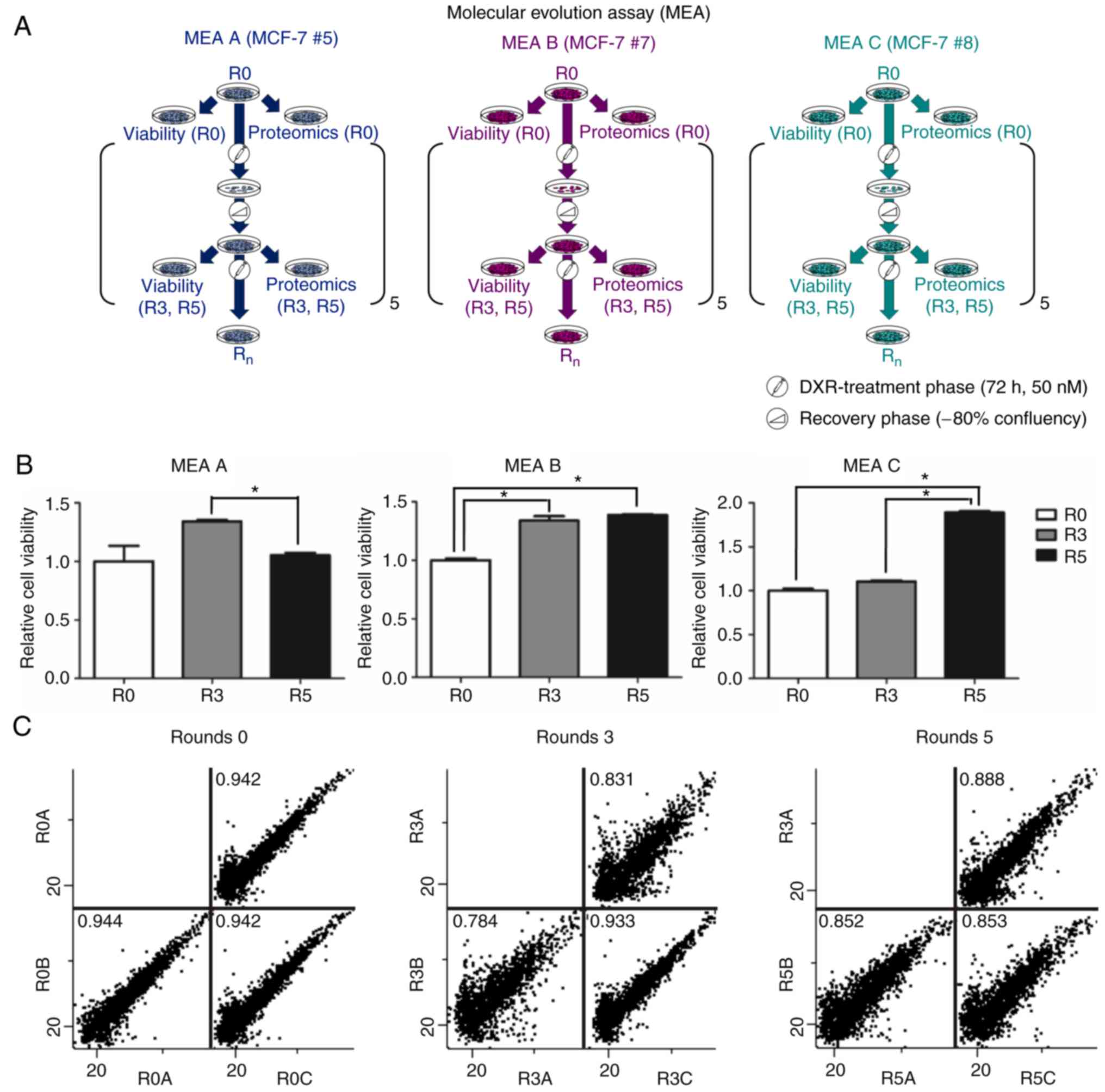
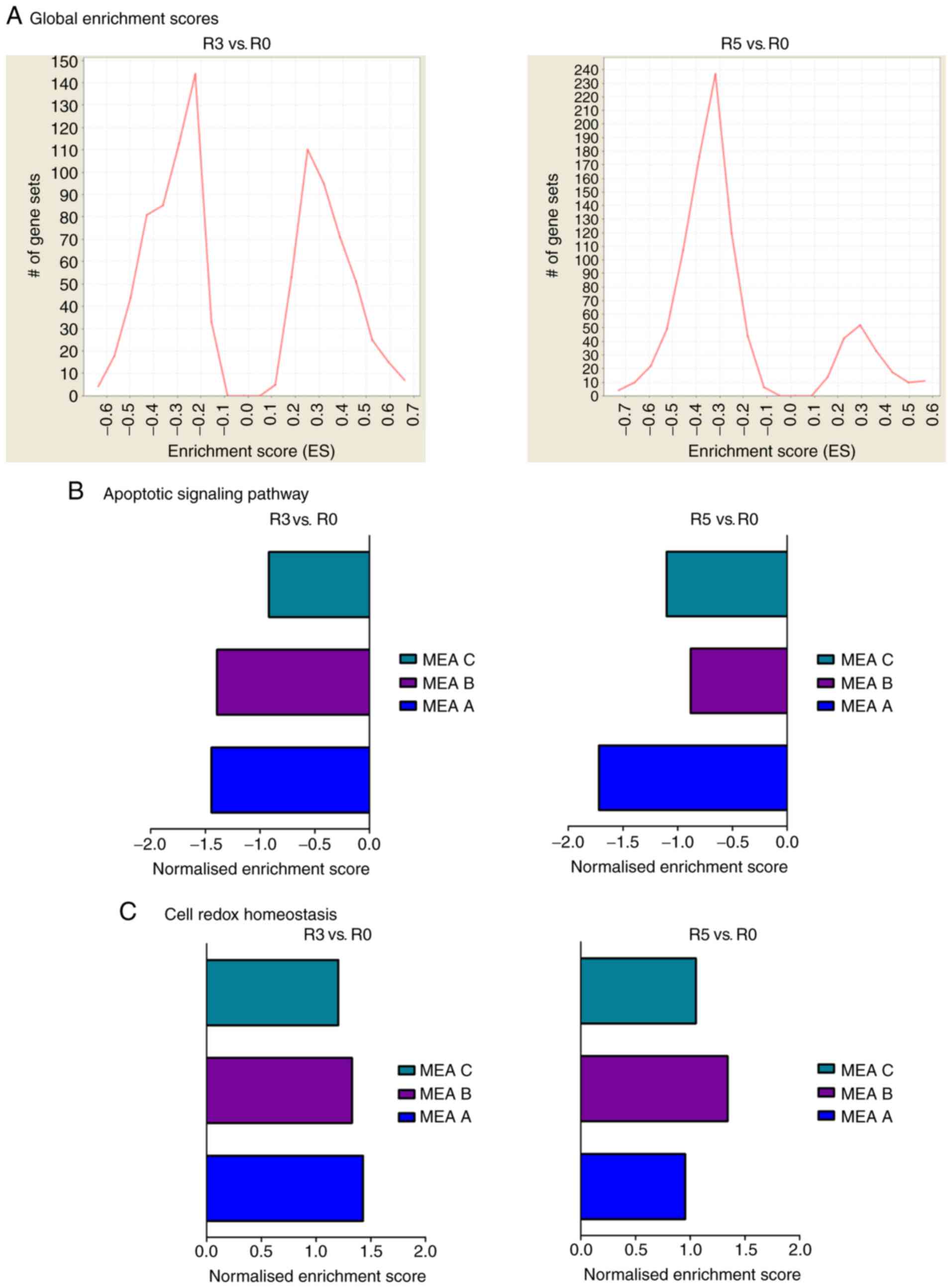
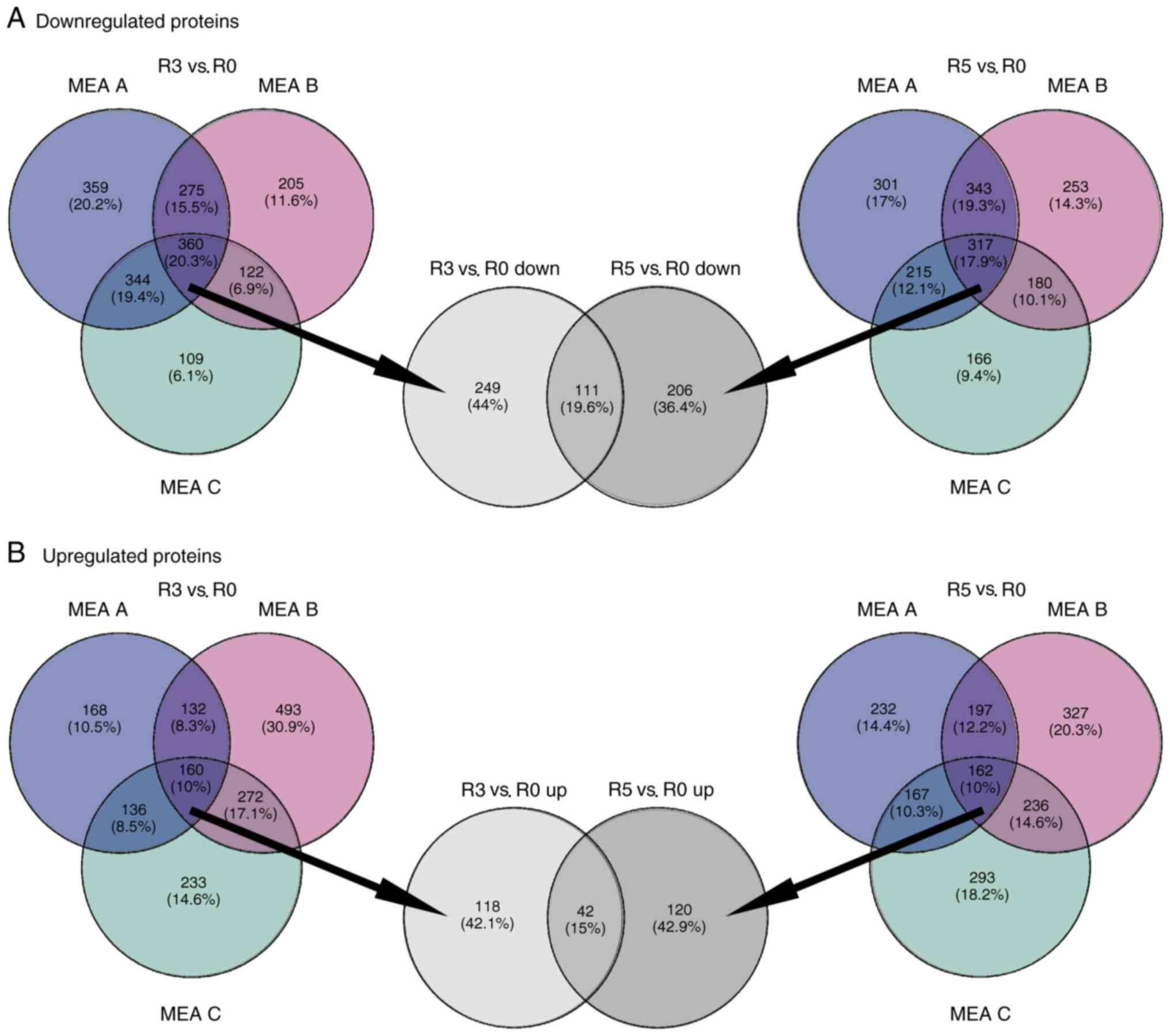
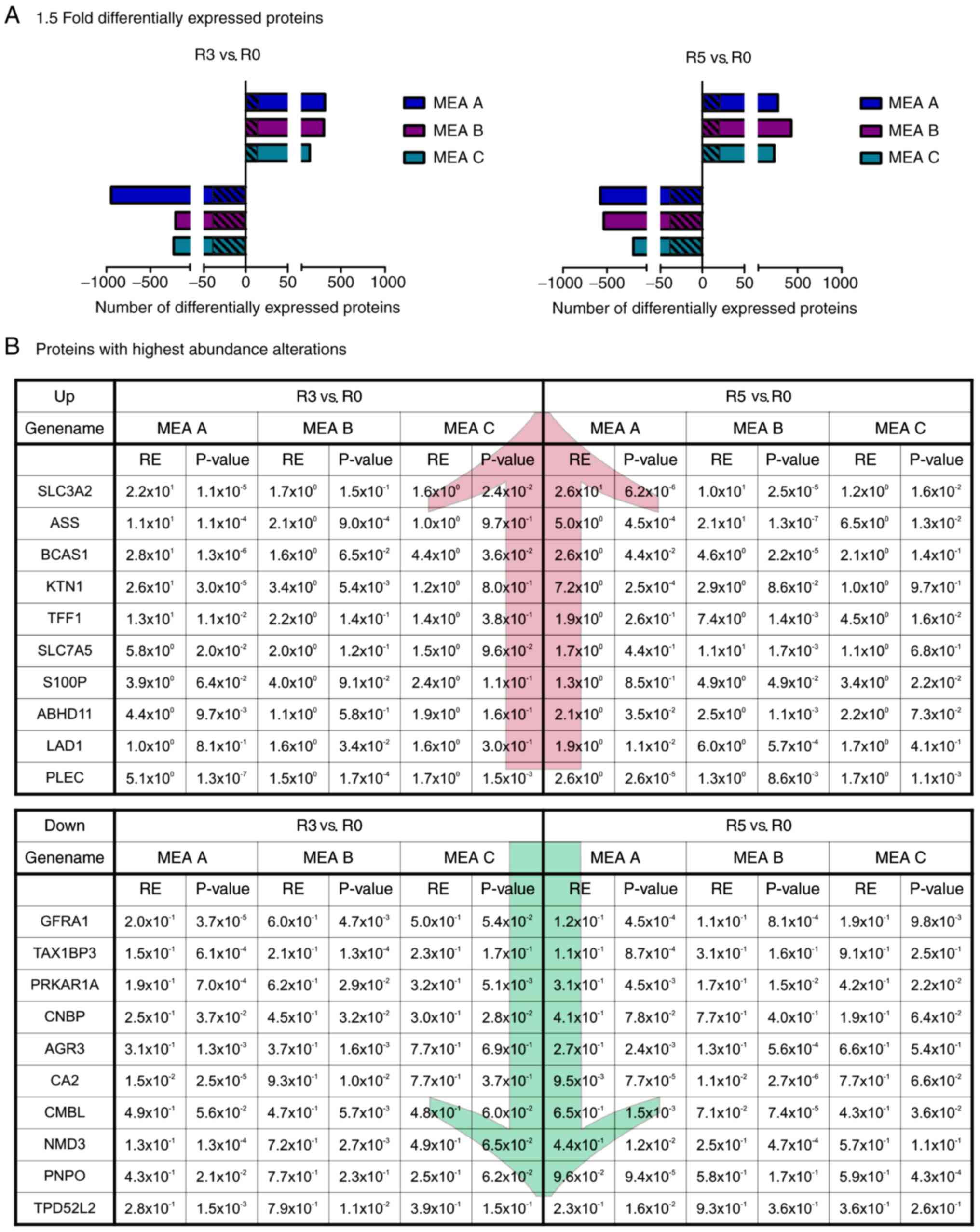
|
1
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer facts
& figures 2018. American Cancer Society; 2018
|
|
2
|
Globocan: Cancer today. International
Agency for Research on Cancer; 2012
|
|
3
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Fantini G, Grein
A, Orezzi P, Pol C and Spalla C: Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin,
a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius.
Biotechnol Bioeng. 11:1101–1110. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tewey KM, Rowe TC, Yang L, Halligan BD and
Liu LF: Adriamycin-induced DNA damage mediated by mammalian DNA
topoisomerase II. Science. 226:466–468. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen NT, Wu CY, Chung CY, Hwu Y, Cheng SH,
Mou CY and Lo LW: Probing the dynamics of doxorubicin-DNA
intercalation during the initial activation of apoptosis by
fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). PLoS One.
7:e449472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mizutani H, Tada-Oikawa S, Hiraku Y,
Kojima M and Kawanishi S: Mechanism of apoptosis induced by
doxorubicin through the generation of hydrogen peroxide. Life Sci.
