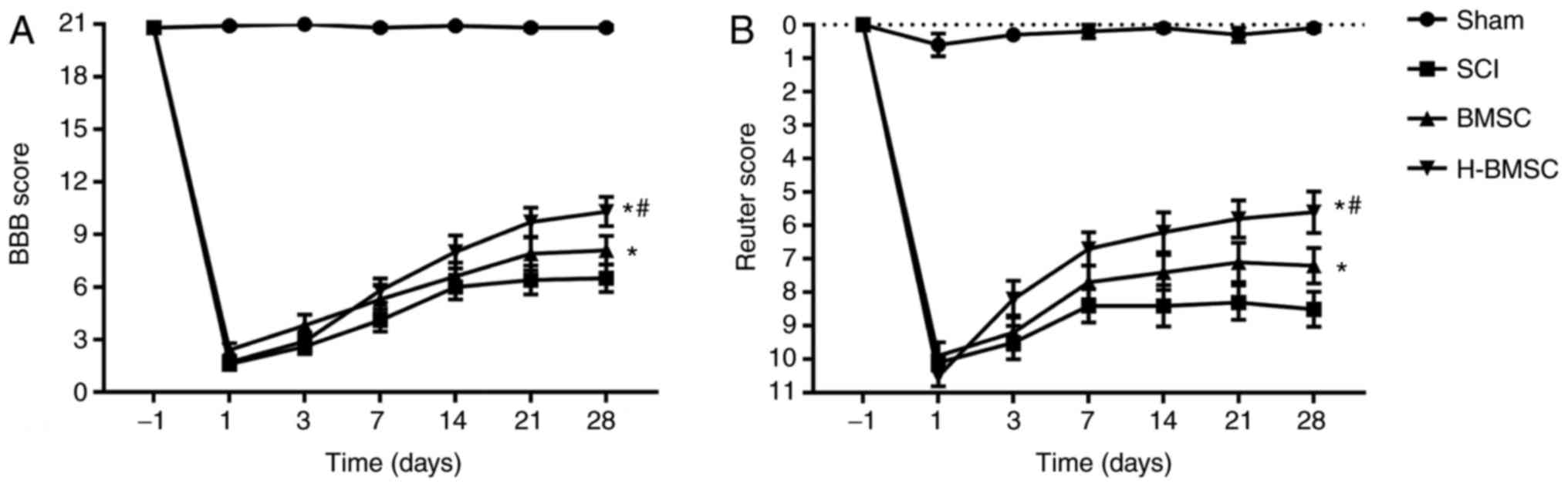
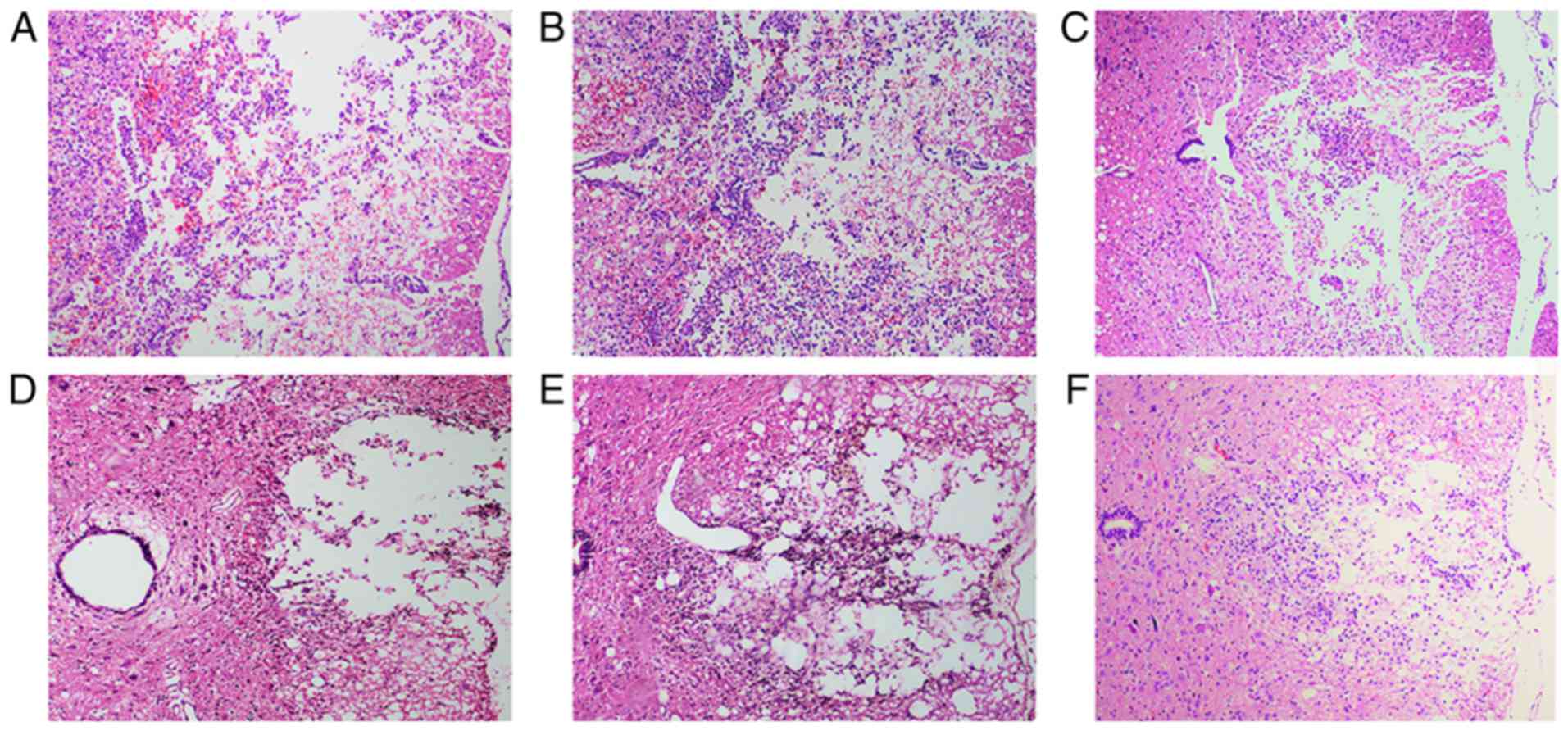
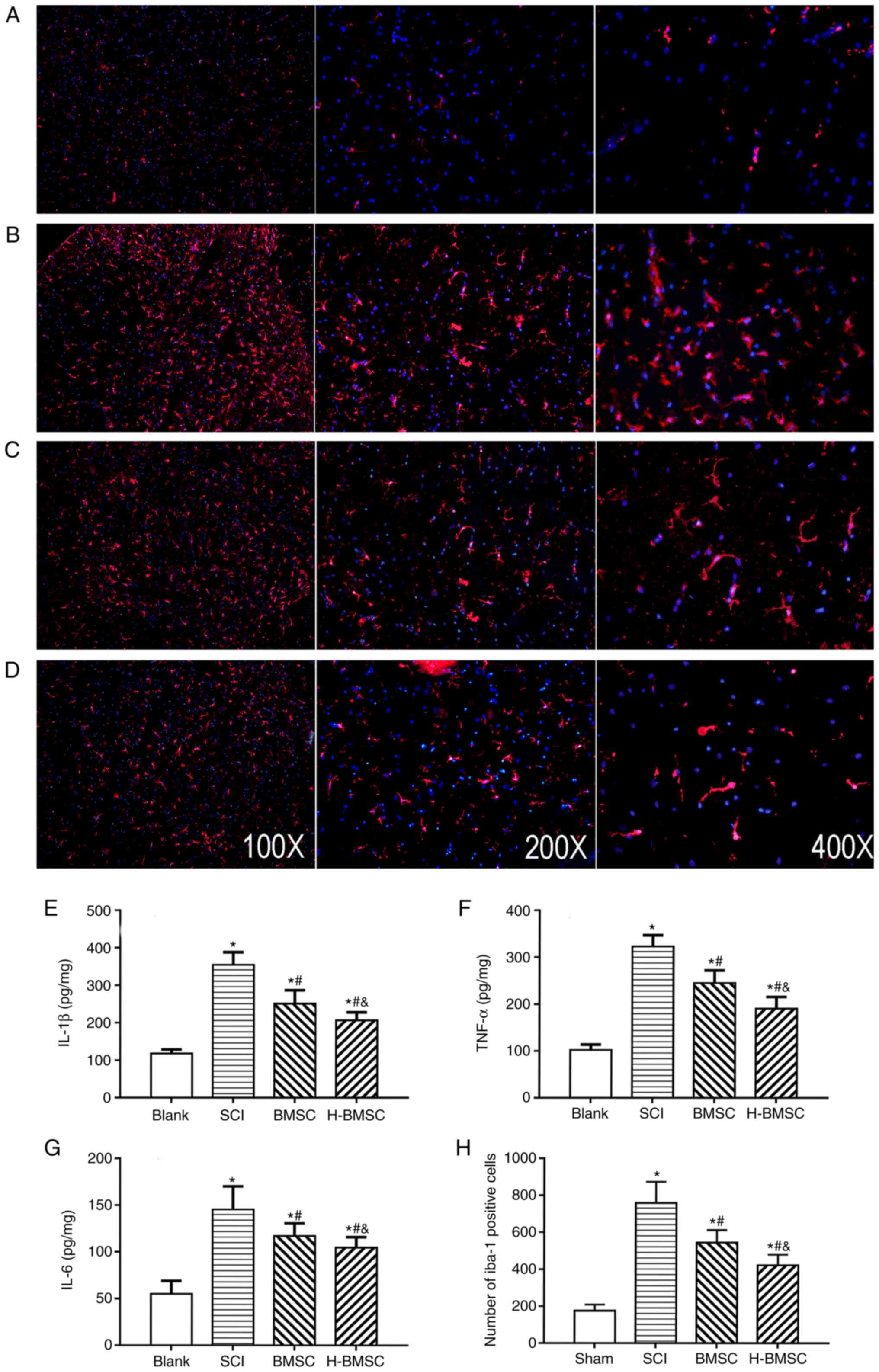
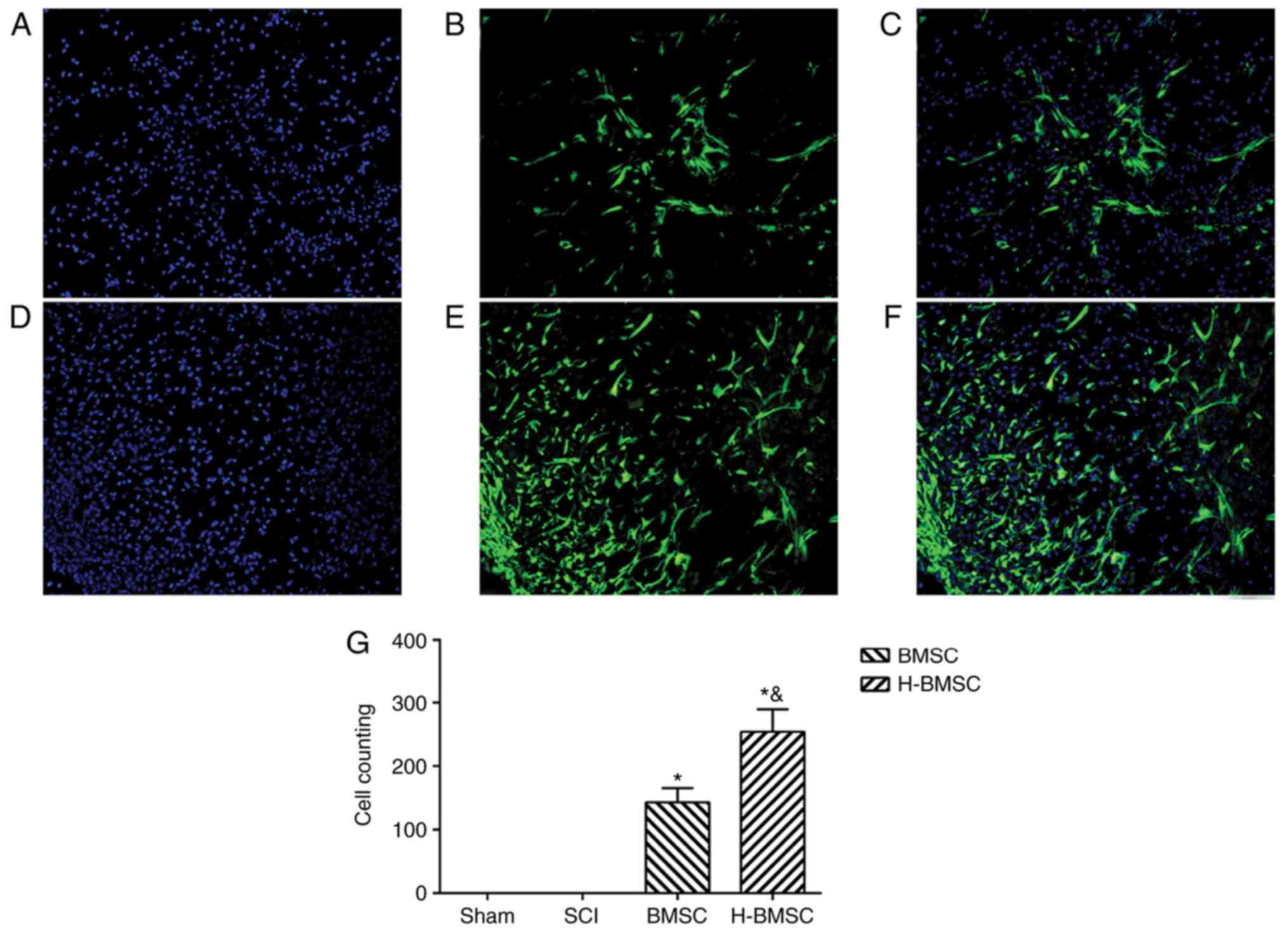
|
1
|
Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W, Grauer JN, Beiner J
and Vaccaro AR: Pathophysiology and Pharmacologic treatment of
acute spinal cord injury. Spine J. 4:451–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Selvarajah S, Hammond ER and Schneider EB:
Trends in traumatic spinal cord injury. Jama. 314:16432015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elshahidi MH, Monir NY, Elzhery MA,
Sharaqi AA, Haedaya H, Awad BI and Zaghloul K: Epidemiological
characteristics of traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) in the
