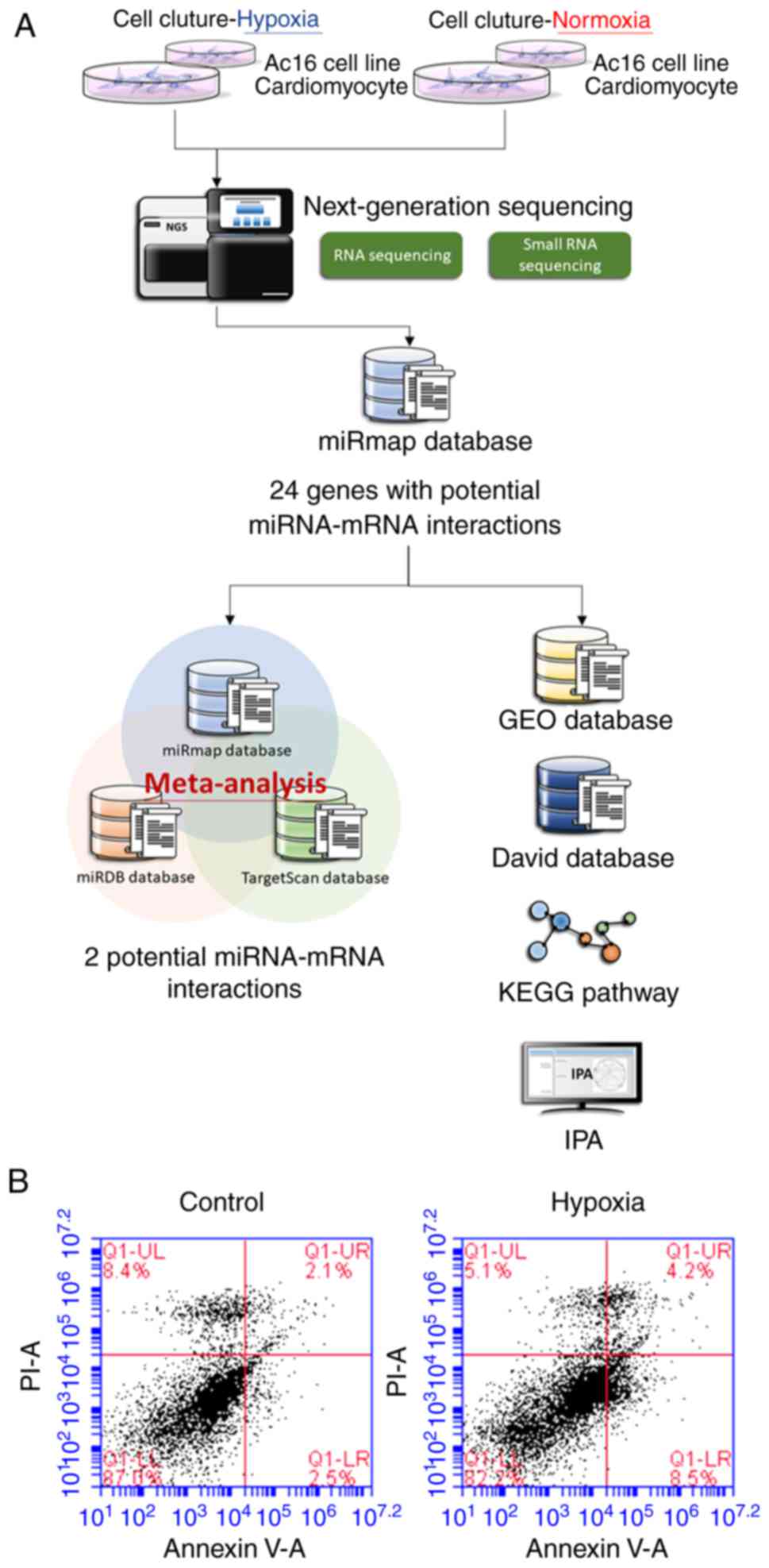
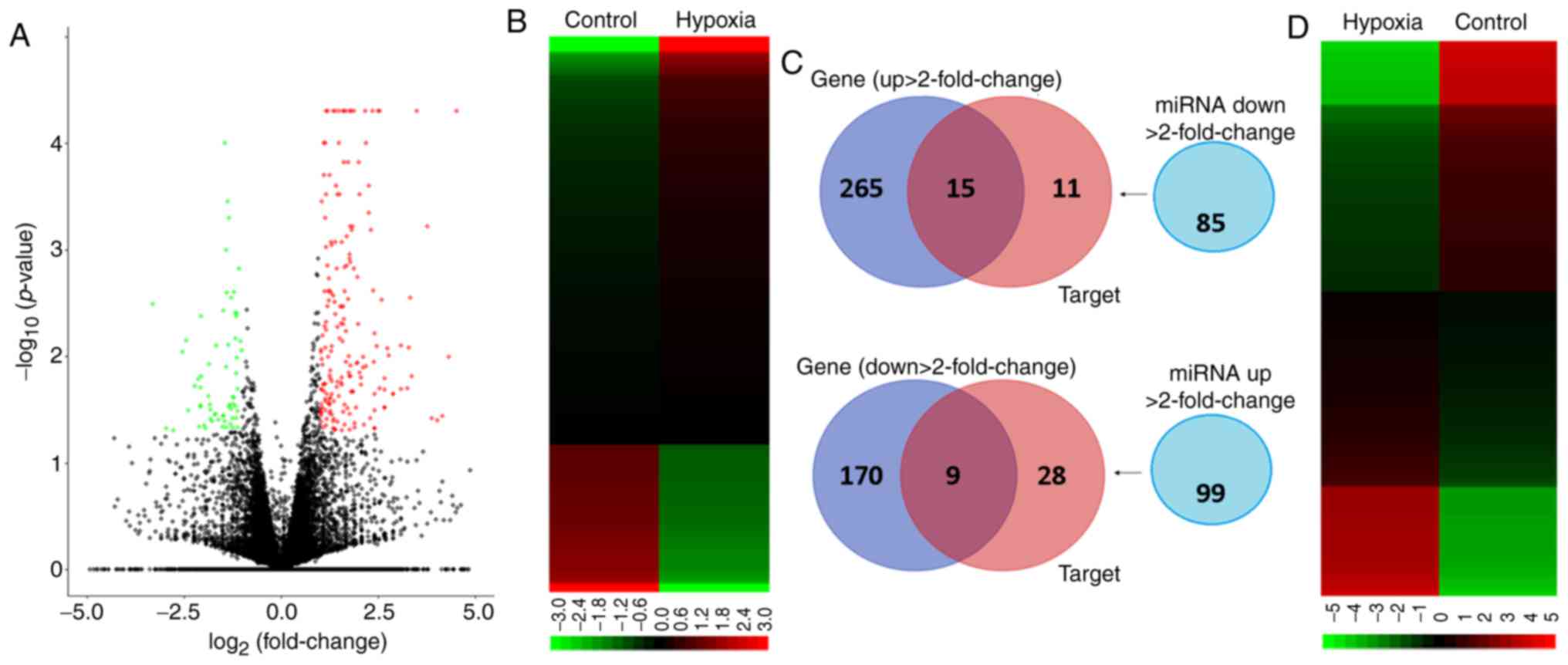
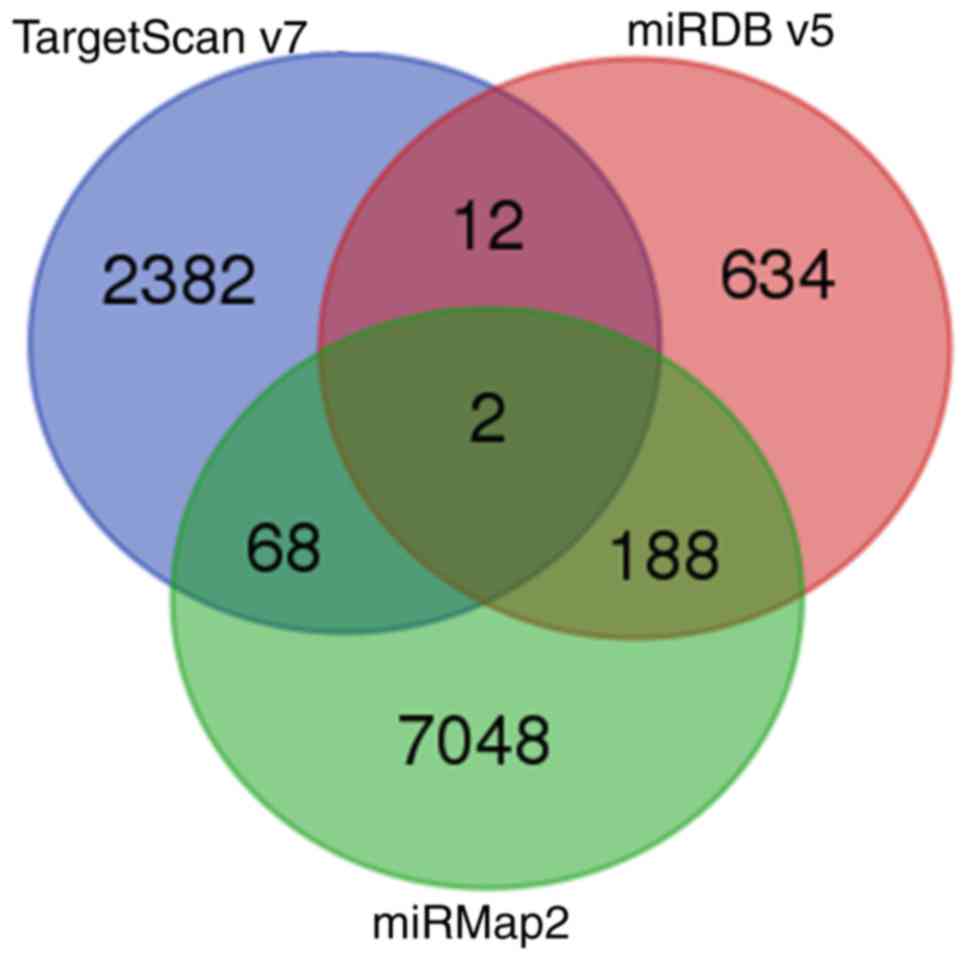
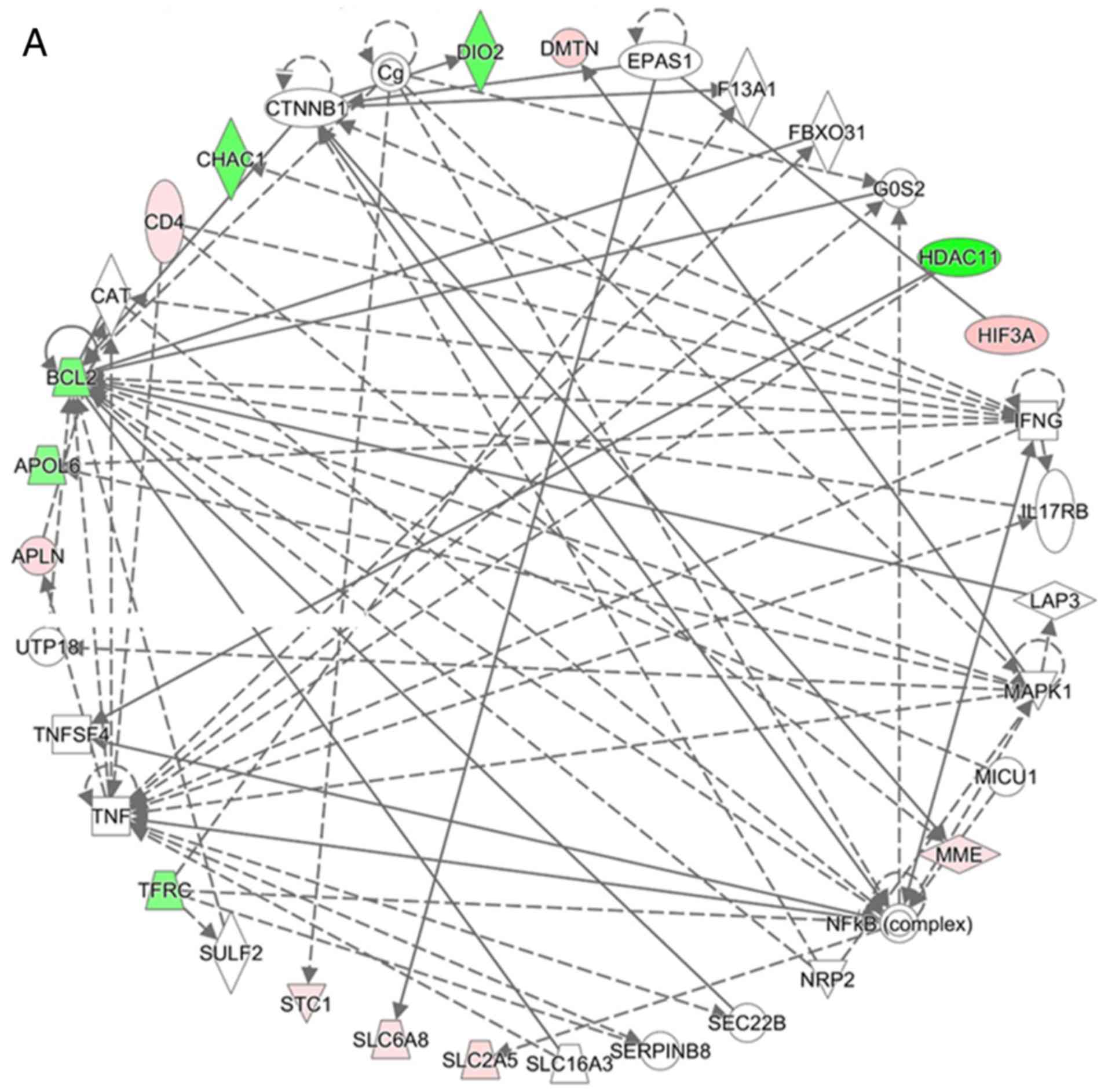
|
1
|
Lee WH, Hsu PC, Chu CY, Su HM, Lee CS, Yen
HW, Lin TH, Voon WC, Lai WT and Sheu SH: Cardiovascular events in
patients with atherothrombotic disease: A population-based
longitudinal study in taiwan. PLoS One. 9:e925772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soler EP and Ruiz VC: Epidemiology and
risk factors of cerebral ischemia and ischemic heart diseases:
Similarities and differences. Curr Cardiol Rev. 6:138–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Kang PM, Haunstetter A, Aoki H, Usheva A
