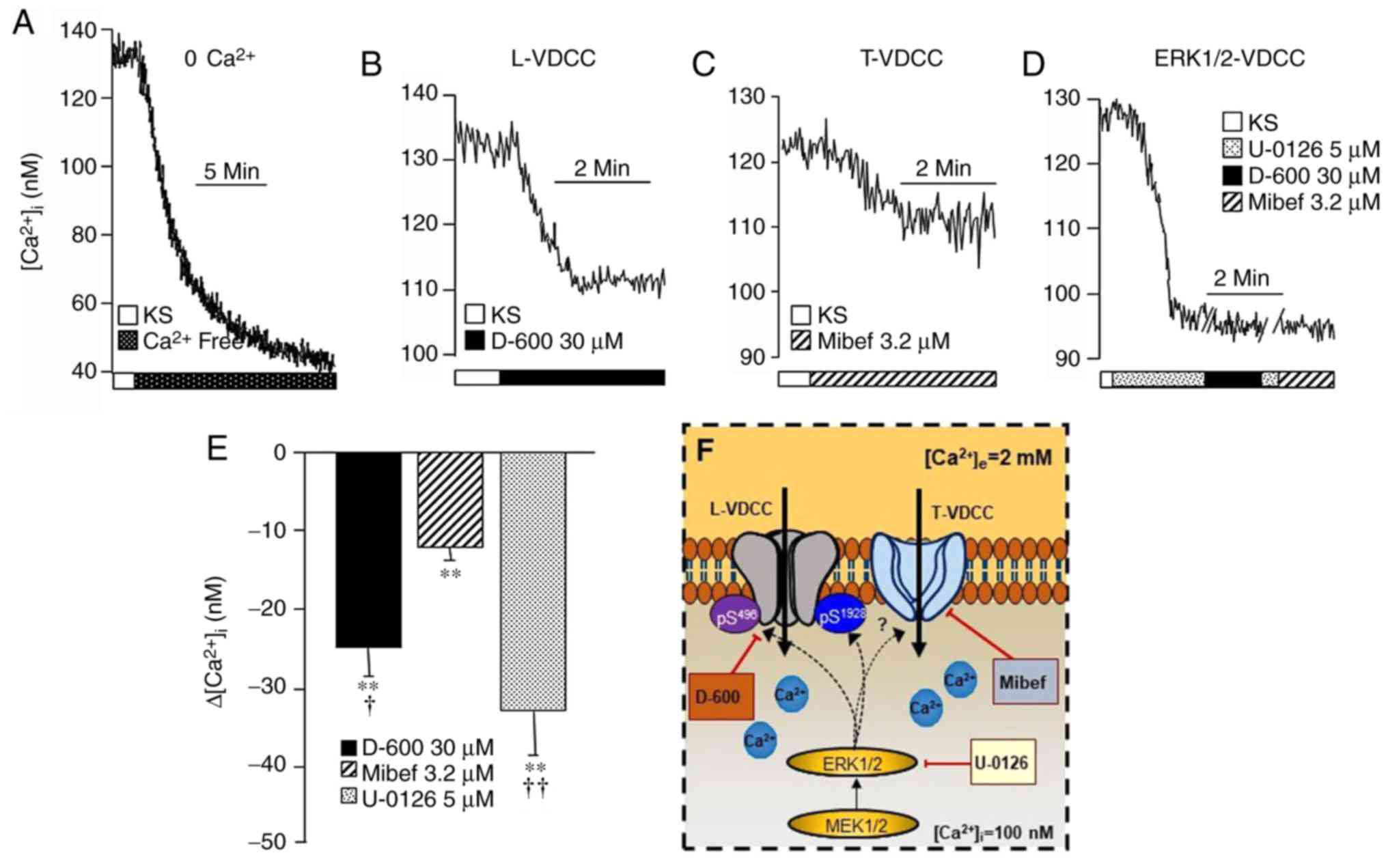
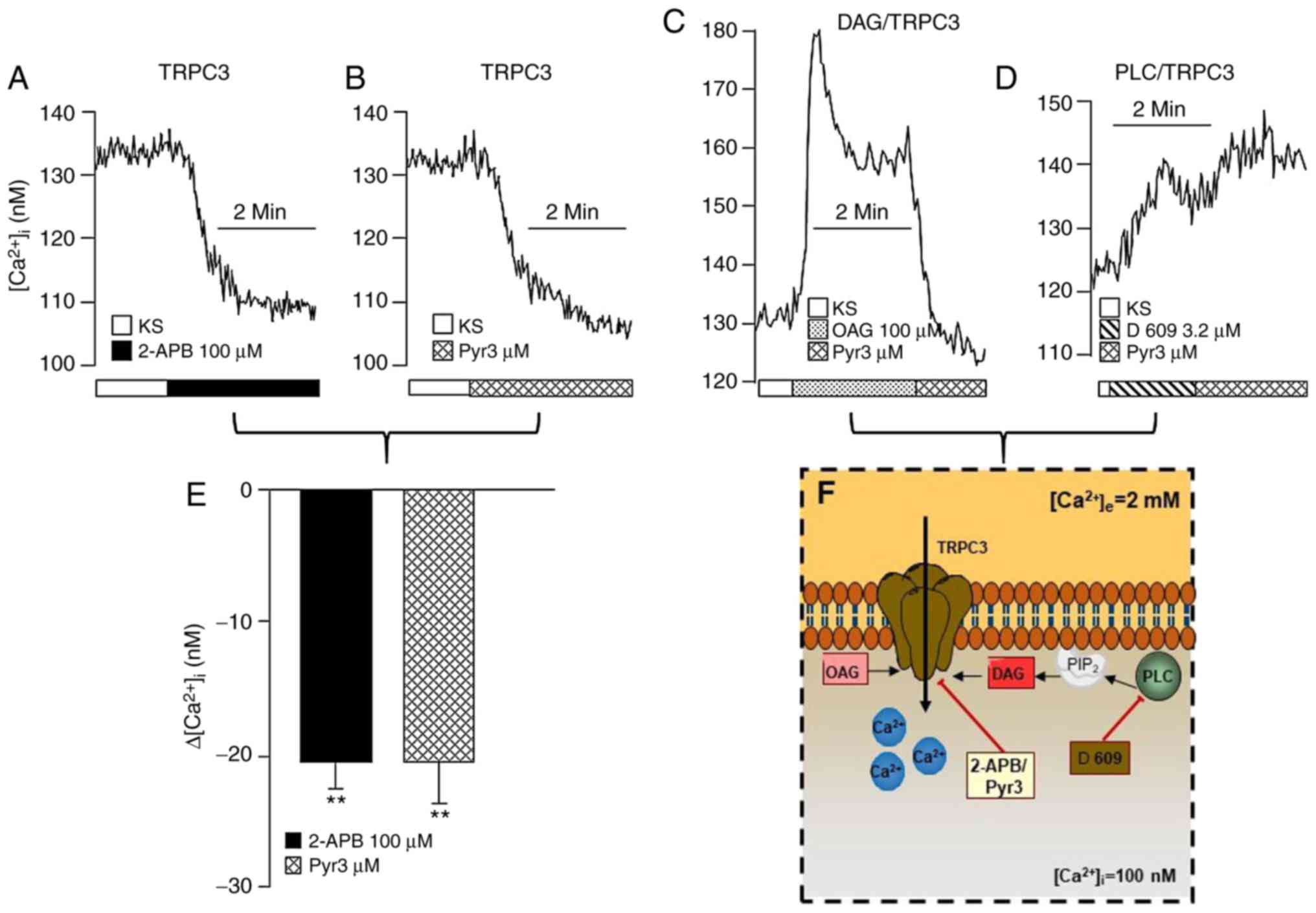
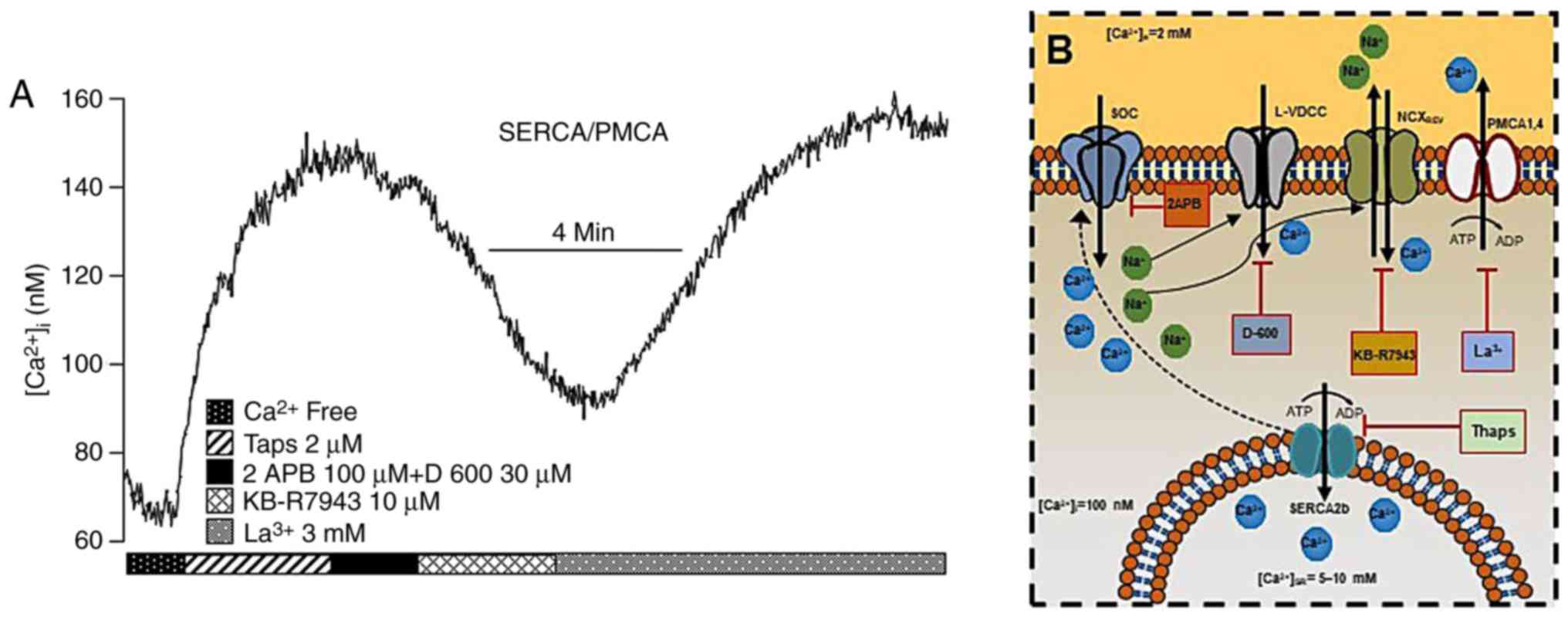
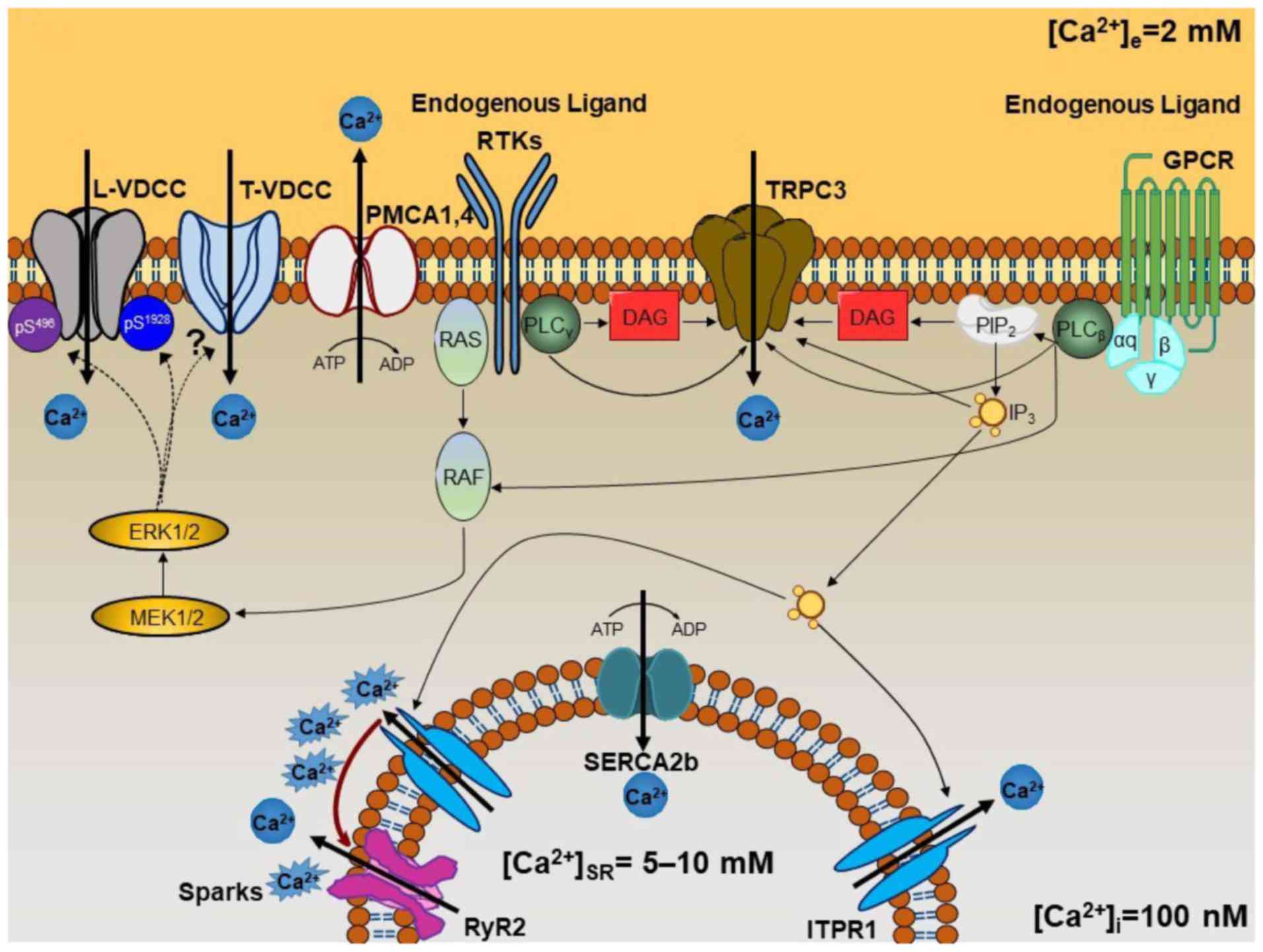
|
1
|
Albert AP, Piper AS and Large WA:
Properties of a constitutively active Ca2+-permeable
non-selective cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes. J
Physiol. 549:143–156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Demirel E, Laskey RE, Purkerson S and van
Breemen C: The passive calcium leak in cultured porcine aortic
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 191:1197–1203. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fayazi AH, Lapidot SA, Huang BK, Tucker RW
and Phair RD: Resolution of the basal plasma membrane calcium flux
in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 270:H1972–H1978.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hodgkin AL and Keynes RD: Movements of
labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 138:253–281.
