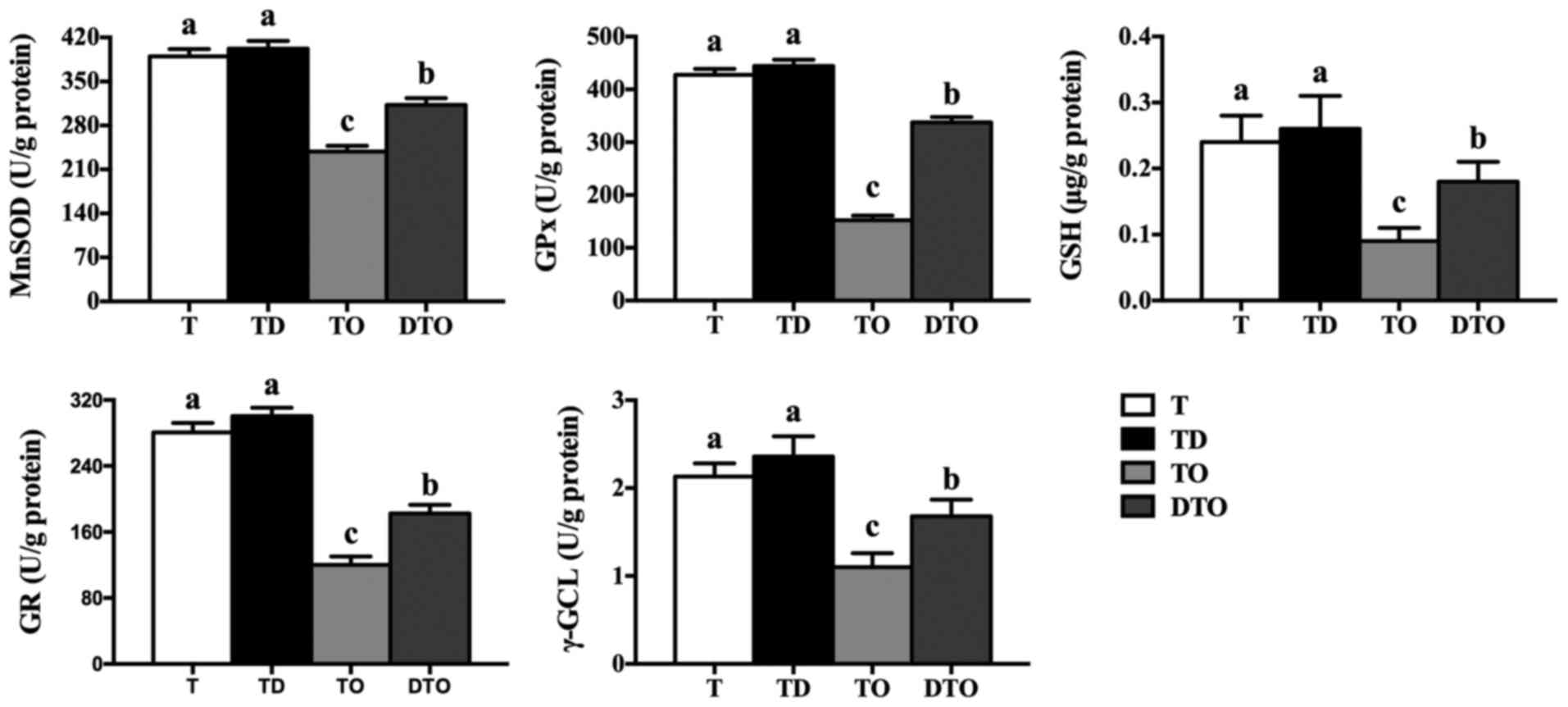
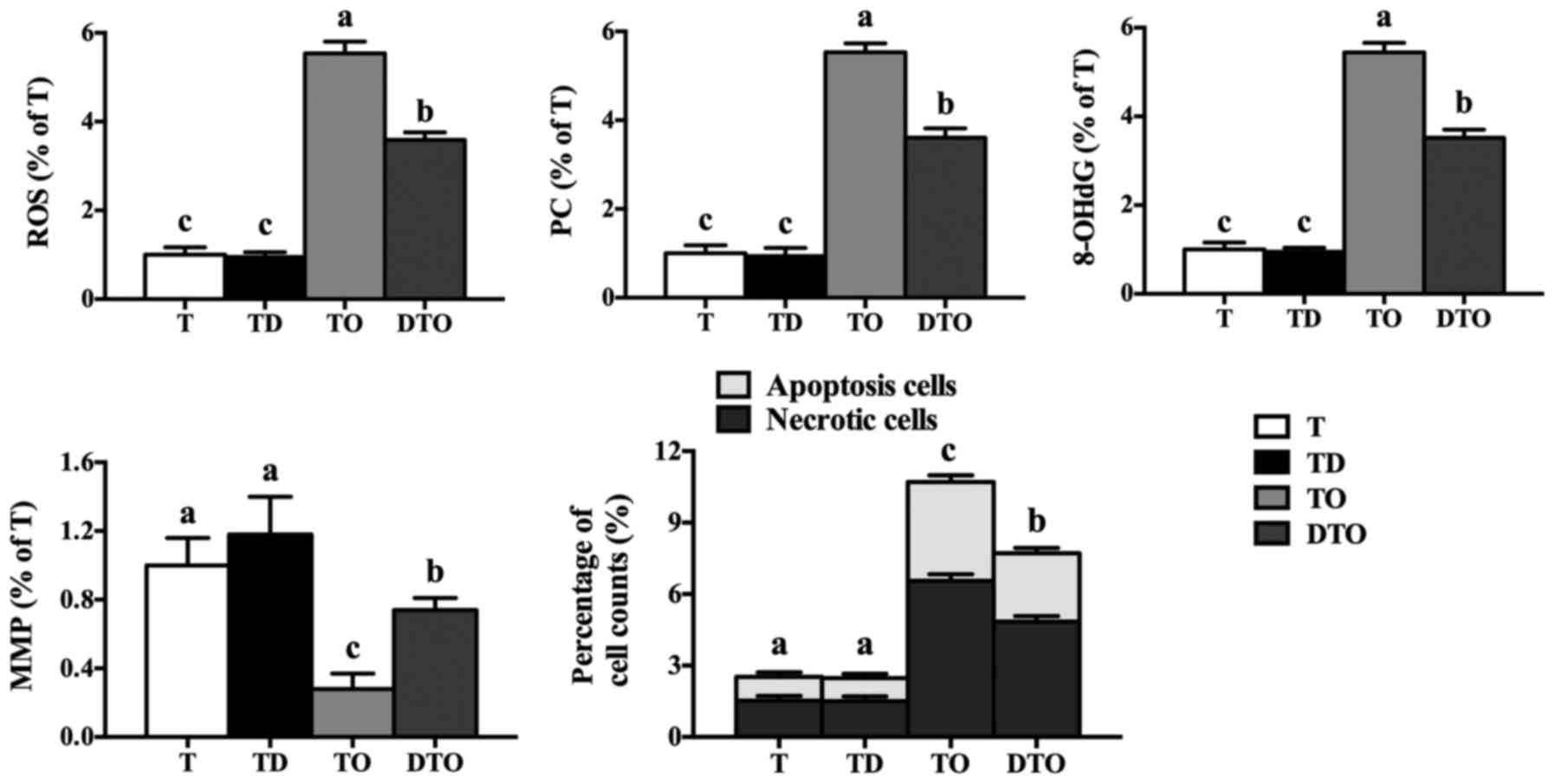
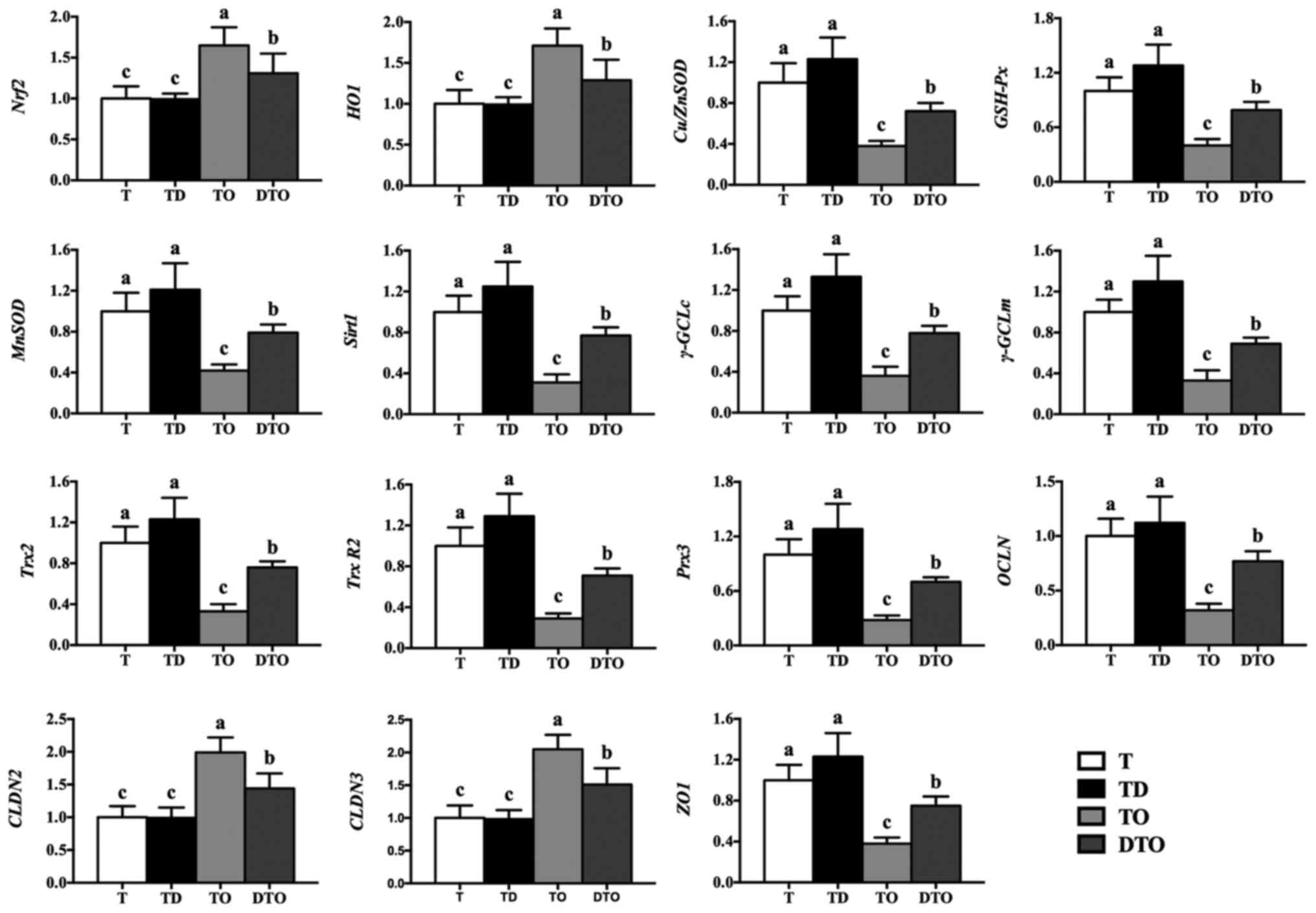
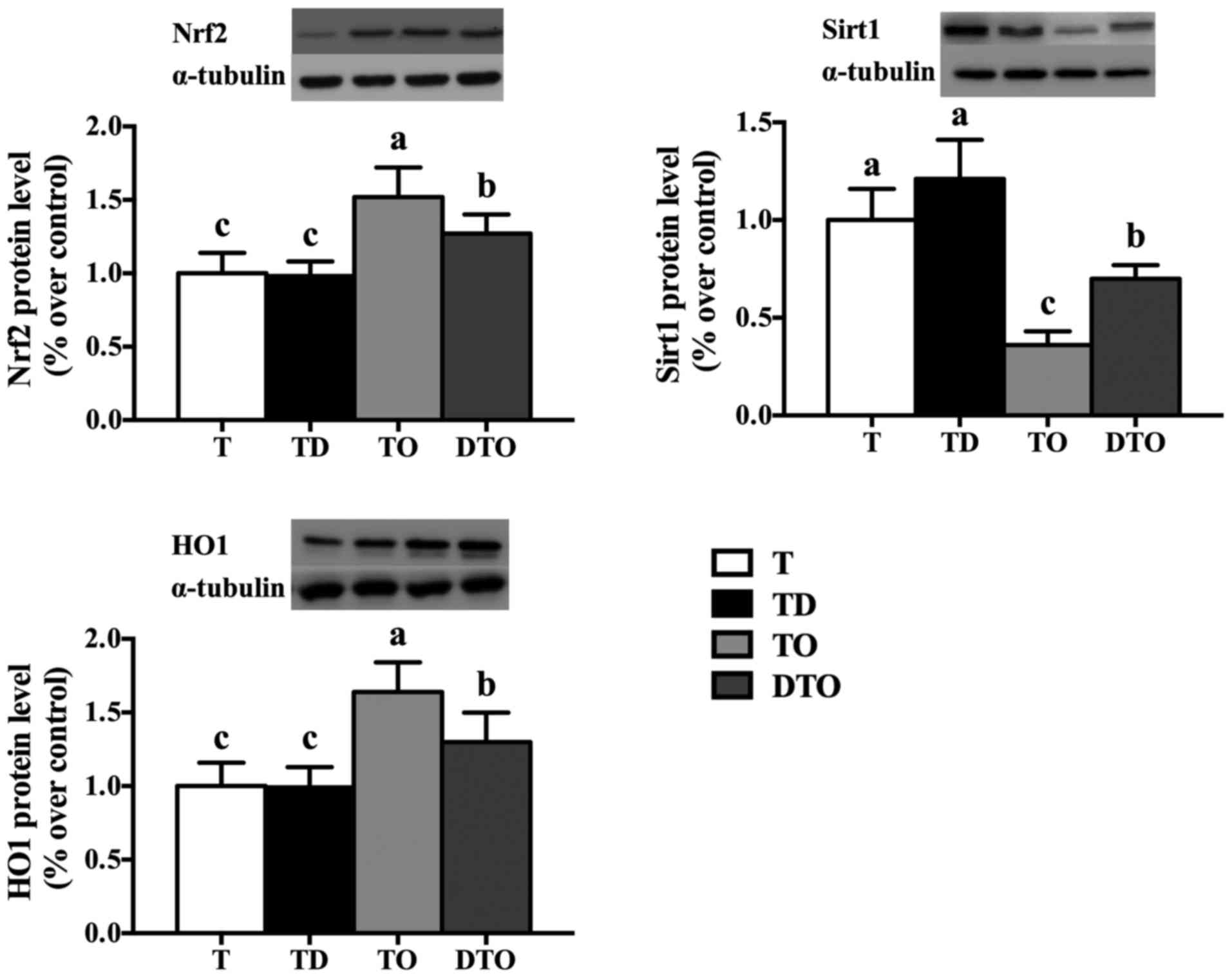
|
1
|
Friesen RW, Novak EM, Hasman D and Inniset
SM: Relationship of dimethylglycine, choline, and betaine with
oxoproline in plasma of pregnant women and their newborn infants. J
Nutr. 137:2641–2646. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hariganesh K and Prathiba J: Effect of
dimethylglycine on gastric ulcers in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol.