and Izumo S: Morphological and molecular characterization of adult
cardiomyocyte apoptosis during hypoxia and reoxygenation. Circ Res.
87:118–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun T, Dong YH, Du W, Shi CY, Wang K,
Tariq MA, Wang JX and Li PF: The Role of MicroRNAs in myocardial
infarction: From molecular mechanism to clinical application. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:pii: E745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Adachi S, Ito H, Tamamori-Adachi M, Ono Y,
Nozato T, Abe S, Ikeda Ma, Marumo F and Hiroe M: Cyclin A/cdk2
activation is involved in hypoxia-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 88:408–414. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ,
Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, Caforio ALP, Crea F, Goudevenos JA,
Halvorsen S, et al: 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute
myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment
elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial
infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the
European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 39:119–177.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Krijnen PA, Nijmeijer R, Meijer CJ, Visser
CA, Hack CE and Niessen HW: Apoptosis in myocardial ischaemia and
infarction. J Clin Pathol. 55:801–811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takemura G and Fujiwara H: Morphological
aspects of apoptosis in heart diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 10:56–75.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Biondi-Zoccai GG, Abbate A, Vasaturo F,
Scarpa S, Santini D, Leone AM, Parisi Q, De Giorgio F, Bussani R,
Silvestri F, et al: Increased apoptosis in remote non-infarcted
myocardium in multivessel coronary disease. Int J Cardiol.
