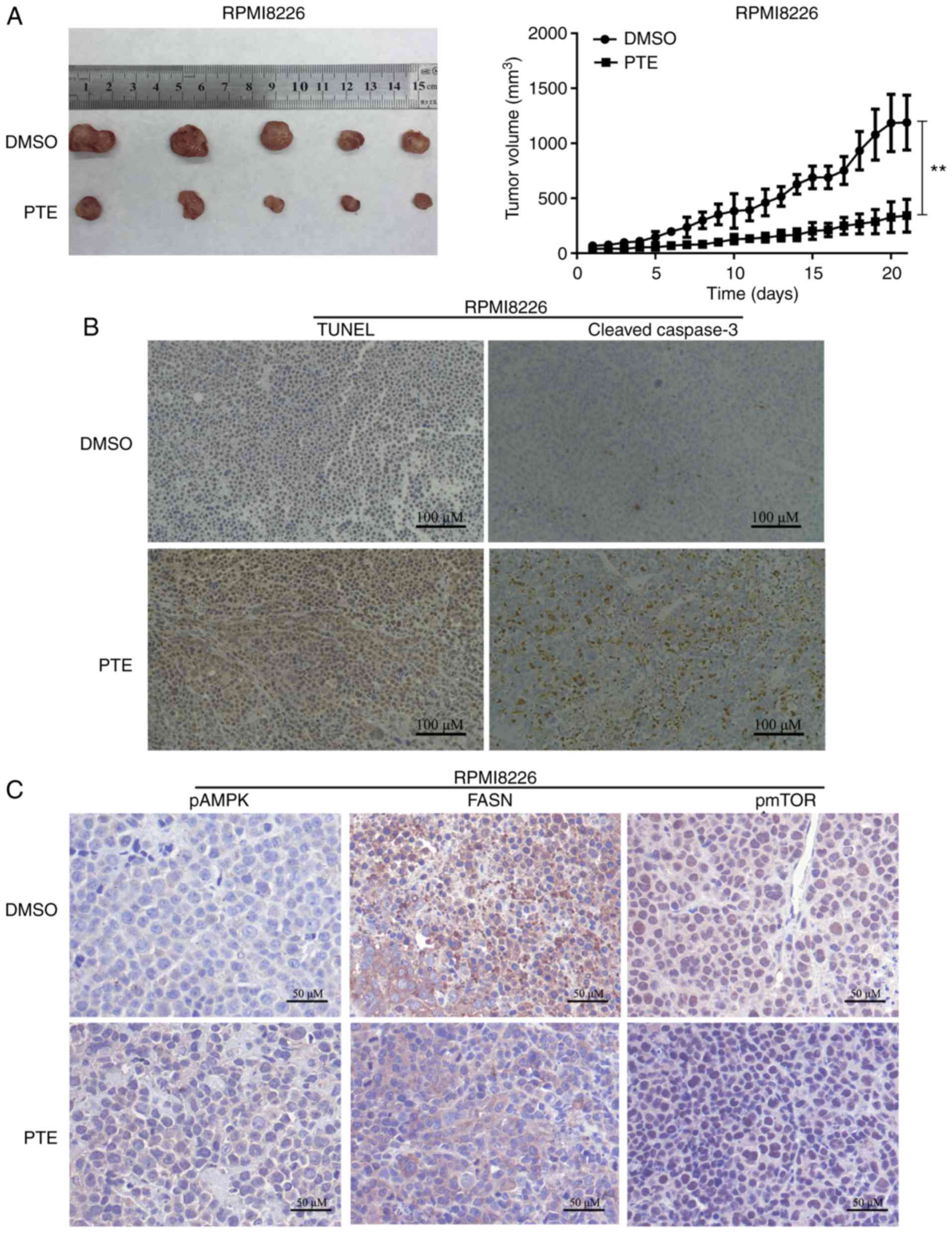
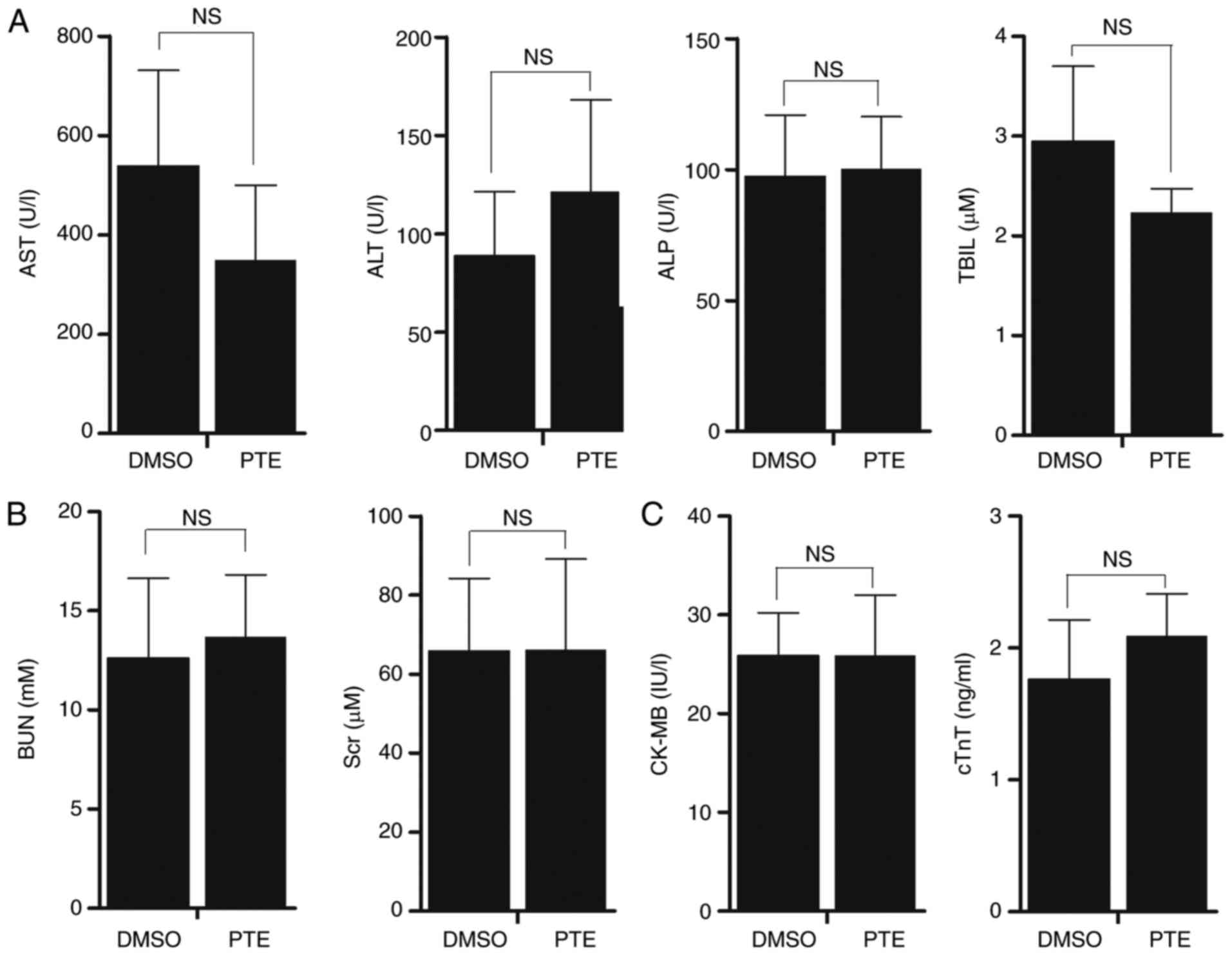
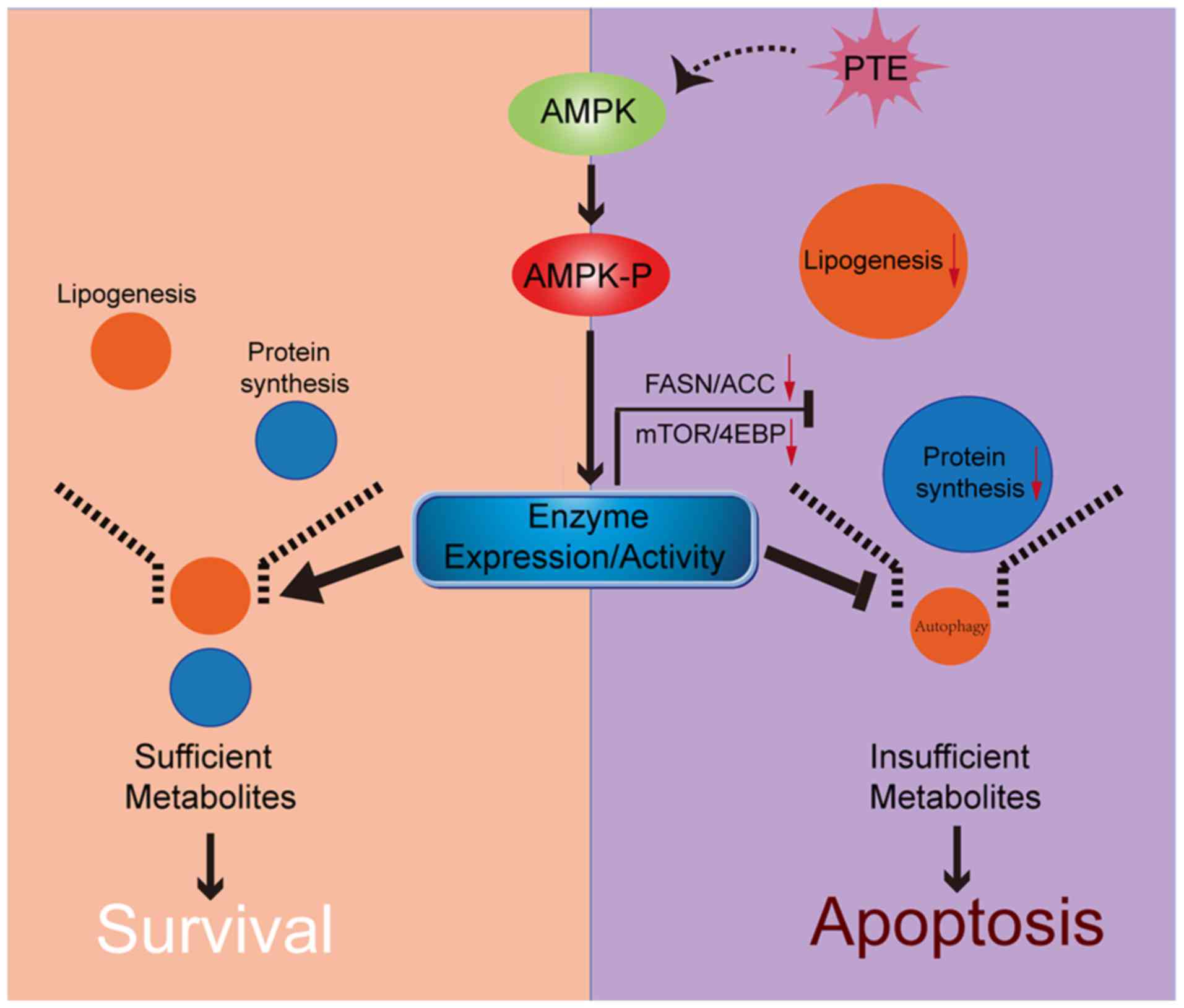
|
1
|
Rajkumar SV, Dimopoulos MA, Palumbo A,
Blade J, Merlini G, Mateos MV, Kumar S, Hillengass J, Kastritis E,
Richardson P, et al: International myeloma working group updated
criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol.
15:e538-e5482014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dimopoulos MA, Richardson PG, Moreau P and
Anderson KC: Current treatment landscape for relapsed and/or
refractory multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:42–54. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Estrela JM, Ortega A, Mena S, Rodriguez ML
and Asensi M: Pterostilbene: Biomedical applications. Crit Rev Clin
Lab Sci. 50:65–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang P and Sang S: Metabolism and
pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and pterostilbene. Biofactors.
44:16–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kosuru R, Rai U, Prakash S, Singh A and
Singh S: Promising therapeutic potential of pterostilbene and its
mechanistic insight based on preclinical evidence. Eur J Pharmacol.