middle-east and North-Africa (MENA) region: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Bull Emerg Trauma. 6:75–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghosh S and Hui SP: Axonal regeneration in
zebrafish spinal cord. Regeneration. 5:43–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vaquero J and Zurita M: Bone marrow
stromal cells for spinal cord repair: A challenge for contemporary
neurobiology. Histol Histopathol. 24:107–116. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Chiba Y, Kuroda S, Osanai T, Shichinohe H,
Houkin K and Iwasaki Y: Impact of ageing on biological features of
bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) in cell transplantation therapy
for CNS disorders: Functional enhancement by granulocyte-colony
stimulating factor (G-CSF). Neuropathology. 32:139–148. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kang ML, Kim JE and Im GI: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-transfected adipose-derived stromal cells
enhance bone regeneration and neovascularization from bone marrow
stromal cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 11:3337–3348. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brock JH, Graham L, Staufenberg E, Collyer
E, Koffler J and Tuszynski MH: Bone marrow stromal cell intraspinal
transplants fail to improve motor outcomes in a severe model of
spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 33:1103–1114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Yang W, Yang Y, Yang JY, Liang M and Song
J: Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with
plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative
stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:1075–1082. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan K, Zhang R, Sun C, Chen L, Li P, Liu
Y, Peng L, Sun H, Qin K, Chen F, et al: Bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells maintain the resting phenotype of microglia
and inhibit microglial activation. PLoS One. 8:e841162013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Forostyak S, Jendelova P and Sykova E: The
role of mesenchymal stromal cells in spinal cord injury,
regenerative medicine and possible clinical applications.
