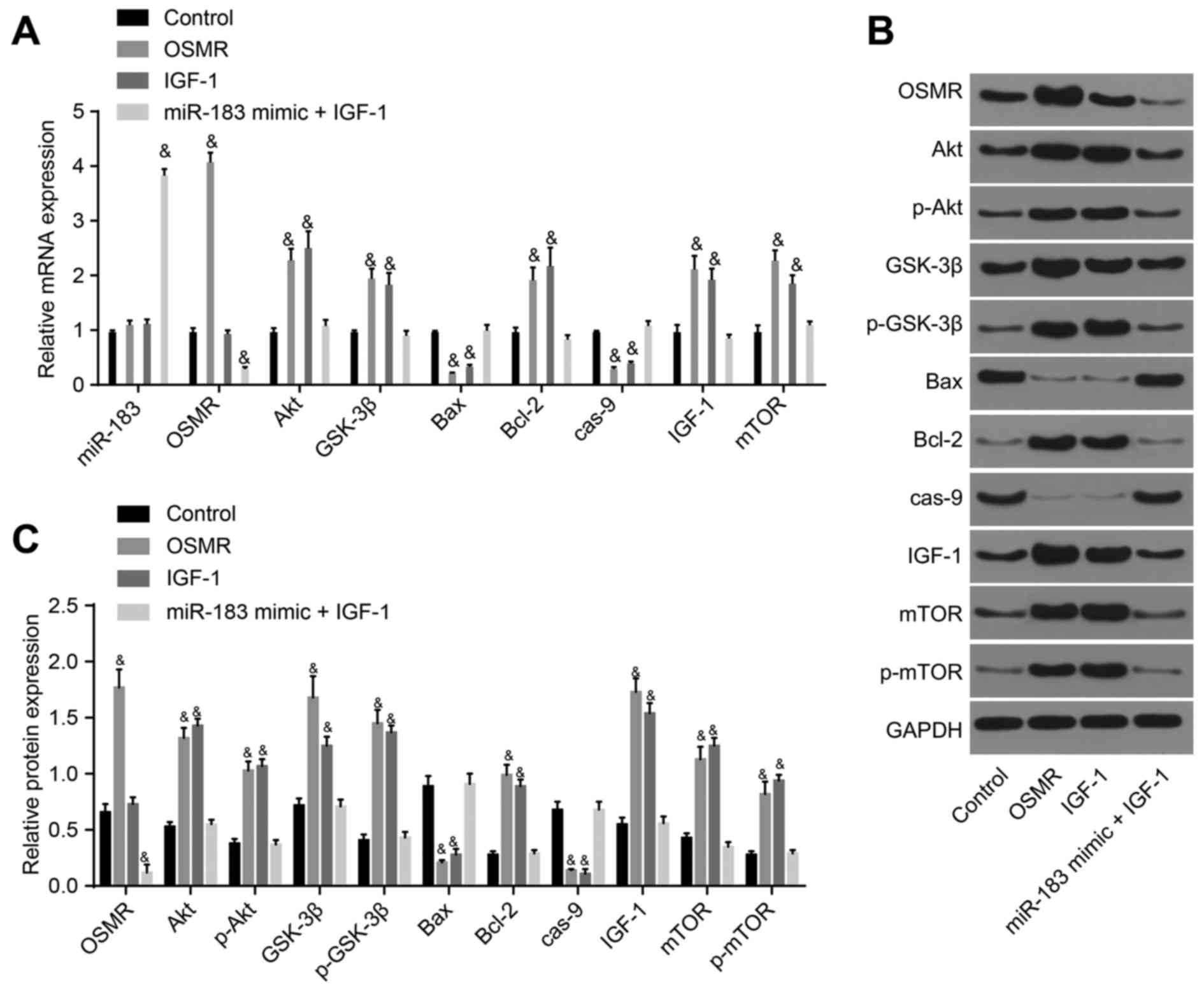
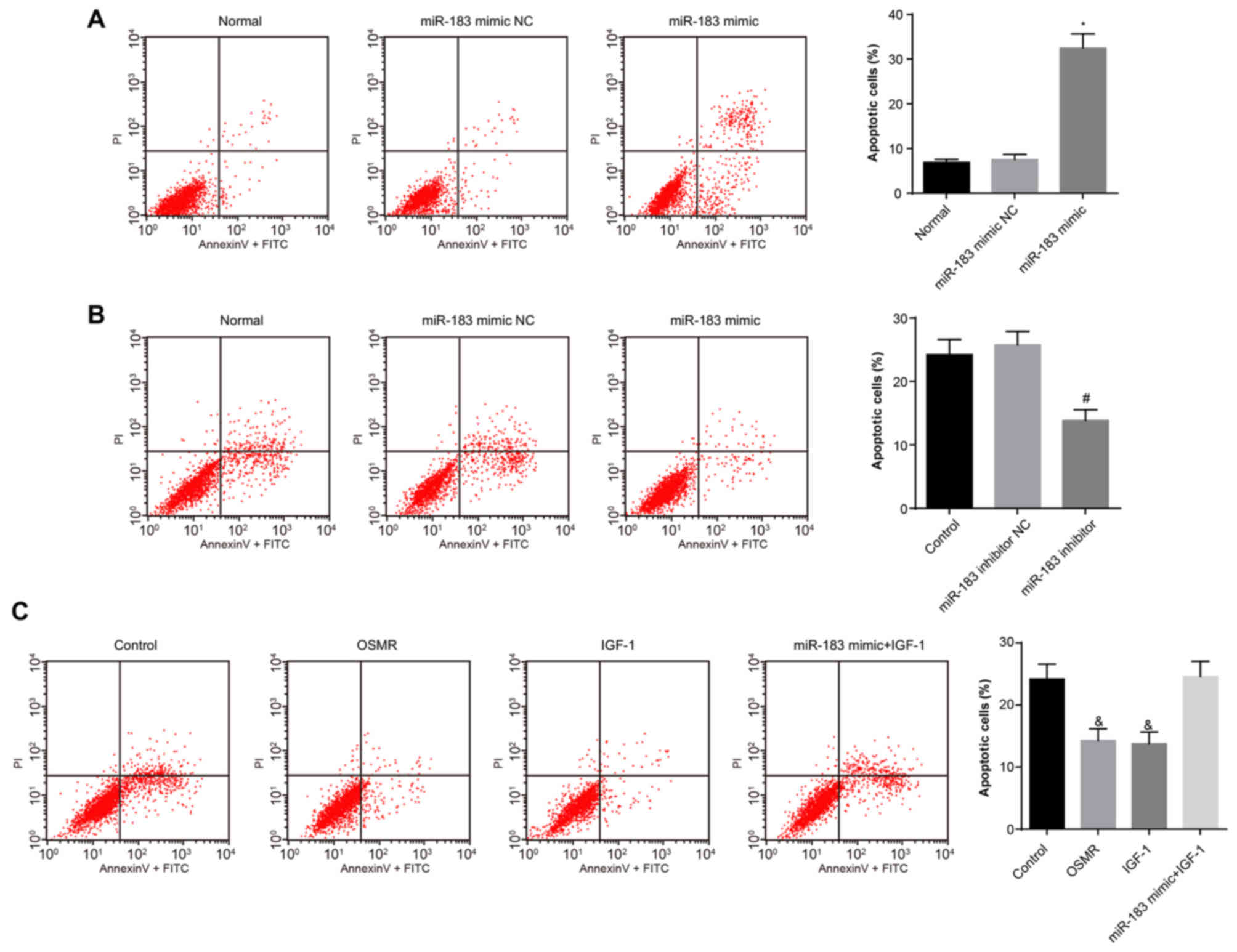
|
1
|
Chong TT, Bonnelle V, Manohar S, Veromann
KR, Muhammed K, Tofaris GK, Hu M and Husain M: Dopamine enhances
willingness to exert effort for reward in Parkinson’s disease.
Cortex. 69:40–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lenka A, Padmakumar C and Pal PK:
Treatment of older Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol.
132:381–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Farooqui T and Farooqui AA: Lipid-mediated
oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of
Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2011.247467:2011.
|
|
4
|
Karunanayaka PR, Lee EY, Lewis MM, Sen S,
Eslinger PJ, Yang QX and Huang X: Default mode network differences
between rigidity- and tremor-predominant Parkinson’s disease.
Cortex. 81:239–250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agim ZS and Cannon JR: Dietary factors in
the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. BioMed Res Int.
2015.672838:2015.
