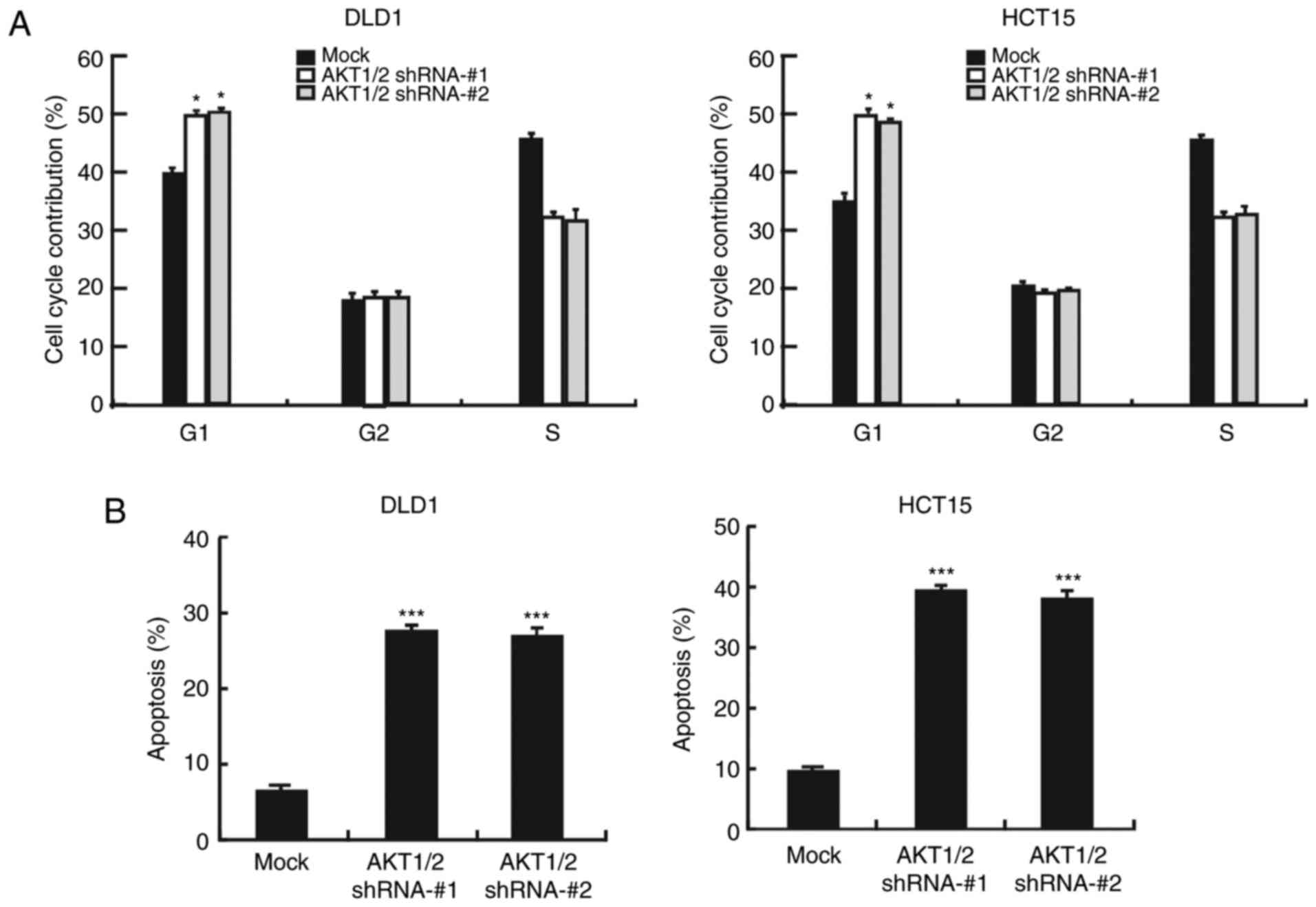
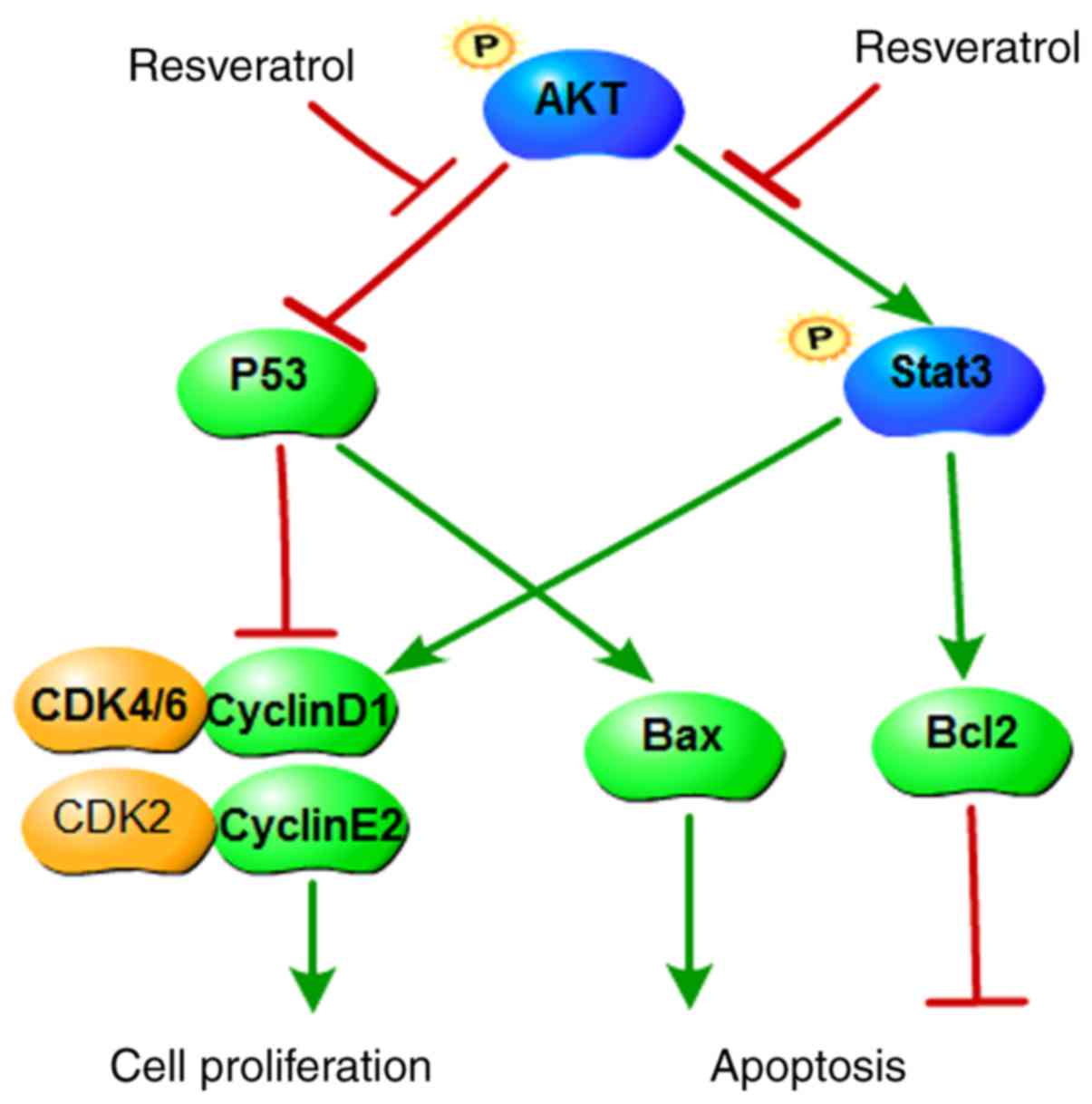
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Juan ME, Vinardell MP and Planas JM: The
daily oral administration of high doses of trans-resveratrol to
rats for 28 days is not harmful. J Nutr. 132:257–260. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Cancer
chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol:
Mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 269:243–261. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aluyen JK, Ton QN, Tran T, Yang AE,
Gottlieb HB and Bellanger RA: Resveratrol: Potential as anticancer
agent. J Dietary. (Suppl 9): S45–S56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bai Y, Yang H, Zhang G, Hu L, Lei Y, Qin
Y, Yang Y, Wang Q, Li R and Mao Q: Inhibitory effects of
resveratrol on the adhesion, migration and invasion of human
bladder cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:885–889. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rossi EL, Khatib SA, Doerstling SS, Bowers
LW, Pruski M, Ford NA, Glickman RD, Niu M, Yang P, Cui Z, et al:
Resveratrol inhibits obesity-associated adipose tissue dysfunction
and tumor growth in a mouse model of postmenopausal claudin-low
breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 57:393–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Jiang Q, Yang M, Qu Z, Zhou J and Zhang Q:
Resveratrol enhances anticancer effects of paclitaxel in HepG2