789:229–243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wakimoto R, Ono M, Takeshima M, Higuchi T
and Nakano S: Differential anticancer activity of pterostilbene
against three subtypes of human breast cancer cells. Anticancer
Res. 37:6153–6159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gomez-Zorita S, Fernandez-Quintela A, Lasa
A, Aguirre L, Rimando AM and Portillo MP: Pterostilbene, a dimethyl
ether derivative of resveratrol, reduces fat accumulation in rats
fed an obesogenic diet. J Agric Food Chem. 62:8371–8378. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kosuru R and Singh S: Pterostilbene
ameliorates insulin sensitivity, glycemic control and oxidative
stress in fructose-fed diabetic rats. Life Sci. 182:112–121. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lin VC, Tsai YC, Lin JN, Fan LL, Pan MH,
Ho CT, Wu JY and Way TD: Activation of AMPK by pterostilbene
suppresses lipogenesis and cell-cycle progression in p53 positive
and negative human prostate cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
60:6399–6407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang MD, Wu H, Fu GB, Zhang HL, Zhou X,
Tang L, Dong LW, Qin CJ, Huang S, Zhao LH, et al: Acetyl-coenzyme A
carboxylase alpha promotion of glucose-mediated fatty acid
synthesis enhances survival of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice and
patients. Hepatology. 63:1272–1286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Okawa Y, Hideshima T, Ikeda H, Raje N,
Vallet S, Kiziltepe T, Yasui H, Enatsu S, Pozzi S, Breitkreutz I,
et al: Fatty acid synthase is a novel therapeutic target in
multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 141:659–671. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Flaveny CA, Griffett K, El-Gendy Bel D,
Kazantzis M, Sengupta M, Amelio AL, Chatterjee A, Walker J, Solt
LA, Kamenecka TM and Burris TP: Broad anti-tumor activity of a
small molecule that selectively targets the warburg effect and
lipogenesis. Cancer Cell. 28:42–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zaytseva YY, Rychahou PG, Gulhati P,
Elliott VA, Mustain WC, O'Connor K, Morris AJ, Sunkara M, Weiss HL,
Lee EY and Evers BM: Inhibition of fatty acid synthase attenuates
CD44-associated signaling and reduces metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 72:1504–1517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li L, Pilo GM, Li X, Cigliano A, Latte G,
Che L, Joseph C, Mela M, Wang C, Jiang L, et al: Inactivation of
fatty acid synthase impairs hepatocarcinogenesis driven by AKT in
mice and humans. J Hepatol. 64:333–341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Svensson RU, Parker SJ, Eichner LJ, Kolar
MJ, Wallace M, Brun SN, Lombardo PS, Van Nostrand JL, Hutchins A,
Vera L, et al: Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses
fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer
in preclinical models. Nat Med. 22:1108–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Medina EA, Oberheu K, Polusani SR, Ortega
V, Velagaleti GV and Oyajobi BO: PKA/AMPK signaling in relation to
adiponectin's antiproliferative effect on multiple myeloma cells.
Leukemia. 28:2080–2089. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zismanov V, Attar-Schneider O, Lishner M,
Heffez Aizenfeld R, Tartakover Matalon S and Drucker L: Multiple
myeloma proteostasis can be targeted via translation initiation
factor eIF4E. Int J Oncol. 46:860–870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Agnelli L, Fabris S, Bicciato S, Basso D,
Baldini L, Morabito F, Verdelli D, Todoerti K,
Lambertenghi-Deliliers G, Lombardi L and Neri A: Upregulation of
translational machinery and distinct genetic subgroups characterise
hyperdiploidy in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 136:565–573.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holcik M and Sonenberg N: Translational
control in stress and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:318–327.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moschetta M, Reale A, Marasco C, Vacca A
and Carratu MR: Therapeutic targeting of the mTOR-signalling
pathway in cancer: Benefits and limitations. Br J Pharmacol.
171:3801–3813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morotomi-Yano K, Oyadomari S, Akiyama H
and Yano K: Nanosecond pulsed electric fields act as a novel
cellular stress that induces translational suppression accompanied
by eIF2alpha phosphorylation and 4E BP1 dephosphorylation. Exp Cell
Res. 318:1733–1744. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Garcia D and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Mechanisms of
cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol
Cell. 66:789–800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Duan W, Chen K, Jiang Z, Chen X, Sun L, Li
J, Lei J, Xu Q, Ma J, Li X, et al: Desmoplasia suppression by
metformin-mediated AMPK activation inhibits pancreatic cancer
progression. Cancer Lett. 385:225–233. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zadra G, Photopoulos C, Tyekucheva S,
Heidari P, Weng QP, Fedele G, Liu H, Scaglia N, Priolo C, Sicinska
E, et al: A novel direct activator of AMPK inhibits prostate cancer
growth by blocking lipogenesis. EMBO Mol Med. 6:519–538. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong GZ, Lee YI, Jeong JH, Zhao HY, Jeon
R, Lee HJ and Ryu JH: Stilbenoids from rheum undulatum protect
hepatocytes against oxidative stress through AMPK activation.
