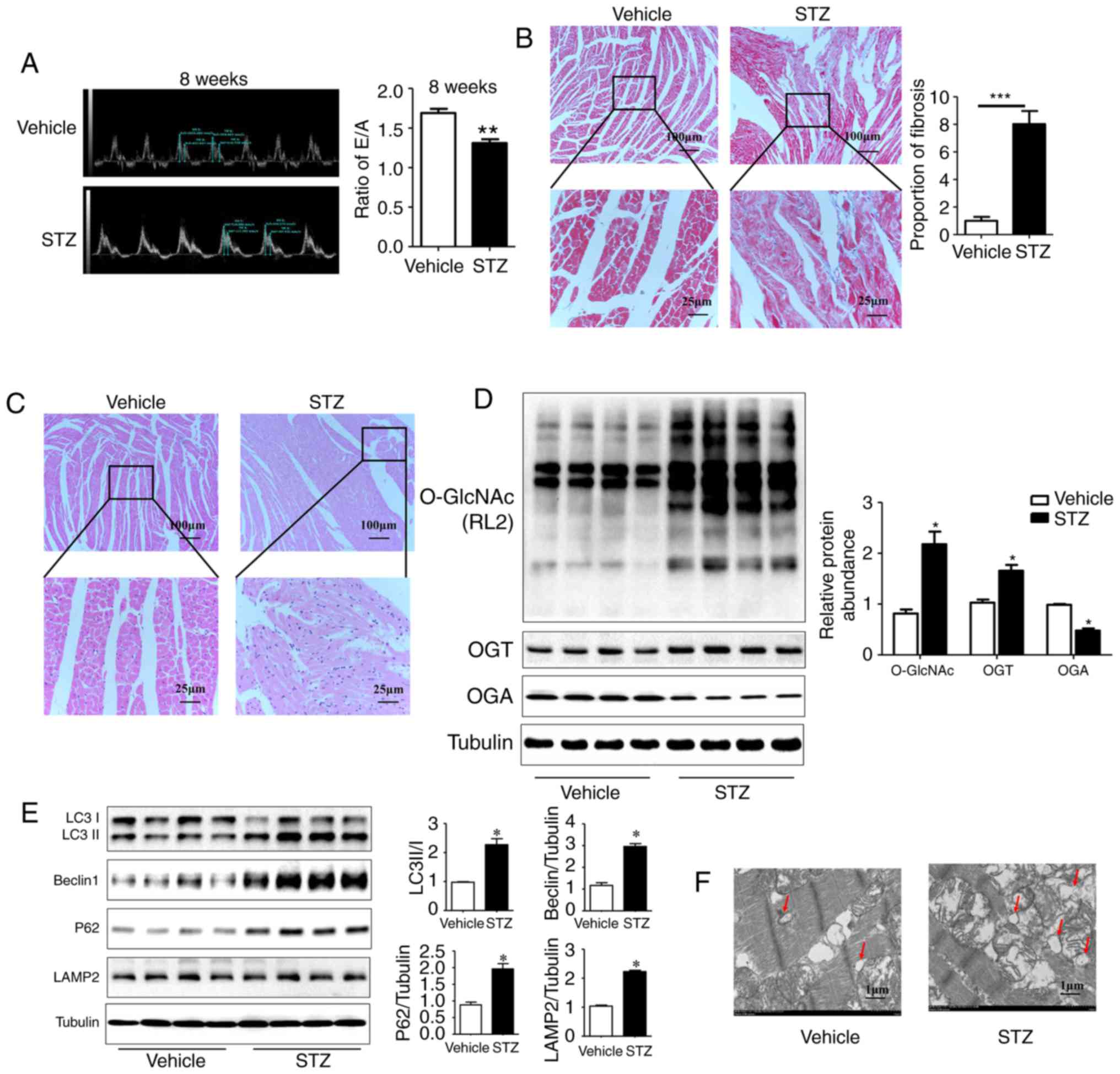
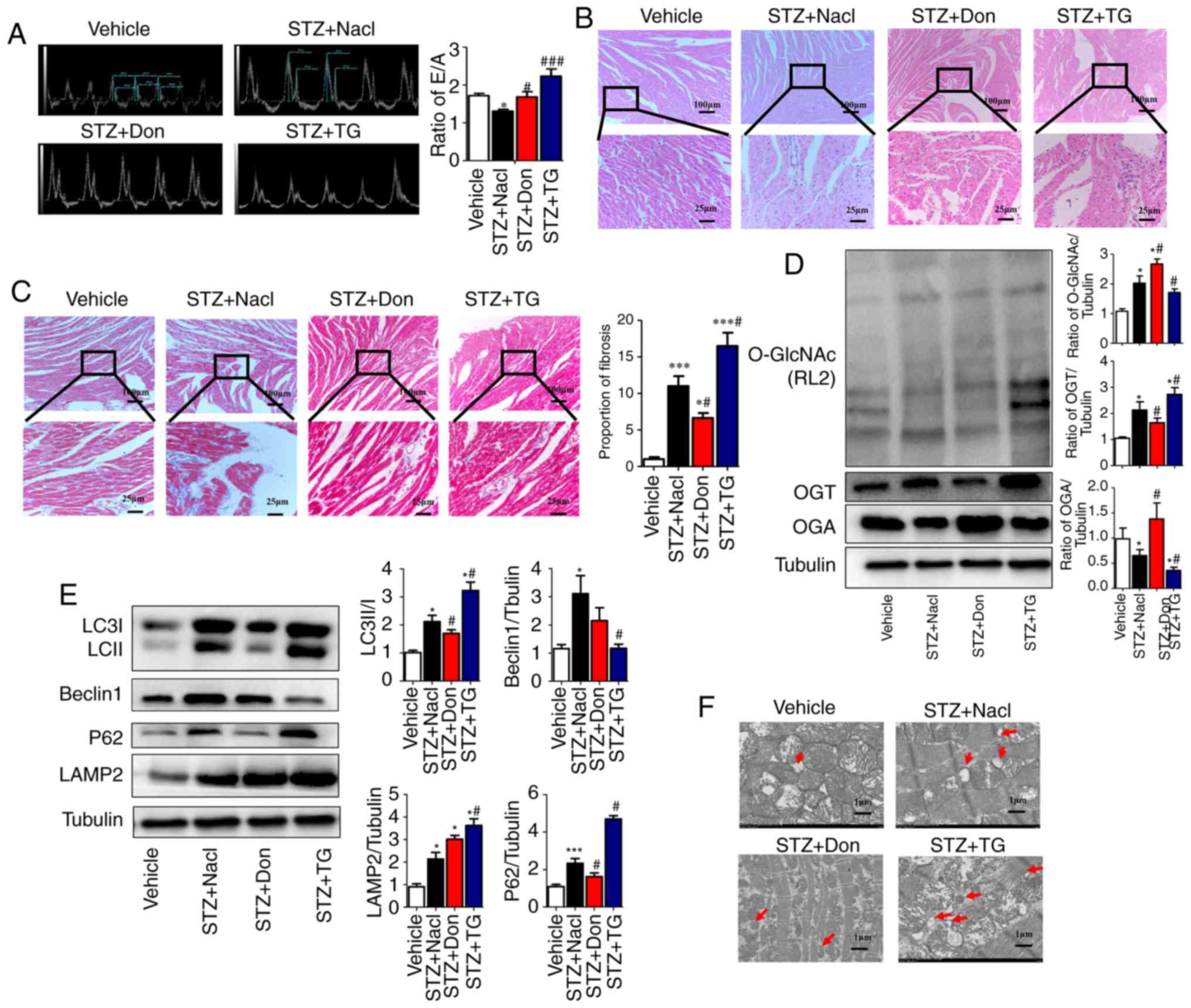
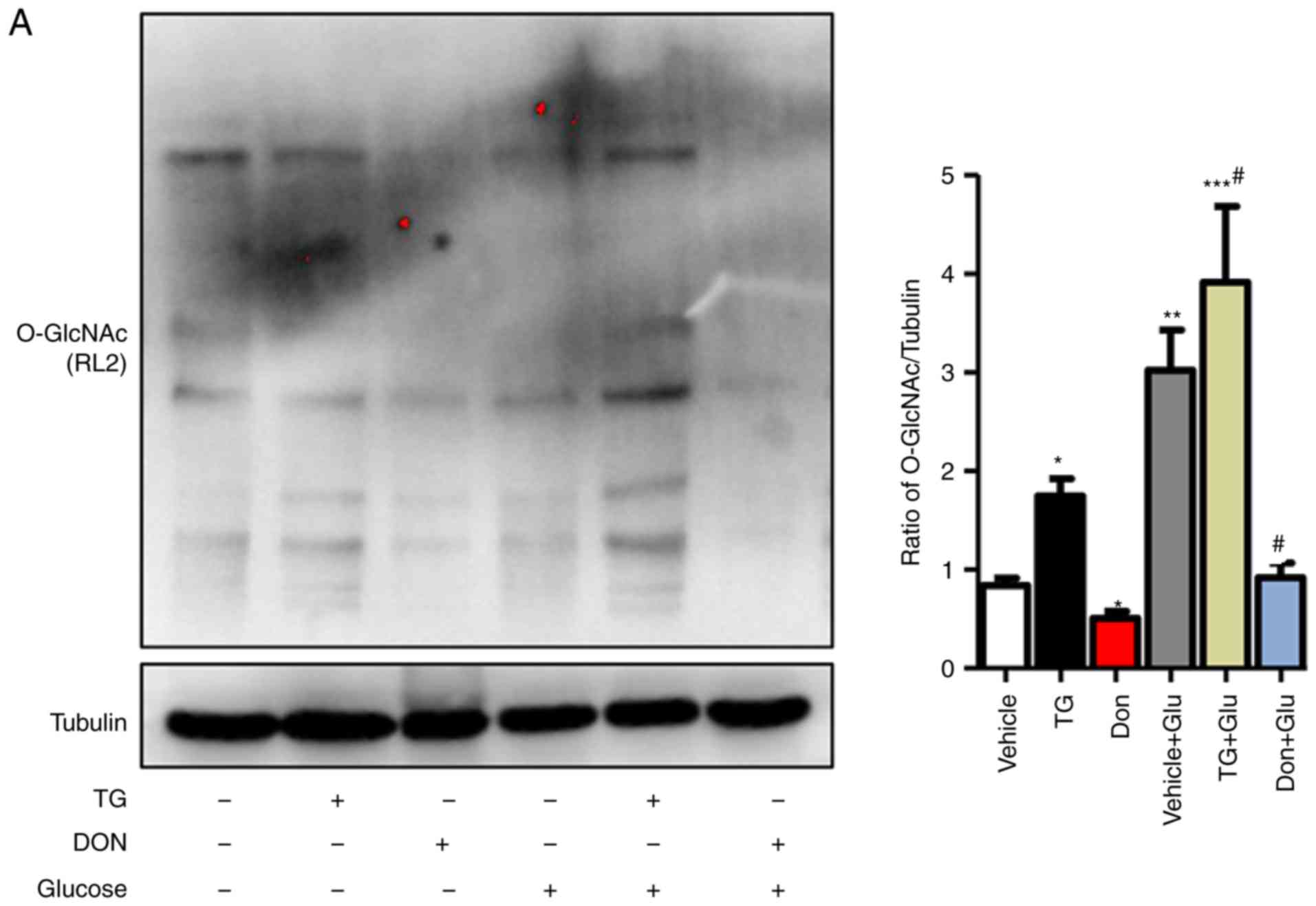
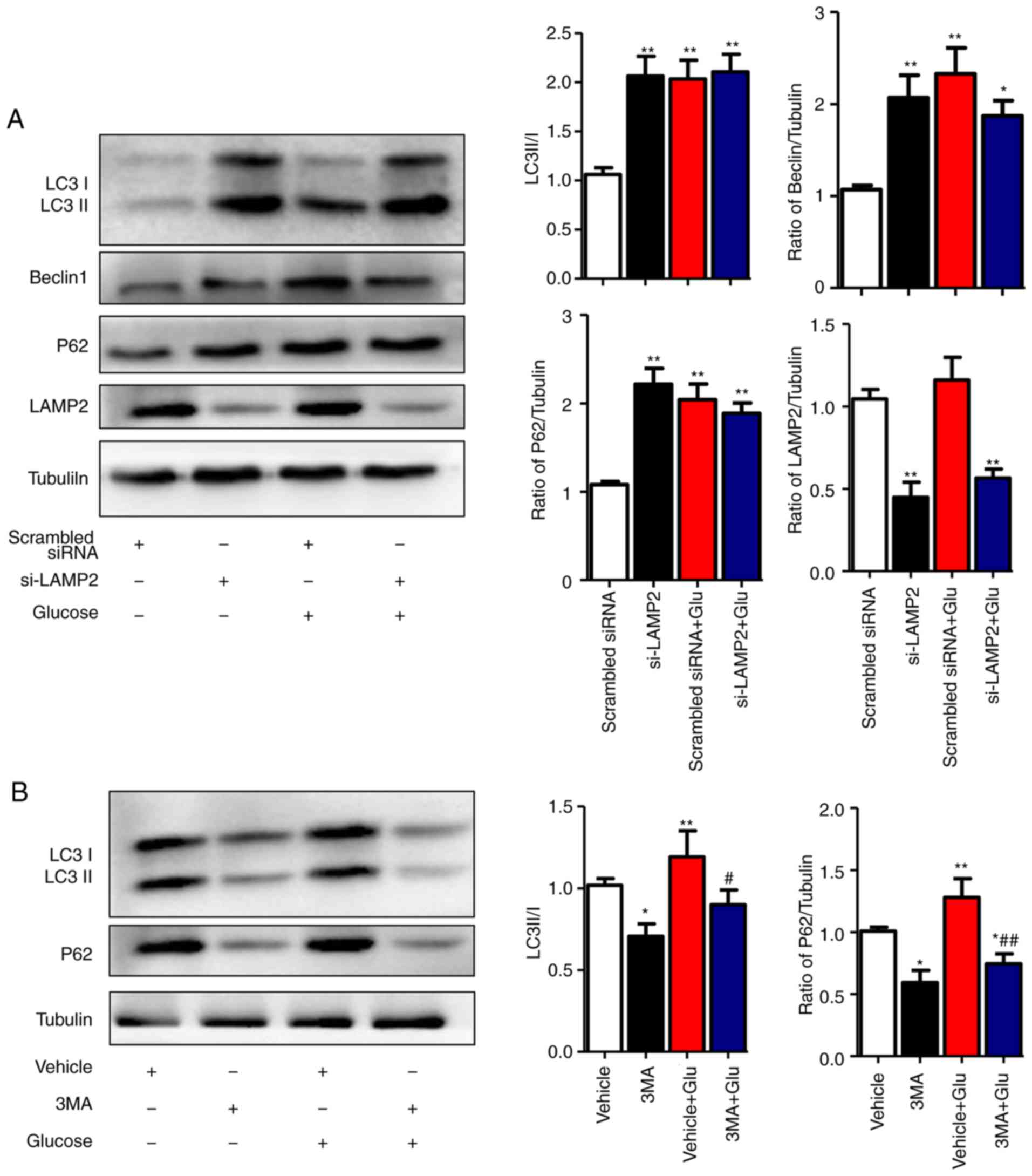
|
1
|
Huynh K, Bernardo BC, McMullen JR and
Ritchie RH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and new treatment
strategies targeting antioxidant signaling pathways. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:375–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chavali V, Tyagi SC and Mishra PK:
Predictors and prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 6:151–160. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dei CA, Khan SS, Butler J, Mentz RJ, Bonow
RO, Avogaro A, Tschoepe D, Doehner W, Greene SJ, Senni M, et al:
Impact of diabetes on epidemiology, treatment, and outcomes of
patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 3:136–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yi W, Clark PM, Mason DE, Keenan MC, Hill
