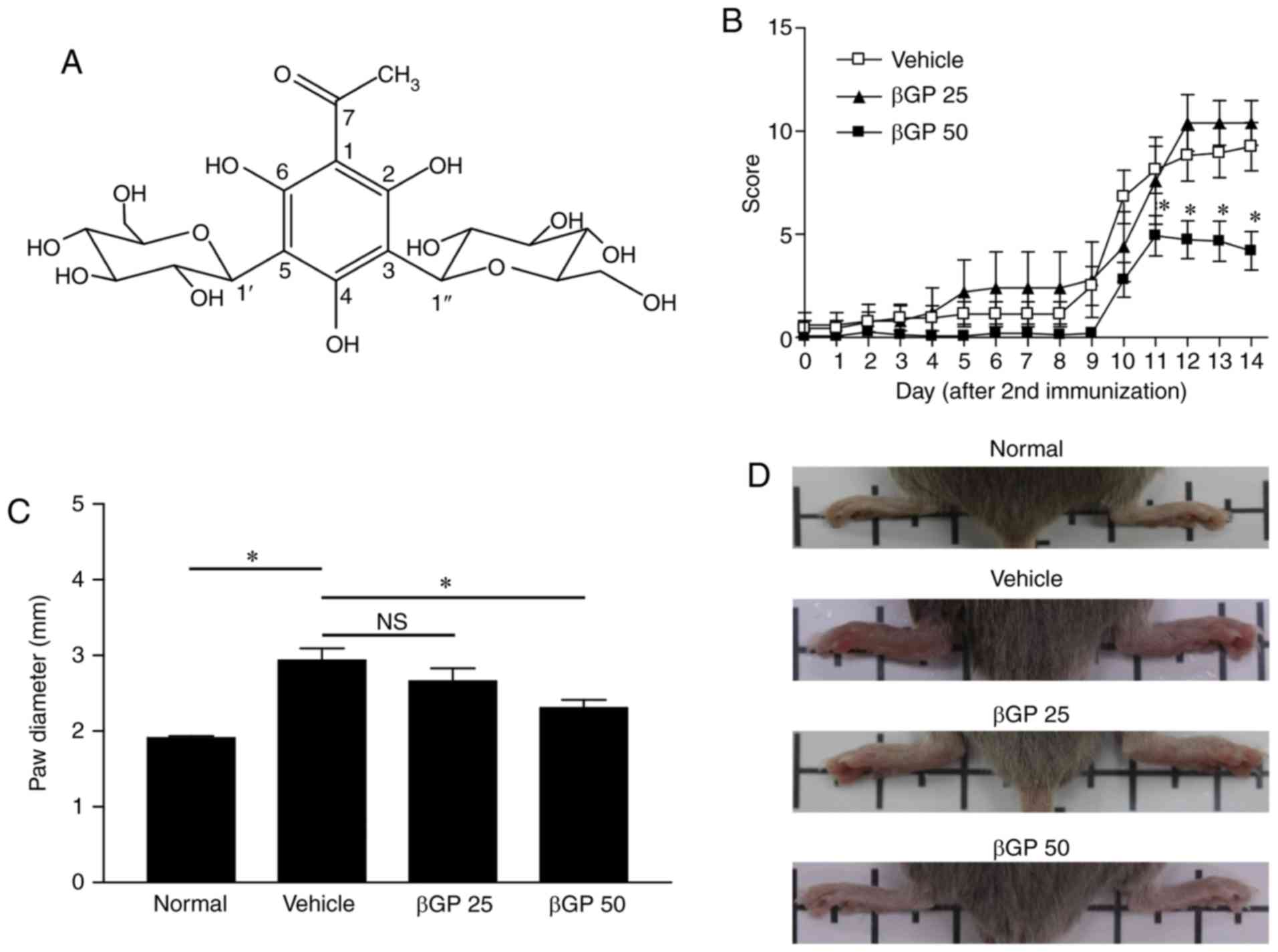
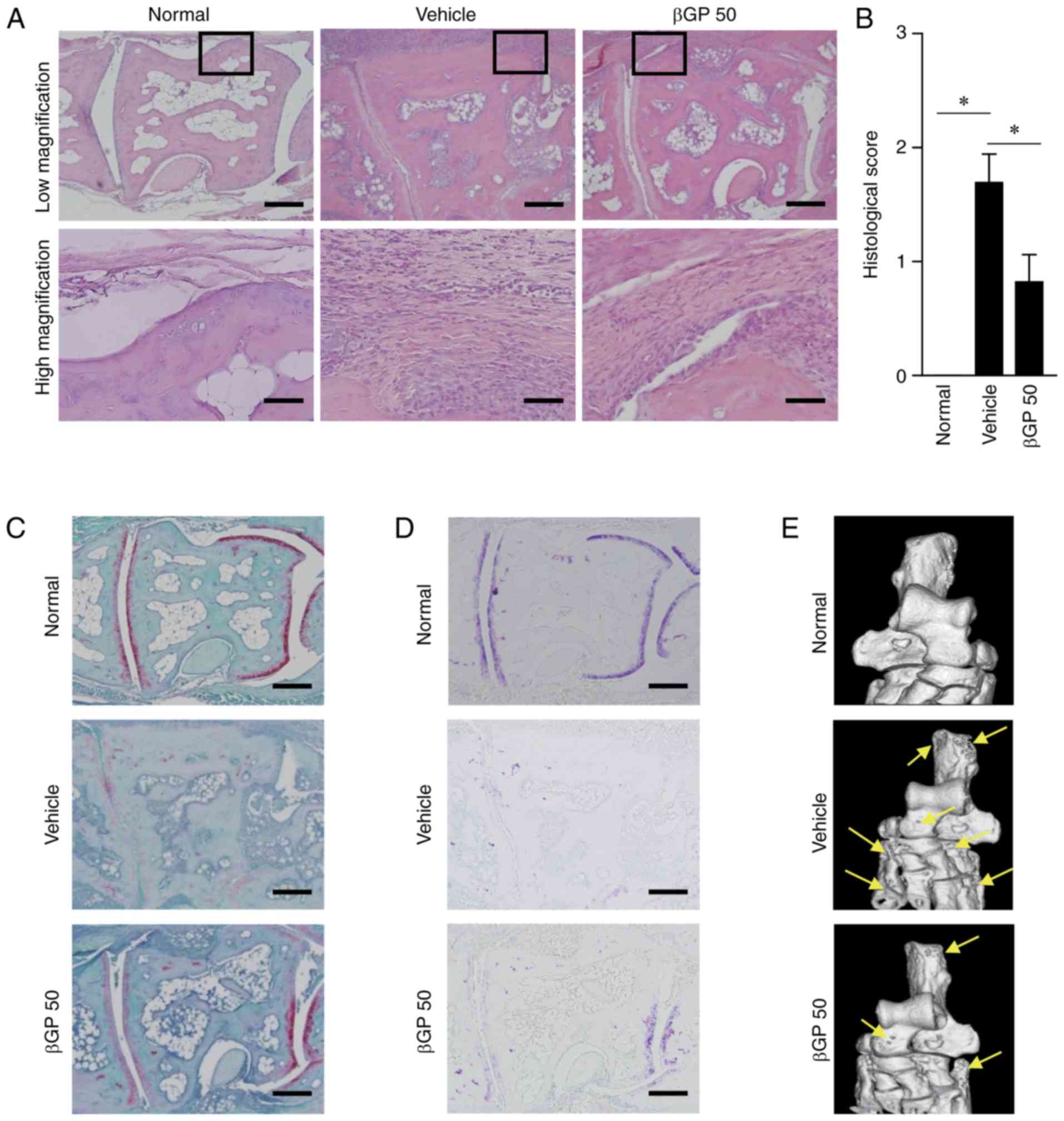
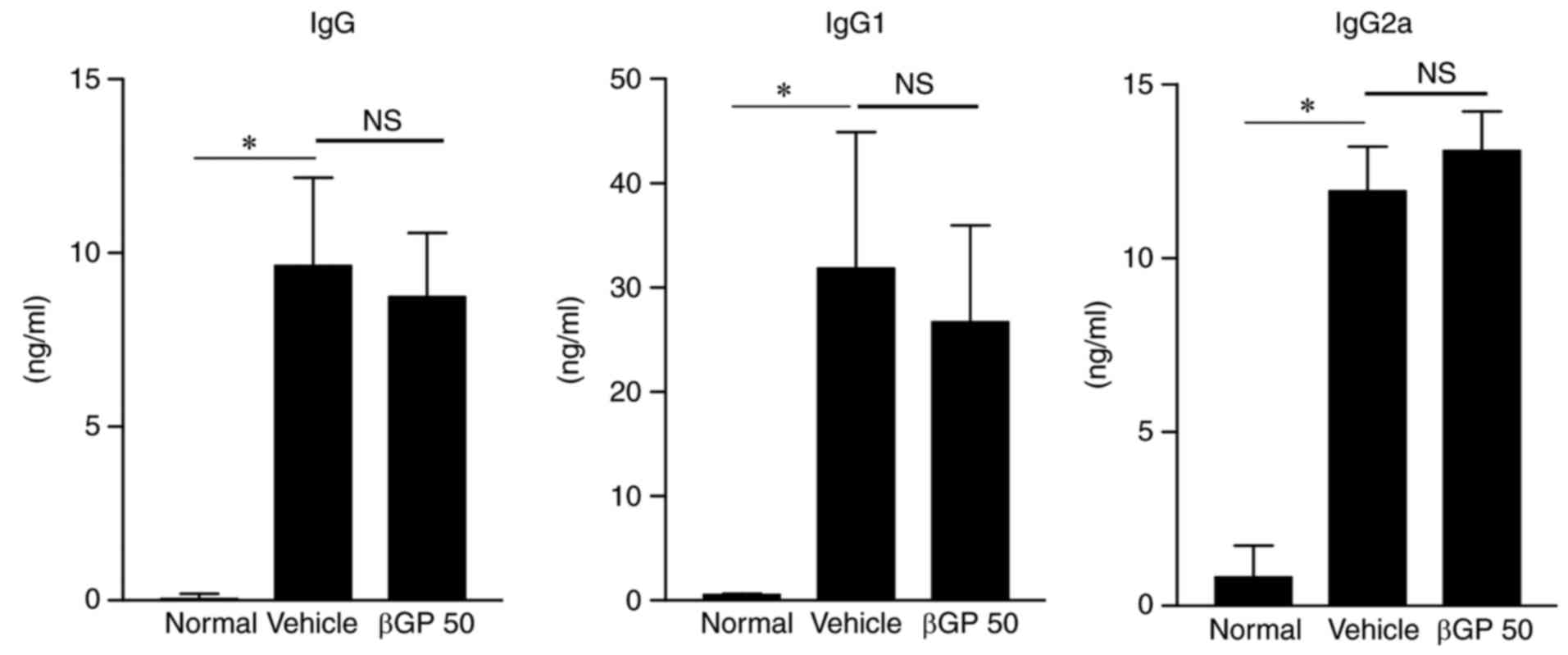
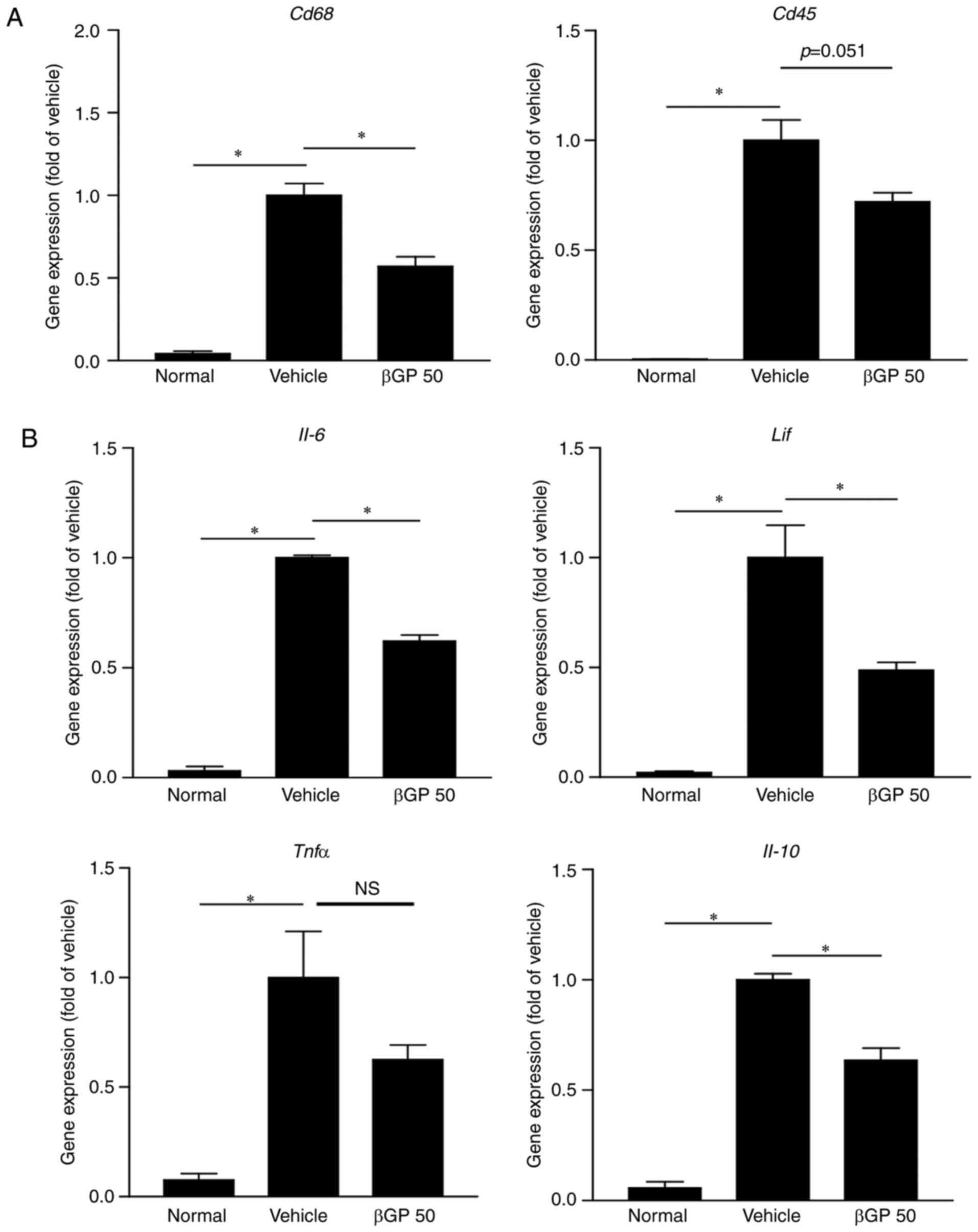
|
1
|
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM,
Therneau TM and Gabriel SE: Is the incidence of rheumatoid
arthritis rising? Results from olmsted county, minnesota,
1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1576–1582. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang SH, Ping LF, Sun FY, Wang XL and Sun
ZJ: Protective effect of taraxasterol against rheumatoid arthritis
by the modulation of inflammatory responses in mice. Exp Ther Med.
