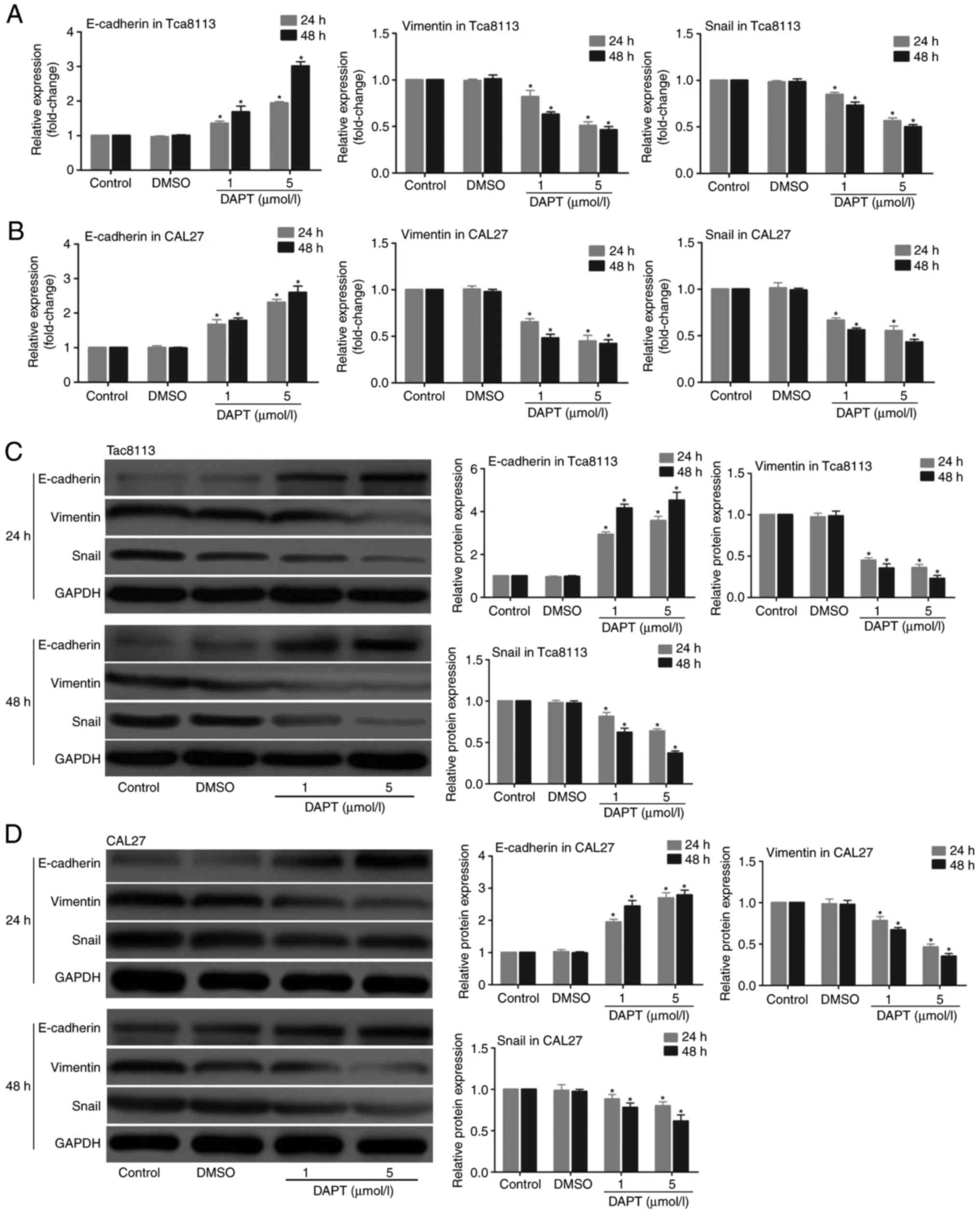
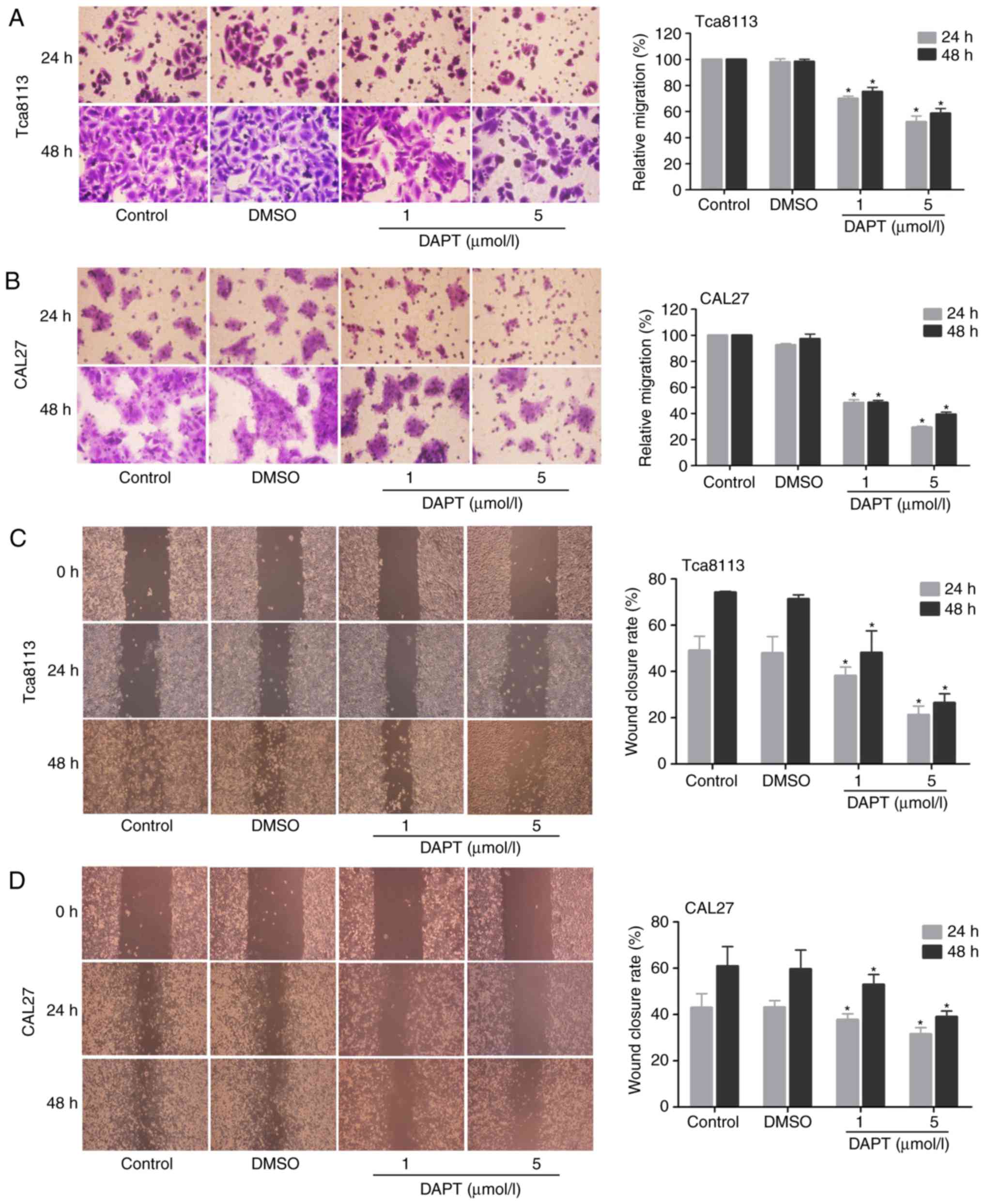
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Living with oral
cancer: Epidemiology with particular reference to prevalence and
life-style changes that influence survival. Oral Oncol. 46:407–410.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta S, Kong W, Peng Y, Miao Q and
Mackillop WJ: Temporal trends in the incidence and survival of
cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract in Ontario and the United
States. Int J Cancer. 125:2159–2165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SY, Nam SY, Choi SH, Cho KJ and Roh
JL: Prognostic value of lymph node density in node-positive
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2310–2317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li L and Li W: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human cancer: Comprehensive reprogramming of
metabolism, epigenetics, and differentiation. Pharmacol Ther.
