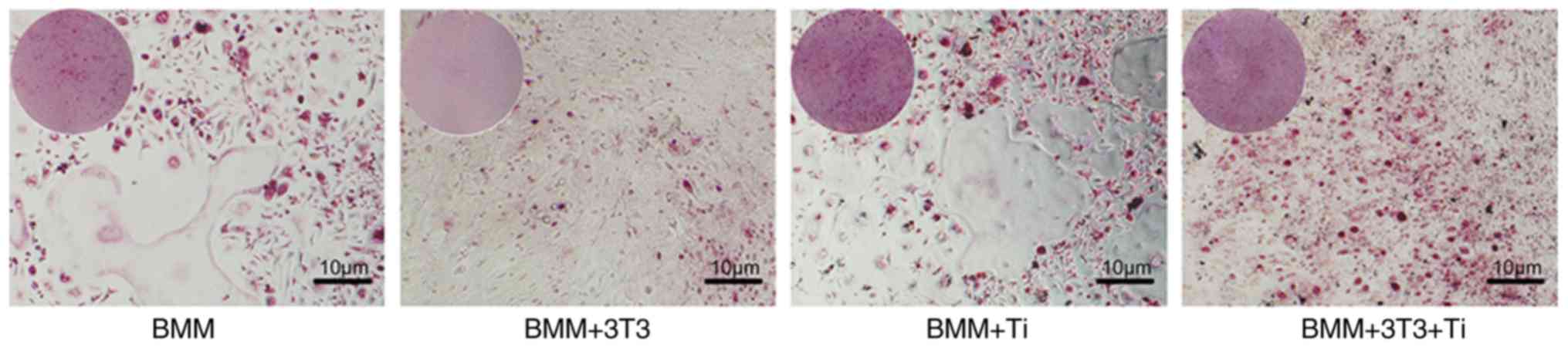
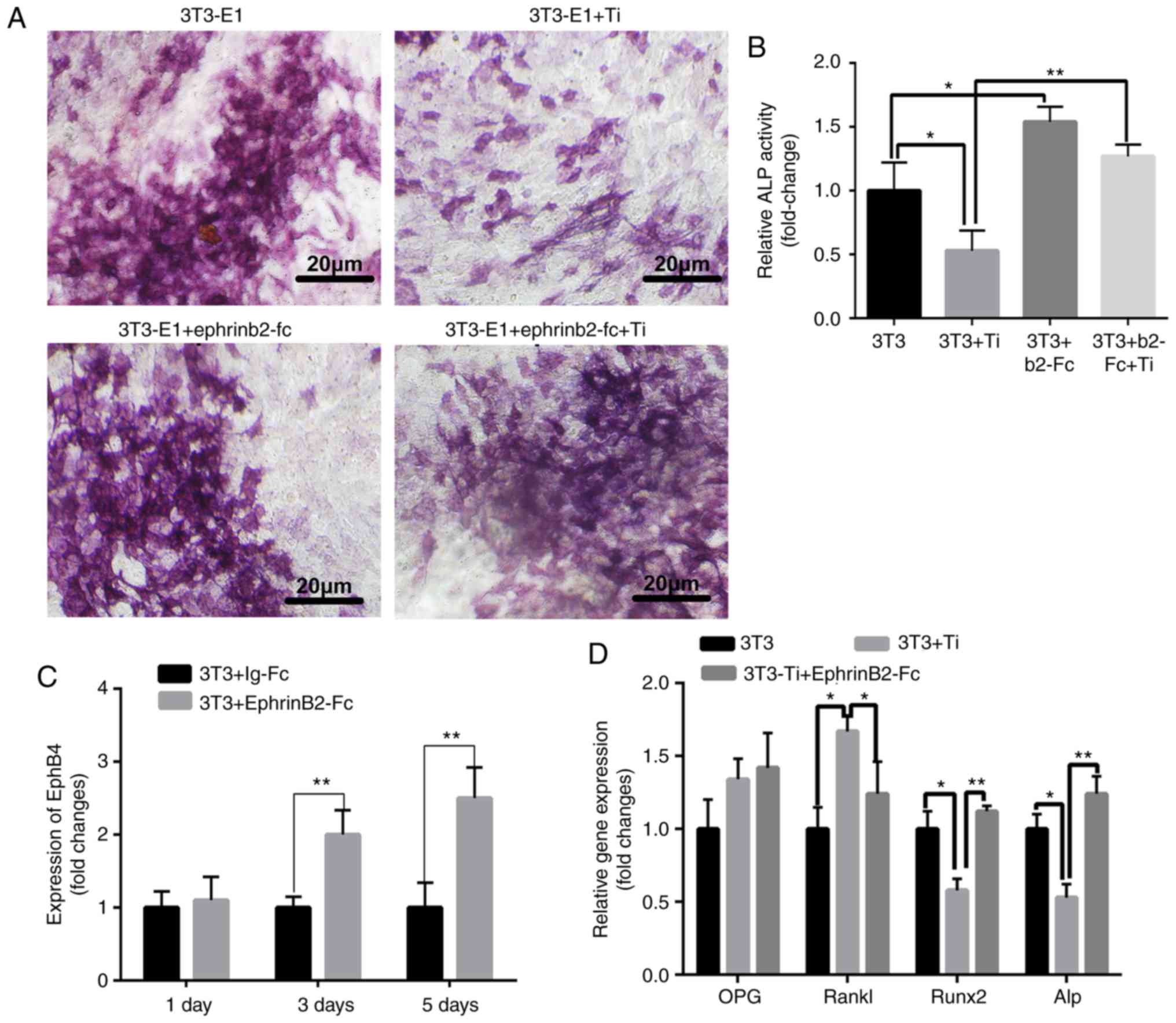
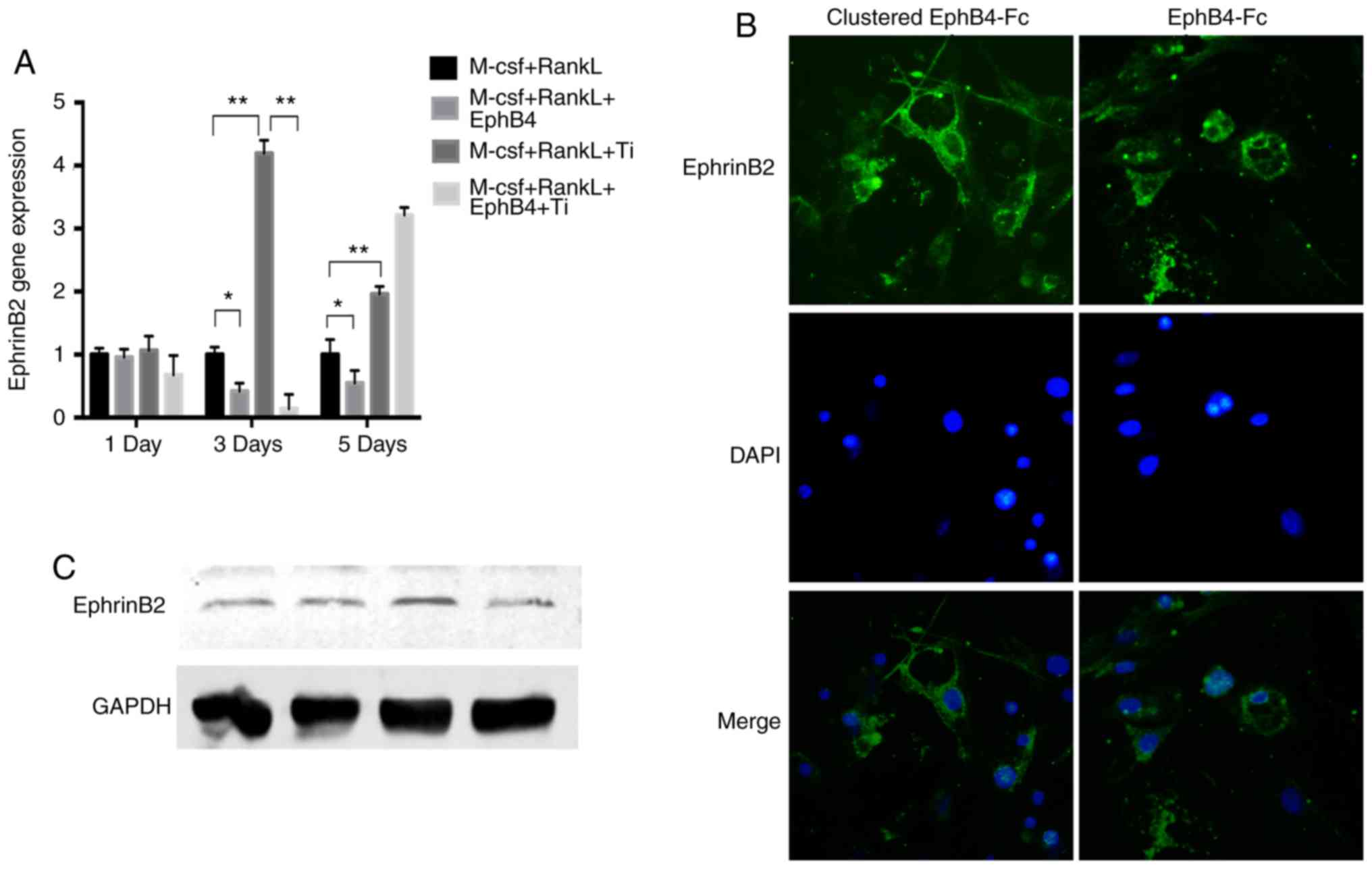
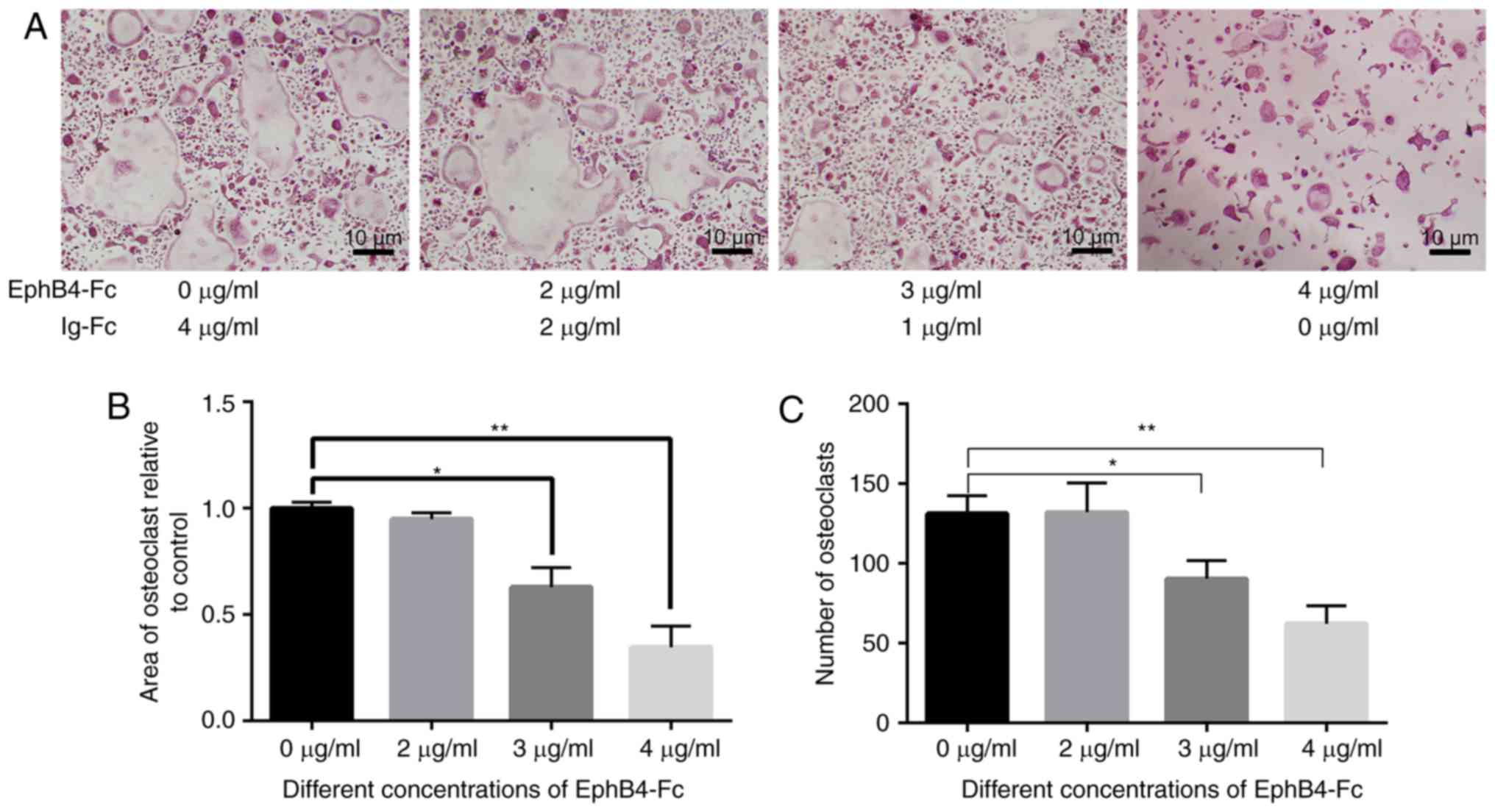
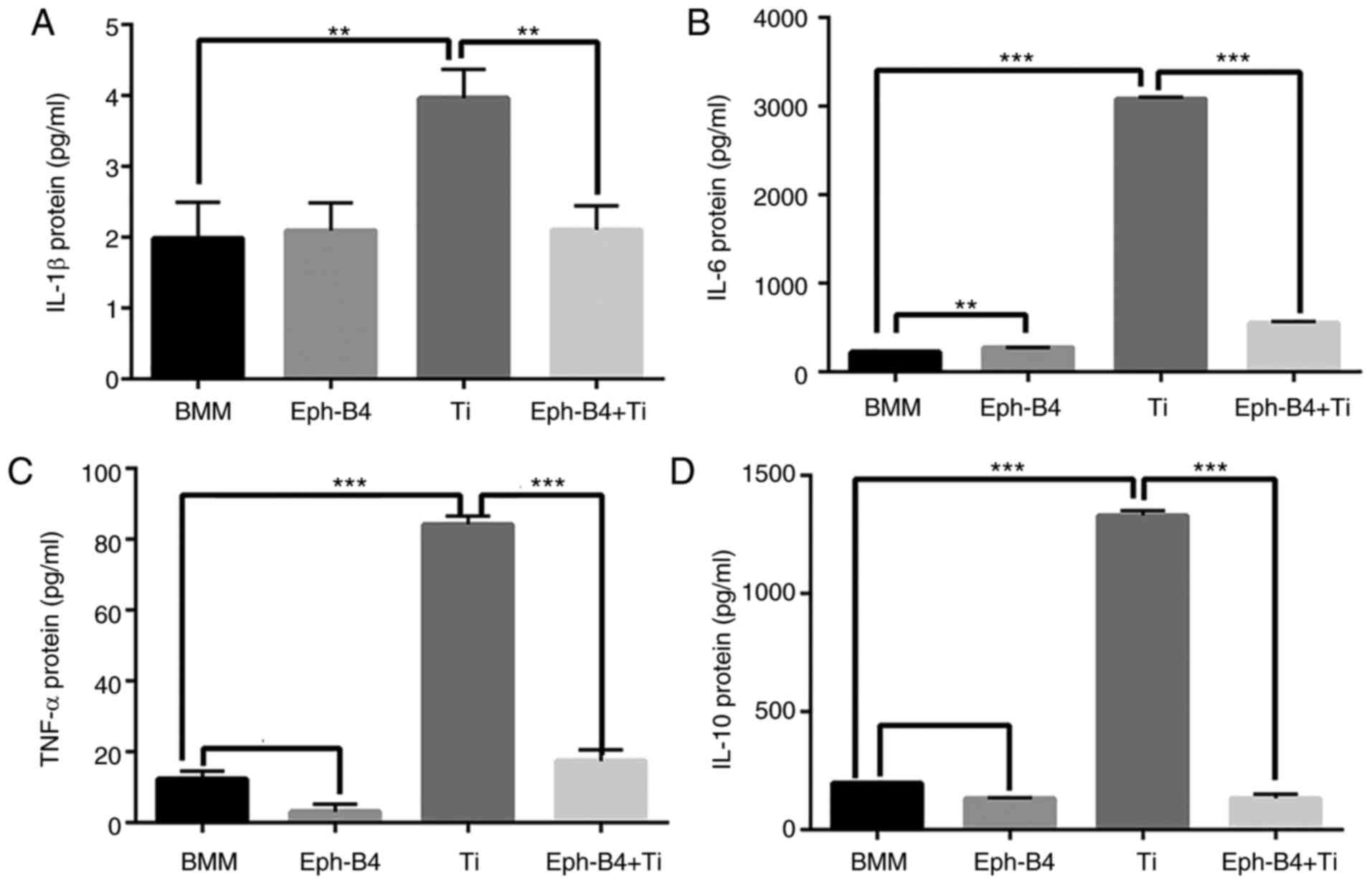
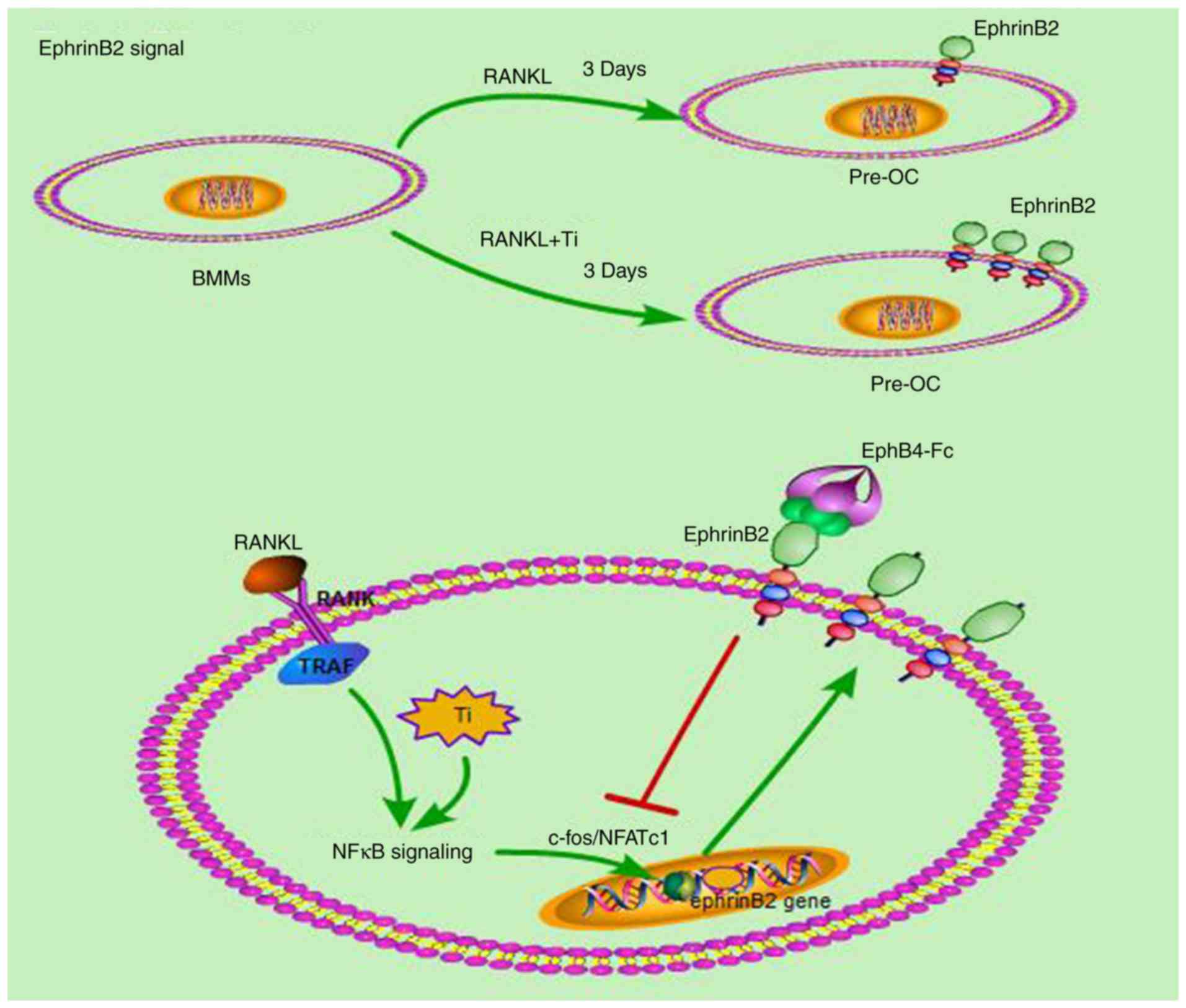
|
1
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu X, Zhu S, Cui J, Shao H, Zhang W, Yang
H, Xu Y, Geng D and Yu L: Strontium ranelate inhibits
titanium-particle-induced osteolysis by restraining inflammatory
osteoclastogenesis in vivo. Acta Biomater. 10:4912–4918. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geng D, Wu J, Shao H, Zhu S, Wang Y, Zhang
W, Ping Z, Hu X, Zhu X, Xu Y and Yang H: Pharmaceutical inhibition
of glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta suppresses wear debris-induced
osteolysis. Biomaterials. 69:12–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT, Wimmer
MA and Holinka M: Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: A
review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 9:8046–8058.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Qu X, Wu C, Zhai Z, Tian B, Li H,
Ouyang Z, Xu X, Wang W, Fan Q, et al: The effect of enoxacin on
osteoclastogenesis and reduction of titanium particle-induced
osteolysis via suppression of JNK signaling pathway. Biomaterials.
