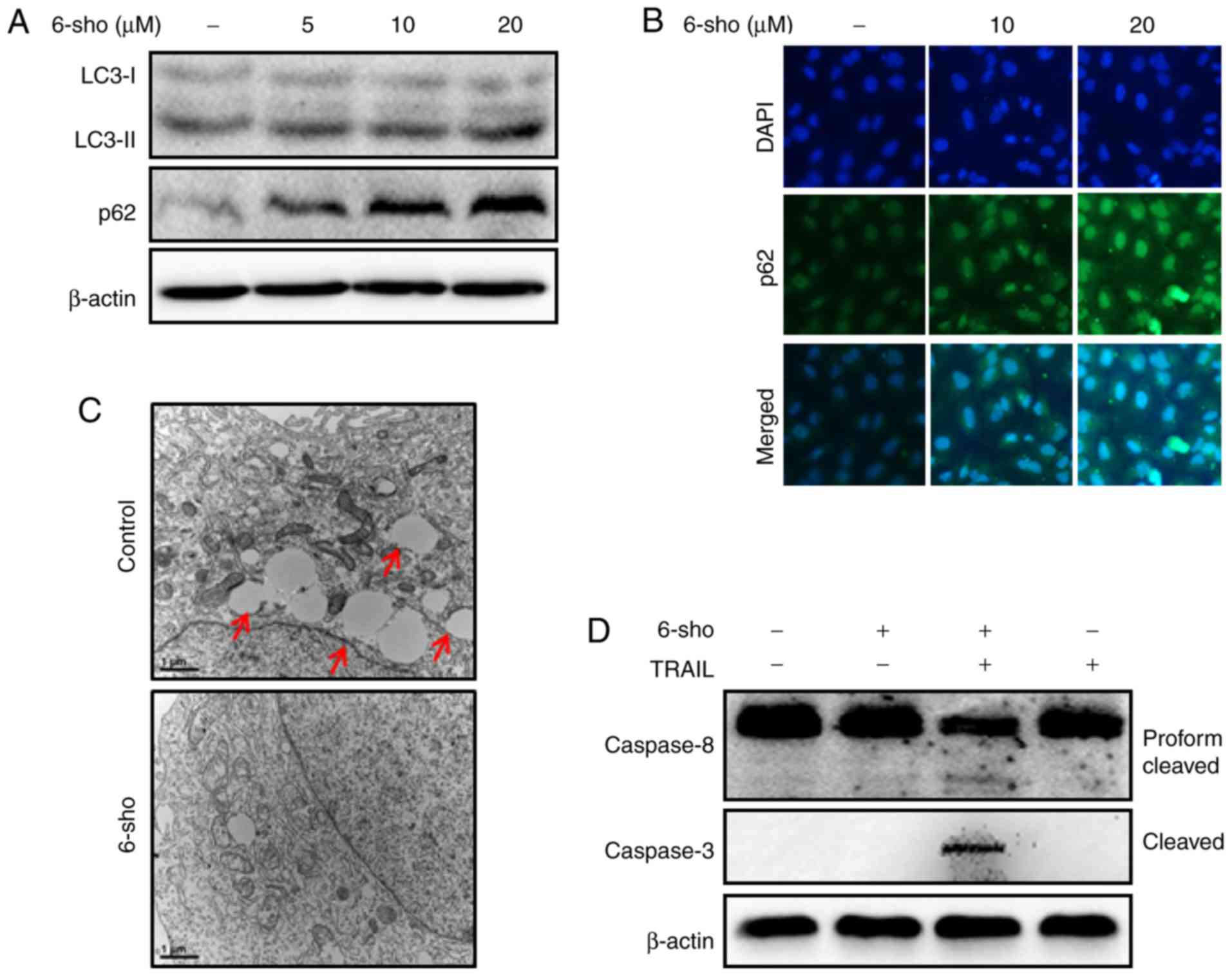
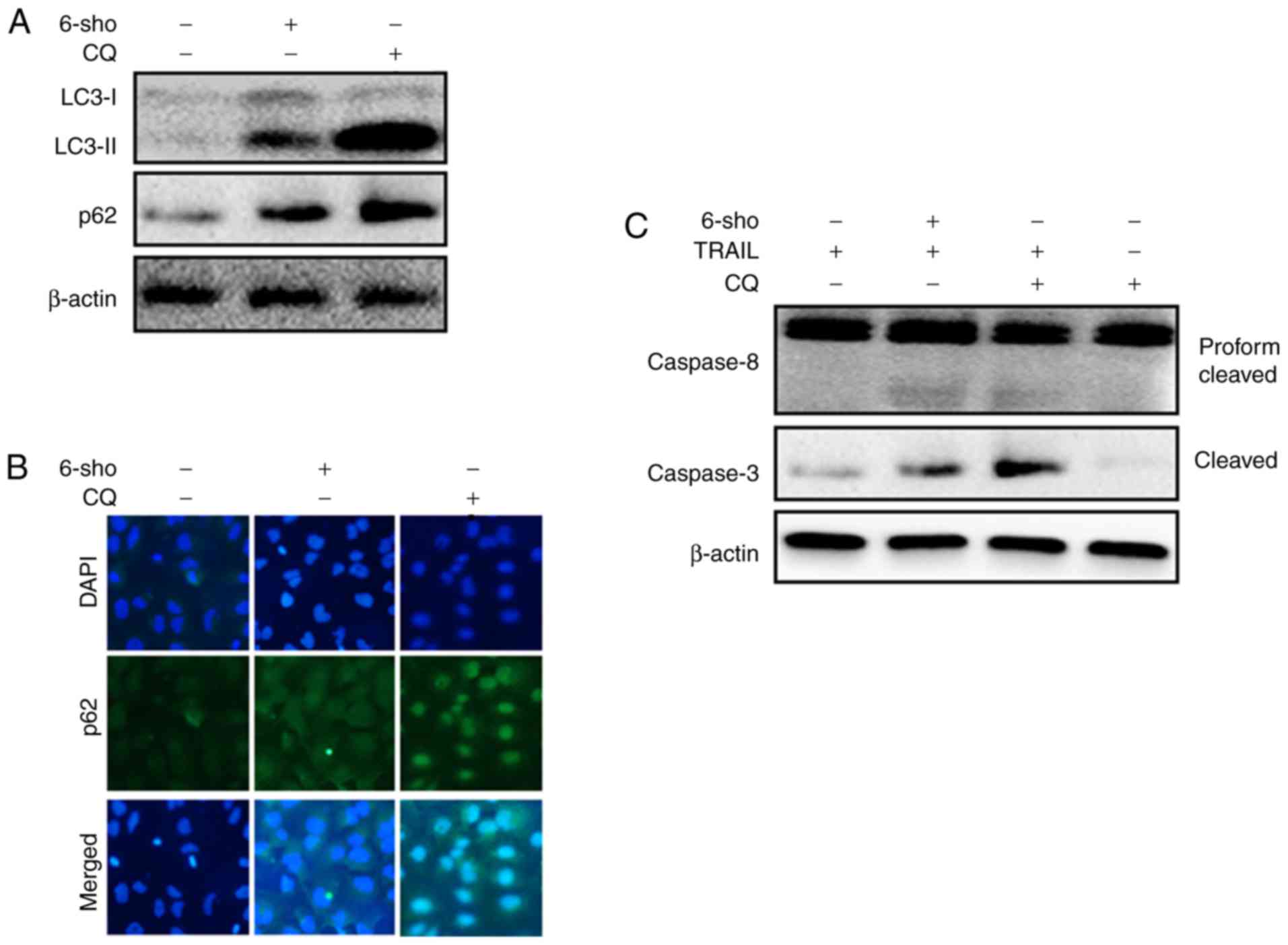
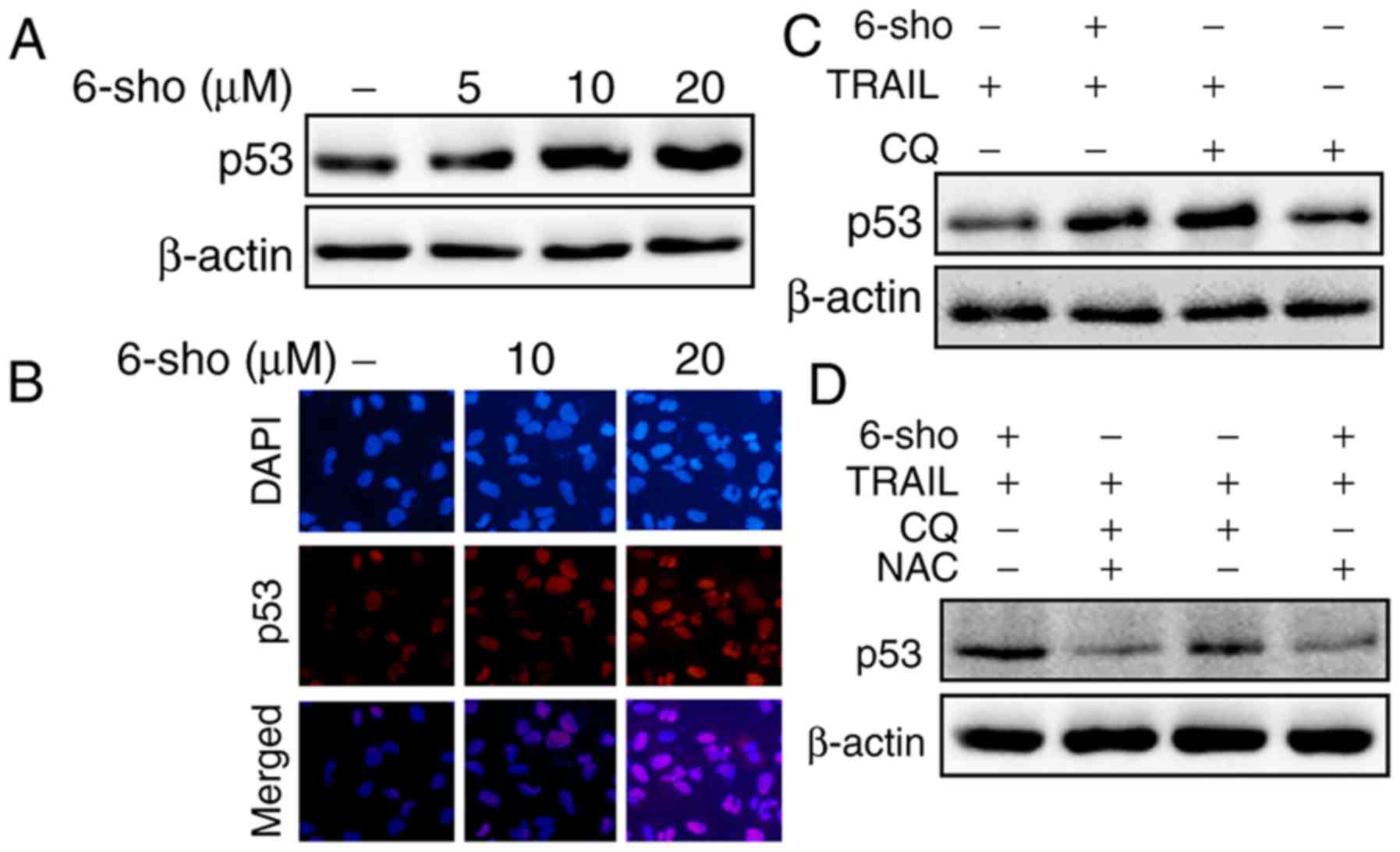
|
1
|
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A and Cabrera R:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends in worldwide epidemiology,
risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 4:19–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chi HC, Chen SL, Cheng YH, Lin TK, Tsai
CY, Tsai MM, Lin YH, Huang YH and Lin KH: Chemotherapy resistance
and metastasis-promoting effects of thyroid hormone in
hepatocarcinoma cells are mediated by suppression of FoxO1 and Bim
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei F, Jiang X, Gao HY and Gao SH:
Liquiritin induces apoptosis and autophagy in cisplatin
(DDP)-resistant gastric cancer cells in vitro and xenograft nude
mic in vivo. Int J Oncol. 51:1383–1394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Helmy SA, El-Mesery M, El-Karef A, Eissa
LA and El Gayar AM: Chloroquine upregulates TRAIL/TRAILR2
expression and potentiates doxorubicin anti-tumor activity in
thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma model. Chem Biol
Interact. 279:84–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Falschlehner C, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B and
Walczak H: TRAIL signalling: Decisions between life and death. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1462–1475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trivedi R and Mishra DP: Trailing TRAIL
resistance: Novel targets for TRAIL sensitization in cancer cells.