C, Goddard WA III, Peters EC, Driggers EM and Hsieh-Wilson LC:
Phosphofructokinase 1 glycosylation regulates cell growth and
metabolism. Science. 337:975–980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang P and Hanover JA: Nutrient-driven
O-GlcNAc cycling influences autophagic flux and neurodegenerative
proteotoxicity. Autophagy. 9:604–606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pekkurnaz G, Trinidad JC, Wang X, Kong D
and Schwarz TL: Glucose regulates mitochondrial motility via Milton
modification by O-GlcNAc transferase. Cell. 158:54–68. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruan HB, Dietrich MO, Liu ZW, Zimmer MR,
Li MD, Singh JP, Zhang K, Yin R, Wu J, Horvath TL and Yang X:
O-GlcNAc transferase enables AgRP neurons to suppress browning of
white fat. Cell. 159:306–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng C, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Liao Q, Chen Y,
Zhao X, Guo Q, Shen P, Zhen B, Qian X, et al: Regulation of the
Hippo-YAP pathway by glucose sensor O-GlcNAcylation. Mol Cell.
68:591–604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ngoh GA, Facundo HT, Zafir A and Jones SP:
O-GlcNAc signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res.
107:171–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Costa FC, Tan EP, Bushue N,
DiTacchio L, Costello CE, McComb ME, Whelan SA, Peterson KR and
Slawson C: O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) Transferase and
O-GlcNAcase Interact with Mi2β Protein at the Aγ-Globin Promoter. J
Biol Chem. 291:15628–15640. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Erickson JR, Pereira L, Wang L, Han G,
Ferguson A, Dao K, Copeland RJ, Despa F, Hart GW, Ripplinger CM and
Bers DM: Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias
by O-linked glycosylation. Nature. 502:372–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park MJ, Kim DI, Lim SK, Choi JH, Han HJ,
Yoon KC and Park SH: High glucose-induced O-GlcNAcylated
carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) mediates
mesangial cell lipogenesis and fibrosis: The possible role in the
development of diabetic nephropathy. J Biol Chem. 289:13519–13530.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie S, Jin N, Gu J, Shi J, Sun J, Chu D,
Zhang L, Dai CL, Gu JH, Gong CX, et al: O-GlcNAcylation of protein
kinase A catalytic subunits enhances its activity: A mechanism
linked to learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease.
Aging Cell. 15:455–464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma J and Hart GW: Protein O-GlcNAcylation
in diabetes and diabetic complications. Expert Rev Proteomics.
