|
1
|
Gemma M, Scola E, Baldoli C, Mucchetti M,
Pontesilli S, De Vitis A, Falini A and Beretta L: Auditory
functional magnetic resonance in awake (nonsedated) and
propofol-sedated children. Paediatr Anaesth. 26:521–530. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu Z, Lu Y, Wang J, Ding X, Chen J and
Miao C: The protective effect of propofol against TNF-alpha-induced
apoptosis was mediated via inhibiting iNOS/NO production and
maintaining intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in mouse
hippocampal HT22 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:664–672. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
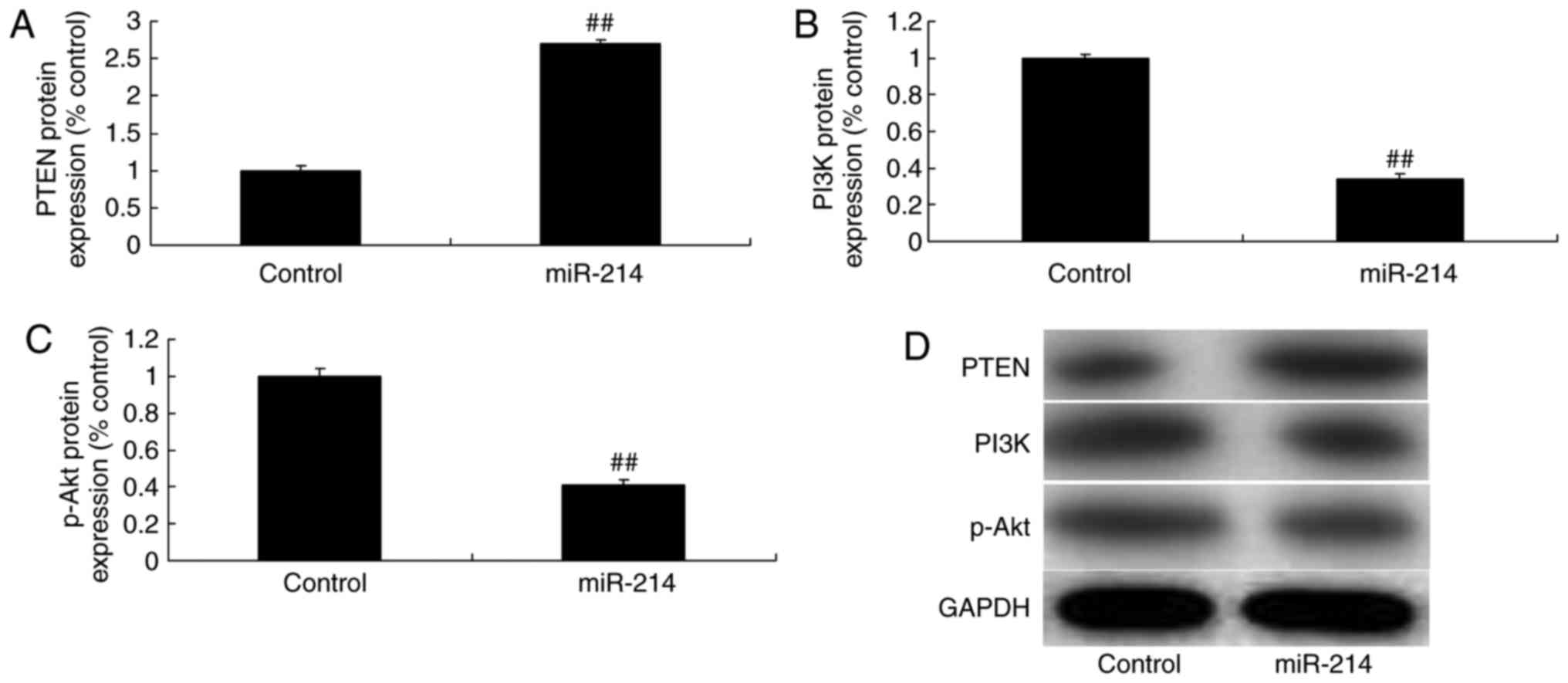
Eberl S, Preckel B, Bergman JJ, van Dieren
S and Hollmann MW: Satisfaction and safety using dexmedetomidine or
propofol sedation during endoscopic oesophageal procedures: A
randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 33:631–637. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim JH, Kim BK, Kim DW, Shin HY, Yu SB,
Kim DS, Ryu SJ, Kim KH, Jang HK and Kim JD: Effect of propofol on
microRNA expression profile in adipocyte-derived adult stem cells.
Chonnam Med J. 50:86–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hua FZ, Ying J, Zhang J, Wang XF, Hu YH,
Liang YP, Liu Q and Xu GH: Naringenin pre-treatment inhibits
neuroapoptosis and ameliorates cognitive impairment in rats exposed
to isoflurane anesthesia by regulating the PI3/Akt/PTEN signalling
pathway and suppressing NF-κB-mediated inflammation. Int J Mol Med.