Front Oncol. 5:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y and Zhang B: TRAIL resistance of
breast cancer cells is associated with constitutive endocytosis of
death receptors 4 and 5. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1861–1871. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ozoren N, Fisher MJ, Kim K, Liu CX, Genin
A, Shifman Y, Dicker DT, Spinner NB, Lisitsyn NA and El-Deiry WS:
Homozygous deletion of the death receptor DR4 gene in a
naso-pharyngeal cancer cell line is associated with TRAIL
resistance. Int J Oncol. 16:917–925. 2000.
|
|
10
|
Sanlioglu AD, Dirice E, Aydin C, Erin N,
Koksoy S and Sanlioglu S: Surface TRAIL decoy receptor-4 expression
is correlated with TRAIL resistance in MCF7 breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 5:542005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO and Nemmar A:
Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of
ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A review of recent research.
Food Chem Toxicol. 46:409–420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Haniadka R, Rajeev AG, Palatty PL, Arora R
and Baliga MS: Zingiber officinale (ginger) as an anti-emetic in
cancer chemotherapy: A review. J Altern Complement Med. 18:440–444.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li F, Nitteranon V, Tang X, Liang J, Zhang
G, Parkin KL and Hu Q: In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
activities of 1-dehydro-[6]-gingerdione, 6-shogaol,
6-dehydroshogaol and hexahydrocurcumin. Food Chem. 135:332–337.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dugasani S, Pichika MR, Nadarajah VD,
Balijepalli MK, Tandra S and Korlakunta JN: Comparative antioxidant
and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol,
[10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. J Ethnopharmacol. 127:515–520. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen CY, Liu TZ, Liu YW, Tseng WC, Liu RH,
Lu FJ, Lin YS, Kuo SH and Chen CH: 6-shogaol (alkanone from ginger)
induces apoptotic cell death of human hepatoma p53 mutant Mahlavu
subline via an oxidative stress-mediated caspase-dependent
mechanism. J Agric Food Chem. 55:948–954. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu R, Zhou P, Peng YB, Xu X, Ma J, Liu Q,
Zhang L, Wen XD, Qi LW, Gao N and Li P: 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis
in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and exhibits anti-tumor
activity in vivo through endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS One.
7:e396642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan MH, Hsieh MC, Kuo JM, Lai CS, Wu H,
Sang S and Ho CT: 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human colorectal
carcinoma cells via ROS production, caspase activation, and GADD
153 expression. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:527–537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Q, Peng YB, Zhou P, Qi LW, Zhang M,
Gao N, Liu EH and Li P: 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human
leukemia cells through a process involving caspase-mediated
cleavage of eIF2α. Mol Cancer. 12:1352013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim MO, Lee MH, Oi N, Kim SH, Bae KB,
Huang Z, Kim DJ, Reddy K, Lee SY, Park SJ, et al: [6]-shogaol
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer
cells by directly regulating Akt1/2. Carcinogenesis. 35:683–691.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bergmann A: Autophagy and cell death: No
longer at odds. Cell. 131:1032–1034. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Codogno P, Mehrpour M and Proikas-Cezanne
T: Canonical and non-canonical autophagy: Variations on a common
theme of self-eating. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:7–12. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Chloroquine in cancer therapy: A double-edged sword of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 73:3–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiu HW, Su YC and Hong JR: Betanodavirus
B2 protein triggers apoptosis and necroptosis in lung cancer cells
that suppresses autophagy. Oncotarget. 8:94129–94141.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kruse JP and Gu W: Modes of p53
regulation. Cell. 137:609–622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Toledo F and Wahl GM: Regulating the p53
pathway: In vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:909–923. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Di J, Huang H, Qu D, Tang J, Cao W, Lu Z,
Cheng Q, Yang J, Bai J, Zhang Y and Zheng J: Rap2B promotes
proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer
through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Sci Rep.
