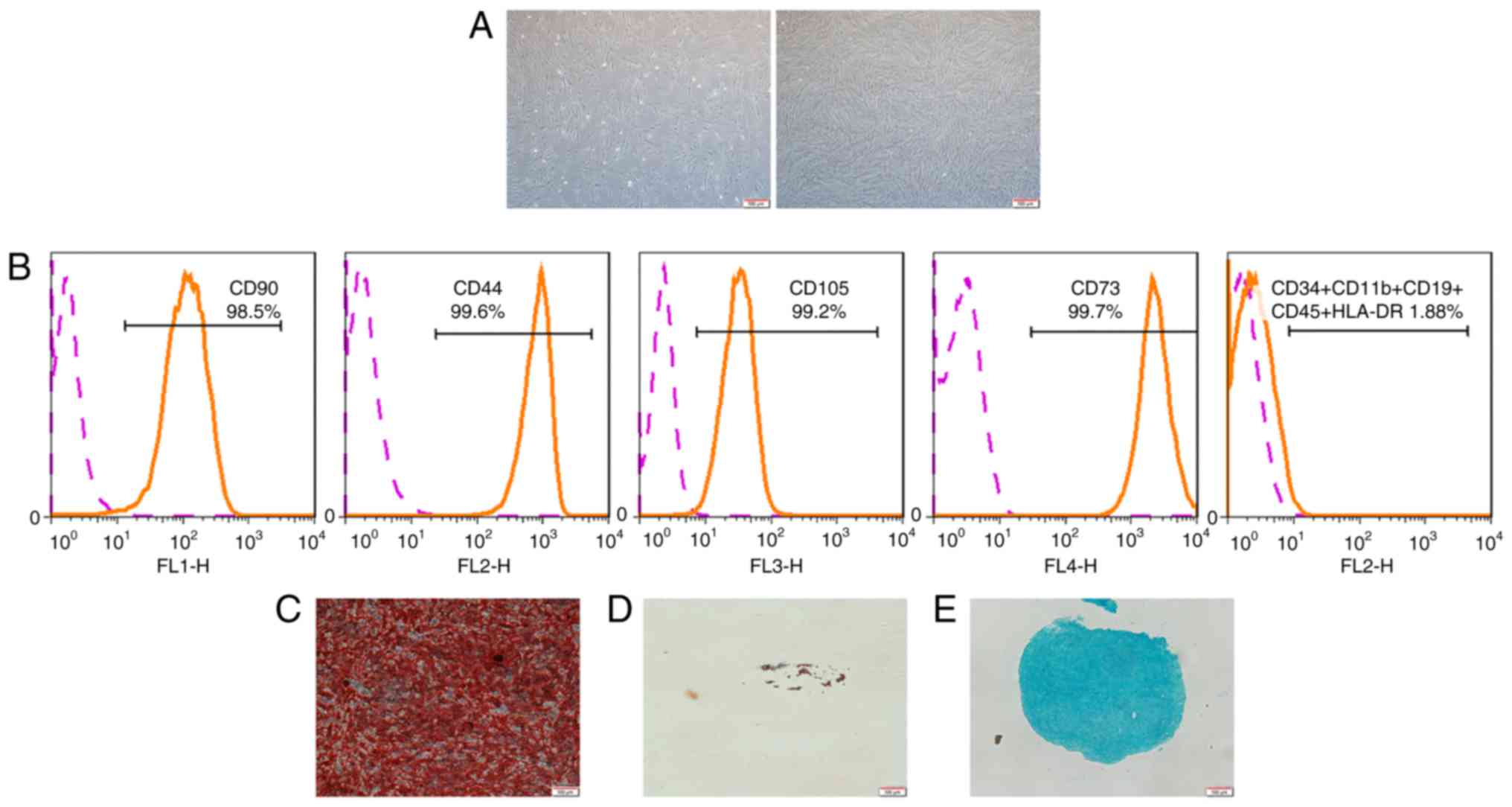
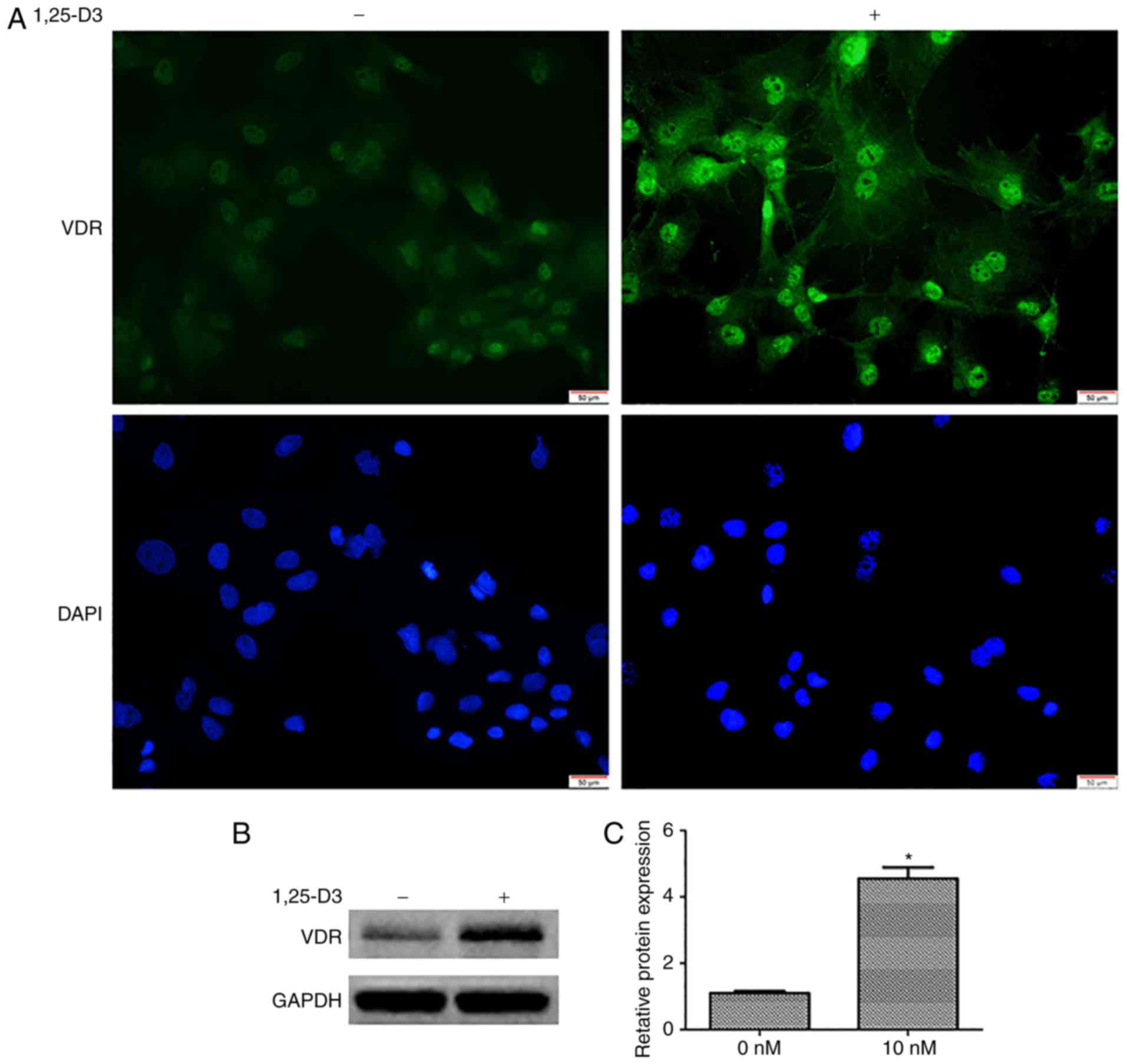
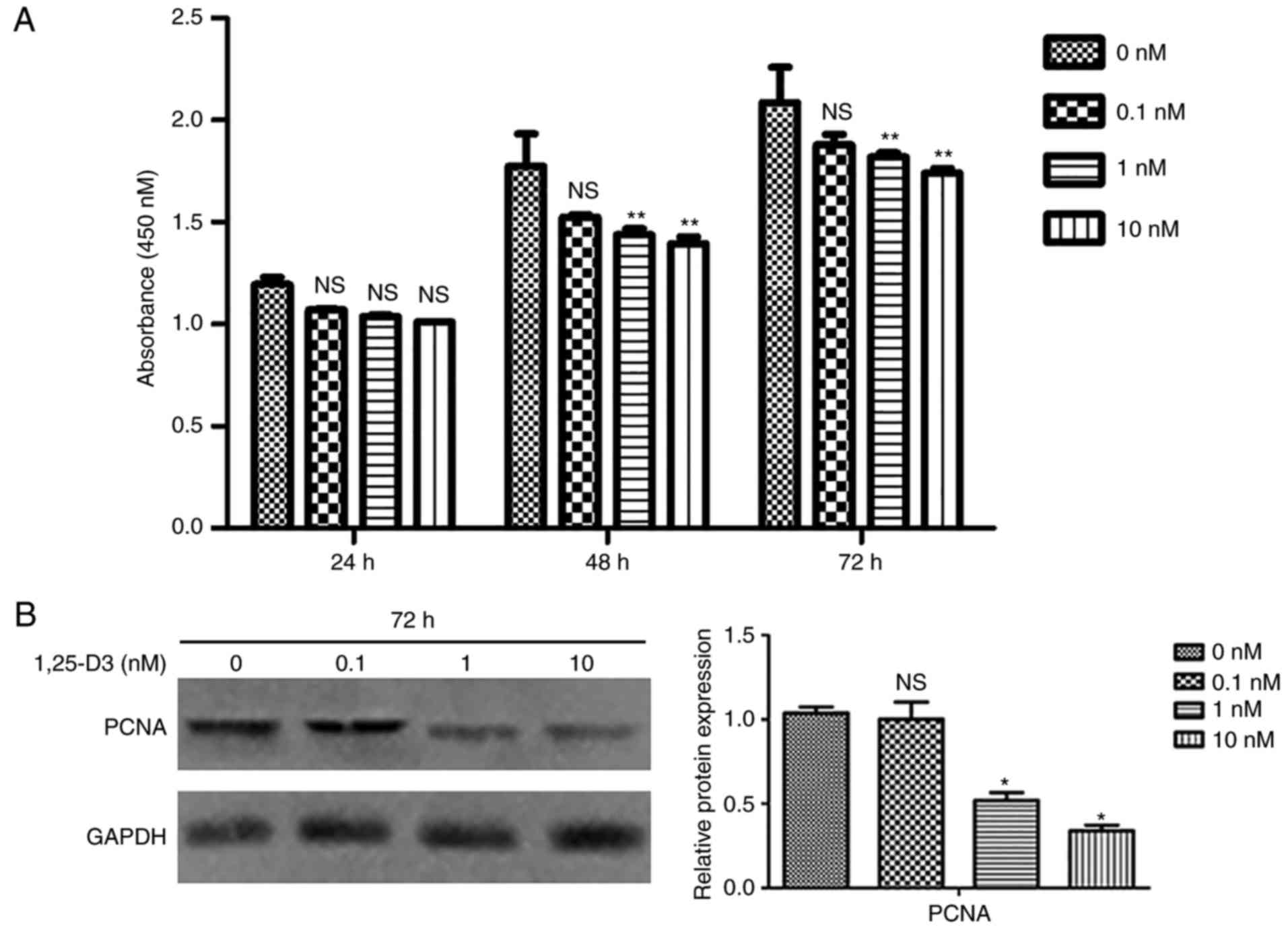
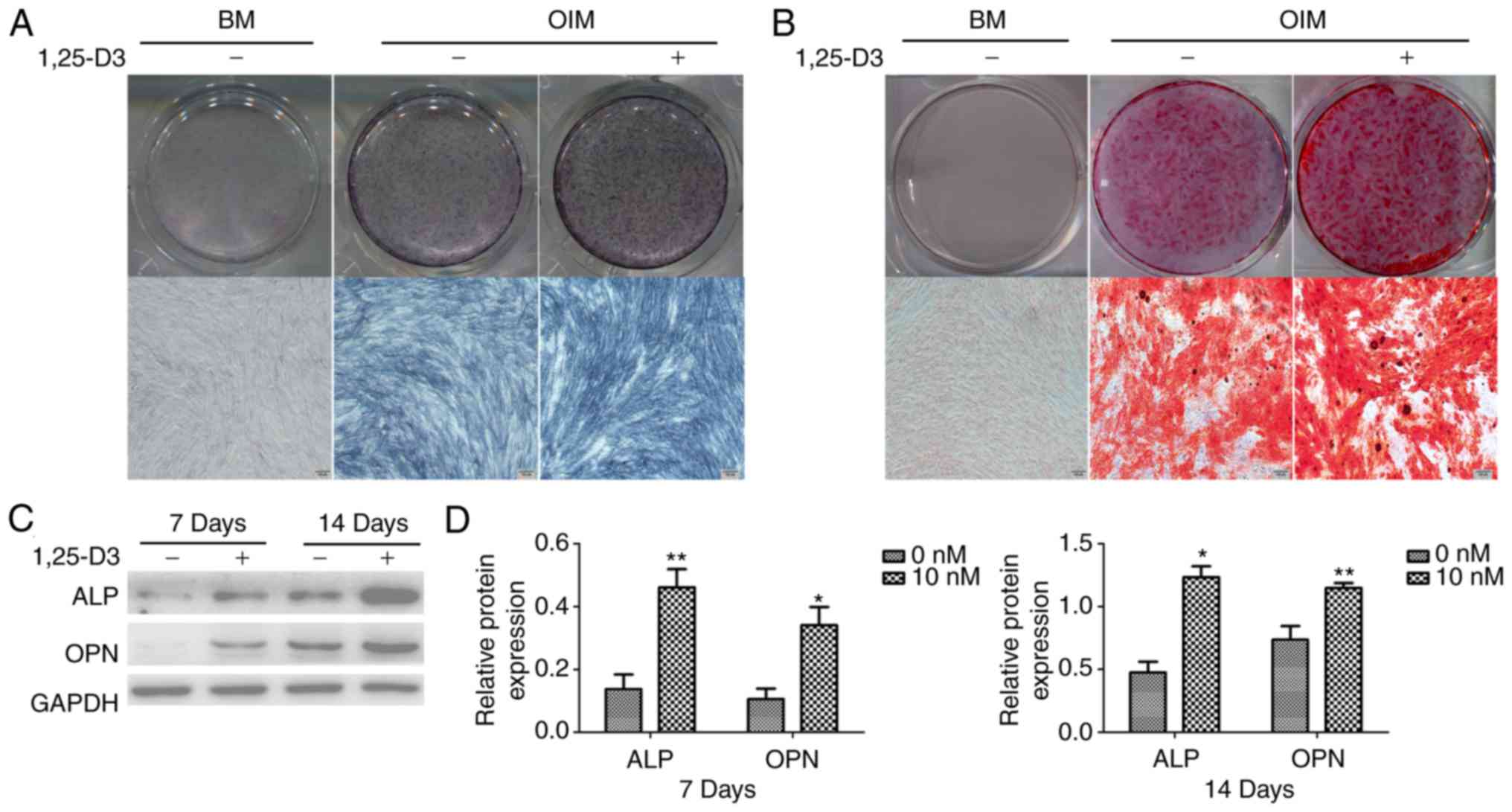
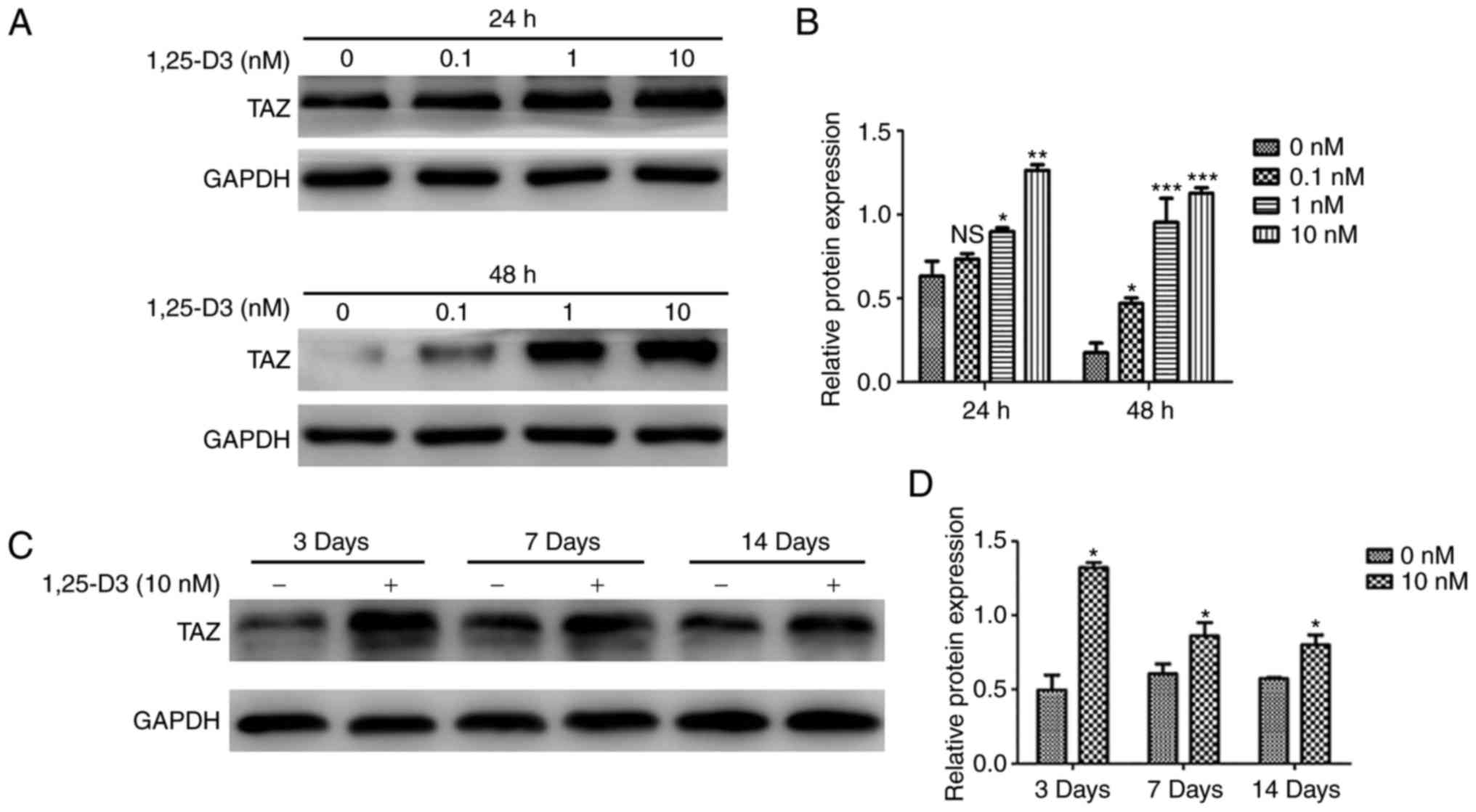
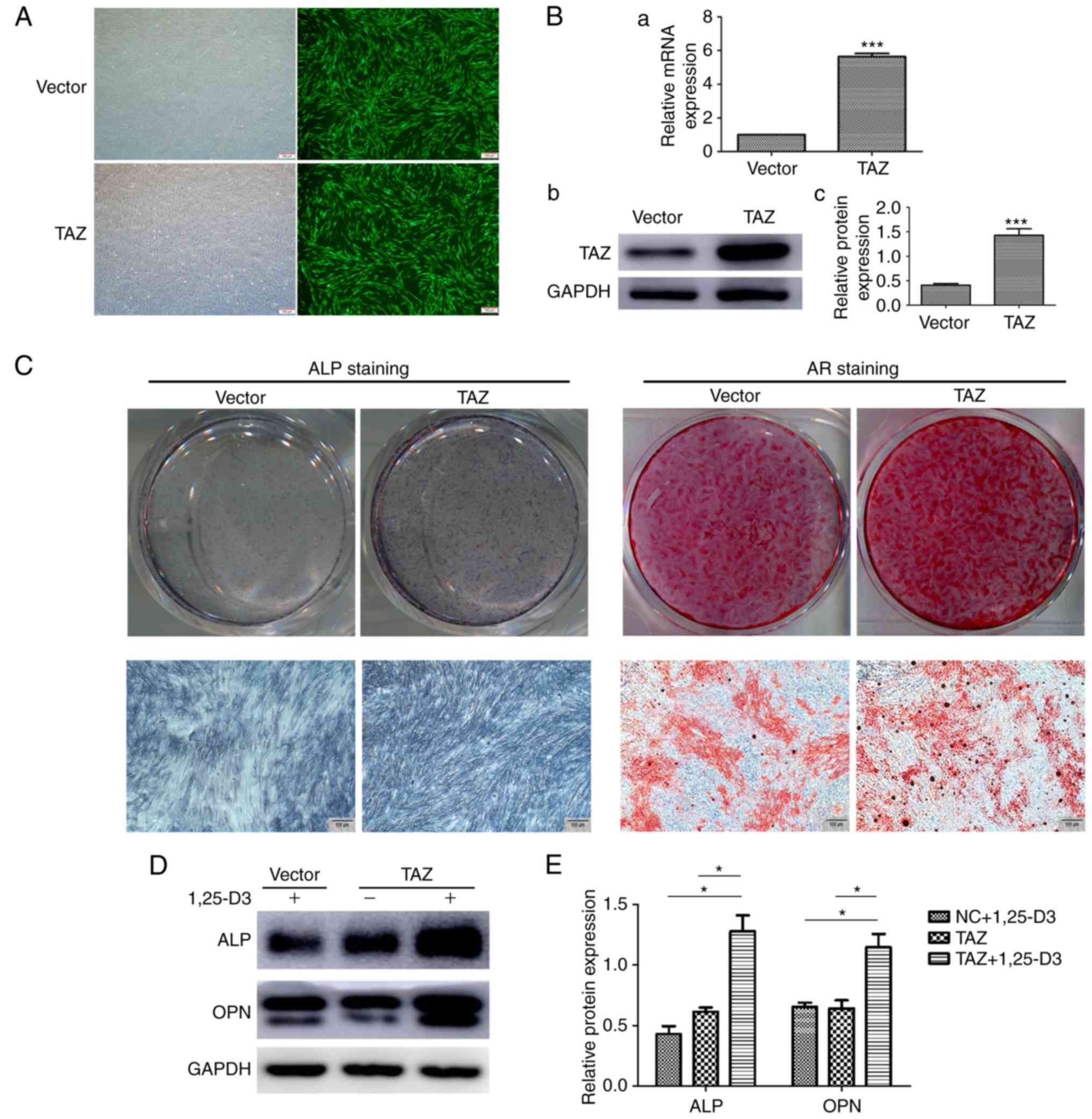
|
1
|
Martínez-Maestre MÁ, González-Cejudo C,