94:105–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abbate A, Melfi R, Patti G, Baldi F,
D'Ambrosio A, Manzoli A, Baldi A and Di Sciascio G: Apoptosis in
recent myocardial infarction. Clin Ter. 151:247–251.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M,
Henriksen K, Parvinen M and Voipio-Pulkki LM: Apoptosis in human
acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 95:320–323. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abbate A, Bussani R, Biondi-Zoccai GG,
Santini D, Petrolini A, De Giorgio F, Vasaturo F, Scarpa S,
Severino A, Liuzzo G, et al: Infarct-related artery occlusion,
tissue markers of ischaemia, and increased apoptosis in the
peri-infarct viable myocardium. Eur Heart J. 26:2039–2045. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van Dijk EL, Auger H, Jaszczyszyn Y and
Thermes C: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology.
Trends Genet. 30:418–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mardis ER: Next-generation sequencing
platforms. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 6:287–303. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen SC, Chen FW, Hsu YL and Kuo PL:
Systematic analysis of transcriptomic profile of renal cell
carcinoma under long-term hypoxia using next-generation sequencing
and bioinformatics. Int J Mol Sci. 18:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Blue GM, Kirk EP, Giannoulatou E,
Dunwoodie SL, Ho JW, Hilton DC, White SM, Sholler GF, Harvey RP and
Winlaw DS: Targeted next-generation sequencing identifies
pathogenic variants in familial congenital heart disease. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 64:2498–2506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lubitz SA and Ellinor PT: Next-generation
sequencing for the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia syndromes. Heart
Rhythm. 12:1062–1070. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia P, Liu Y and Cheng Z: Signaling
Pathways in Cardiac Myocyte Apoptosis. Biomed Res Int.
2016:95832682016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chiong M, Wang ZV, Pedrozo Z, Cao DJ,
Troncoso R, Ibacache M, Criollo A, Nemchenko A, Hill JA and
Lavandero S: Cardiomyocyte death: Mechanisms and translational
implications. Cell Death Dis. 2:e2442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Regula KM, Ens K and Kirshenbaum LA:
Inducible expression of BNIP3 provokes mitochondrial defects and
hypoxia-mediated cell death of ventricular myocytes. Circ Res.
91:226–231. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yen MC, Shih YC, Hsu YL, Lin ES, Lin YS,
Tsai EM, Ho YW, Hou MF and Kuo PL: Isolinderalactone enhances the
inhibition of SOCS3 on STAT3 activity by decreasing miR-30c in
breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1356–1364. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sheu CC, Tsai MJ, Chen FW, Chang KF, Chang
WA, Chong IW, Kuo PL and Hsu YL: Identification of novel genetic
regulations associated with airway epithelial homeostasis using
next-generation sequencing data and bioinformatics approaches.
Oncotarget. 8:82674–82688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bolger AM, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Friedlander MR, Mackowiak SD, Li N, Chen W
and Rajewsky N: miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds
of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:37–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vejnar CE and Zdobnov EM: MiRmap:
Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:11673–11683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Costello CM, Howell K, Cahill E, McBryan
J, Konigshoff M, Eickelberg O, Gaine S, Martin F and McLoughlin P:
Lung-selective gene responses to alveolar hypoxia: Potential role
for the bone morphogenetic antagonist gremlin in pulmonary
hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 295:L272–L284.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kacimi R, Chentoufi J, Honbo N, Long CS
and Karliner JS: Hypoxia differentially regulates stress proteins
in cultured cardiomyocytes: Role of the p38 stress-activated kinase
signaling cascade, and relation to cytoprotection. Cardiovasc Res.