Biochimie. 95:2257–2270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roh DH, Seo MS, Choi HS, Park SB, Han HJ,
Beitz AJ, Kang KS, Lee JH, et al: Transplantation of human
umbilical cord blood or amniotic epithelial stem cells alleviates
mechanical allodynia after spinal cord injury in rats. Cell
Transplant. 22:1577–1590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Himes BT, Neuhuber B, Coleman C, Kushner
R, Swanger SA, Kopen GC, Wagner J, Shumsky JS and Fischer I:
Recovery of function following grafting of human bone
marrow-derived stromal cells into the injured spinal cord.
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 20:278–296. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dedeepiya V, Manjunath S, Murugan P,
Srinivasan V, Thamaraikannan P, Tholcopiyan L, Justin William B,
Ayyappan S and Abraham S: Autologous bone marrow stem cells in
spinal cord injury; our experience in clinical studies, animal
studies, obstacles faced and steps for future. J Stem Cells Regen
Med. 6:177–179. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eghwrudjakpor PO and Allison AB: Oxidative
stress following traumatic brain injury: Enhancement of endogenous
antioxidant defense systems and the promise of improved outcome.
Niger J Med. 19:14–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su M, Guan H, Zhang F, Gao Y, Teng X and
Yang W: HDAC6 regulates the chaperone-mediated autophagy to prevent
oxidative damage in injured neurons after experimental spinal cord
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:72637362016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fleming JC, Norenberg MD, Ramsay DA,
Dekaban GA, Marcillo AE, Saenz AD, Pasquale-Styles M, Dietrich WD
and Weaver LC: The cellular inflammatory response in human spinal
cords after injury. Brain. 129:3249–3269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li CM, Xie SJ, Wang T, Du WB, Yang ZB and
Quan RF: Effects of electro-acupuncture on neuronal apoptosis and
associative function in rats with spinal cord injury. Zhongguo Gu
Shang. 28:733–738. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rossi F and Cattaneo E: Opinion: Neural
stem cell therapy for neurological diseases: Dreams and reality.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 3:401–409. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Theus MH, Wei L, Cui L, Francis K, Hu X,
Keogh C and Yu SP: In vitro hypoxic preconditioning of embryonic
stem cells as a strategy of promoting cell survival and functional
benefits after transplantation into the ischemic rat brain. Exp
Neurol. 210:656–670. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lotfinia M, Lak S, Mohammadi Ghahhari N,
Johari B, Maghsood F, Parsania S, Sadegh Tabrizi B and Kadivar M:
Hypoxia pre-conditioned embryonic mesenchymal stem cell secretome
reduces IL-10 production by peripheral blood mono-nuclear cells.
Iran Biomed J. 21:24–31. 2016.
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Fang B, Tan Z, Zhang D and Ma H:
Hypoxic preconditioning increases the protective effect of bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells on spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Mol Med Rep. 13:1953–1960. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M
and Marini F: Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: Defining
the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther.