52:1519–1522. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Clapes P and Infante MR: Amino acid-based
surfactants: Enzymatic synthesis, properties and potential
applications. J Biocatalys Biotransformation. 20:215–233. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–1070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grune T: Oxidative stress, aging and the
proteasomal system. Biogerontology. 1:31–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ma K, Zhang Y, Zhu D and Lou Y: Protective
effects of asiatic acid against
D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced hepa-totoxicity in
hepatocytes and kupffer cells co-cultured system via
redox-regulated leukotriene C4 synthase expression pathway. Eur J
Pharmacol. 603:98–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Balaban RS, Nemoto S and Finkel T:
Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell. 120:4832005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andreyev AY, Kushnareva YE and Starkov AA:
Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 70:200–214. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dong L, Zhong X, He J, Zhang L, Bai K, Xu
W, Wang T and Huang X: Supplementation of tributyrin improves the
growth and intestinal digestive and barrier functions in
intrauterine growth-restricted piglets. Clin Nutr. 35:399–407.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Inoue J, Miki I, Tanahashi T, Kawauchi S,
Azuma T and Mizuno S: Mo2016 effect of ghrelin on
indomethacin-induced small intestinal injury in mice.
Gastroenterology. 144:S-7192013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Konaka A, Kato S, Tanaka A, Kunikata T,
Korolkiewicz R and Takeuchi K: Roles of enterobacteria, nitric
oxide and neutrophil in pathogenesis of indomethacin-induced small
intestinal lesions in rats. Pharmacol Res. 40:517–524. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu F, Li G, Wen K, Bui T, Cao D, Zhang Y
and Yuan L: Porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2)
of rotavirus infection as a new model for the study of innate
immune responses to rota-viruses and probiotics. Viral Immunol.
23:135–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brosnahan AJ and Brown DR: Porcine IPEC-J2
intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet
Microbiol. 156:229–237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Arce C, Ramírez-Boo M, Lucena C and
Garrido JJ: Innate immune activation of swine intestinal epithelial
cell lines (IPEC-J2 and IPI-2I) in response to LPS from salmonella
typhimurium. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 33:161–174. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Moon JK and Shibamoto T: Antioxidant
assays for plant and food components. J Agric Food Chem.
57:1655–1666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Siddhuraju P and Manian S: The antioxidant
activity and free radical-scavenging capacity of dietary phenolic
extracts from horse gram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam) Verdc) seeds.
Food Chem. 105:950–958. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen HY and Yen GC: Antioxidant activity
and free radical-scavenging capacity of extracts from guava
(Psidium guajava L.) leaves. Food Chem. 101:686–694. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Hou X, Ahmad H, Zhang H, Zhang L
and Wang T: Assessment of free radicals scavenging activity of
seven natural pigments and protective effects in AAPH-challenged
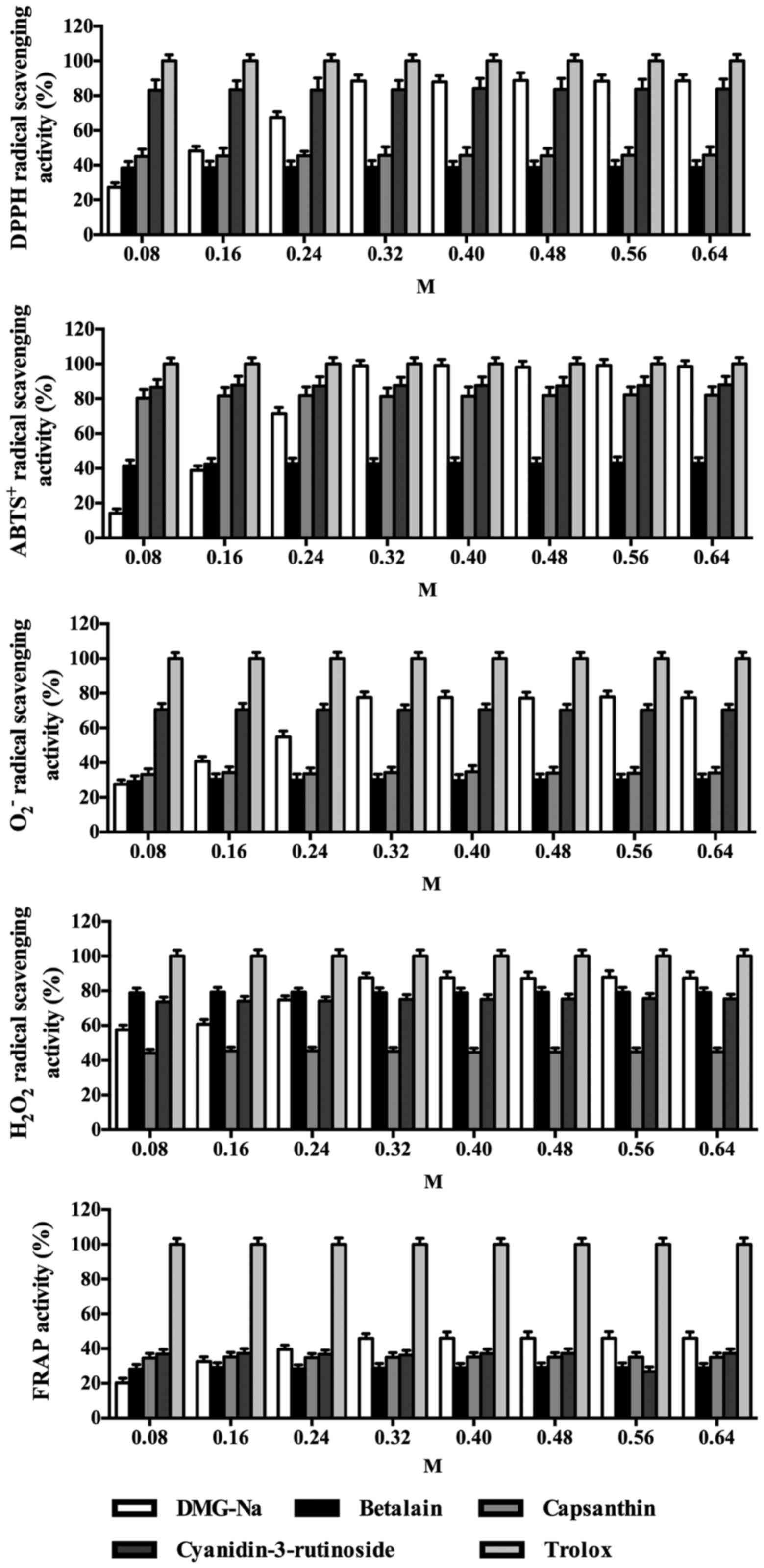
chicken erythrocytes. Food Chem. 145:57–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Benzie IF and Strain JJ: The ferric
reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of ‘antioxidant
power’: The frap assay. Anal Biochem. 239:70–76. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magalhães AS, Silva BM, Pereira JA,
Andrade PB, Valentão P and Carvalho M: Protective effect of quince
(cydonia oblonga miller) fruit against oxidative hemolysis of human
erythrocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:1372–1377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lawrence RA and Burk RF: Glutathione
peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 71:952–958. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Panchenko LF, Brusov OS, Gerasimov AM and