12:4035–4040. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xu H, Wang J, Wang C, Chang G, Lin Y,
Zhang H, Zhang H, Li Q and Pang T: Therapeutic effects of
micheliolide on a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med
Rep. 11:489–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Choy E: Understanding the dynamics:
Pathways involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 5(Suppl 51): pp. v3–v11. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shin JS, Yun CH, Chung KS, Bang MH, Baek
NI, Chung HG, Cho YW and Lee KT: Standardized ethyl acetate
fraction from the roots of brassica rapa attenuates the
experimental arthritis by down regulating inflammatory responses
and inhibiting NF-κB activation. Food Chem Toxicol. 66:96–106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song YW and Kang EH: Autoantibodies in
rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid factors and anticitrullinated
protein antibodies. QJM. 103:139–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Hashizume M, Hayakawa N and Mihara M: IL-6
trans-signalling directly induces RANKL on fibroblast-like synovial
cells and is involved in RANKL induction by TNF-alpha and IL-17.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 47. pp. 1635–1640. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Weitzmann MN: The role of inflammatory
cytokines, the RANKL/OPG axis, and the immunoskeletal interface in
physiological bone turnover and osteoporosis. Scientifica (Cairo).
2013:1257052013.
|
|
9
|
Srirangan S and Choy EH: The role of
interleukin 6 in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Ther
Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2:247–256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwan Tat S, Padrines M, Théoleyre S,
Heymann D and Fortun Y: IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: Interrelations
in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
15:49–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Charles JF and Aliprantis AO: Osteoclasts:
More than 'bone eaters'. Trends Mol Med. 20:449–459. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kamperdick C, Van NH, Sung TV and Adam G:
Benzopyrans from Melicope ptelefolia leaves. Phytochemistry.
45:1049–1056. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hong Van N, Kamperdick C, Van Sung T and
Adam G: Benzopyran dimers from Melicope ptelefolia. Phytochemistry.
48:1055–1057. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nguyen NH, Ha TK, Choi S, Eum S, Lee CH,
Bach TT, Chinh VT and Oh WK: Chemical constituents from Melicope
pteleifolia leaves. Phytochemistry. 130:291–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sulaiman MR, Mohd Padzil A, Shaari K,
Khalid S, Shaik Mossadeq WM, Mohamad AS, Ahmad S, Akira A, Israf D
and Lajis N: Antinociceptive activity of Melicope ptelefolia
ethanolic extract in experimental animals. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:9376422010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Loi DT: Nhung cay Thuoc va vi thuoc Viet
Nam (Glossary of Vietnamese Medicinal Plants). Science and Technics
Publication; Hanoi, Vietnam: 1977
|
|
17
|
Perry LM and Metzger J: Medicinal Plants
of East and Southeast Asia: Attributed Properties and Uses. MIT
Press; Cambridge, UK: 1980
|
|
18
|
Lee CH, Bae SJ and Kim M:
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation 1 as a
novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep.
7:118892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun J, Jia Y, Li R, Guo J, Sun X, Liu Y,
Li Y, Yao H, Liu X, Zhao J and Li Z: Altered influenza virus
haemagglutinin (HA)-derived peptide is potent therapy for CIA by
inducing Th1 to Th2 shift. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:348–358. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Schett G and Gravallese E: Bone erosion in
rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 8:656–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmitz N, Laverty S, Kraus VB and Aigner
T: Basic methods in histopathology of joint tissues. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 3(Suppl 18): S113–S116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van Boekel MA, Vossenaar ER, van den
Hoogen FH and van Venrooij WJ: Autoantibody systems in rheumatoid
arthritis: Specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic value. Arthritis
Res. 4:87–93. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yanni G, Whelan A, Feighery C and
Bresnihan B: Synovial tissue macrophages and joint erosion in
rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 53:39–44. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kinne RW, Bräuer R, Stuhlmüller B,
Palombo-Kinne E and Burmester GR: Macrophages in rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2:189–202. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Davignon JL, Hayder M, Baron M, Boyer JF,
Constantin A, Apparailly F, Poupot R and Cantagrel A: Targeting
monocytes/macrophages in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 52. pp. 590–598. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Baumann H and Kushner I: Production of
interleukin-6 by synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J
Pathol. 152:641–644. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Palmqvist P, Persson E, Conaway HH and
Lerner UH: IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M
stimulate bone resorption and regulate the expression of receptor
activator of NF-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and receptor
activator of NF-kappa B in mouse calvariae. J Immunol.