Machuca G, Torrejón R and Castelo-Branco C: Periodontitis and
osteoporosis: A systematic review. Climacteric. 13:523–529. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang J, An Y, Gao LN, Zhang YJ, Jin Y and
Chen FM: The effect of aging on the pluripotential capacity and
regenerative potential of human periodontal ligament stem cells.
Biomaterials. 33:6974–6986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reddy MS and Morgan SL: Decreased bone
mineral density and periodontal management. Periodontol, 2000.
61:195–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang GT, Gronthos S and Shi S:
Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from
other sources: Their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J
Dent Res. 88:792–806. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lindroos B, Mäenpää K, Ylikomi T, Oja H,
Suuronen R and Miettinen S: Characterisation of human dental stem
cells and buccal mucosa fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
368:329–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Ding G, Fang D, Zhang C,
Bartold PM, Gronthos S, Shi S and Wang S: Periodontal ligament stem
cell-mediated treatment for periodontitis in miniature swine. Stem
Cells. 26:1065–1073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ding G, Liu Y, Wang W, Wei F, Liu D, Fan
Z, An Y, Zhang C and Wang S: Allogeneic periodontal ligament stem
cell therapy for periodontitis in swine. Stem Cells. 28:1829–1838.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen FM, Sun HH, Lu H and Yu Q: Stem
cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration.