Loktaeva TD: Intramitochondrial localization and release of rat
liver superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett. 55:84–87. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sang H, Zhang L and Li J:
Anti-benzopyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide induces apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway in human bronchiolar epithelium cells
independent of the mitochondria permeability transition pore. Food
Chem Toxicol. 50:2417–2423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis. 14th
edition. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Washington,
DC: 1985
|
|
25
|
Aw TY, Williams MW and Gray L: Absorption
and lymphatic transport of peroxidized lipids by rat small
intestine in vivo: Role of mucosal GSH. Am J Physiol. 262:G99–G106.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Repetto G, Peso AD and Zurita JL: Neutral
red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity.
Nat Protoc. 3:1125–1131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang X, Gao J, Wang Y, Fan YM, Xu LZ, Zhao
XN, Xu Q and Qian ZM: Effective protection of terminalia catappa l.
Leaves from damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in liver
mitochondria. J Nutr Biochem. 17:177–182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Langston JW, Li W, Harrison L and Aw TY:
Activation of promoter activity of the catalytic subunit of
γ-glutamylcysteine ligase (GCL) in brain endothelial cells by
insulin requires antioxidant response element 4 and altered
glycemic status: Implication for GCL expression and GSH synthesis.
Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1749–1757. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Remmen H, Ikeno Y, Hamilton M,
Pahlavani M, Wolf N, Thorpe SR, Alderson NL, Baynes JW, Epstein CJ,
Huang TT, et al: Life-long reduction in MnSOD activity results in
increased DNA damage and higher incidence of cancer but does not
accelerate aging. Physiol Genomics. 16:29–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei QY, Chen WF, Zhou B, Yang L and Liu
ZL: Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in rat
liver mitochondria by curcumin and its analogues. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1760:70–77. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Q, Zou P, Zhan H, Zhang M, Zhang L,
Ge RS and Huang Y: Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase and cAMP are
associated with cadmium-mediated leydig cell damage. Toxicol Lett.
205:183–189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Naik GH, Priyadarsini KI, Satav JG,
Banavalikar MM, Sohoni DP, Biyani MK and Mohan H: Comparative
antioxidant activity of individual herbal components used in
ayurvedic medicine. Phytochemistry. 63:97–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
JiSang K and YoungSoon L: Antioxidant
activity of Maillard reaction products derived from aqueous
glucose/glycine, diglycine, and triglycine model systems as a
function of heating time. Food Chem. 116:227–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rollet-Labelle E, Grange MJ, Elbim C,
Marquetty C, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA and Pasquier C: Hydroxyl radical
as a potential intracellular mediator of polymorphonuclear
neutrophil apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 24:563–572. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Yuan X, Jin Z, Tian Y and Song H:
Free radical and reactive oxygen species scavenging activities of
peanut skins extract. Food Chem. 104:242–250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bernaert N, De Paepe D, Bouten C, De
Clercq H, Stewart D, Van Bockstaele E, De Loose M and Van
Droogenbroeck B: Antioxidant capacity, total phenolic and ascorbate
content as a function of the genetic diversity of leek (Allium
ampeloprasum var. porrum) Food Chem. 134:669–677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ajila CM and Prasada Rao UJ: Protection
against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative damage in rat
erythrocytes by mangifera indica L. peel extract. Food Chem
Toxicol. 46:303–309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mendes L, de Freitas V, Baptista P and
Carvalho M: Comparative antihemolytic and radical scavenging
activities of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) leaf and fruit.