human liver cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17:4772017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aggarwal BB, Bhardwaj A, Aggarwal RS,
Seeram NP, Shishodia S and Takada Y: Role of resveratrol in
prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical studies.
Anticancer Res. 24:2783–2840. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou HB, Yan Y, Sun YN and Zhu JR:
Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human esophageal carcinoma cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 9:408–411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng X, Jia B, Song X, Kong QY, Wu ML,
Qiu ZW, Li H and Liu J: Preventive potential of resveratrol in
carcinogen-induced rat thyroid tumorigenesis. Nutrients.
10:E2792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang Z, Chen K, Cheng L, Yan B, Qian W,
Cao J, Li J, Wu E, Ma Q and Yang W: Resveratrol and cancer
treatment: Updates. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1403:59–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu YZ, Wu K, Huang J, Liu Y, Wang X, Meng
ZJ, Yuan SX, Wang DX, Luo JY, Zuo GW, et al: The PTEN/PI3K/Akt and
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways are involved in the inhibitory
effect of resveratrol on human colon cancer cell proliferation. Int
J Oncol. 45:104–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saiko P, Szakmary A, Jaeger W and Szekeres
T: Resveratrol and its analogs: Defense against cancer, coronary
disease and neuro-degenerative maladies or just a fad? Mutat Res.