46:139–150. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koeppen M, Lee JW, Seo SW, Brodsky KS,
Kreth S, Yang IV, Buttrick PM, Eckle T and Eltzschig HK:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 2-alpha-dependent induction of
amphiregulin dampens myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nat
Commun. 9:8162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matkovich SJ, Van Booven DJ, Youker KA,
Torre-Amione G, Diwan A, Eschenbacher WH, Dorn LE, Watson MA,
Margulies KB and Dorn GW II: Reciprocal regulation of myocardial
microRNAs and messenger RNA in human cardiomyopathy and reversal of
the microRNA signature by biomechanical support. Circulation.
119:1263–1271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nallamshetty S, Chan SY and Loscalzo J:
Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity.
Free Radic Biol Med. 64:20–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ong SB, Katwadi K, Kwek XY, Ismail NI,
Chinda K, Ong SG and Hausenloy DJ: Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic
targets for preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 22:247–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zhou M and Liu C:
MicroRNA-129-5p inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
by targeting Wnt5a. Exp Ther Med. 12:2651–2656. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng A, Yin J, Li Y, Li R, Wang Z, Zhou X,
Jin X, Shen F, Yan W and You Y: miR-129-5p targets Wnt5a to block
PKC/ERK/NF-kappaB and JNK pathways in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
9:3942018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Majumdar G and Raghow R: Trichostatin A
induces a unique set of microRNAs including miR-129-5p that blocks
cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression and proliferation in H9c2
cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 415:39–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q and Yu J: MiR-129-5p suppresses
gastric cancer cell invasion and proliferation by inhibiting
COL1A1. Biochem Cell Biol. 96:19–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zheng Z, Bao F, Chen X, Huang H and Zhang
X: MicroRNA-330-3p Expression Indicates Good Prognosis and
Suppresses Cell Proliferation by Targeting Bmi-1 in Osteosarcoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:442–450. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guan A, Wang H, Li X, Xie H, Wang R, Zhu Y
and Li R: MiR-330-3p inhibits gastric cancer progression through
targeting MSI1. Am J Transl Res. 8:4802–4811. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee KH, Chen YL, Yeh SD, Hsiao M, Lin JT,
Goan YG and Lu PJ: MicroRNA-330 acts as tumor suppressor and
induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through E2F1-mediated
suppression of Akt phosphorylation. Oncogene. 28:3360–3370. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qu S, Yao Y, Shang C, Xue Y, Ma J, Li Z
and Liu Y: MicroRNA-330 is an oncogenic factor in glioblastoma
cells by regulating SH3GL2 gene. PLoS One. 7:e460102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ren J, Ma R, Zhang ZB, Li Y, Lei P and Men
JL: Effects of microRNA-330 on vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques
formation and vascular endothelial cell proliferation through the
WNT signaling pathway in acute coronary syndrome. J Cell Biochem.
119:4514–4527. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shih YP, Sun P, Wang A and Lo SH: Tensin1
positively regulates RhoA activity through its interaction with
DLC1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:3258–3265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bernau K, Torr EE, Evans MD, Aoki JK, Ngam
CR and Sandbo N: Tensin 1 Is essential for myofibroblast
differentiation and extracellular matrix formation. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 56:465–476. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Zhan Y, Liang X, Li L, Wang B, Ding F, Li
Y, Wang X, Zhan Q and Liu Z: MicroRNA-548j functions as a
metastasis promoter in human breast cancer by targeting Tensin1.
Mol Oncol. 10:838–849. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dorn GW II: Mitochondrial pruning by Nix
and BNip3: An essential function for cardiac-expressed death
factors. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:374–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ney PA: Mitochondrial autophagy: Origins,
significance, and role of BNIP3 and NIX. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1853:2775–2783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S and Gibson
SB: BNIP3 subfamily BH3-only proteins: Mitochondrial stress sensors
in normal and pathological functions. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1):
S114–S127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
O'Sullivan TE, Johnson LR, Kang HH and Sun
JC: BNIP3- and BNIP3L-mediated mitophagy promotes the generation of
natural killer cell memory. Immunity. 43:331–342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mazure NM and Pouyssegur J: Atypical
BH3-domains of BNIP3 and BNIP3L lead to autophagy in hypoxia.