|
|
6
|
Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J and
Pollak P: Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the
treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 8:67–81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gonzales-Portillo GS, Reyes S, Aguirre D,
Pabon MM and Borlongan CV: Stem cell therapy for neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Neurol. 5:1472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kahn E, D’Haese PF, Dawant B, Allen L, Kao
C, Charles PD and Konrad P: Deep brain stimulation in early stage
Parkinson’s disease: operative experience from a prospective
randomised clinical trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
83:164–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Scatena R, Martorana GE, Bottoni P, Botta
G, Pastore P and Giardina B: An update on pharmacological
approaches to neuro-degenerative diseases. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 16:59–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schapira AH, Bezard E, Brotchie J, Calon
F, Collingridge GL, Ferger B, Hengerer B, Hirsch E, Jenner P, Le
Novère N, et al: Novel pharmacological targets for the treatment of
Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:845–854. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miñones-Moyano E, Porta S, Escaramís G,
Rabionet R, Iraola S, Kagerbauer B, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Ferrer I,
Estivill X and Martí E: MicroRNA profiling of Parkinson’s disease
brains identifies early downregulation of miR-34b/c which modulate
mitochondrial function. Hum Mol Genet. 20:3067–3078. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Dwyer RM and Kerin
MJ: Dysregulated miR-183 inhibits migration in breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 10:5022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu W, Zhou K, Zha Y, Chen D, He J, Ma H,
Liu X, Le H and Zhang Y: Diagnostic Value of Serum miR-182,
miR-183, miR-210, and miR-126 levels in patients with early-stage
non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01530462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan D, Li K, Zhu K, Yan R and Dang C:
Plasma miR-183 predicts recurrence and prognosis in patients with
colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:268–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pierce ML, Weston MD, Fritzsch B, Gabel
HW, Ruvkun G and Soukup GA: MicroRNA-183 family conservation and
ciliated neurosensory organ expression. Evol Dev. 10:106–113. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arita K, South AP, Hans-Filho G, Sakuma
TH, Lai-Cheong J, Clements S, Odashiro M, Odashiro DN, Hans-Neto G,
Hans NR, et al: Oncostatin M receptor-beta mutations underlie
familial primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Am J Hum Genet.
82:73–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isozaki O, Tsushima T, Miyakawa M, Emoto
N, Demura H, Arai M and Sato-Nozoe Y: Oncostatin M: a new potent
inhibitor of iodine metabolism inhibits thyroid peroxidase gene
expression but not DNA synthesis in porcine thyroid cells in
culture. Thyroid. 7:71–77. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway--beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:530–543. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Zhang W, He H, Song H, Zhao J, Li T, Wu L,
Zhang X and Chen J: Neuroprotective effects of salidroside in the
MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of the
PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Parkinsons Dis. 2016.9450137:2016.
|
|
20
|
Shao JL, Wan XH, Chen Y, Bi C, Chen HM,
Zhong Y, Heng XH and Qian JQ: H2S protects hippocampal neurons from
anoxia-reoxygenation through cAMP-mediated PI3K/Akt/p70S6K
cell-survival signaling pathways. Journal of molecular
neuroscience: J Mol Neurosci. 43:453–460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Qu Y, Tang J, Chen D, Fu X, Mao M
and Mu D: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is required for
neuroprotection of thalidomide on hypoxic-ischemic cortical neuron
in vitro. Brain Res. 1357:157–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhong Z, Wang Y, Guo H, Sagare A,
Fernández JA, Bell RD, Barrett TM, Griffin JH, Freeman RS and
Zlokovic BV: Protein S protects neurons from excitotoxic injury by
activating the TAM receptor Tyro3-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt
pathway through its sex hormone-binding globulin-like region. J
Neurosci. 30:15521–15534. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choe G, Horvath S, Cloughesy TF, Crosby K,
Seligson D, Palotie A, Inge L, Smith BL, Sawyers CL and Mischel PS:
Analysis of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase signaling pathway in
glioblastoma patient in vivo. Cancer Res. 63:2742–2746.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Neve RM, Holbro T and Hynes NE: Distinct
roles for phosphoinositide 3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein
kinase and p38 MAPK in mediating cell cycle progression of breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 21:4567–4576. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Philp AJ, Campbell IG, Leet C, Vincan E,
Rockman SP, Whitehead RH, Thomas RJ and Phillips WA: The
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase p85alpha gene is an oncogene in
human ovarian and colon tumors. Cancer Res. 61:7426–7429.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee J, Zhu WM, Stanic D, Finkelstein DI,
Horne MH, Henderson J, Lawrence AJ, O’Connor L, Tomas D, Drago J,
et al: Sprouting of dopamine terminals and altered dopamine release
and uptake in Parkinsonian dyskinaesia. Brain. 131:1574–1587. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee SY, Moon Y, Hee Choi D, Jin Choi H and
Hwang O: Particular vulnerability of rat mesencephalic dopaminergic
neurons to tetrahydrobiopterin: Relevance to Parkinson’s disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 25:112–120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ayuk SM, Abrahamse H and Houreld NN: The
role of photo-biomodulation on gene expression of cell adhesion
molecules in diabetic wounded fibroblast in vitro. J Photochem
Photobiol B. 161:368–374. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Sen G, Lu Y, Zheng A and Li M:
Function and application of type-II oncostatin-M receptor (OSMR) in
cerebral apoplexy diseases. CN Patent 104083754A. Filed July 8,
2014 issued October 8, 2018.
|
|
30
|
Weiss TW, Samson AL, Niego B, Daniel PB
and Medcalf RL: Oncostatin M is a neuroprotective cytokine that
inhibits excitotoxic injury in vitro an in vivo. FASEB J.