35:5721–5730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vallés G, Pérez C, Boré A, Martín-Saavedra
F, Saldaña L and Vilaboa N: Simvastatin prevents the induction of
interleukin-6 gene expression by titanium particles in human
osteoblastic cells. Acta Biomater. 9:4916–4925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nich C, Takakubo Y, Pajarinen J, Ainola M,
Salem A, Sillat T, Rao AJ, Raska M, Tamaki Y, Takagi M, et al:
Macrophages-Key cells in the response to wear debris from joint
replacements. J Biomed Mater Res A. 101:3033–3045. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pajarinen J, Kouri VP, Jämsen E, Li TF,
Mandelin J and Konttinen YT: The response of macrophages to
titanium particles is determined by macrophage polarization. Acta
Biomater. 9:9229–9240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee HG, Minematsu H, Kim KO, Celil Aydemir
AB, Shin MJ, Nizami SA, Chung KJ, Hsu AC, Jacobs CR and Lee FY:
Actin and ERK1/2-CEBPβ signaling mediates phagocytosis-induced
innate immune response of osteoprogenitor cells. Biomaterials.
32:9197–9206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang JB, Ding Y, Huang DS, Zeng WK, Guan
ZP and Zhang ML: rna interference targeting p110β reduces tumor
necrosis factor-alpha production in cellular response to wear
particles in vitro and osteolysis in vivo. Inflammation.
36:1041–1054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu FX, Wu CL, Zhu ZA, Li MQ, Mao YQ, Liu
M, Wang XQ, Yu DG and Tang TT: Calcineurin/NFAT pathway mediates
wear particle-induced TNF-alpha release and osteoclastogenesis from
mice bone marrow macrophages in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:1457–1466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JA, Ihn HJ, Park JY, Lim J, Hong JM,
Kim SH, Kim SY, Shin HI and Park EK: Inhibitory effects of
triptolide on titanium particle-induced osteolysis and receptor
activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-mediated osteoclast
differentiation. Int Orthop. 39:173–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhao C, Irie N, Takada Y, Shimoda K,
Miyamoto T, Nishiwaki T, Suda T and Matsuo K: Bidirectional
ephrinB2-EphB4 signaling controls bone homeostasis. Cell Metab.
4:111–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Henriksen K, Neutzsky-Wulff AV, Bonewald
LF and Karsdal MA: Local communication on and within bone controls
bone remodeling. Bone. 44:1026–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng L, Wang Y, Peng Y, Wu Y, Ding Y,
Jiang Y, Shen Z and Fu Q: Osteoblast-derived microvesicles: A novel
mechanism for communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Bone. 79:37–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsuo K and Otaki N: Bone cell
interactions through Eph/ephrin: Bone modeling, remodeling and
associated diseases. Cell Adh Migr. 6:148–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsuo K: Eph and ephrin interactions in
bone. Adv Exp Med Biol. 658:95–103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Luiz de Freitas PH, Li M, Ninomiya T,
Nakamura M, Ubaidus S, Oda K, Udagawa N, Maeda T, Takagi R and
Amizuka N: Intermittent PTH administration stimulates
pre-osteoblastic proliferation without leading to enhanced bone
formation in osteoclast-less c-fos(−/−) mice. J Bone Miner Res.