Phytother Res. 29:1605–1609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Cui L, Zhou G, Jing H, Guo Y and
Sun W: Pterostilbene, a natural small-molecular compound, promotes
cytoprotective macroautophagy in vascular endothelial cells. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:903–911. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dhar S, Kumar A, Zhang L, Rimando AM, Lage
JM, Lewin JR, Atfi A, Zhang X and Levenson AS: Dietary
pterostilbene is a novel MTA1-targeted chemopreventive and
therapeutic agent in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 7:18469–18484.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McCormack DE, Mannal P, McDonald D, Tighe
S, Hanson J and McFadden D: Genomic analysis of pterostilbene
predicts its antiproliferative effects against pancreatic cancer in
vitro and in vivo. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:1136–1143. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wawszczyk J, Kapral M, Hollek A and
Weglarz L: In vitro evaluation of antiproliferative and cytotoxic
properties of pterostilbene against human colon cancer cells. Acta
Pol Pharm. 71:1051–1055. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Wu Y, Lv C, Li X, Cao X,
Yang M, Feng D and Luo Z: Pterostilbene exerts antitumor activity
against human osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Toxicology. 304:120–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maiso P, Huynh D, Moschetta M, Sacco A,
Aljawai Y, Mishima Y, Asara JM, Roccaro AM, Kimmelman AC and
Ghobrial IM: Metabolic signature identifies novel targets for drug
resistance in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 75:2071–2082. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma J, Duan W, Han S, Lei J, Xu Q, Chen X,
Jiang Z, Nan L, Li J, Chen K, et al: Ginkgolic acid suppresses the
development of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting pathways driving
lipogenesis. Oncotarget. 6:20993–21003. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernando RC, de Carvalho F, Mazzotti DR,
Evangelista AF, Braga WMT, de Lourdes Chauffaille M, Leme AFP and
Colleoni GWB: Multiple myeloma cell lines and primary tumors
proteoma: Protein biosynthesis and immune system as potential
therapeutic targets. Genes Cancer. 6:462–471. 2015.
|
|
35
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lv S, Xu Q, Sun E, Zhang J and Wu D:
Impaired cellular energy metabolism contributes to
bluetongue-virus-induced autophagy. Arch Virol. 161:2807–2811.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jing K, Song KS, Shin S, Kim N, Jeong S,
Oh HR, Park JH, Seo KS, Heo JY, Han J, et al: Docosahexaenoic acid
induces autophagy through p53/AMPK/mTOR signaling and promotes
apoptosis in human cancer cells harboring wild-type p53. Autophagy.
7:1348–1358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Han C, Lu L, Magliato S and Wu T:
Hedgehog signaling pathway .regulates autophagy in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 58:995–1010. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chim CS, Kumar SK, Orlowski RZ, Cook G,
Richardson PG, Gertz MA, Giralt S, Mateos MV, Leleu X and Anderson
KC: Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Novel
agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia.
32:252–262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Yao Z, Xie F, Li M, Liang Z, Xu W, Yang J,
Liu C, Li H, Zhou H and Qu LH: Oridonin induces autophagy via
inhibition of glucose metabolism in p53-mutated colorectal cancer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 8:e26332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang CH, Lee CY, Lu CC, Tsai FJ, Hsu YM,
Tsao JW, Juan YN, Chiu HY, Yang JS and Wang CC: Resveratrol-induced
autophagy and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer
CAR cells: A key role of AMPK and Akt/mTOR signaling. Int J Oncol.
50:873–882. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xie B, Xu Z, Hu L, Chen G, Wei R, Yang G,
Li B, Chang G, Sun X, Wu H, et al: Pterostilbene inhibits human
multiple myeloma cells via ERK1/2 and JNK pathway in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E19272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen G, Xu Z, Chang G, Hou J, Hu L, Zhang
Y, Yu D, Li B, Chang S, Xie Y, et al: The blueberry component
pterostilbene has potent anti-myeloma activity in
bortezomib-resistant cells. Oncol Rep. 38:488–496. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nagao K, Jinnouchi T, Kai S and Yanagita
T: Pterostilbene, a dimethylated analog of resveratrol, promotes
energy metabolism in obese rats. J Nutr Biochem. 43:151–155. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao D, Zhou H, Zhao J, Jin L, Yu W, Yan H,
Hu Y and Guo T: PGC-1α integrates glucose metabolism and
angiogenesis in multiple myeloma cells by regulating VEGF and
GLUT-4. Oncol Rep. 31:1205–1210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu W, Cao D, Zhou H, Hu Y and Guo T:
PGC-1α is responsible for survival of multiple myeloma cells under
hyperglycemia and chemotherapy. Oncol Rep. 33:2086–2092. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cao D, Jin L, Zhou H, Yu W, Hu Y and Guo
T: Inhibition of PGC-1α after chemotherapy-mediated insult confines
multiple myeloma cell survival by affecting ROS accumulation. Oncol
Rep. 33:899–904. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yu W, Cao DD, Li QB, Mei HL, Hu Y and Guo
T: Adipocytes secreted leptin is a pro-tumor factor for survival of
multiple myeloma under chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 7:86075–86086.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pandey PR, Xing F, Sharma S, Watabe M, Pai
SK, Iiizumi-Gairani M, Fukuda K, Hirota S, Mo YY and Watabe K:
Elevated lipogenesis in epithelial stem-like cell confers survival
advantage in ductal carcinoma in situ of breast cancer. Oncogene.