20:2369–2371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pelletier JP and Martel-Pelletier J:
Oncostatin M: Foe or friend. Arthritis Rheum. 48:3301–3303. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Timmons S, Coakley MF, Moloney AM and
O’Neill C: Akt signal transduction dysfunction in Parkinson’s
disease. Neurosci Lett. 467:30–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Malagelada C, Ryu EJ, Biswas SC,
Jackson-Lewis V and Greene LA: RTP801 is elevated in Parkinson
brain substantia nigral neurons and mediates death in cellular
models of Parkinson’s disease by a mechanism involving mammalian
target of rapamycin inactivation. J Neurosci. 26:9996–10005. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsuan SL, Klintworth HM and Xia Z: Basic
fibroblast growth factor protects against rotenone-induced
dopaminergic cell death through activation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
pathways. J Neurosci. 26:4481–4491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwon DH, Kim JM, Oh SH, Jeong HJ, Park SY,
Oh ES, Chi JG, Kim YB, Jeon BS and Cho ZH: Seven-Tesla magnetic
resonance images of the substantia nigra in Parkinson disease. Ann
Neurol. 71:267–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Matus S, Castillo K and Hetz C: Hormesis:
Protecting neurons against cellular stress in Parkinson disease.
Autophagy. 8:997–1001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harms AS, Barnum CJ, Ruhn KA, Varghese S,
Treviño I, Blesch A and Tansey MG: Delayed dominant-negative TNF
gene therapy halts progressive loss of nigral dopaminergic neurons
in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Ther. 19:46–52. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jha SK, Jha NK, Kar R, Ambasta RK and
Kumar P: p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signalling Cascades inParkinson’s
Disease. Int J Mol Cell Med. 4:67–86. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
LeWitt PA, Rezai AR, Leehey MA, Ojemann
SG, Flaherty AW, Eskandar EN, Kostyk SK, Thomas K, Sarkar A,
Siddiqui MS, et al: AAV2-GAD gene therapy for advanced Parkinson’s
disease: a double-blind, sham-surgery controlled, randomised trial.
Lancet Neurol. 10:309–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Wei Q, Chen X, Li C, Cao B, Ou R,
Hadano S and Shang HF: Aberration of miRNAs expression in
leukocytes from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Mol
Neurosci. 9:692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Takatsuno Y, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Uetake H, Sugihara K and Mori M: Over- and
under-expressed microRNAs in human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:1069–1075. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tanaka M, Hirabayashi Y, Sekiguchi T,
Inoue T, Katsuki M and Miyajima A: Targeted disruption of
oncostatin M receptor results in altered hematopoiesis. Blood.
102:3154–3162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hibi K, Goto T, Sakuraba K, Shirahata A,
Saito M, Ishibashi K, Kigawa G, Nemoto H and Sanada Y: Methylation
of OSMR gene is frequently observed in non-invasive colorectal
cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:1293–1295. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Deng G, Kakar S, Okudiara K, Choi E,
Sleisenger MH and Kim YS: Unique methylation pattern of oncostatin
m receptor gene in cancers of colorectum and other digestive
organs. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1519–1526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Auernhammer CJ, Dorn F, Vlotides G, Hengge
S, Kopp FB, Spoettl G, Cengic N, Engelhardt D and Weber MM: The
oncostatin M receptor/gp130 ligand murine oncostatin M induces
apoptosis in adrenocortical Y-1 tumor cells. J Endocrinol.
180:479–486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao Y, Li J, Wu L, Zhou C, Wang Q, Li X,
Zhou M and Wang H: Tetrahydrocurcumin provides neuroprotection in
rats after traumatic brain injury: Autophagy and the PI3K/AKT
pathways as a potential mechanism. J Surg Res. 206:67–76. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Quesada A, Lee BY and Micevych PE: PI3
kinase/Akt activation mediates estrogen and IGF-1 nigral DA
neuronal neuroprotection against a unilateral rat model of
Parkinson’s disease. Dev Neurobiol. 68:632–644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cross DA, Culbert AA, Chalmers KA, Facci
L, Skaper SD and Reith AD: Selective small-molecule inhibitors of
glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from
death. J Neurochem. 77:94–102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Credle JJ, George JL, Wills J, Duka V,
Shah K, Lee YC, Rodriguez O, Simkins T, Winter M, Moechars D, et
al: GSK-3β dysregulation contributes to parkinson’s-like
pathophysiology with associated region-specific phosphorylation and
accumulation of tau and α-synuclein. Cell Death Differ. 22:838–851.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bibollet-Bahena O and Almazan G:
IGF-1-stimulated protein synthesis in oligodendrocyte progenitors
requires PI3K/mTOR/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. J Neurochem.