10:365–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Banerjee PS, Ma J and Hart GW:
Diabetes-associated dysregulation of O-GlcNAcylation in rat cardiac
mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:6050–6055. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu Y, Belke D, Suarez J, Swanson E, Clark
R, Hoshijima M and Dillmann WH: Adenovirus-mediated overexpression
of O-GlcNAcase improves contractile function in the diabetic heart.
Circ Res. 96:1006–1013. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gustafsson AB and Gottlieb RA: Recycle or
die: The role of autophagy in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
44:654–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yorimitsu T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy:
Molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ. 12(Suppl
2): S1542–S1552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hohenstein AC and Roche PA: SNAP-29 is a
promiscuous syntaxin-binding SNARE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
285:167–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Diao J, Liu R, Rong Y, Zhao M, Zhang J,
Lai Y, Zhou Q, Wilz LM, Li J, Vivona S, et al: ATG14 promotes
membrane tethering and fusion of autophagosomes to endolysosomes.
Nature. 520:563–566. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bernard A and Klionsky DJ: Toward an
understanding of autophagosome-lysosome fusion: The unsuspected
role of ATG14. Autophagy. 11:583–584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu R, Zhi X and Zhong Q: ATG14 controls
SNARE-mediated autophagosome fusion with a lysosome. Autophagy.
11:847–849. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo B, Liang Q, Li L, Hu Z, Wu F, Zhang P,
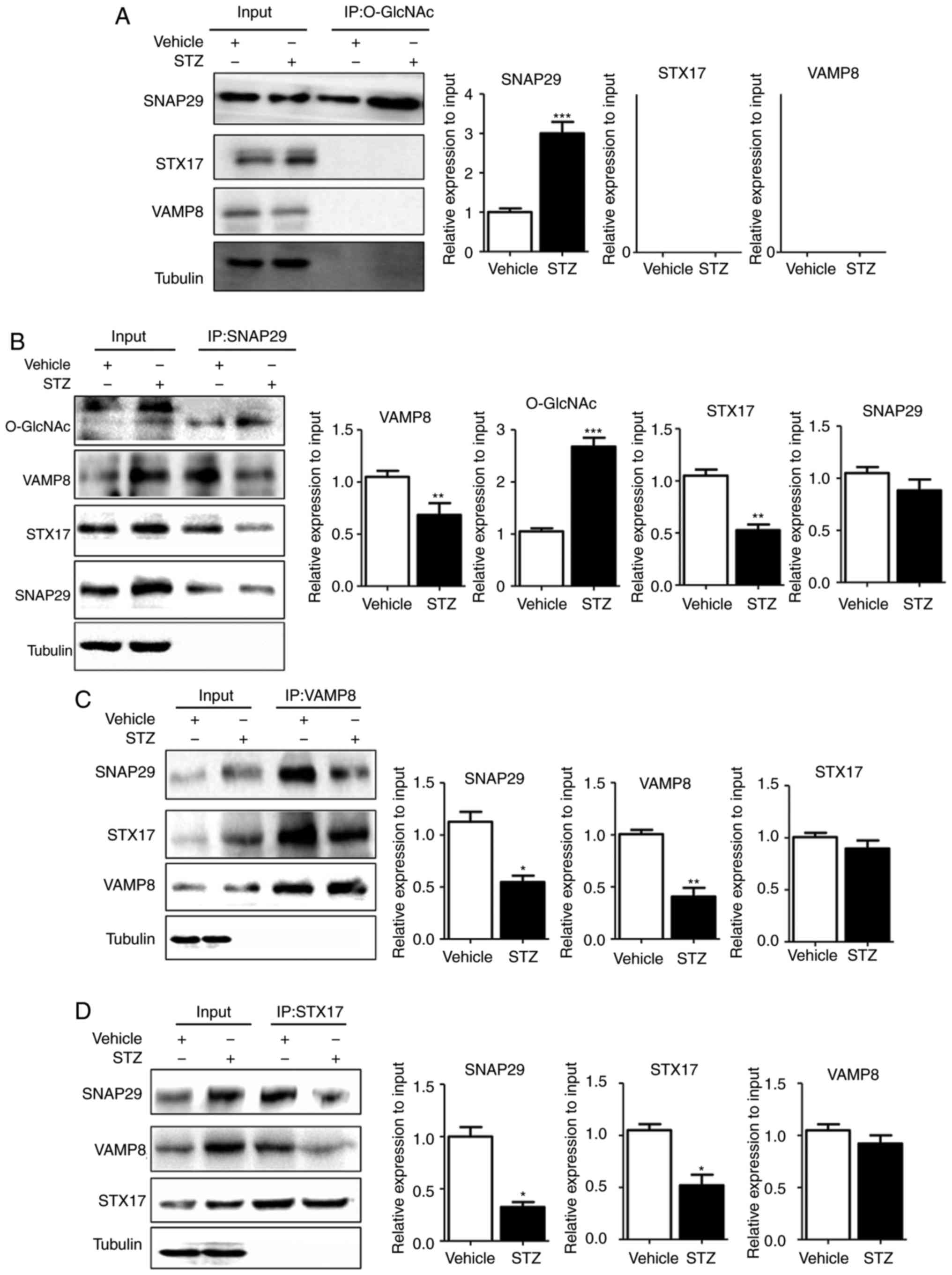
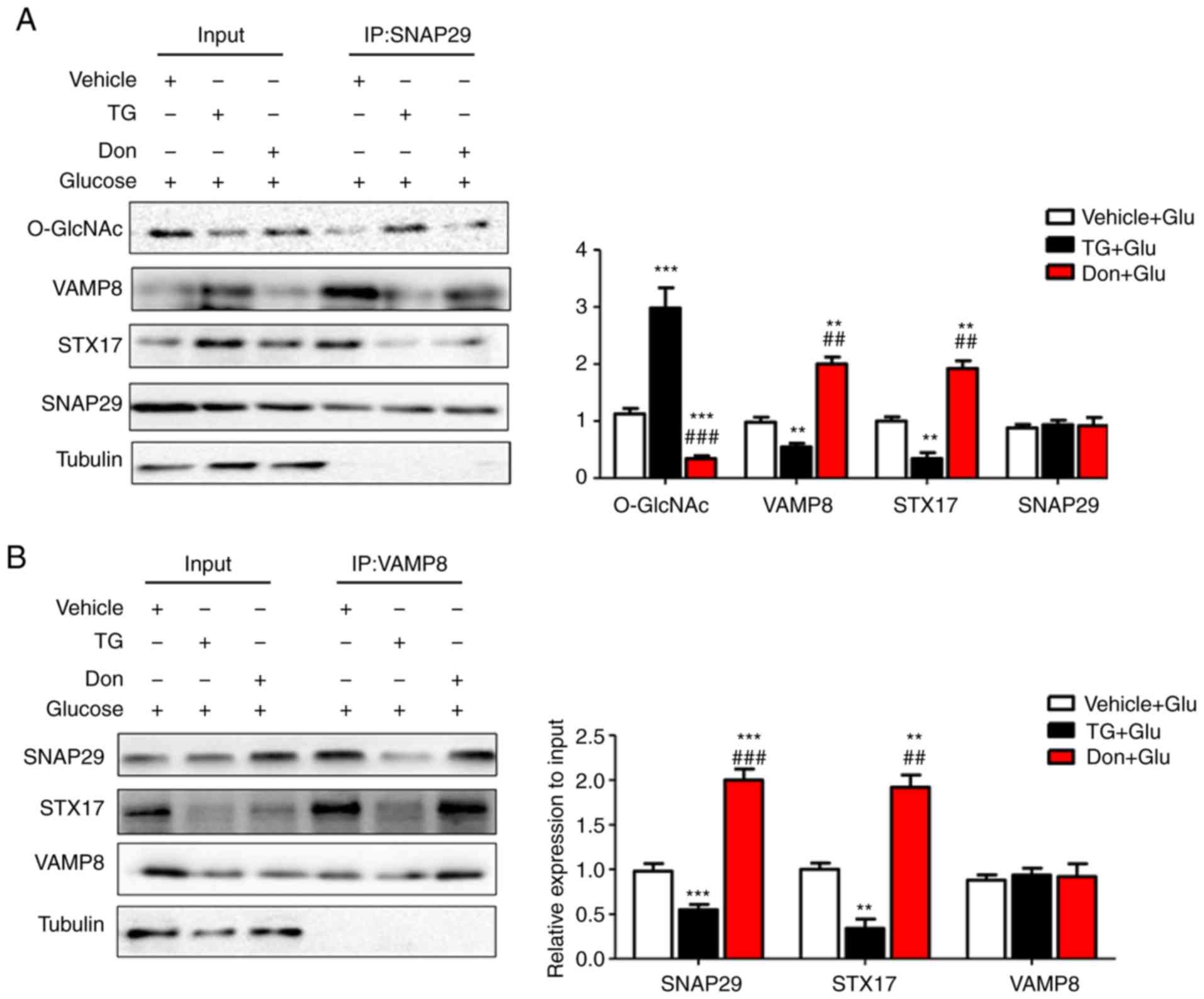
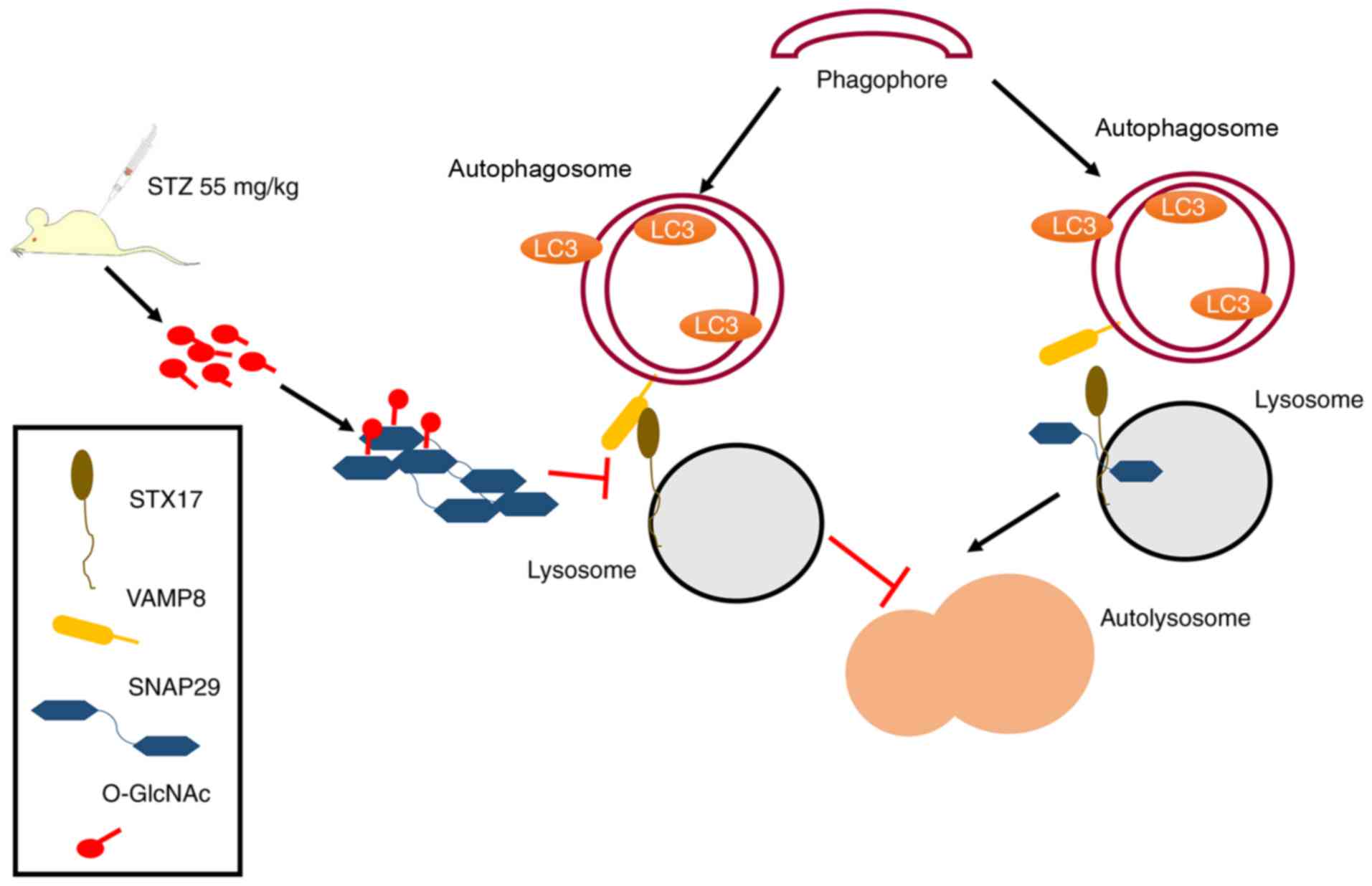
Ma Y, Zhao B, Kovács AL, Zhang Z, et al: O-GlcNAc-modification of
SNAP-29 regulates autophagosome maturation. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1215–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bell RC, Carlson JC, Storr KC, Herbert K
and Sivak J: High-fructose feeding of streptozotocin-diabetic rats
is associated with increased cataract formation and increased
oxidative stress in the kidney. Br J Nutr. 84:575–582.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto
A, Mikami A, Ogino A, Watanabe T, Morishita K, Okada H, Kawasaki M,
et al: Autophagic adaptations in diabetic cardiomyopathy differ
between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Autophagy. 11:1146–1160. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barefield DY, Puckelwartz MJ, Kim EY,
Wilsbacher LD, Vo AH, Waters EA, Earley JU, Hadhazy M,
Dellefave-Castillo L, Pesce LL and McNally EM: Experimental
modeling supports a role for MyBP-HL as a Novel myofilament
component in arrhythmia and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation.
