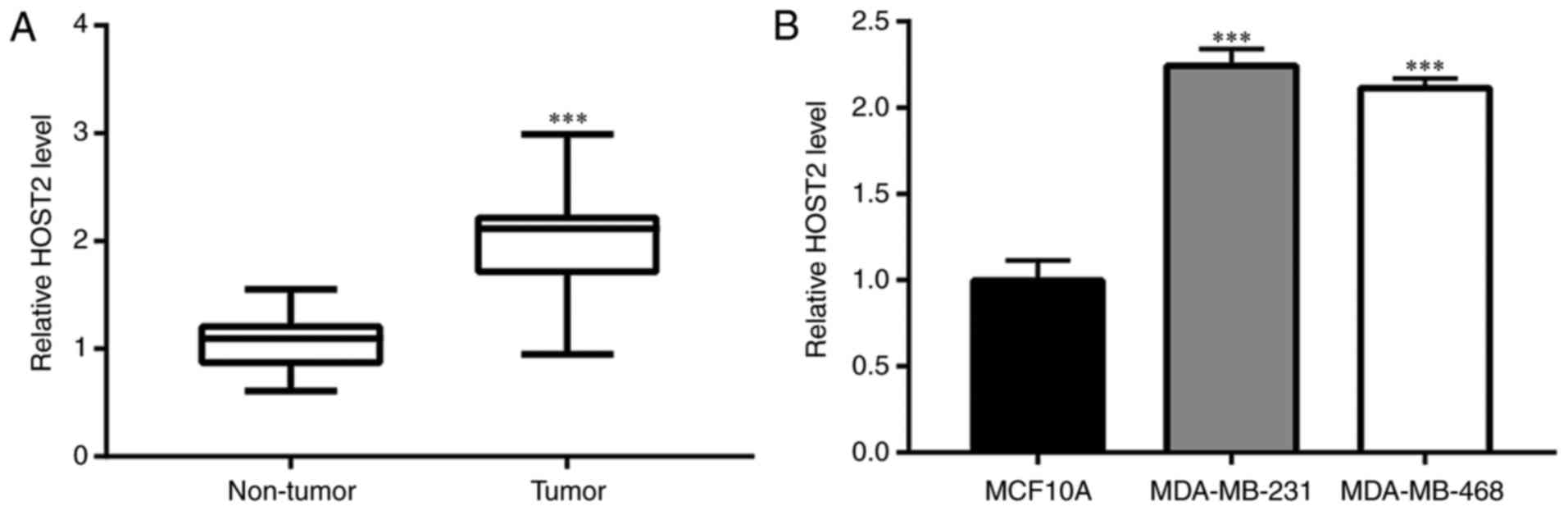
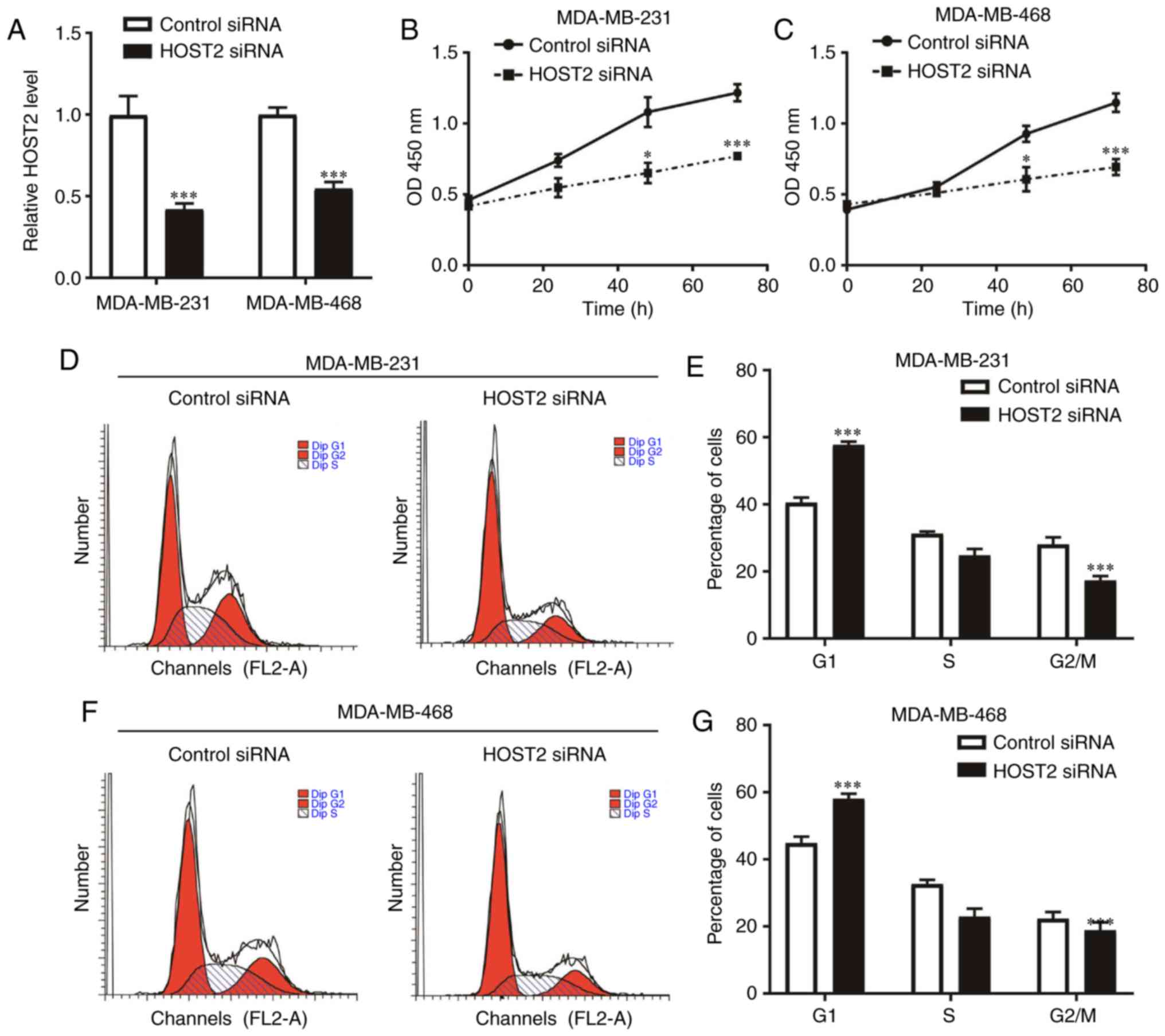