109:1440–1451. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kouroupi G, Lavdas AA, Gaitanou M,
Thomaidou D, Stylianopoulou F and Matsas R: Lentivirus-mediated
expression of insulin-like growth factor-I promotes neural
stem/precursor cell proliferation and enhances their potential to
generate neurons. J Neurochem. 115:460–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hellerstein MK: Relationship between
precursor enrichment and ratio of excess M2/excess M1 isotopomer
frequencies in a secreted polymer. J Biol Chem. 266:10920–10924.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li H, Gong Y, Qian H, Chen T, Liu Z, Jiang
Z and Wei S: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a novel target
gene of the has-miR-183/96/182 cluster in retinal pigment
epithelial cells following visible light exposure. Mol Med Rep.
12:2793–2799. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Budzinska M, Owczarz M, Pawlik-Pachucka E,
Roszkowska- Gancarz M, Slusarczyk P and Puzianowska-Kuznicka M:
miR-96, miR-145 and miR-9 expression increases, and IGF-1R and
FOXO1 expression decreases in peripheral blood mono-nuclear cells
of aging humans. BMC Geriatr. 16:2002016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Weeraratne SD, Amani V, Teider N,
Pierre-Francois J, Winter D, Kye MJ, Sengupta S, Archer T, Remke M,
Bai AH, et al: Pleiotropic effects of miR-183~96~182 converge to
regulate cell survival, proliferation and migration in
medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 123:539–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Radtke S, Hermanns HM, Haan C, De
Schmitz-Van Leur H, Gascan H, Heinrich PC and Behrmann I: Novel
role of Janus kinase 1 in the regulation of oncostatin M receptor
surface expression. J Biol Chem. 277:11297–11305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yamanaka K, Rocchi P, Miyake H, Fazli L,
Vessella B, Zangemeister-Wittke U and Gleave ME: A novel antisense
oligonucleotide inhibiting several antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family
members induces apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity in
androgen-independent human prostate cancer PC3 cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:1689–1698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang L, Yu J, Park BH, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Role of BAX in the apoptotic response to anticancer
agents. Science. 290:989–992. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee JS, Jung WK, Jeong MH, Yoon TR and Kim
HK: Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of HT-29 human colon cancer
cells via the regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-9-dependent
pathway. Int J Toxicol. 31:70–77. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xu BB, Liu CQ, Gao X, Zhang WQ, Wang SW
and Cao YL: Possible mechanisms of the protection of ginsenoside Re
against MPTP-induced apoptosis in substantia nigra neurons of
Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 7:215–224.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Rekha KR and Selvakumar GP: Gene
expression regulation of Bcl2, Bax and cytochrome-C by geraniol on
chronic MPTP/probenecid induced C57BL/6 mice model of Parkinson’s
disease. Chem Biol Interact. 217:57–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kuida K: Caspase-9. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 32:121–124. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu R, Tang S, Wang M, Xu X, Yao C and Wang
S: microRNA-497 induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation via
the Bcl-2/Bax-caspase9-caspase3 pathway and Cyclin D2 protein in
HUVECs. PLoS One. 11:e01670522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sangawa A, Shintani M, Yamao N and
Kamoshida S: Phosphorylation status of Akt and caspase-9 in gastric
and colorectal carcinomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3312–3317.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Papadopoulos EI, Yousef GM and Scorilas A:
Cytotoxic activity of sunitinib and everolimus in Caki-1 renal
cancer cells is accompanied by modulations in the expression of
apoptosis-related microRNA clusters and BCL2 family genes. Biomed
Pharmacother. 70:33–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tang H, Bian Y, Tu C, Wang Z, Yu Z, Liu Q,
Xu G, Wu M and Li G: The miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates oxidative
apoptosis and sensitizes cells to chemotherapy in gliomas. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 13:221–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Oussaief L, Fendri A, Chane-Woon-Ming B,
Poirey R, Delecluse HJ, Joab I and Pfeffer S: Modulation of
microRNA cluster miR-183-96-182 expression by Epstein-Barr virus
latent membrane protein 1. J Virol. 89:12178–12188. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|