1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Holland WC and Sekul A: Influence of
potassium and calcium ions on the effect of ouabain on
Ca45 entry and contracture in rabbit atria. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 133:288–294. 1961.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rutter GA, Hodson DJ, Chabosseau P,
Haythorne E, Pullen TJ and Leclerc I: Local and regional control of
calcium dynamics in the pancreatic islet. Diabetes Obes Metab.
19(Suppl 1): S30–S41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu X, Weng L, Zhang J, Liu X and Huang J:
The plasma membrane calcium ATPases in calcium signaling network.
Curr Protein Pept Sci. 19:813–822. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bazan-Perkins B, Flores-Soto E,
Barajas-Lopez C and Montaño LM: Role of sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ content in Ca2+ entry of bovine airway
smooth muscle cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
368:277–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Carbajal V, Vargas MH, Flores-Soto E,
Martinez-Cordero E, Bazán-Perkins B and Montaño LM: LTD4
induces hyperresponsiveness to histamine in bovine airway smooth
muscle: Role of SR-ATPase Ca2+ pump and tyrosine kinase.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L84–L92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Flores-Soto E, Reyes-Garcia J, Sommer B
and Montaño LM: Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ refilling is
determined by L-type Ca2+ and store operated
Ca2+ channels in guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Eur J
Pharmacol. 721:21–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Montaño LM and Bazán-Perkins B: Resting
calcium influx in airway smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
83:717–723. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu Z, Ma R and Gong J: Investigation of
testosterone-mediated non-transcriptional inhibition of
Ca2+ in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biomed Rep.
4:197–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Braunstein TH, Inoue R, Cribbs L, Oike M,
Ito Y, Holstein-Rathlou NH and Jensen LJ: The role of L- and T-type
calcium channels in local and remote calcium responses in rat
mesenteric terminal arterioles. J Vasc Res. 46:138–151. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wakle-Prabagaran M, Lorca RA, Ma X,
Stamnes SJ, Amazu C, Hsiao JJ, Karch CM, Hyrc KL, Wright ME and
England SK: BKCa channel regulates calcium oscillations induced by
alpha-2-macroglobulin in human myometrial smooth muscle cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E2335–E2344. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aguilar HN and Mitchell BF: Physiological
pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating uterine contractility.
Hum Reprod Update. 16:725–744. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Asano M, Nomura Y, Hayakawa M, Ito KM,
Uyama Y, Imaizumi Y and Watanabe M: Increased Ca2+ influx in the
resting state maintains the myogenic tone and activates
charyb-dotoxin-sensitive K+ channels in femoral arteries from young
SHR. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 22(Suppl): S225–S227. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bae YM, Park MK, Lee SH, Ho WK and Earm
YE: Contribution of Ca2+-activated K+
channels and non-selective cation channels to membrane potential of
pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol.
514:747–758. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Flores-Soto E, Reyes-García J,
Carbajal-García A, Campuzano-González E, Perusquía M, Sommer B and
Montaño LM: Sex steroids effects on guinea pig airway smooth muscle
tone and intracellular Ca2+ basal levels. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 439:444–456. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Janssen LJ: T-type and L-type
Ca2+ currents in canine bronchial smooth muscle:
Characterization and physiological roles. Am J Physiol.
272:C1757–C1765. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montaño LM, Barajas-Lopez C and Daniel EE:
Canine bronchial sustained contraction in Ca2+-free
medium: Role of intracellular Ca2+. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 74:1236–1248. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sommer B, Flores-Soto E, Reyes-García J,
Diaz-Hernández V, Carbajal V and Montaño LM: Na+
permeates through L-type Ca2+ channel in bovine airway
smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 782:77–88. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Worley JF III and Kotlikoff MI:
Dihydropyridine-sensitive single calcium channels in airway smooth
muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 259:L468–L480. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bolton TB: Mechanisms of action of
transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev.
59:606–718. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Godin N and Rousseau E: TRPC6 silencing in
primary airway smooth muscle cells inhibits protein expression
without affecting OAG-induced calcium entry. Mol Cell Biochem.
296:193–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hallam TJ and Rink TJ: Receptor-mediated
Ca2+ entry: Diversity of function and mechanism. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 10:8–10. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martinsen A, Dessy C and Morel N:
Regulation of calcium chan-nels in smooth muscle: New insights into
the role of myosin light chain kinase. Channels (Austin).
8:402–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
McFadzean I and Gibson A: The developing
relationship between receptor-operated and store-operated calcium
channels in smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 135:1–13. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murray RK and Kotlikoff MI:
Receptor-activated calcium influx in human airway smooth muscle
cells. J Physiol. 435:123–144. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ay B, Prakash YS, Pabelick CM and Sieck
GC: Store-operated Ca2+ entry in porcine airway smooth
muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L909–L917. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bazan-Perkins B, Carbajal V, Sommer B,
Macías-Silva M, González-Martínez M, Valenzuela F, Daniel EE and
Montaño LM: Involvement of different Ca2+ pools during
the canine bronchial sustained contraction in Ca2+-free
medium: Lack of effect of PKC inhibition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 358:567–573. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Putney JW Jr: A model for
receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 7:1–12. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sweeney M, McDaniel SS, Platoshyn O, Zhang
S, Yu Y, Lapp BR, Zhao Y, Thistlethwaite PA and Yuan JX: Role of
capacitative Ca2+ entry in bronchial contraction and
remodeling. J Appl Physiol 1985. 92:1594–1602. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Avila-Medina J, Mayoral-González I,
Domínguez-Rodriguez A, Gallardo-Castillo I, Ribas J, Ordoñez A,
Rosado JA and Smani T: The complex role of store operated calcium
entry pathways and related proteins in the function of cardiac,
skeletal and vascular smooth muscle cells. Front Physiol.
