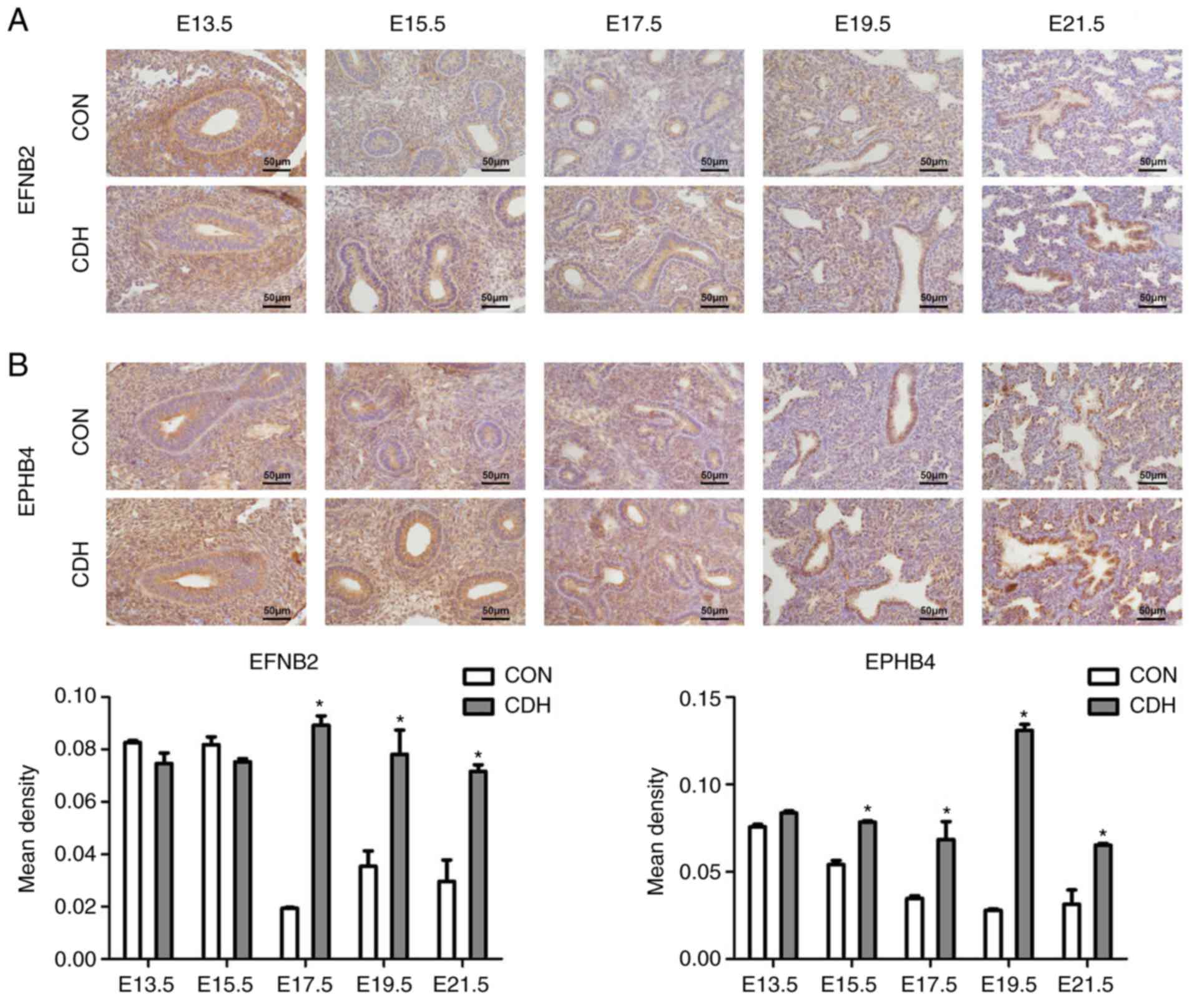
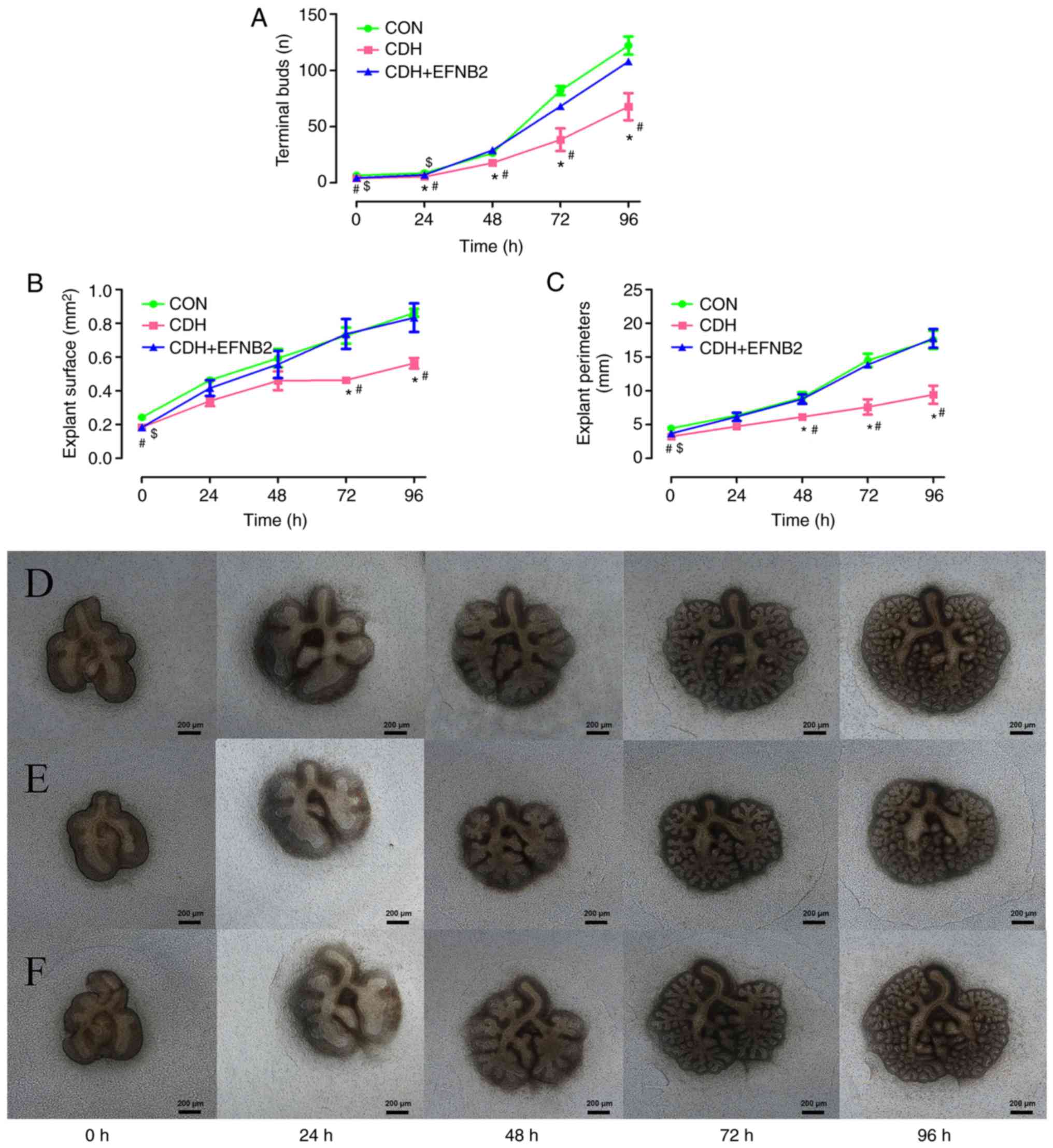
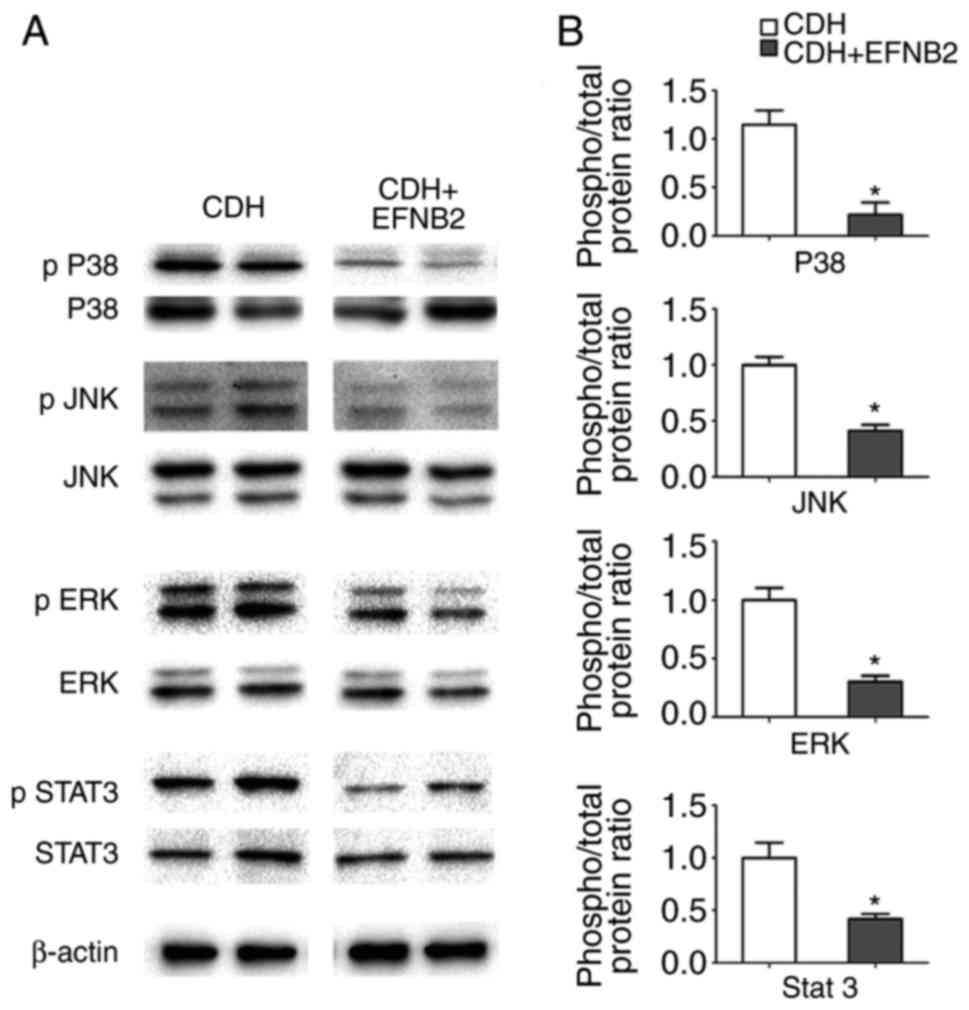
|
1
|
Torfs CP, Curry CJ, Bateson TF and Honoré
LH: A population-based study of congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Teratology. 46:555–565. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Skari H, Bjornland K, Haugen G, Egeland T
and Emblem R: Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: A meta-analysis of
mortality factors. J Pediatr Surg. 35:1187–1197. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pober BR, Russell MK and Ackerman KG:
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Overview.
|
|
4
|
van Loenhout RB, Tibboel D, Post M and
Keijzer R: Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: Comparison of animal
models and relevance to the human situation. Neonatology.
96:137–149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pober BR: Overview of epidemiology,
genetics, birth defects, and chromosome abnormalities associated
with CDH. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 145C:158–171. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peetsold MG, Heij HA, Kneepkens CM,
Nagelkerke AF, Huisman J and Gemke RJ: The long-term follow-up of
patients with a congenital diaphragmatic hernia: A broad spectrum
of morbidity. Pediatr Surg Int. 25:1–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Muratore CS, Kharasch V, Lund DP, Sheils
C, Friedman S, Brown C, Utter S, Jaksic T and Wilson JM: Pulmonary
morbidity in 100 survivors of congenital diaphragmatic hernia
monitored in a multidisciplinary clinic. J Pediatr Surg.
36:133–140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Badillo A and Gingalewski C: Congenital
diaphragmatic hernia: Treatment and outcomes. Semin Perinatol.
38:92–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bargy F, Beaudoin S and Barbet P: Fetal
lung growth in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Fetal Diagn Ther.