169:3353–3362. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ospelt C: Synovial fibroblasts in 2017.
RMD Open. 3:e0004712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Durand M, Boire G, Komarova SV, Dixon SJ,
Sims SM, Harrison RE, Nabavi N, Maria O, Manolson MF, Mizianty M,
et al: The increased in vitro osteoclastogenesis in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis is due to increased percentage of precursors
and decreased apoptosis-the In vitro osteoclast differentiation in
arthritis (IODA) study. Bone. 48:588–596. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hikata T, Takaishi H, Takito J, Hakozaki
A, Furukawa M, Uchikawa S, Kimura T, Okada Y, Matsumoto M,
Yoshimura A, et al: PIAS3 negatively regulates RANKL-mediated
osteoclastogenesis directly in osteoclast precursors and indirectly
via osteoblasts. Blood. 113:2202–2212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H and Aringer M:
The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 25(Suppl 46): S4–S11. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaplan C, Valdez JC, Chandrasekaran R,
Eibel H, Mikecz K, Glant TT and Finnegan A: Th1 and Th2 cytokines
regulate proteoglycan-specific autoantibody isotypes and arthritis.
Arthritis Res. 4:54–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J,
Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, Stevens RM and Shaw T:
Efficacy of B-Cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 350:2572–2281. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brennan F and Foey A: Cytokine regulation
in RA synovial tissue: Role of T cell/macrophage contact-dependent
interactions. Arthritis Res. 3(Suppl 4): S177–S182. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Alves CH, Farrell E, Vis M, Colin EM and
Lubberts E: Animal models of bone loss in inflammatory arthritis:
From cytokines in the bench to novel treatments for bone loss in
the bedside-a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
51:27–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Siebert S, Tsoukas A, Robertson J and
McInnes I: Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis
and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev. 67:280–309. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
St C: Interleukin 10 treatment for
rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 58(Suppl 1): I99–I102. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Brzustewicz E and Bryl E: The role of
cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-practical and
potential application of cytokines as biomarkers and targets of
personalized therapy. Cytokine. 76:527–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vane JR: Inhibition of prostaglandin
synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New
Biol. 231:232–235. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ogston NC, Karastergiou K,
Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Bhome R, Madani R, Stables M, Gilroy D,
Flachs P, Hensler M, Kopecky J and Mohamed-Ali V: Low-dose
acetylsalicylic acid inhibits the secretion of interleukin-6 from
white adipose tissue. Int J Obes (Lond). 32:1807–1815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nakao S, Ogtata Y, Shimizu E, Yamazaki M,
Furuyama S and Sugiya H: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
(TNF-alpha)-induced prostaglandin E2 release is mediated by the
activation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription via NFkappaB
in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 238:11–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jones DH, Kong YY and Penninger JM: Role
of RANKL and RANK in bone loss and arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
2(Suppl 61): ii32–ii39. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Feng X: RANKing intracellular signaling in
osteoclasts. IUBMB Life. 57:389–395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Boyce BF and Xing L: Functions of
RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 473:139–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tawara K; Oxford JT; Jorcyk CL: Clinical
significance of interleukin (IL)-6 in cancer metastasis to bone:
Potential of anti-IL-6 therapies. Cancer Manag Res. 3:177–189.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miyamoto T, Mori T, Yoshimura A and Toyama
T: STAT3 is critical to promote inflammatory cytokines and RANKL
expression in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 14(Suppl
1): P432012. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
O'Brien CA, Gubrij I, Lin SC, Saylorsi RL
and Manolagas SC: STAT3 activation in stromal/osteoblastic cells is
required for induction of the receptor activator of NF-κB ligand
and stimulation of osteoclastogenesis by gp130-utilizing cytokines
or interleukin-1 but not 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 or parathyroid
hormone. J Biol Chem. 274:19301–19308. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|