9:2572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baron CB, Cunningham M, Strauss JF III and
Coburn RF: Pharmacomechanical coupling in smooth muscle may involve
phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
81:6899–6903. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Berridge MJ: Inositol trisphosphate and
calcium signalling. Nature. 361:315–325. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song T, Hao Q, Zheng YM, Liu QH and Wang
YX: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates TRPC3 channels to cause
extracellular Ca2+ influx in airway smooth muscle cells.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L1455–L1466. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bazan-Perkins B, Sánchez-Guerrero E,
Carbajal V, Barajas-López C and Montaño LM: Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ depletion by caffeine and changes of
[Ca2+]i during refilling in bovine airway
smooth muscle cells. Arch Med Res. 31:558–563. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sieck GC, Kannan MS and Prakash YS:
Heterogeneity in dynamic regulation of intracellular calcium in
airway smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 75:878–888.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matsuki K, Kato D, Takemoto M, Suzuki Y,
Yamamura H, Ohya S, Takeshima H and Imaizumi Y: Negative regulation
of cellular Ca2+ mobilization by ryanodine receptor type
3 in mouse mesenteric artery smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 315:C1–C9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhao C, Wu AY, Yu X, Gu Y, Lu Y, Song X,
An N and Shang Y: Microdomain elements of airway smooth muscle in
calcium regulation and cell proliferation. J Physiol Pharmacol.
69:2018.
|
|
41
|
Blaustein MP and Lederer WJ:
Sodium/calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol
Rev. 79:763–854. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Eisner DA and Lederer WJ: Na-Ca exchange:
Stoichiometry and electrogenicity. Am J Physiol. 248:C189–C202.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Janssen LJ, Walters DK and Wattie J:
Regulation of [Ca2+]i in canine airway smooth muscle by
Ca2+-ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange
mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 273:L322–L330. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lipskaia L, Bobe R, Chen J, Turnbull IC,
Lopez JJ, Merlet E, Jeong D, Karakikes I, Ross AS, Liang L, et al:
Synergistic role of protein phosphatase inhibitor 1 and
sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in the
acquisition of the contractile phenotype of arterial smooth muscle
cells. Circulation. 129:773–785. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu B, Zhang B, Huang S, Yang L, Roos CM,
Thompson MA, Prakash YS, Zang J, Miller JD and Guo R:
Ca2+ Entry through reverse mode
Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger contributes to store
operated channel-mediated neointima formation after arterial
injury. Can J Cardiol. 34:791–799. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mazur II, Veklich TO, Shkrabak OA, Mohart
NA, Demchenko AM, Gerashchenko IV, Rodik RV, Kalchenko VI and
Kosterin SO: Selective inhibition of smooth muscle plasma membrane
transport Ca2+, Mg2+-ATPase by calixarene
C-90 and its activation by IPT-35 compound. Gen Physiol Biophys.
37:223–231. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nishiyama K, Azuma YT, Morioka A, Yoshida
N, Teramoto M, Tanioka K, Kita S, Hayashi S, Nakajima H, Iwamoto T
and Takeuchi T: Roles of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
isoforms NCX1 and NCX2 in motility in mouse ileum. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 389:1081–1090. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sommer B, Flores-Soto E and González-Avila
G: Cellular Na+ handling mechanisms involved in airway
smooth muscle contraction (Review). Int J Mol Med. 40:3–9. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang WB and Kwan CY: Pharmacological
evidence that potentiation of plasmalemmal
Ca2+-extrusion is functionally coupled to inhibition of
SR Ca2+-ATPases in vascular smooth muscle cells. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 389:447–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Poburko D, Lhote P, Szado T, Behra T,
Rahimina R, McManus B, Van Breemen C and Ruegg UT: Basal calcium
entry in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 505:19–29. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bean BP: Classes of calcium channels in
vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 51:367–384. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yu J and Bose R: Calcium channels in
smooth muscle. Gastroenterology. 100:1448–1460. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Green KA, Small RC and Foster RW: The
properties of voltage-operated Ca2+-channels in bovine
isolated trachealis cells. Pulm Pharmacol. 6:49–62. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hisada T, Kurachi Y and Sugimoto T:
Properties of membrane currents in isolated smooth muscle cells
from guineapig trachea. Pflugers Arch. 416:151–161. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kotlikoff MI: Calcium currents in isolated
canine airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 254:C793–C801.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Marthan R, Martin C, Amedee T and
Mironneau J: Calcium channel currents in isolated smooth muscle
cells from human bronchus. J Appl Physiol (1985). 66:1706–1714.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hirota S and Janssen LJ: Store-refilling
involves both L-type calcium channels and reverse-mode
sodium-calcium exchange in airway smooth muscle. Eur Respir J.