Food Chem Toxicol. 49:2285–2291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lang F, Lang KS, Lang PA, Huber SM and
Wieder T: Mechanisms and significance of eryptosis. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 8:1183–1192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bayrak O, Uz E, Bayrak R, Turgut F, Atmaca
AF, Sahin S, Yildirim ME, Kaya A, Cimentepe E and Akcayet A:
Curcumin protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat
kidneys. World J Urol. 26:285–291. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Forman HJ, Zhang H and Rinna A:
Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and
biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 30:1–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Deng SL, Chen WF, Zhou B, Yang L and Liu
ZL: Protective effects of curcumin and its analogues against free
radical-induced oxidative haemolysis of human red blood cells. Food
Chem. 98:112–119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tedesco I, Luigi Russo G, Nazzaro F, Russo
M and Palumbo R: Antioxidant effect of red wine anthocyanins in
normal and catalase-inactive human erythrocytes. J Nutr Biochem.
12:505–511. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Nusrat A, Parkos CA, Verkade P, Foley CS,
Liang TW, Innis-Whitehouse W, Eastburn KK and Madara JL: Tight
junctions are membrane microdomains. J Cell Sci. 113:1771–1781.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kowaltowski AJ and Vercesi AE:
Mitochondrial damage induced by conditions of oxidative stress.