136:1477–1491. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Riha H, Papoušek F, Neckář J, Pirk J and
Ošťádal B: Effects of isoflurane concentration on basic
echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricle in rats. Physiol
Res. 61:419–423. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reinecke H, Zhang M, Bartosek T and Murry
CE: Survival, integration, and differentiation of cardiomyocyte
grafts: A study in normal and injured rat hearts. Circulation.
100:193–202. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peng X, Shao J, Shen Y, Zhou Y, Cao Q, Hu
J, He W, Yu X, Liu X, Marian AJ and Hong K: FAT10 protects cardiac
myocytes against apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 59:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mellor KM, Bell JR, Young MJ, Ritchie RH
and Delbridge LM: Myocardial autophagy activation and suppressed
survival signaling is associated with insulin resistance in
fructose-fed mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 50:1035–1043. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tanida I, Wakabayashi M, Kanematsu T,
Minematsu-Ikeguchi N, Sou YS, Hirata M, Ueno T and Kominami E:
Lysosomal turnover of GABARAP-phospholipid conjugate is activated
during differentiation of C2C12 cells to myotubes without
inactivation of the mTor kinase-signaling pathway. Autophagy.
2:264–271. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Darley-Usmar VM, Ball LE and Chatham JC:
Protein O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine: A novel effector of
cardiomyocyte metabolism and function. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:538–549. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jesmin S, Zaedi S, Shimojo N, Iemitsu M,
Masuzawa K, Yamaguchi N, Mowa CN, Maeda S, Hattori Y and Miyauchi
T: Endothelin antagonism normalizes VEGF signaling and cardiac
function in STZ-induced diabetic rat hearts. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 292:E1030–E1040. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen ZC, Cheng YZ, Chen LJ, Cheng KC, Li Y
and Cheng J: Increase of ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels
in the heart of type-1 diabetic rats. Cardiovasc DiabetoL.
11:82012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li HT, Wu XD, Davey AK and Wang J:
Antihyperglycemic effects of baicalin on
streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Phytother Res.
25:189–194. 2011.
|
|
36
|
Sun D, Shen M, Li J, Li W, Zhang Y, Zhao
L, Zhang Z, Yuan Y, Wang H and Cao F: Cardioprotective effects of
tanshinone IIA pretreatment via kinin B2 receptor-Akt-GSK-3β
dependent pathway in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 10:42011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Qiao L, Guo B, Zhang H, Yang R, Chang L,
Wang Y, Jin X, Liu S and Li Y: The clock gene, brain and muscle
Arnt-like 1, regulates autophagy in high glucose-induced
cardiomyocyte injury. Oncotarget. 8:80612–80624. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xie Z, Lau K, Eby B, Lozano P, He C,
Pennington B, Li H, Rathi S, Dong Y, Tian R, et al: Improvement of
cardiac functions by chronic metformin treatment is associated with
enhanced cardiac autophagy in diabetic OVE26 mice. Diabetes.
60:1770–1778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang B, Yang Q, Sun YY, Xing YF, Wang YB,
Lu XT, Bai WW, Liu XQ and Zhao YX: Resveratrol-enhanced autophagic
flux ameliorates myocardial oxidative stress injury in diabetic
mice. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1599–1611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Q, Frank M, Akiyama M, Shimizu H, Ho
SY, Thisse C, Thisse B, Sprecher E and Uitto J: Abca12-mediated
lipid transport and Snap29-dependent trafficking of lamellar
granules are crucial for epidermal morphogenesis in a zebrafish
model of ichthyosis. Dis Model Mech. 4:777–785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Morelli E, Ginefra P, Mastrodonato V,
Beznoussenko GV, Rusten TE, Bilder D, Stenmark H, Mironov AA and
Vaccari T: Multiple functions of the SNARE protein Snap29 in
autophagy, endocytic, and exocytic trafficking during epithelial
formation in Drosophila. Autophagy. 10:2251–2268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jiu Y, Hasygar K, Tang L, Liu Y, Holmberg
CI, Bürglin TR, Hietakangas V and Jäntti J: par-1, atypical pkc,
and PP2A/B55 sur-6 are implicated in the regulation of
exocyst-mediated membrane trafficking in Caenorhabditis elegans. G3
(Bethesda). 4:173–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sato M, Saegusa K and Sato K, Hara T,
Harada A and Sato K: Caenorhabditis elegans SNAP-29 is required for
organellar integrity of the endomembrane system and general
exocytosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell.
22:2579–2587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Itakura E, Kishi-Itakura C and Mizushima
N: The hairpin-type tail-anchored SNARE syntaxin 17 targets to
autophagosomes for fusion with endosomes/lysosomes. Cell.
151:1256–1269. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|