30:269–278. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP and
Striessnig J: International union of pharmacology. XLVIII.
Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated
calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 57:411–425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Du W, McMahon TJ, Zhang ZS, Stiber JA,
Meissner G and Eu JP: Excitation-contraction coupling in airway
smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 281:30143–30151. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Reyes-Garcia J, Flores-Soto E,
Solis-Chagoyan H, Sommer B, Diaz-Hernandez V, Garcia-Hernandez LM
and Montaño LM: Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits L-type Ca2+
channels in sensitized guinea pig airway smooth muscle through ERK
1/2 pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2016.5972302:2016.
|
|
61
|
Janssen LJ and Daniel EE: Depolarizing
agents induce oscillations in canine bronchial smooth muscle
membrane potential: Possible mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
259:110–117. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xu KY, Zhu W and Xiao RP:
Serine496 of β2 subunit of L-type
Ca2+ channel participates in molecular crosstalk between
activation of (Na++K+)-ATPase and the
channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:319–323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang Y, Sun J, Jin R, Liang Y, Liu YY and
Xu YD: Influence of acupuncture on expression of T-type calcium
channel protein in airway smooth muscle cell in airway remodeling
rats with asthma. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 32:534–540. 2012.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Blesneac I, Chemin J, Bidaud I, Huc-Brandt
S, Vandermoere F and Lory P: Phosphorylation of the Cav3.2 T-type
calcium channel directly regulates its gating properties. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:13705–13710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wylam ME, Gungor N, Mitchell RW and Umans
JG: Eosinophils, major basic protein, and polycationic peptides
augment bovine airway myocyte Ca2+ mobilization. Am J
Physiol. 274:L997–L1005. 1998.
|
|
66
|
Yocum GT, Chen J, Choi CH, Townsend EA,
Zhang Y, Xu D, Fu XW, Sanderson MJ and Emala CW: Role of transient
receptor potential vanilloid 1 in the modulation of airway smooth
muscle tone and calcium handling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 312:L812–L821. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dietrich A, Chubanov V, Kalwa H, Rost BR
and Gudermann T: Cation channels of the transient receptor
potential superfamily: Their role in physiological and
pathophysiological processes of smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol
Ther. 112:744–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ong HL, Brereton HM, Harland ML and
Barritt GJ: Evidence for the expression of transient receptor
potential proteins in guinea pig airway smooth muscle cells.
Respirology. 8:23–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hofmann T, Obukhov AG, Schaefer M,
Harteneck C, Gudermann T and Schultz G: Direct activation of human
TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels by diacylglycerol. Nature. 397:259–263.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Storch U, Forst AL, Pardatscher F,
Erdogmus S, Philipp M and Gregoritza M: Dynamic NHERF interaction
with TRPC4/5 proteins is required for channel gating by
diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E37–E46. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Li SW, Westwick J and Poll CT:
Receptor-operated Ca2+ influx channels in leukocytes: A
therapeutic target. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 23:63–70. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zitt C, Zobel A, Obukhov AG, Harteneck C,
Kalkbrenner F, Luckhpoff A and Schultz G: Cloning and functional
expression of a human Ca2+-permeable cation channel
activated by calcium store depletion. Neuron. 16:1189–1196. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu SZ and Beech DJ: TrpC1 is a
membrane-spanning subunit of store-operated Ca2+
channels in native vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res.
88:84–87. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wu X, Babnigg G and Villereal ML:
Functional significance of human trp1 and trp3 in store-operated
Ca2+ entry in HEK-293 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
278:C526–C536. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Gailly P and Colson-Van Schoor M:
Involvement of trp-2 protein in store-operated influx of calcium in
fibroblasts. Cell Calcium. 30:157–165. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Okada T, Inoue R, Yamazaki K, Maeda A,
Kurosaki T, Yamakuni T, Tanaka I, Shimizu S, Ikenaka K, Imoto K, et
al: Molecular and functional characterization of a novel mouse
transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP7.
Ca2+-permeable cation channel that is constitutively
activated and enhanced by stimulation of G protein-coupled
receptor. J Biol Chem. 274:27359–27370. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Vandebrouck C, Martin D, Colson-Van Schoor
M, Debaix H and Gailly P: Involvement of TRPC in the abnormal
calcium influx observed in dystrophic (mdx) mouse skeletal muscle
fibers. J Cell Biol. 158:1089–1096. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Albert AP, Pucovsky V, Prestwich SA and
Large WA: TRPC3 properties of a native constitutively active
Ca2+-permeable cation channel in rabbit ear artery myocytes. J
Physiol. 571:361–369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xiao JH, Zheng YM, Liao B and Wang YX:
Functional role of canonical transient receptor potential 1 and
canonical transient receptor potential 3 in normal and asthmatic
airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:17–25.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Trebak M, Bird GS, McKay RR and Putney JW
Jr: Comparison of human TRPC3 channels in receptor-activated and
store-operated modes. Differential sensitivity to channel blockers
suggests fundamental differences in channel composition. J Biol
Chem. 277:21617–21623. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kiyonaka S, Kato K, Nishida M, Mio K,
Numaga T, Sawaguchi Y, Yoshida T, Wakamori M, Mori E, Numata T, et
al: Selective and direct inhibition of TRPC3 channels underlies
biological activities of a pyrazole compound. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:5400–5405. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Albert AP, Piper AS and Large WA: Role of
phospholipase D and diacylglycerol in activating constitutive
TRPC-like cation channels in rabbit ear artery myocytes. J Physiol.