38:1271–1280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Wang W, Zhang J, Li S, Zhao Y, Tan
L and Luo A: Involvement of caspase-3/PTEN signaling pathway in
isoflurane-induced decrease of self-renewal capacity of hippocampal
neural precursor cells. Brain Res. 1625:275–286. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang LY, Tang ZJ and Han YZ:
Neuroprotective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester against
sevofluraneinduced neuronal degeneration in the hippocampus of
neonatal rats involve MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Mol Med
Rep. 14:3403–3412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karnati HK, Panigrahi MK, Gutti RK, Greig
NH and Tamargo IA: miRNAs: Key players in neurodegenerative
disorders and epilepsy. J Alzheimers Dis. 48:563–580. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu EY, Cali CP and Lee EB: RNA metabolism
in neurodegenerative disease. Dis Model Mech. 10:509–518. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tanaka P, Goodman S, Sommer BR, Maloney W,
Huddleston J and Lemmens HJ: The effect of desflurane versus
propofol anesthesia on postoperative delirium in elderly obese
patients undergoing total knee replacement: A randomized,
controlled, double-blinded clinical trial. J Clin Anesth. 39:17–22.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu L, Wu AP, Yang Y, Liu SQ, Huang YZ,
Xie JF, Pan C, Yang CS and Qiu HB: Effects of propofol on
respiratory drive and patient-ventilator synchrony during pressure
support ventilation in postoperative patients: A prospective study.
Chin Med J (Engl). 130:1155–1160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Gong Y, Wang C, Wang X, Zhou Q,
Wang D, Guo L, Pi X, Zhang X, Luo S, et al: Online breath analysis
of propofol during anesthesia: Clinical application of membrane
inlet-ion mobility spectrometry. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.
59:319–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang ZH, Zhang JL, Duan YL, Zhang QS, Li
GF and Zheng DL: MicroRNA-214 participates in the neuroprotective
effect of Resveratrol via inhibiting alpha-synuclein expression in
MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mouse. Biomed Pharmacother.
74:252–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen B, Deng X, Wang B and Liu H:
Persistent neuronal apoptosis and synaptic loss induced by multiple
but not single exposure of propofol contribute to long-term
cognitive dysfunction in neonatal rats. J Toxicol Sci. 41:627–636.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Wu C, Han B, XU F, MAO M, GUO X
and Wang J: Dexmedetomidine attenuates repeated propofol
exposure-induced hippocampal apoptosis, PI3K/Akt/Gsk-3β signaling
disruption, and juvenile cognitive deficits in neonatal rats. Mol
Med Rep. 14:769–775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Xia Y, Xu Z and Deng X: Propofol
suppressed hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in HBVSMC by
regulation of the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase3, Kir6.1, and
p-JNK. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:15187382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
An K, Shu H, Huang W, Huang X, Xu M, Yang
L, Xu K and Wang C: Effects of propofol on pulmonary inflammatory
response and dysfunction induced by cardiopulmonary bypass.
Anaesthesia. 63:1187–1192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou CH, Zhu YZ, Zhao PP, Xu CM, Zhang MX,
Huang H, Li J, Liu L and Wu YQ: Propofol inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in spinal
astrocytes via the toll-like receptor 4/MyD88-dependent nuclear
Factor-κB, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases1/2, and
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Anesth Analg.
120:1361–1368. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma J, Xiao W, Wang J, Wu J, Ren J, Hou J,
Gu J, Fan K and Yu B: Propofol inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome and
attenuates blast-induced traumatic brain injury in rats.
Inflammation. 39:2094–2103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li D, Liu J, Guo B, Liang C, Dang L, Lu C,
He X, Cheung HY, Xu L, Lu C, et al: Osteoclast-derived exosomal
miR-2143p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun.
7:108722016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Du YM, Xu F, Liu D and Wang YL:
Propofol prevents hippocampal neuronal loss and memory impairment
in cerebral ischemia injury through promoting PTEN degradation. J
Mol Neurosci. 60:63–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng Y, Bu J, Yu L, Chen J and Liu H:
Nobiletin improves propofol-induced neuroprotection via regulating
Akt/mTOR and TLR 4/NF-κB signaling in ischemic brain injury in
rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:494–503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Ha T, Hu Y, Lu C, Liu L, Zhang X,
Kao R, Kalbfleisch J, Williams D and Li C: MicroRNA-214 protects
against hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cell damage and myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of PTEN and Bim1
expression. Oncotarget. 7:86926–86936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chu Q, Sun Y, Cui J and Xu T: Inducible
microRNA-214 contributes to the suppression of NF-kappaB-mediated
inflammatory response via targeting myd88 gene in fish. J Biol
Chem. 292:5282–5290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|