76:1439–1453. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hilmer SN, Cogger VC, Muller M and Le
Couteur DG: The hepatic pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin and
liposomal doxorubicin. Drug Metab Dispos. 32:794–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gewirtz DA: A critical evaluation of the
mechanisms of action proposed for the antitumor effects of the
anthracycline antibiotics adriamycin and daunorubicin. Biochem
Pharmacol. 57:727–741. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo
G and Gianni L: Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and
pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and
cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 56:185–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P and Dass CR:
Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and
novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:157–170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benchekroun MN, Sinha BK and Robert J:
Doxorubicin-induced oxygen free radical formation in sensitive and
doxorubicin-resistant variants of rat glioblastoma cell lines
[corrected and republished erratum originally printed in FEBS Lett
1993 May 17;322(3):295–8]. FEBS Lett. 326:302–305. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG); Peto R, Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R,
Pan HC, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Taylor C, et al:
Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early
breast cancer: Meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000
women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 379:432–444. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Meacham CE and Morrison SJ: Tumour
heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature. 501:328–337.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greaves M and Maley CC: Clonal evolution
in cancer. Nature. 481:306–313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shackleton M, Quintana E, Fearon ER and
Morrison SJ: Heterogeneity in cancer: Cancer stem cells versus
clonal evolution. Cell. 138:822–829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cairns J: Mutation selection and the
natural history of cancer. Nature. 255:197–200. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nowell PC: The clonal evolution of tumor
cell populations. Science. 194:23–28. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kopp F, Hermawan A, Oak PS, Ulaganathan
VK, Herrmann A, Elnikhely N, Thakur C, Xiao Z, Knyazev P, Ataseven
B, et al: Sequential salinomycin treatment results in resistance
formation through clonal selection of epithelial-like tumor cells.
Transl Oncol. 7:702–711. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Turner NC and Reis-Filho JS: Genetic
heterogeneity and cancer drug resistance. Lancet Oncol.
13:e178–e185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bedard PL, Hansen AR, Ratain MJ and Siu
LL: Tumour heterogeneity in the clinic. Nature. 501:355–364. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bankusli I, Yin MB, Mazzoni A, Abdellah AJ
and Rustum YM: Enhancement of adriamycin-induced cytotoxicity by
increasing retention and inhibition of DNA repair in DOX-resistant
P388 cell lines with new calcium channel blocker, DMDP. Anticancer
Res. 9:567–574. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Jong S, Zijlstra JG, de Vries EG and
Mulder NH: Reduced DNA topoisomerase II activity and drug-induced
DNA cleavage activity in an adriamycin-resistant human small cell
lung carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 50:304–309. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Liang S, Lian X, Liu L, Zhao S,
Xuan Q, Guo L, Liu H, Yang Y, Dong T, et al: Identification of
proteins responsible for adriamycin resistance in breast cancer
cells using proteomics analysis. Sci Rep. 5:93012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gehrmann ML, Fenselau C and Hathout Y:
Highly altered protein expression profile in the adriamycin
resistant MCF-7 cell line. J Proteome Res. 3:403–409. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aas T, Børresen AL, Geisler S,
Smith-Sørensen B, Johnsen H, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA and Lønning PE:
Specific P53 mutations are associated with de novo resistance to
doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. Nat Med. 2:811–814. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gottesman MM: Mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance. Annu Rev Med. 53:615–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hermawan A, Wagner E and Roidl A:
Consecutive salinomycin treatment reduces doxorubicin resistance of
breast tumor cells by diminishing drug efflux pump expression and
activity. Oncol Rep. 35:1732–1740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kopp F, Oak PS, Wagner E and Roidl A:
miR-200c sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin treatment by
decreasing TrkB and Bmi1 expression. PLoS One. 7:e504692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tyanova S, Temu T, Carlson A, Sinitcyn P,
Mann M and Cox J: Visualization of LC-MS/MS proteomics data in
MaxQuant. Proteomics. 15:1453–1456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tyanova S, Temu T, Sinitcyn P, Carlson A,
Hein MY, Geiger T, Mann M and Cox J: The perseus computational
platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat
Methods. 13:731–740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES, et al: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes
involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately
downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oliveros JC: Venny. An interactive tool
for comparing lists with Venn's diagrams. 2007–2015.
|
|
37
|
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi HS, Kim DA, Chung H, Park IH, Kim BH,
Oh ES and Kang DH: Screening of breast cancer stem cell inhibitors
using a protein kinase inhibitor library. Cancer Cell Int.
17:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pertea M: The human transcriptome: An
unfinished story. Genes. 3:344–360. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim MS, Pinto SM, Getnet D, Nirujogi RS,
Manda SS, Chaerkady R, Madugundu AK, Kelkar DS, Isserlin R, Jain S,
et al: A draft map of the human proteome. Nature. 509:575–581.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holm M, Saraswat M, Joenväärä S, Ristimäki
A, Haglund C and Renkonen R: Colorectal cancer patients with
different C-reactive protein levels and 5-year survival times can
be differentiated with quantitative serum proteomics. PLoS One.
13:e01953542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Koplev S, Lin K, Dohlman AB and Ma'ayan A:
Integration of pan-cancer transcriptomics with RPPA proteomics
reveals mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS
Comput Biol. 14:e10059112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marin JJ, Al-Abdulla R, Lozano E, Briz O,
Bujanda L, Banales JM and Macias RI: Mechanisms of resistance to
chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
16:318–334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pfeffer CM and Singh ATK: Apoptosis: A
target for anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E4482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Poettler M, Unseld M, Braemswig K, Haitel
A, Zielinski CC and Prager GW: CD98hc (SLC3A2) drives
integrin-dependent renal cancer cell behavior. Mol Cancer.
12:1692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Prager GW, Poettler M, Schmidinger M,
Mazal PR, Susani M, Zielinski CC and Haitel A: CD98hc (SLC3A2), a
novel marker in renal cell cancer. Eur J Clin Invest. 39:304–310.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bai B, Moore HM and Laiho M: CRM1 and its
ribosome export adaptor NMD3 localize to the nucleolus and affect
rRNA synthesis. Nucleus. 4:315–325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schwab M: Encyclopedia of cancer.
Springer; Heidelberg: 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sommer AK, Hermawan A, Mickler FM, Ljepoja
B, Knyazev P, Bräuchle C, Ullrich A, Wagner E and Roidl A:
Salinomycin co-treatment enhances tamoxifen cytotoxicity in luminal
A breast tumor cells by facilitating lysosomal degradation of
receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncotarget. 7:50461–50476. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490:61–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nik-Zainal S, Davies H, Staaf J,
Ramakrishna M, Glodzik D, Zou X, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB,
Martin S, Wedge DC, et al: Landscape of somatic mutations in 560
breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature. 534:47–54. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S,
Voduc D, Vickery T, Davies S, Fauron C, He X, Hu Z, et al:
Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic
subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 27:1160–1167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Goswami S, Wang W, Wyckoff JB and
Condeelis JS: Breast cancer cells isolated by chemotaxis from
primary tumors show increased survival and resistance to
chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 64:7664–7667. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Goswami S, Philippar U, Sun D, Patsialou
A, Avraham J, Wang W, Di Modugno F, Nistico P, Gertler FB and
Condeelis JS: Identification of invasion specific splice variants
of the cytoskeletal protein Mena present in mammary tumor cells
during invasion in vivo. Clin Exp Metastasis. 26:153–159. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Patsialou A, Wang Y, Lin J, Whitney K,
Goswami S, Kenny PA and Condeelis JS: Selective gene-expression
profiling of migratory tumor cells in vivo predicts clinical
outcome in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang W, Wyckoff JB, Wang Y, Bottinger EP,
Segall JE and Condeelis JS: Gene expression analysis on small
numbers of invasive cells collected by chemotaxis from primary
mammary tumors of the mouse. BMC Biotechnol. 3:132003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wyckoff JB, Segall JE and Condeelis JS:
The collection of the motile population of cells from a living
tumor. Cancer Res. 60:5401–5404. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yates LR, Knappskog S, Wedge D, Farmery
JHR, Gonzalez S, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB, Van Loo P, Haugland
HK, Lilleng PK, et al: Genomic evolution of breast cancer
metastasis and relapse. Cancer Cell. 32:169–184.e7. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Koike Folgueira MA, Brentani H, Carraro
DM, De Camargo Barros Filho M, Hirata Katayama ML, Santana de Abreu
AP, Mantovani Barbosa E, De Oliveira CT, Patrão DF, Mota LD, et al:
Gene expression profile of residual breast cancer after doxorubicin
and cyclophosphamide neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Rep.
22:805–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tomasetti C, Li L and Vogelstein B: Stem
cell divisions, somatic mutations, cancer etiology, and cancer
prevention. Science. 355:1330–1334. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|