566:769–780. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mamoon AM, Smith J, Baker RC and Farley
JM: Activation of protein kinase A increases phospholipase D
activity and inhibits phospholipase D activation by acetylcholine
in tracheal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 291:1188–1195.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Monick MM, Carter AB, Gudmundsson G,
Mallampalli R, Powers LS and Hunninghake GW: A
phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C regulates activation
of p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human alveolar macrophages. J
Immunol. 162:3005–3012. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ito S, Kume H, Naruse K, Kondo M, Takeda
N, Iwata S, Hasegawa Y and Sokabe M: A novel Ca2+ influx
pathway activated by mechanical stretch in human airway smooth
muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 38:407–413. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Leung FP, Yung LM, Yao X, Laher I and
Huang Y: Store-operated calcium entry in vascular smooth muscle. Br
J Pharmacol. 153:846–857. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S,
Rao A and Hogan PG: Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC
channel. Nature. 443:230–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Roos J, DiGregorio PJ, Yeromin AV, Ohlsen
K, Lioudyno M, Zhang S, Safrina O, Kozak JA, Wagner SL, Cahalan MD,
et al: STIM1, an essential and conserved component of
store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J Cell Biol.
169:435–445. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Peel SE, Liu B and Hall IP: ORAI and
store-operated calcium influx in human airway smooth muscle cells.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 38:744–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Potier M, Gonzalez JC, Motiani RK,
Abdullaev IF, Bisaillon JM, Singer HA and Treback M: Evidence for
STIM1- and Orai1-dependent store-operated calcium influx through
ICRAC in vascular smooth muscle cells: Role in proliferation and
migration. FASEB J. 23:2425–2437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Shuttleworth TJ: Orai3-the ‘exceptional’
Orai. J Physiol. 590:241–257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Liou J, Kim ML, Heo WD, Jones JT, Myers
JW, Ferrel JE Jr and Meyer T: STIM is a Ca2+ sensor
essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered
Ca2+ influx. Curr Biol. 15:1235–1241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Prakriya M and Lewis RS: Store-operated
calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 95:1383–1436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Peel SE, Liu B and Hall IP: A key role for
STIM1 in store operated calcium channel activation in airway smooth
muscle. Respir Res. 7:1192006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhang SL, Yu Y, Roos J, Kozak JA, Deerinck
TJ, Ellisman MH, Stauderman KA and Cahalan MD: STIM1 is a
Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates
from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature.
437:902–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liao Y, Erxleben C, Yildirim E, Abramowitz
J, Armstrong DL and Birnbaumer L: Orai proteins interact with TRPC
channels and confer responsiveness to store depletion. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:4682–4687. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Dai JM, Kuo KH, Leo JM, van Breemen C and
Lee CH: Mechanism of ACh-induced asynchronous calcium waves and
tonic contraction in porcine tracheal muscle bundle. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L459–L469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
DiPolo R and Beaugé L: Sodium/calcium
exchanger: Influence of metabolic regulation on ion carrier
interactions. Physiol Rev. 86:155–203. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Philipson KD and Nicoll DA: Sodium-calcium
exchange: A molecular perspective. Annu Rev Physiol. 62:111–133.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lytton J: Na+/Ca2+
exchangers: Three mammalian gene families control Ca2+
transport. Biochem J. 406:365–382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Khananshvili D: The SLC8 gene family of
sodium-calcium exchangers (NCX)-structure, function, and regulation
in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med. 34:220–235. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
A lga ra-Sua rez P, Mejia-Elizondo R, Sims
SM, Saavedra-Alanis VM and Espinosa-Tanguma R: The 1.3 isoform of
Na+-Ca2+ exchanger expressed in guinea pig
tracheal smooth muscle is less sensitive to KB-R7943. J Physiol
Biochem. 66:117–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Rahman M, Inman M, Kiss L and Janssen LJ:
Reverse-mode NCX current in mouse airway smooth muscle:
Na+ and voltage dependence, contributions to
Ca2+ influx and contraction, and altered expression in a
model of allergen-induced hyperresponsiveness. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
205:279–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Sathish V, Delmotte PF, Thompson MA,
Pabelick CM, Sieck GC and Prakash YS: Sodium-calcium exchange in
intracellular calcium handling of human airway smooth muscle. PLoS
One. 6:e236622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Brini M and Carafoli E: Calcium pumps in
health and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1341–1378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Carafoli E: Calcium pump of the plasma
membrane. Physiol Rev. 71:129–153. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Darby PJ, Kwan CY and Daniel EE: Caveolae
from canine airway smooth muscle contain the necessary components
for a role in Ca2+ handling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 279:L1226–L1235. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chen YF, Cao J, Zhong JN, Chen X, Cheng M,
Yang J and Gao YD: Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase regulates
Ca2+ signaling and the proliferation of airway smooth
muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 740:733–741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Bobe R, Bredoux R, Corvazier E, Andersen
JP, Clausen JD, Dode L, Kovács T and Enouf J: Identification,
expression, function, and localization of a novel (sixth) isoform
of the human sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase 3
gene. J Biol Chem. 279:24297–24306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Mahn K, Hirst SJ, Ying S, Holt MR,
Lavender P, Ojo OO, Siew L, Simcock DE, McVicker CG, Kanabar V, et
al: Diminished sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
(SERCA) expression contributes to airway remodelling in bronchial
asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:10775–10780. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Helli PB and Janssen LJ: Properties of a
store-operated nonse-lective cation channel in airway smooth
muscle. Eur Respir J. 32:1529–1539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Perusquia M, Flores-Soto E, Sommer B,
Campuzano-González E, Martinez-Villa I, Martinez-Banderas AI and
Montaño LM: Testosterone-induced relaxation involves L-type and
store-operated Ca2+ channels blockade, and
PGE2 in guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch.