658:68–94. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mahyar-Roemer M, Katsen A, Mestres P and
Roemer K: Resveratrol induces colon tumor cell apoptosis
independently of p53 and precede by epithelial differentiation,
mitochondrial proliferation and membrane potential collapse. Int J
Cancer. 94:615–622. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Malhotra A, Bath S and Elbarbry F: An
organ system approach to explore the antioxidative,
anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective actions of resveratrol. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2015:8039712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tessitore L, Davit A, Sarotto I and
Caderni G: Resveratrol depresses the growth of colorectal aberrant
crypt foci by affecting bax and p21(CIP) expression.
Carcinogenesis. 21:1619–1622. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheaib B, Auguste A and Leary A: The
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer: Therapeutic opportunities
and challenges. Chin J Cancer. 34:4–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Colakoglu T, Yildirim S, Kayaselcuk F,
Nursal TZ, Ezer A, Noyan T, Karakayali H and Haberal M:
Clinicopathological significance of PTEN loss and the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in sporadic colorectal
neoplasms: Is PTEN loss predictor of local recurrence? Am J Surg.
195:719–725. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Polivka J Jr and Janku F: Molecular
targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fumarola C, Bonelli MA, Petronini PG and
Alfieri RR: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung
cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 90:197–207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Agarwal E, Chaudhuri A, Leiphrakpam PD,
Haferbier KL, Brattain MG and Chowdhury S: Akt inhibitor MK-2206
promotes anti-tumor activity and cell death by modulation of AIF
and Ezrin in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:1452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun Z, Wang Z, Liu X and Wang D: New
development of inhibitors targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in
personalized treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer
Drugs. 26:1–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pal I and Mandal M: PI3K and Akt as
molecular targets for cancer therapy: Current clinical outcomes.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:1441–1458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsieh TC, Lin CY, Bennett DJ, Wu E and Wu
JM: Biochemical and cellular evidence demonstrating AKT-1 as a
binding partner for resveratrol targeting protein NQO2. PLoS One.
9:e1010702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Neradugomma NK, Subramaniam D, Tawfik OW,
Goffin V, Kumar TR, Jensen RA and Anant S: Prolactin signaling
enhances colon cancer stemness by modulating Notch signaling in a
Jak2-STAT3/ERK manner. Carcinogenesis. 35:795–806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Kang FB, Wang L, Jia HC, Li D, Li HJ,
Zhang YG and Sun DX: B7-H3 promotes aggression and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition via JAK2/STAT3/Slug signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
15:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Turkson J: STAT proteins as novel targets
for cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 8:409–422.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roig AI, Eskiocak U, Hight SK, Kim SB,
Delgado O, Souza RF, Spechler SJ, Wright WE and Shay JW:
Immortalized epithelial cells derived from human colon biopsies
express stem cell markers and differentiate in vitro.
Gastroenterology. 138:1012–1021. e1011–e1015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schrödinger Suite 2017. Schrödinger LLC;
New York, NY: 2017
|
|
32
|
Vang O: Resveratrol: Challenges in
analyzing its biological effects. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1348:161–170.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carter LG, D’Orazio JA and Pearson KJ:
Resveratrol and cancer: Focus on in vivo evidence. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 21:R209–R225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim SY, Hyun MY, Go KC, Zouboulis CC and
Kim BJ: Resveratrol exerts growth inhibitory effects on human SZ95
sebocytes through the inactivation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 35:1042–1050. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang F, Gao JY, Chen H, Du ZH, Zhang XQ
and Gao W: Targeted inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase
impairs cell proliferation, survival, and invasion in colon cancer.
Onco Targets Ther. 10:4413–4422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Zhu W, Li J, Liu M and Wei M:
Resveratrol suppresses the STAT3 signaling pathway and inhibits
proliferation of high glucose-exposed HepG2 cells partly through
SIRT1. Oncol Rep. 30:2820–2828. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nguyen AV, Martinez M, Stamos MJ, Moyer
MP, Planutis K, Hope C and Holcombe RF: Results of a phase I pilot
clinical trial examining the effect of plant-derived resveratrol
and grape powder on Wnt pathway target gene expression in colonic
mucosa and colon cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 1:25–37. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patel KR, Brown VA, Jones DJ, Britton RG,
Hemingway D, Miller AS, West KP, Booth TD, Perloff M, Crowell JA,
et al: Clinical pharmacology of resveratrol and its metabolites in
colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 70:7392–7399. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Howells LM, Berry DP, Elliott PJ, Jacobson
EW, Hoffmann E, Hegarty B, Brown K, Steward WP and Gescher AJ:
Phase I randomized, double-blind pilot study of micronized
resveratrol (SRT501) in patients with hepatic metastases-safety,
pharmaco-kinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Cancer Prev Res.
4:1419–1425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|