Autophagy. 5:868–869. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yussman MG, Toyokawa T, Odley A, Lynch RA,
Wu G, Colbert MC, Aronow BJ, Lorenz JN and Dorn GW II:
Mitochondrial death protein Nix is induced in cardiac hypertrophy
and triggers apoptotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. 8:725–730. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dorn GW II and Kirshenbaum LA: Cardiac
reanimation: Targeting cardiomyocyte death by BNIP3 and NIX/BNIP3L.
Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1): S158–S167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Diwan A, Krenz M, Syed FM, Wansapura J,
Ren X, Koesters AG, Li H, Kirshenbaum LA, Hahn HS, Robbins J, et
al: Inhibition of ischemic cardiomyocyte apoptosis through targeted
ablation of Bnip3 restrains postinfarction remodeling in mice. J
Clin Invest. 117:2825–2833. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pan JS, Huang L, Belousova T, Lu L, Yang
Y, Reddel R, Chang A, Ju H, DiMattia G, Tong Q and Sheikh-Hamad D:
Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an
AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol.
26:364–378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Tang SE, Wu CP, Wu SY, Peng CK, Perng WC,
Kang BH, Chu SJ and Huang KL: Stanniocalcin-1 ameliorates
lipopolysac-charide-induced pulmonary oxidative stress,
inflammation, and apoptosis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:321–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sheikh-Hamad D, Bick R, Wu GY, Christensen
BM, Razeghi P, Poindexter B, Taegtmeyer H, Wamsley A, Padda R,
Entman M, et al: Stanniocalcin-1 is a naturally occurring L-channel
inhibitor in cardiomyocytes: Relevance to human heart failure. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 285:H442–H448. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu D, Huang L, Wang Y, Wang W, Wehrens
XH, Belousova T, Abdelrahim M, DiMattia G and Sheikh-Hamad D: Human
stanniocalcin-1 suppresses angiotensin II-induced superoxide
generation in cardiomyocytes through UCP3-mediated anti-oxidant
pathway. PLoS One. 7:e369942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Guan J, Mishra S, Shi J, Plovie E, Qiu Y,
Cao X, Gianni D, Jiang B, Del Monte F, Connors LH, et al:
Stanniocalcin1 is a key mediator of amyloidogenic light chain
induced cardiotoxicity. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:3782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xu W, Barrientos T, Mao L, Rockman HA,
Sauve AA and Andrews NC: Lethal cardiomyopathy in mice lacking
transferrin receptor in the heart. Cell Rep. 13:533–545. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Naito Y, Hosokawa M, Sawada H, Oboshi M,
Hirotani S, Iwasaku T, Okuhara Y, Morisawa D, Eguchi A, Nishimura
K, et al: Transferrin receptor 1 in chronic hypoxia-induced
pulmonary vascular remodeling. Am J Hypertens. 29:713–718. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Qi L, Song Y, Chan THM, Yang H, Lin CH,
Tay DJT, Hong H, Tang SJ, Tan KT, Huang XX, et al: An RNA
editing/dsRNA binding-independent gene regulatory mechanism of
ADARs and its clinical implication in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:10436–10451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cheng J, Tang L, Hong Q, Ye H, Xu X, Xu L,
Bu S, Wang Q, Dai D, Jiang D and Duan S: Investigation into the
promoter DNA methylation of three genes (CAMK1D, CRY2 and CALM2) in
the peripheral blood of patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp Ther
Med. 8:579–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Imamura M, Iwata M, Maegawa H, Watada H,
Hirose H, Tanaka Y, Tobe K, Kaku K, Kashiwagi A, Kawamori R, et al:
Genetic variants at CDC123/CAMK1D and SPRY2 are associated with
susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population.
Diabetologia. 54:3071–3077. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bergamaschi A, Kim YH, Kwei KA, La Choi Y,
Bocanegra M, Langerød A, Han W, Noh DY, Huntsman DG, Jeffrey SS, et
al: CAMK1D amplification implicated in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in basal-like breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2:327–339. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|