15:730–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bakshi A, Hunter C, Swanger S, Lepore A
and Fischer I: Minimally invasive delivery of stem cells for spinal
cord injury: Advantages of the lumbar puncture technique. J
Neurosurg Spine. 1:330–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bakshi A, Barshinger AL, Swanger SA,
Madhavani V, Shumsky JS, Neuhuber B and Fischer I: Lumbar puncture
delivery of bone marrow stromal cells in spinal cord contusion: A
novel method for minimally invasive cell transplantation. J
Neurotrauma. 23:55–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shin DA, Kim JM, Kim HI, Yi S, Ha Y, Yoon
DH and Kim KN: Comparison of functional and histological outcomes
after intralesional, intracisternal, and intravenous
transplantation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal
cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Acta Neurochir.
155:1943–1950. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Paul C, Samdani AF, Betz RR, Fischer I and
Neuhuber B: Grafting of human bone marrow stromal cells into spinal
cord injury: A comparison of delivery methods. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 34:328–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Anttila V, Haapanen H, Yannopoulos F,
Herajärvi J, Anttila T and Juvonen T: Review of remote ischemic
preconditioning: From laboratory studies to clinical trials. Scand
Cardiovasc J. 50:355–361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Torras J, Herrero-Fresneda I, Lloberas N,
Riera M, Ma Cruzado and Ma Grinyó J: Promising effects of ischemic
preconditioning in renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 61:2218–2227.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu X, Yu SP, Fraser JL, Lu Z, Ogle ME,
Wang JA and Wei L: Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned
mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via
enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 135:799–808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei L, Fraser JL, Lu ZY, Hu X and Yu SP:
Transplantation hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 46:635–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yuan LL, Guan YJ, Ma DD and Du HM: Optimal
concentration and time window for proliferation and differentiation
of neural stem cells from embryonic cerebral cortex: 5% oxygen
preconditioning for 72 hours. Neural Regen Res. 10:1516–1522. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fynes K, Tostoes R, Ruban L, Weil B, Mason
C and Veraitch FS: The differential effects of 2% oxygen
preconditioning on the subsequent differentiation of mouse and
human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1910–1922. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng G, Wang W, Yang C, Gao R, Yang X and
Ye X: Shaking improves the whole bone marrow adherent method of
purification. Mol Med Rep. 13:3133–3138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Okabe M, Ikawa M, Kominami K, Nakanishi T
and Nishimune Y: 'Green mice' as a source of ubiquitous green
cells. FEBS Lett. 407:313–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tan Q, Lui PP, Rui YF and Wong YM:
Comparison of potentials of stem cells isolated from tendon and
bone marrow for musculo-skeletal tissue engineering. Tissue Eng
Part A. 18:840–851. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fan W, Crawford R and Xiao Y: Enhancing in
vivo vascularized bone formation by cobalt chloride-treated bone
marrow stromal cells in a tissue engineered periosteum model.
Biomaterials. 31:3580–3589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang W, Wang Y, Deng G, Ma J, Huang X, Yu
J, Xi Y and Ye X: Transplantation of Hypoxic-Preconditioned bone
mesenchymal stem cells retards intervertebral disc degeneration via
enhancing implanted cell survival and migration in rats. Stem Cells
Int. 2018:75641592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Khan T, Havey RM, Sayers ST, Patwardhan A
and King WW: Animal models of spinal cord contusion injuries. Lab
Anim Sci. 49:161–172. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Falconer JC, Narayana PA, Bhattacharjee M
and Liu SJ: Characterization of an experimental spinal cord injury
model using waveform and morphometric analysis. Spine. 21:104–112.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC:
Graded histological and locomotor outcomes after spinal cord
contusion using the NYU weight-drop device versus transection. Exp
Neurol. 139:244–256. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Piotrowska A, Kwiatkowski K, Rojewska E,
Makuch W and Mika J: Maraviroc reduces neuropathic pain through
polarization of microglia and astroglia-Evidence from in vivo and
in vitro studies. Neuropharmacology. 108:207–219. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He FY, Feng WZ, Zhong J, Xu W, Shao HY and
Zhang YR: Effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine anesthesia on
Th1/Th2 of rat spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1355–1361. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chiaramonte R, Colombo M, Bulfamante G,
Falleni M, Tosi D, Garavelli S, De Simone D, Vigolo E, Todoerti K,
Neri A and Platonova N: Notch pathway promotes ovarian cancer
growth and migration via CXCR4/SDF1alpha chemokine system. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 66:134–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee SY, Kim HJ, Oh SC and Lee DH: Genipin
inhibits the invasion and migration of colon cancer cells by the
suppression of HIF-1α accumulation and VEGF expression Food Chem
Toxicol. 116:70–76. 2018.