24:1586–1597. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fan WB, Zhao JN and Bao NR: Effects of
bidirectional EphB4-EphrinB2 signaling on bone remodeling. Zhongguo
Gu Shang. 26:705–708. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zuo C, Huang Y, Bajis R, Sahih M, Li YP,
Dai K and Zhang X: Osteoblastogenesis regulation signals in bone
remodeling. Osteoporos Int. 23:1653–1663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
von Knoch M, Jewison DE, Sibonga JD,
Sprecher C, Morrey BF, Loer F, Berry DJ and Scully SP: The
effectiveness of polyethylene versus titanium particles in inducing
osteolysis in vivo. J Orthop Res. 22:237–243. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SS, Woo CH, Chang JD and Kim JH: Roles
of Rac and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in the intracellular
signalling in response to titanium particles. Cell Signal.
15:339–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takyar FM, Tonna S, Ho PW, Crimeen-Irwin
B, Baker EK, Martin TJ and Sims NA: EphrinB2/EphB4 inhibition in
the osteoblast lineage modifies the anabolic response to
parathyroid hormone. J Bone Miner Res. 28:912–925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ouyang Z, Zhai Z, Li H, Liu X, Qu X, Li X,
Fan Q, Tang T, Qin A and Dai K: Hypericin suppresses osteoclast
formation and wear particle-induced osteolysis via modulating ERK
signalling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 90:276–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Wang XC, Bao XF, Hu M and Yu WX:
Effects of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide on
osteoblast-osteoclast bidirectional EphB4-EphrinB2 signaling. Exp
Ther Med. 7:80–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu C, Wang W, Tian B, Liu X, Qu X, Zhai Z,
Li H, Liu F, Fan Q, Tang T, et al: Myricetin prevents titanium
particle-induced osteolysis in vivo and inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 93:59–71. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shao H, Shen J, Wang M, Cui J, Wang Y, Zhu
S, Zhang W, Yang H, Xu Y and Geng D: Icariin protects against
titanium particle-induced osteolysis and inflammatory response in a
mouse calvarial model. Biomaterials. 60:92–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhai Z, Qu X, Li H, Yang K, Wan P, Tan L,
Ouyang Z, Liu X, Tian B, Xiao F, et al: The effect of metallic
magnesium degradation products on osteoclast-induced osteolysis and
attenuation of NF-κB and NFATc1 signaling. Biomaterials.
35:6299–6310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsuo K and Irie N: Osteoclast-osteoblast
communication. Arch Biochem Biophys. 473:201–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Wang Z, Duan N, Zhu G, Schwarz EM
and Xie C: Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res.
59:99–107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Martin TJ, Allan EH, Ho PW, Gooi JH, Quinn
JM, Gillespie MT, Krasnoperov V and Sims NA: Communication between
ephrinB2 and EphB4 within the osteoblast lineage. Adv Exp Med Biol.
658:51–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gooi JH, Pompolo S, Karsdal MA, Kulkarni
NH, Kalajzic I, McAhren SH, Han B, Onyia JE, Ho PW, Gillespie MT,
et al: Calcitonin impairs the anabolic effect of PTH in young rats
and stimulates expression of sclerostin by osteocytes. Bone.
46:1486–1497. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Benson MD, Opperman LA, Westerlund J,
Fernandez CR, San Miguel S, Henkemeyer M and Chenaux G: Ephrin-B
stimulation of calvarial bone formation. Dev Dyn. 241:1901–1910.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arthur A, Panagopoulos RA, Cooper L,
Menicanin D, Parkinson IH, Codrington JD, Vandyke K, Zannettino AC,
Koblar SA, Sims NA, et al: EphB4 enhances the process of
endochondral ossification and inhibits remodeling during bone
fracture repair. J Bone Miner Res. 28:926–935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Allan EH, Häusler KD, Wei T, Gooi JH,
Quinn JM, Crimeen-Irwin B, Pompolo S, Sims NA, Gillespie MT, Onyia
JE and Martin TJ: EphrinB2 regulation by PTH and PTHrP revealed by
molecular profiling in differentiating osteoblasts. J Bone Miner
Res. 23:1170–1181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J and
Takaku F: A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the
eph gene. Science. 238:1717–1720. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang L, Zhang J, Wang C, Qi Y, Du M, Liu
W, Yang C and Yang P: Low concentrations of TNF-alpha promote
osteogenic differentiation via activation of the ephrinB2-EphB4
signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 50:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li C, Shi C, Kim J, Chen Y, Ni S, Jiang L,
Zheng C, Li D, Hou J, Taichman RS and Sun H: Erythropoietin
promotes bone formation through EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling. J Dent
Res. 94:455–463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|