Free Radic Biol Med. 26:463–471. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bai K, Xu W, Zhang J, Kou T, Niu Y, Wan X,
Zhang L, Wang C and Wang T: Assessment of free radical scavenging
activity of dimethylglycine sodium salt and its role in providing
protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in
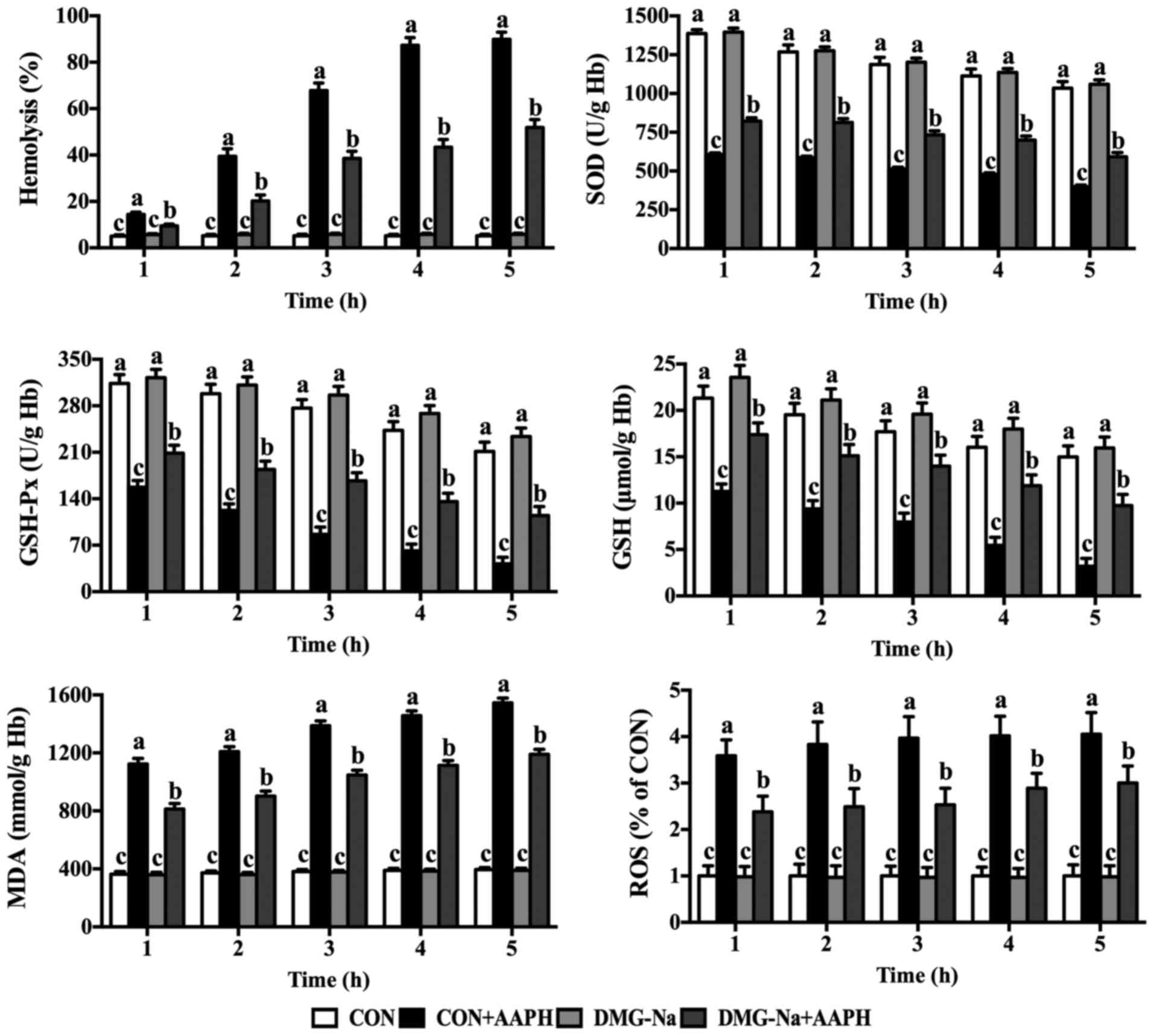
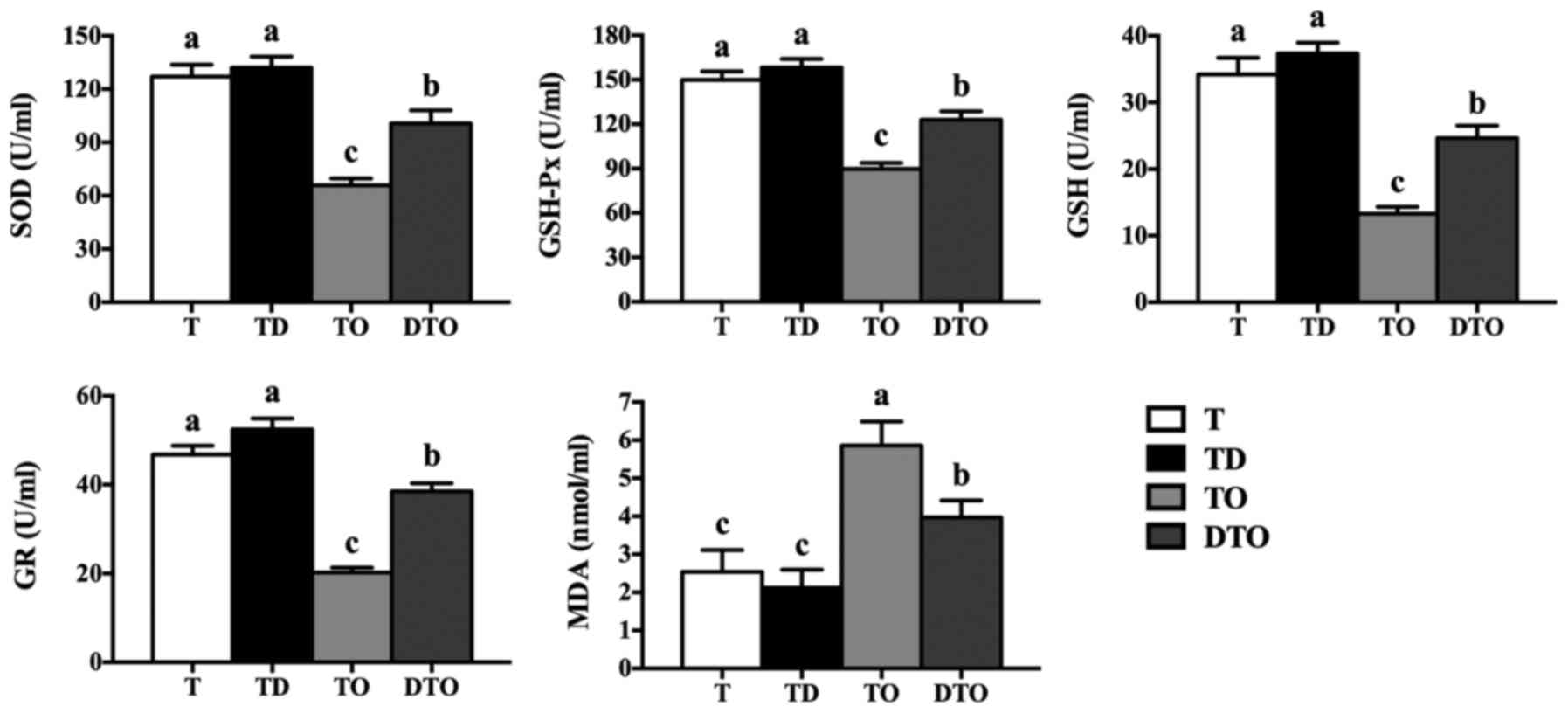
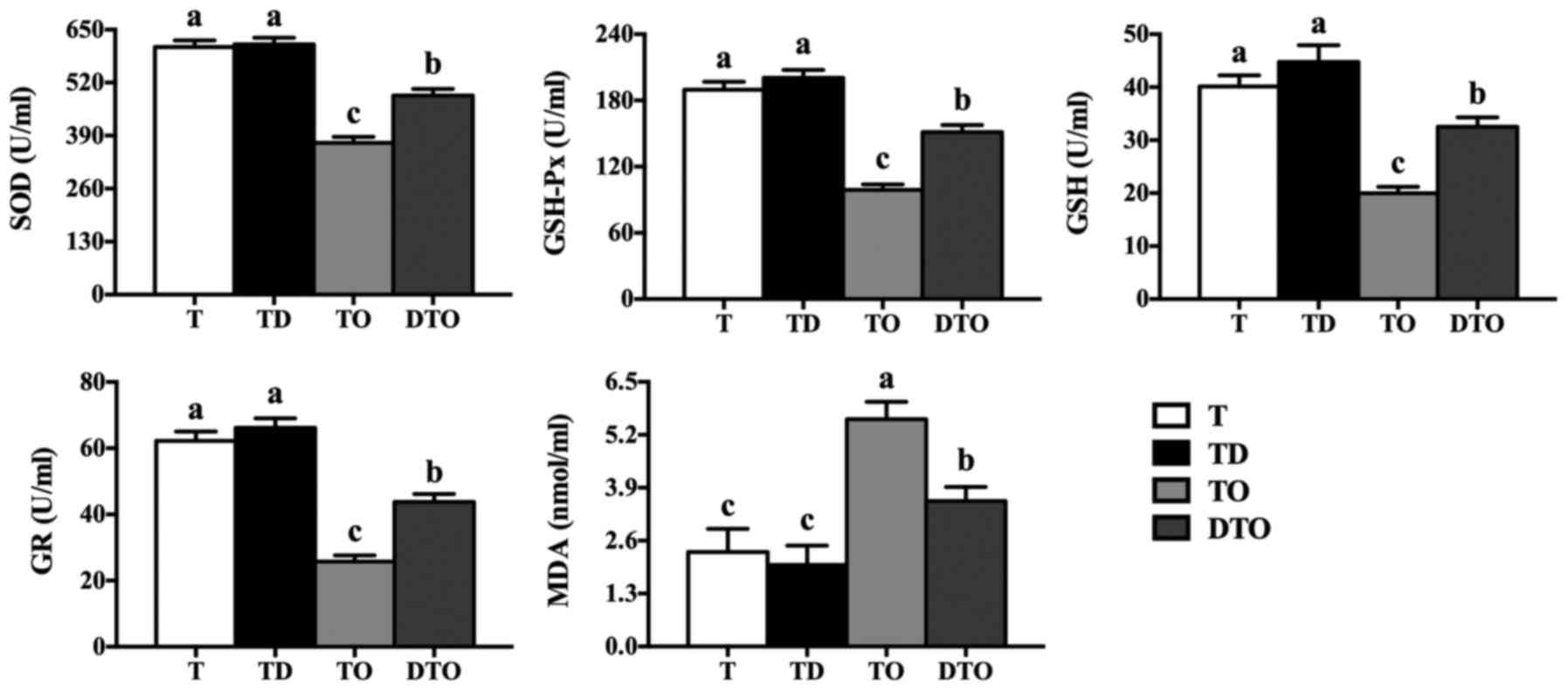
mice. PLoS One. 11:e01553932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee HJ, Oh YK, Rhee M, Lim JY, Hwang JY,
Park YS, Kwon Y, Choi KH, Jo I, Park SI, et al: The role of
STAT1/IRF-1 on synergistic ROS production and loss of mitochondrial
transmembrane potential during hepatic cell death induced by
LPS/d-GalN. J Mol Biol. 369:967–984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wilhelm EA, Jesse CR, Roman SS, Nogueira
CW and Savegnago L: Hepatoprotective effect of 3-alkynyl
selenophene on acute liver injury induced by D-galactosamine and
lipopoly-saccharide. Exp Mol Pathol. 87:20–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen JJ and Yu BP: Alterations in
mitochondrial membrane fluidity by lipid peroxidation products.
Free Radic Biol Med. 17:411–418. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang J, Xu L, Zhang L, Ying Z, Su W and
Wang T: Curcumin attenuates
D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury and
mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. J Nutr. 144:1211–1218. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chiu H, Brittingham JA and Laskin DL:
Differential induction of heme oxygenase-1 in macrophages and
hepatocytes during acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat:
Effects of hemin and biliverdin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
181:106–115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chung S, Yao H, Caito S, Hwang JW,
Arunachalam G and Rahman I: Regulation of SIRT1 in cellular
functions: Role of polyphenols. Arch Biochem Biophys. 501:79–90.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hwang JW, Yao H, Caito S, Sundar IK and
Rahman I: Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular
senescence. Free Radic Biol Med. 61:95–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee JM and Johnson JA: An important role
of Nrf2-are pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 37:139–143. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Michelet L, Zaffagnini M, Massot V, Keryer
E, Vanacker H, Miginiac-Maslow M, Issakidis-Bourguet E and Lemai
SD: Thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and glutathionylation: New
crosstalks to explore. Photosynth Res. 89:225–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gu L, Li N, Gong J, Li Q, Zhu W and Li J:
Berberine ameliorates intestinal epithelial tight-junction damage
and down-regulates myosin light chain kinase pathways in a mouse
model of endotoxinemia. J Infect Dis. 203:1602–1612. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|