150:33–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scanlon CS, Van Tubergen EA, Inglehart RC
and D’Silva NJ: Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. 92:114–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Nijkamp MM, Span PN, Hoogsteen IJ, van der
Kogel AJ, Kaanders JH and Bussink J: Expression of E-cadherin and
vimentin correlates with metastasis formation in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma patients. Radiother Oncol. 99:344–348.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamamoto S, Schulze KL and Bellen HJ:
Introduction to Notch signaling. Methods Mol Biol. 1187:1–14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bray SJ: Notch signalling: A simple
pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:678–689. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang TH, Liu HC, Zhu LJ, Chu M, Liang YJ,
Liang LZ and Liao GQ: Activation of Notch signaling in human tongue
carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:37–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Osathanon T, Nowwarote N and Pavasant P:
Expression and influence of Notch signaling in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. J Oral Sci. 58:283–294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hijioka H, Setoguchi T, Miyawaki A, Gao H,
Ishida T, Komiya S and Nakamura N: Upregulation of Notch pathway
molecules in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 36:817–822.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chaw SY, Majeed AA, Dalley AJ, Chan A,
Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers-E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin - in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Angadi PV, Patil PV, Angadi V, Mane D,
Shekar S, Hallikerimath S, Kale AD and Kardesai SG:
Immunoexpression of epithelial mesenchymal transition proteins
E-cadherin, β-catenin, and N-cadherin in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Surg Pathol. 24:696–703. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krisanaprakornkit S and Iamaroon A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
ISRN Oncol. 2012:6814692012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie SM, Lu ZY, Lin YZ, Shen LJ and Yin C:
Upregulation of PTEN suppresses invasion in Tca8113 tongue cancer
cells through repression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT). Tumor Biol. 37:6681–6689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhao XP, Zhang H, Jiao JY, Tang DX, Wu YL
and Pan CB: Overexpression of HMGA2 promotes tongue cancer
metastasis through EMT pathway. J Transl Med. 14:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pu Y, Wang L, Wu H, Feng Z, Wang Y and Guo
C: High MMP-21 expression in metastatic lymph nodes predicts
unfavorable overall survival for oral squamous cell carcinoma
patients with lymphatic metastasis. Oncol Rep. 31:2644–2650. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye F, Chen C, Qin J, Liu J and Zheng C:
Genetic profiling reveals an alarming rate of cross-contamination
among human cell lines used in China. FASEB J. 29:4268–4272. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Liu S, Cai G, Kong L, Zhang T, Ren
Y, Wu Y, Mei M, Zhang L and Wang X: Long Non Coding RNA MALAT1
promotes tumor growth and metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 5:159722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diepenbruck M and Christofori G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis: Yes, no,
maybe? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 43:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davis FM, Stewart TA, Thompson EW and
Monteith GR: Targeting EMT in cancer: Opportunities for
pharmacological intervention. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 35:479–488.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
da Silva SD, Morand GB, Alobaid FA, Hier
MP, Mlynarek AM, Alaoui-Jamali MA and Kowalski LP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers have prognostic
impact in multiple primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp
Metastas. 32:55–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Giroldi LA, Bringuier PP, de Weijert M,
Jansen C, van Bokhoven A and Schalken JA: Role of E boxes in the
repression of E-cadherin expression. Biochem Bioph Res Commun.
241:453–458. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of Snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Tar.
13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li YY, Zhou CX and Gao Y: Snail regulates
the motility of oral cancer cells via RhoA/Cdc42/p-ERM pathway.
Biochem Bioph Res Commun. 452:490–496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhu LF, Hu Y, Yang CC, Xu XH, Ning TY,
Wang ZL, Ye JH and Liu LK: Snail overexpression induces an
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like
properties in SCC9 cells. Lab Invest. 92:744–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang ZW, Li YW, Kong DJ and Sarkar FH: The
role of Notch signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) during development and tumor aggressiveness. Curr
Drug Targets. 11:745–751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li YM, Ma J, Qian XJ, Wu Q, Xia J, Miele
L, Sarkar FH and Wang ZW: Regulation of EMT by Notch signaling
pathway in tumor progression. Curr Cancer Drug Tar. 13:957–962.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li LC, Peng Y, Liu YM, Wang LL and Wu XL:
Gastric cancer cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
are inhibited by γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT. Oncol Lett.
7:2160–2164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|