|
|
47
|
Wang W, Huang X, Li J, Sun A, Yu J, Xie N
and Xi Y: Methane suppresses microglial activation related to
oxidative inflammatory, and apoptotic injury during spinal cord
injury in rats. 21908972017.
|
|
48
|
Shin T, Ahn M, Moon C, Kim S and Sim KB:
Alternatively activated macrophages in spinal cord injury and
remission: Another mechanism for repair? Mol Neurobiol.
47:1011–1019. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Murray M and Fischer I: Transplantation
and gene therapy: Combined approaches for repair of spinal cord
injury. Neuroscientist. 7:28–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yousefifard M, Rahimi-Movaghar V,
Nasirinezhad F, Baikpour M, Safari S, Saadat S, Moghadas Jafari A,
Asady H, Razavi Tousi SM and Hosseini M: Neural stem/progenitor
cell transplantation for spinal cord injury treatment; A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Neuroscience. 322:377–397. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ide C, Nakano N and Kanekiyo K: Cell
transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury-Bone marrow
stromal cells and choroid plexus epithelial cells. Neural Regen
Res. 11:1385–1388. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ide C and Kanekiyo K: Points regarding
cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury.
Neural Regen Res. 11:1046–1049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shroff G, Thakur D, Dhingra V, Baroli DS,
Khatri D and Gautam RD: Role of physiotherapy in the mobilization
of patients with spinal cord injury undergoing human embryonic stem
cells transplantation. Clin Transl Med. 5:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Botero L, Gomez RM and Chaparro O:
Pathogenesis of spinal cord injuries and mechanisms of repair
induced by olfactory ensheathing cells. Rev Neurol. 56:521–531.
2013.In Spanish. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kanno H, Pearse DD, Ozawa H, Itoi E and
Bunge MB: Schwann cell transplantation for spinal cord injury
repair: Its significant therapeutic potential and prospectus. Rev
Neurol. 26:121–128. 2015.
|
|
56
|
Saito F, Nakatani T, Iwase M, Maeda Y,
Murao Y, Suzuki Y, Fukushima M and Ide C: Administration of
cultured autologous bone marrow stromal cells into cerebrospinal
fluid in spinal injury patients: A pilot study. Restor Neurol
Neurosci. 30:127–136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Suzuki Y, Ishikawa N, Omae K, Hirai T,
Ohnishi K, Nakano N, Nishida H, Nakatani T, Fukushima M and Ide C:
Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell transplantation in spinal cord
injury patients by lumbar puncture. Restor Neurol Neurosci.
32:473–482. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tabak O, Gelisgen R, Erman H, Erdenen F,
Muderrisoglu C, Aral H and Uzun H: Oxidative lipid, protein, and
DNA damage as oxidative stress markers in vascular complications of
diabetes mellitus. Clin Invest Med. 34:E163–E171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jung K, Min DS, Sim KB, Ahn M, Kim H,
Cheong J and Shin T: Upregulation of phospholipase D1 in the spinal
cords of rats with clip compression injury. Neurosci Lett.