Biomaterials. 33:6320–6344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haussler MR, Haussler CA, Jurutka PW,
Thompson PD, Hsieh JC, Remus LS, Selznick SH and Whitfield GK: The
vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: Molecular actions and
disease states. J Endocrinol. 154(Suppl): S57–S73. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Amling M, Priemel M, Holzmann T, Chapin K,
Rueger JM, Baron R and Demay MB: Rescue of the skeletal phenotype
of vitamin D receptor-ablated mice in the setting of normal mineral
ion homeostasis: Formal histomorphometric and biomechanical
analyses. Endocrinology. 140:4982–4987. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gurlek A, Pittelkow MR and Kumar R:
Modulation of growth factor/cytokine synthesis and signaling by 1α,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: Implications in cell growth and
differentiation. Endocr Rev. 23:763–786. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ueno K, Katayama T, Miyamoto T and
Koshihara Y: Interleukin-4 enhances in vitro mineralization in
human osteoblast-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
189:1521–1526. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prince M, Banerjee C, Javed A, Green J,
Lian JB, Stein GS, Bodine PV and Komm BS: Expression and regulation
of Runx2/Cbfa1 and osteoblast phenotypic markers during the growth
and differentiation of human osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem.
80:424–440. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jørgensen NR, Henriksen Z, Sørensen OH and
Civitelli R: Dexamethasone, BMP-2, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
enhance a more differentiated osteoblast phenotype: Validation of
an in vitro model for human bone marrow-derived primary
osteoblasts. Steroids. 69:219–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Driel MV, Koedam M, Buurman CJ, Hewison M,
Chiba H, Uitterlinden AG, Pols HA and van Leeuwen JP: Evidence for
auto/paracrine actions of vitamin D in bone: 1α-hydroxylase
expression and activity in human bone cells. FASEB J. 20:2417–2419.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou YS, Liu YS and Tan JG: Is 1,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 an ideal substitute for dexamethasone for
inducing osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived
stromal cells in vitro. Chin Med J. 119:1278–1286. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Nebel D, Svensson D, Arosenius K, Larsson
E, Jönsson D and Nilsson BO: 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes
osteogenic activity and downregulates proinflammatory cytokine
expression in human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res.
50:666–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Uchiyama M, Nakamichi Y, Nakamura M,
Kinugawa S, Yamada H, Udagawa N and Miyazawa H: Dental pulp and
periodontal ligament cells support osteoclastic differentiation. J
Dent Res. 88:609–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Staley BK and Irvine KD: Hippo signaling
in Drosophila: Recent advances and insights. Dev Dyn. 241:3–15.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Ramos A and Camargo FD: The Hippo
signaling pathway and stem cell biology. Trends Cell Biol.
22:339–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu FX and Guan KL: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao B, Tumaneng K and Guan KL: The Hippo
pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell
self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 13:877–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moroishi T, Park HW, Qin B, Chen Q, Meng
Z, Plouffe SW, Taniguchi K, Yu FX, Karin M, Pan D, et al: A
YAP/TAZ-induced feedback mechanism regulates Hippo pathway
homeostasis. Genes Dev. 29:1271–1284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hong JH, Hwang ES, Mcmanus MT, Amsterdam
A, Tian Y, Kalmukova R, Mueller E, Benjamin T, Spiegelman BM, Sharp
PA, et al: TAZ, a transcriptional modulator of mesen-chymal stem
cell differentiation. Science. 309:1074–1078. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui CB, Cooper LF, Yang X, Karsenty G and
Aukhil I: Transcriptional coactivation of bone-specific
transcription factor Cbfa1 by TAZ. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1004–1013.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kawano S, Maruyama J, Nagashima S, Inami
K, Qiu W, Iwasa H, Nakagawa K, Ishigami-Yuasa M, Kagechika H,
Nishina H and Hata Y: A cell-based screening for TAZ activators
identifies ethacridine, a widely used antiseptic and abortifacient,
as a compound that promotes dephosphorylation of TAZ and inhibits
adipogenesis in C3H10T1/2 cells. J Biochem. 158:413–423. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang EJ, Jeong H, Kang JO, Kim NJ, Kim MS,
Choi SH, Yoo SE, Hong JH, Bae MA and Hwang ES: TM-25659 enhances
osteogenic differentiation and suppresses adipogenic
differentiation by modulating the transcriptional co-activator TAZ.