467:767–777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Sathish V, Thompson MA, Bailey JP,
Pabelick CM, Prakash YS and Sieck GC: Effect of proinflammatory
cytokines on regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+
reuptake in human airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 297:L26–L34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Sathish V, Leblebici F, Kip SN, Thompson
A, Pabelick CM, Prakash YS and Sieck GC: Regulation of sarcoplasmic
reticulum Ca2+ reuptake in porcine airway smooth muscle.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L787–L796. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Guerrero-Hernandez A, Ávila G and Rueda A:
Ryanodine receptors as leak channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 739:26–38.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Liu QH, Zheng YM, Korde AS, Yadav VR,
Rathore R, Wess J and Wang YX: Membrane depolarization causes a
direct activation of G protein-coupled receptors leading to local
Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:11418–11423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Deshpande DA, Walseth TF, Panettieri RA
and Kannan MS: CD38/cyclic ADP-ribose-mediated Ca2+
signaling contributes to airway smooth muscle hyper-responsiveness.
FASEB J. 17:452–454. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Rusinko N and Lee HC: Widespread
occurrence in animal tissues of an enzyme catalyzing the conversion
of NAD+ into a cyclic metabolite with intracellular
Ca2+-mobilizing activity. J Biol Chem. 264:11725–11731.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
White TA, Johnson S, Walseth TF, Lee HC,
Graeff RM, Munshi CB, Prakash YS, Sieck GC and Kannan MS:
Subcellular localization of cyclic ADP-ribosyl cyclase and cyclic
ADP-ribose hydrolase activities in porcine airway smooth muscle.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1498:64–71. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ross CA, Danoff SK, Schell MJ, Snyder SH
and Ullrich A: Three additional inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
receptors: Molecular cloning and differential localization in brain
and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:4265–4269. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Taylor CW, Genazzani AA and Morris SA:
Expression of inositol trisphosphate receptors. Cell Calcium.
26:237–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Narayanan D, Adebiyi A and Jaggar JH:
Inositol trisphosphate receptors in smooth muscle cells. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H2190–H2210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wang YX, Zheng YM, Mei QB, Wang QS,
Collier ML, Fleischer S, Xin HB and Kotlikoff MI: FKBP12.6 and
cADPR regulation of Ca2+ release in smooth muscle cells.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C538–C546. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Montaño LM, Flores-Soto E, Reyes-Garcia J,
Diaz Hernández V, Carbajal-Garcia A, Campuzáno González E,
Ramirez-Salinas GL, Velasco-Velázquez M and Sommer B: Testosterone
induces hyporesponsiveness by interfering with IP3
receptors in guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
473:17–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Cheng H, Lederer WJ and Cannell MB:
Calcium sparks: Elementary events underlying excitation-contraction
coupling in heart muscle. Science. 262:740–744. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Fabiato A: Calcium-induced release of
calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol.
245:C1–C14. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
ZhuGe R, Sims SM, Tuft RA, Fogarty KE and
Walsh JV Jr: Ca2+ sparks activate K+ and
Cl- channels, resulting in spontaneous transient
currents in guineapig tracheal myocytes. J Physiol. 513:711–718.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Collier ML, Ji G, Wang Y and Kotlikoff MI:
Calcium-induced calcium release in smooth muscle: Loose coupling
between the action potential and calcium release. J Gen Physiol.
115:653–662. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Liu QH, Zheng YM and Wang YX: Two distinct
signaling pathways for regulation of spontaneous local
Ca2+ release by phospholipase C in airway smooth muscle
cells. Pflugers Arch. 453:531–541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Zhang WM, Yip KP, Lin MJ, Shimoda LA, Li
WH and Sham JS: ET-1 activates Ca2+ sparks in PASMC:
Local Ca2+ signaling between inositol trisphosphate and
ryanodine receptors. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
285:L680–L690. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Jude JA, Solway J, Panettieri RA Jr,
Walseth TF and Kannan MS: Differential induction of CD38 expression
by TNF-α in asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 299:L879–L890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Hotta K, Emala CW and Hirshman CA: TNF-α
upregulates Giα and Gqα protein expression and function in human
airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 276:L405–L411.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|