32:5111–5122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Inoki K, Kim J and Guan KL: AMPK and mTOR
in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 52:381–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shieh JM, Chen YC, Lin YC, Lin JN, Chen
WC, Chen YY, Ho CT and Way TD: Demethoxycurcumin inhibits energy
metabolic and oncogenic signaling pathways through AMPK activation
in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
61:6366–6375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter
M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M,
Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S, et al: Regulation of mammalian
autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
90:1383–1435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Riche DM, McEwen CL, Riche KD, Sherman JJ,
Wofford MR, Deschamp D and Griswold M: Analysis of safety from a
human clinical trial with pterostilbene. J Toxicol.
2013:4635952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen RJ, Tsai SJ, Ho CT, Pan MH, Ho YS, Wu
CH and Wang YJ: Chemopreventive effects of pterostilbene on
urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis in mice via the inhibition of
EGFR-mediated pathways and the induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. J Agric Food Chem. 60:11533–11541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mohanti BK, Rath GK, Anantha N, Kannan V,
Das BS, Chandramouli BA, Banerjee AK, Das S, Jena A, Ravichandran
R, et al: Improving cancer radiotherapy with 2-deoxy-D-glucose:
Phase I/II clinical trials on human cerebral gliomas. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 35:103–111. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bjarnadottir O, Romero Q, Bendahl PO,
Jirstrom K, Ryden L, Loman N, Uhlen M, Johannesson H, Rose C,
Grabau D and Borgquist S: Targeting HMG-CoA reductase with statins
in a window-of-opportunity breast cancer trial. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 138:499–508. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang Y, Xu W, Yan Z, Zhao W, Mi J, Li J
and Yan H: Metformin induces autophagy and G0/G1 phase cell cycle
arrest in myeloma by targeting the AMPK/mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pellat-Deceunynk C, Amiot M, Bataille R,
Van Riet I, Van Camp B, Omede P and Boccadoro M: Human myeloma cell
lines as a tool for studying the biology of multiple myeloma: A
reappraisal 18 years after. Blood. 86:4001–4002. 1995.
|
|
60
|
Drexler HG, Dirks WG and MacLeod RA: False
human hematopoietic cell lines: Cross-contaminations and
misinterpretations. Leukemia. 13:1601–1607. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Farnoushi Y, Cipok M, Kay S, Jan H, Ohana
A, Naparstek E, Goldstein RS and Deutsch VR: Rapid in vivo testing
of drug response in multiple myeloma made possible by xenograft to
turkey embryos. Br J Cancer. 105:1708–1718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lin L, Benson DM Jr, DeAngelis S, Bakan
CE, Li PK, Li C and Lin J: A small molecule, LLL12 inhibits
constitutive STAT3 and IL-6-induced STAT3 signaling and exhibits
potent growth suppressive activity in human multiple myeloma cells.
Int J Cancer. 130:1459–1469. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yan H, Wu QL, Sun CY, Ai LS, Deng J, Zhang
L, Chen L, Chu ZB, Tang B, Wang K, et al: piRNA-823 contributes to
tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and
angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 29:196–206. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Besse A, Stolze SC, Rasche L, Weinhold N,
Morgan GJ, Kraus M, Bader J, Overkleeft HS, Besse L and Driessen C:
Carfilzomib resistance due to ABCB1/MDR1 overexpression is overcome
by nelfinavir and lopinavir in multiple myeloma. Leukemia.
32:391–401. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|