21:39–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Acker SN, Mandell EW, Sims-Lucas S, Gien
J, Abman SH and Galambos C: Histologic identification of prominent
intrapul-monary anastomotic vessels in severe congenital
diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr. 166:178–183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sluiter I, Reiss I, Kraemer U, Krijger Rd,
Tibboel D and Rottier RJ: Vascular abnormalities in human newborns
with pulmonary hypertension. Expert Rev Respir Med. 5:245–256.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guilbert TW, Gebb SA and Shannon JM: Lung
hypoplasia in the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia
occurs early in development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
279:L1159–L1171. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J and
Takaku F: A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the
eph gene. Science. 238:1717–1720. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pasquale EB: Eph-ephrin bidirectional
signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 133:38–52. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Klein R: Eph/ephrin signalling during
development. Development. 139:4105–4109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kania A and Klein R: Mechanisms of
ephrin-eph signalling in development, physiology and disease. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:240–256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G and Pasquale EB:
Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0091592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng N, Brantley DM and Chen J: The
ephrins and eph receptors in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 13:75–85. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Downard CD, Jaksic T, Garza JJ, Dzakovic
A, Nemes L, Jennings RW and Wilson JM: Analysis of an improved
survival rate for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg.
38:729–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kinane TB: Lung development and
implications for hypoplasia found in congenital diaphragmatic
hernia. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 145C:117–124. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Warburton D, Schwarz M, Tefft D,
Flores-Delgado G, Anderson KD and Cardoso WV: The molecular basis
of lung morphogenesis. Mech Dev. 92:55–81. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cardoso WV: Molecular regulation of lung
development. Annu Rev Physiol. 63:471–494. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Groenman F, Unger S and Post M: The
molecular basis for abnormal Human lung development. Biol Neonate.
87:164–177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cardoso WV and Lü J: Regulation of early
lung morphogenesis: Questions, facts and controversies.
Development. 133:1611–1124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: Keratinocyte and
hepatocyte growth factors in the lung: Roles in lung development
inflammation and repair. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
282:L924–L940. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Nakayama M, Pitulescu ME, Schmidt
TS, Bochenek ML, Sakakibara A, Adams S, Davy A, Deutsch U, Lüthi U,
et al: Ephrin-B2 controls VEGF-induced angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis. Nature. 465:483–486. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vadivel A, van Haaften T, Alphonse RS,
Rey-Parra GJ, Ionescu L, Haromy A, Eaton F, Michelakis E and
Thébaud B: Critical role of the axonal guidance cue EphrinB2 in
lung growth, angiogenesis, and repair. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
185:564–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bennett KM, Afanador MD, Lal CV, Xu H,
Persad E, Legan SK, Chenaux G, Dellinger M, Savani RC, Dravis C, et
al: Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling increases α5β1 integrin mediated
fibronectin deposition and reduces distal lung compliance. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:680–687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sikkema AH, den Dunnen WF, Hulleman E, van
Vuurden DG, Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Scherpen FJ, Kampen KR, Hoving
EW, Kamps EW, et al: EphB2 activity plays a pivotal role in
pediatric medulloblastoma cell adhesion and invasion. Neuro Oncol.
14:1125–1135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nogueira-Silva C, Piairo P, Carvalho-Dias
E, Veiga C, Moura RS and Correia-Pinto J: The role of glycoprotein
130 family of cytokines in fetal rat lung development. PLoS One.
8:e676072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nogueira-Silva C, Piairo P, Carvalho-Dias
E, Peixoto FO, Moura RS and Correia-Pinto J: Leukemia inhibitory
factor in rat fetal lung development: Expression and functional
studies. PLoS One. 7:e305172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kling DE, Lorenzo HK, Trbovich AM, Kinane
TB, Donahoe PK and Schnitzer JJ: MEK-1/2 inhibition reduces
branching morphogenesis and causes mesenchymal cell apoptosis in
fetal rat lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L370–L378.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Piairo P, Moura RS, Nogueira-Silva C and
Correia-Pinto J: The apelinergic system in the developing lung:
Expression and signaling. Peptides. 32:2474–2483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boucherat O, Nadeau V, Bérubé-Simard FA,
Charron J and Jeannotte L: Crucial requirement of ERK/MAPK
signaling in respiratory tract development. Development.
21:3197–3211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Boucherat O, Landry-Truchon K, Aoidi R,
Houde N, Nadeau V, Charron J and Jeannotte L: Lung development
requires an active ERK/MAPK pathway in the lung mesenchyme. Dev
Dyn. 246:72–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|