and Murr MM: The role of p65 NF-kappaB/RelA in pancreatitis-induced
Kupffer cell apoptosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 10:837–847. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sheehy AM and Schlissel MS: Overexpression
of RelA causes G1 arrest and apoptosis in a pro-B cell line. J Biol
Chem. 274:8708–8716. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz
A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere
CA, et al: Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from
Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med.
14:837–842. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGeer EG and McGeer PL: Inflammatory
processes in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 27:741–749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dobrenis K: Microglia in cell culture and
in transplantation therapy for central nervous system disease.
Methods. 16:320–344. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tan AM, Zhao P, Waxman SG and Hains BC:
Early microglial inhibition preemptively mitigates chronic pain
development after experimental spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res
Dev. 46:123–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roth R, Madhani HD and Garcia JF: Total
RNA isolation and quantification of specific RNAs in fission yeast.
Methods Mol Biol. 1721:63–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu P, Zuo X, Deng H, Liu X, Liu L and Ji
A: Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional
diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull.
97:69–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang LK, Chen XF, He DD, Li Y and Fu J:
Dissection of functional lncRNAs in Alzheimer's disease by
construction and analysis of lncRNA-mRNA networks based on
competitive endogenous RNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
485:569–576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ciarlo E, Massone S, Penna I, Nizzari M,
Gigoni A, Dieci G, Russo C, Florio T, Cancedda R and Pagano A: An
intronic ncRNA-dependent regulation of SORL1 expression affecting
Aβ formation is upregulated in post-mortem Alzheimer's disease
brain samples. Dis Model Mech. 6:424–433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mus E, Hof PR and Tiedge H: Dendritic
BC200 RNA in aging and in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:10679–10684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou X and Xu J: Identification of
Alzheimer's disease-associated long noncoding RNAs. Neurobiol
Aging. 36:2925–2931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan B and Wang Z: Long noncoding RNA: Its
physiological and pathological roles. DNA Cell Biol. 31(Suppl 1):
S34–S41. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu J, Ai Q, Cao H and Liu Q: MiR-185-3p
and miR-324-3p predict radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and modulate cancer cell growth and apoptosis by targeting SMAD7.
Med Sci Monit. 21:2828–2836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuo WT, Yu SY, Li SC, Lam HC, Chang HT,
Chen WS, Yeh CY, Hung SF, Liu TC, Wu T, et al: MicroRNA-324 in
human cancer: miR-324-5p and miR-324-3p have distinct biological
functions in human cancer. Anticancer Res. 36:5189–5196. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu N, Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Xiong S and Chu Y:
Selective impairment of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by
paclitaxel is explained by Bcl-2/Bax mediated apoptosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:212–219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang Q, Yang K and Li A: microRNA-21
protects against ischemia-reperfusion and
hypoxia-reperfusion-induced cardiocyte apoptosis via the
phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt-dependent mechanism. Mol Med
Rep. 9:2213–2220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moshrefi M, Spotin A, Kafil HS,
Mahami-Oskouei M, Baradaran B, Ahmadpour E and Mansoori B: Tumor
suppressor p53 induces apoptosis of host lymphocytes experimentally
infected by Leishmania major, by activation of Bax and caspase-3: A
possible survival mechanism for the parasite. Parasitol Res.
116:2159–2166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lukiw WJ: NF-κB-regulated, proinflammatory
miRNAs in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 4:472012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lee M: Neurotransmitters and
microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. Curr Protein Pept Sci.
14:21–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|