5:123632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Zhang L, Li J, Wu T, Wang M, Xu G,
Zhang F, Liu L, Yang J and Sun S: A novel pyrazolone-based
derivative induces apoptosis in human esophageal cells via reactive
oxygen species (ROS) generation and caspase-dependent
mitochondria-mediated pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 231:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Menzies FM, Fleming A and Rubinsztein DC:
Compromised autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 16:345–357. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee JH, Lee YJ, Seol
JW, Eo SK, Lee JH and Park SY: Activation of autophagy flux by
metformin down-regulates cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein and
enhances TRAIL- induced apoptosis. Oncotarget. 7:23468–23481. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee YJ, Seol JW and
Park SY: PPARγ activation by troglitazone enhances human lung
cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via autophagy flux.
Oncotarget. 8:26819–26831. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Falschlehner C, Ganten TM, Koschny R,
Schaefer U and Walczak H: TRAIL and other TRAIL receptor agonists
as novel cancer therapeutics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 647:195–206. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Green KL, Brown C, Roeder GE, Southgate TD
and Gaston K: A cancer cell-specific inducer of apoptosis. Hum Gene
Ther. 18:547–561. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han MA, Woo SM, Min KJ, Kim S, Park JW,
Kim DE, Kim SH, Choi YH and Kwon TK: 6-Shogaol enhances renal
carcinoma Caki cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through reactive
oxygen species-mediated cytochrome c release and down-regulation of
c-FLIP(L) expression. Chem Biol Interact. 228:69–78. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ferraro E and Cecconi F: Autophagic and
apoptotic response to stress signals in mammalian cells. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 462:210–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xie Z and Klionsky DJ: Autophagosome
formation: Core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol.
9:1102–1109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ohsumi Y and Mizushima N: Two
ubiquitin-like conjugation systems essential for autophagy. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 15:231–236. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jia L, Macey MG, Yin Y, Newland AC and
Kelsey SM: Subcellular distribution and redistribution of Bcl-2
family proteins in human leukemia cells undergoing apoptosis.
Blood. 93:2353–2359. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen L, Xiong YQ, Xu J, Wang JP, Meng ZL
and Hong YQ: Juglanin inhibits lung cancer by regulation of
apoptosis, ROS and autophagy induction. Oncotarget. 8:93878–93898.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park SY and Kim Y: Surfactin inhibits
immunostimulatory function of macrophages through blocking
NK-kappaB, MAPK and Akt pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:886–893.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang TC, Lai CC, Shiu SL, Chuang PH, Tzou
BC, Lin YY, Tsai FJ and Lin CW: Japanese encephalitis virus
down-regulates thioredoxin and induces ROS-mediated ASK1-ERK/p38
MAPK activation in human promonocyte cells. Microbes Infect.
12:643–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways. J Signal
Transduct. 2011:7926392011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yamanaka T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Ito T,
Fujikawa K, Ito M, Takase K, Moriyama M, Nakano T and Suzuki A:
Chemotherapeutic agents augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Hepatology. 32:482–490. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Enhancement
of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and
irradiation: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:139–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hung JY, Hsu YL, Li CT, Ko YC, Ni WC,
Huang MS and Kuo PL: 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of dietary
ginger, induces autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR pathway in
human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Agric Food Chem.
57:9809–9816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T,
Christophorou MA, Evan GI, Thomas-Tikhonenko A and Thompson CB:
Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a
Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 117:326–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Saleem A, Dvorzhinski D, Santanam U,
Mathew R, Bray K, Stein M, White E and DiPaola RS: Effect of dual
inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer. Prostate.
72:1374–1381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|