Br J Pharmacol. 165:1584–1594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Byun MR, Kim AR, Hwang JH, Kim KM, Hwang
ES and Hong JH: FGF2 stimulates osteogenic differentiation through
ERK induced TAZ expression. Bone. 58:72–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Byun MR, Kim AR, Hwang JH, Sung MK, Lee
YK, Hwang BS, Rho JR, Hwang ES and Hong JH: Phorbaketal A
stimulates osteoblast differentiation through TAZ mediated Runx2
activation. FEBS Lett. 586:1086–1092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen Y, Lan J, Huang H, Yu M, Cui J, Liang
J, Jiang B and Xu X: Application of eGFP to label human periodontal
ligament stem cells in periodontal tissue engineering. Arch Oral
Biol. 57:1241–1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang B, Wen Y, Huang H, Cui J, Liang J,
Ma X, Lan J and Xu X: Study of labeling human periodontal ligament
stem cells with enhanced green fluorescent protein by lentivirus
vector infection. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 30:82–86. 2012.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Essers J, Theil AF, Baldeyron C, van
Cappellen WA, Houtsmuller AB, Kanaar R and Vermeulen W: Nuclear
dynamics of PCNA in DNA replication and repair. Mol Cell Biol.
25:9350–9359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Daley GQ: The promise and perils of stem
cell therapeutics. Cell Stem Cell. 10:740–749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM,
Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY and Shi S:
Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human
periodontal ligament. Lancet. 364:149–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Khanna-Jain R, Vuorinen A, Sándor GK,
Suuronen R and Miettinen S: Vitamin D3 metabolites
induce osteogenic differentiation in human dental pulp and human
dental follicle cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 122:133–141.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hlaing SM, Garcia LA, Contreras JR, Norris
KC, Ferrini MG and Artaza JN: 1,25-Vitamin D3 promotes
cardiac differentiation through modulation of the WNT signaling
pathway. J Mol Endocrinol. 53:303–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reichrath J: Vitamin D and the skin: An
ancient friend, revisited. Exp Dermatol. 16:618–625. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng Y, Sun Y, Jia W and Zhang C:
Platelet-rich plasma and 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3
synergistically stimulate osteogenic differentiation of adult human
mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 32:635–642. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Atkins GJ, Anderson PH, Findlay DM,
Welldon KJ, Vincent C, Zannettino AC, O’Loughlin PD and Morris HA:
Metabolism of vitamin D3 in human osteoblasts: Evidence for
autocrine and paracrine activities of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3. Bone. 40:1517–1528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shiba H, Uchida Y, Kamihagi K, Sakata M,
Fujita T, Nakamura S, Takemoto T, Kato Y and Kurihara H:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 and basic fibroblast growth factor
modulate osteo-calcin and osteonectin/SPARC syntheses in
vitamin-D-activated pulp cells. J Dent Res. 80:1653–1659. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shigetani Y, Ohkura N, Yoshiba K, Ohshima
H, Hosoya A, Yoshiba N and Okiji T: GaAlAs laser-induced pulp
mineralization involves dentin matrix protein 1 and osteopontin
expression. Oral Dis. 22:399–405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Campos JM, Prati AJ, Cirano FR, Pimentel
SP, Pastore GP, Pecorari VG, Ribeiro FV, Casati MZ and Casarin RC:
Smoking modulates gene expression of type I collagen, bone
sialoprotein, and osteocalcin in human alveolar bone. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 73:2123–2131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Meng Z, Moroishi T and Guan KL: Mechanisms
of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 30:1–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Byun MR, Hwang JH, Kim AR, Kim KM, Hwang
ES, Yaffe MB and Hong JH: Canonical Wnt signalling activates TAZ
through PP1A during osteogenic differentiation. Cell Death Differ.
21:854–863. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yi T and Weiss SJ: Snail/Slug-YAP/TAZ
complexes cooperatively regulate mesenchymal stem cell function and
bone formation. Cell Cycle. 16:399–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yang JY, Sun WC, An JH, Ju YJ, Sang WK,
Kim SY, Kim JE and Chan SS: Osteoblast-targeted overexpression of
TAZ increases bone mass in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e565852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiao H, Tong R, Yang B, Lv Z, Du C, Peng
C, Ding C, Cheng S, Zhou L, Xie H, et al: TAZ regulates cell
proliferation and sensitivity to vitamin D3 in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 381:370–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|