336:126–130. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ahmed Z: Effects of cathodal trans-spinal
direct current stimulation on lower urinary tract function in
normal and spinal cord injury mice with overactive bladder. J
Neural Eng. 14:0560022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Barboglio Romo PG and Gupta P: Peripheral
and sacral neuro-modulation in the treatment of neurogenic lower
urinary tract dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 44:453–461. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Miyazato M, Kadekawa K, Kitta T, Wada N,
Shimizu N, de Groat WC, Birder LA, Kanai AJ, Saito S and Yoshimura
N: New frontiers of basic science research in neurogenic lower
urinary tract dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 44:491–505. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wein AJ: Re: The management of neurogenic
lower urinary tract dysfunction after spinal cord injury. J Urol.
198:4882017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pearse DD, Lo TP Jr, Cho KS, Lynch MP,
Garg MS, Marcillo AE, Sanchez AR, Cruz Y and Dietrich WD:
Histopathological and behavioral characterization of a novel
cervical spinal cord displacement contusion injury in the rat. J
Neurotrauma. 22:680–702. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Falavigna A, Figueiró MP, Silva PGD,
Conzatti LP, Rizkalla EB, Santos SCD, Quadros FW and Radaelli L:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy after acute thoracic spinal cord injury:
Improvement of locomotor recovery in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
43:E442–E447. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Bu Z, Zheng L, Li A, Tu S and Shi Y:
Experimental study on gender difference in the recovery of nerve
function after spinal cord injury in rats. Chin J Exp Surg.
31:1440–1442. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
67
|
Lu Y, Chen W, Lin C, Wang J, Zhu M, Chen J
and Miao C: The protective effects of propofol against
CoCl2-induced HT22 cell hypoxia injury via
PP2A/CAMKIIalpha/nNOS pathway. BMC Anesthesiol. 17:322017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhang N, Hong B, Zhou C, Du X, Chen S,
Deng X, Duoerkun S, Li Q, Yang Y and Gong K: Cobalt
chloride-induced hypoxia induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in renal carcinoma cell lines. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 47:40–46.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pinzón-Daza ML, Cuellar-Saenz Y, Nualart
F, Ondo-Mendez A, Del Riesgo L, Castillo-Rivera F and Garzón R:
Oxidative stress promotes doxorubicin-induced pgp and BCRP
expression in colon Cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. J Cell
Biochem. 118:1868–1878. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kim YJ, Park SJ, Kim NR and Chin HS:
Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor (Valproic acid) on the
expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in human retinal
Müller cells. Korean J Ophthalmol. 31:80–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhu H and Bunn HF: Oxygen sensing and
signaling: Impact on the regulation of physiologically important
genes. Respir Physiol. 115:239–247. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rani A and Prasad S: CoCl2-induced
biochemical hypoxia down regulates activities and expression of
super oxide dismutase and catalase in cerebral cortex of mice.
Neurochem Res. 39:1787–1796. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Schumacker PT: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1
(HIF-1). Crit Care Med. 33:S423–S425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wright DE, Bowman EP, Wagers AJ, Butcher
EC and Weissman IL: Hematopoietic stem cells are uniquely selective
in their migratory response to chemokines. J Exp Med.
195:1145–1154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, Ghiran
I, Glodek AM and Silberstein LE: Human bone marrow stromal cells
express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine
receptors. Stem Cells. 24:1030–1041. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Derubeis AR and Cancedda R: Bone marrow
stromal cells (BMSCs) in bone engineering: Limitations and recent
advances. Ann Biomed Eng. 32:160–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Saeed H and Iqtedar M: Bone marrow stromal
cell (BMSC) and skeletal aging: Role of telomerase enzyme. Pak J
Pharm Sci. 27:321–333. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S, Jürgensen
JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Günzler V and Amann
K: Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors
ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol.
17:1970–1978. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Madonna R, Görbe A, Ferdinandy P and De
Caterina R: Glucose metabolism, hyperosmotic stress, and
reprogramming of somatic cells. Mol Biotechnol. 55:169–178. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Nallamshetty S, Chan SY and Loscalzo J:
Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity.
Free Radic Biol Med. 64:20–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|