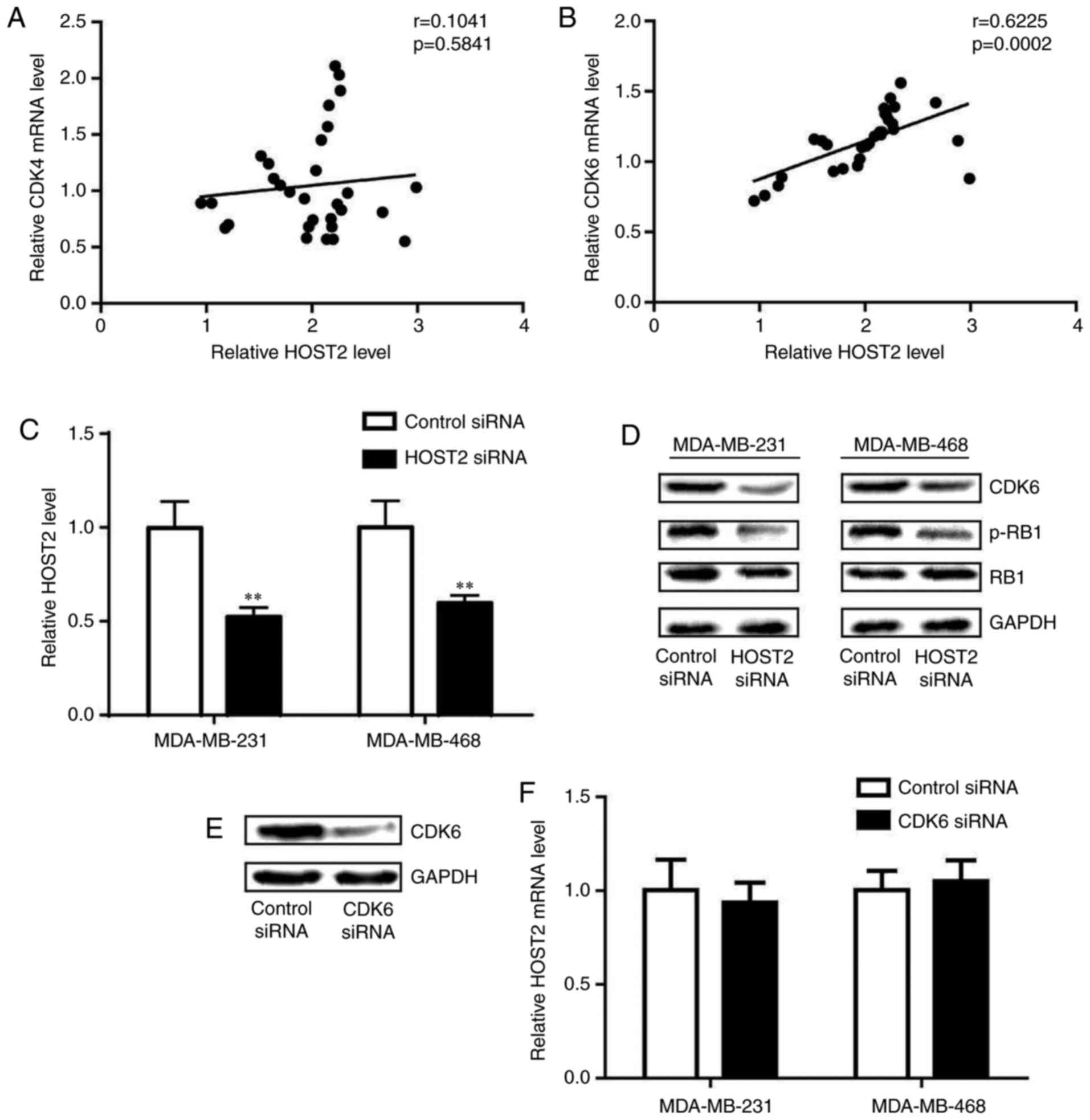
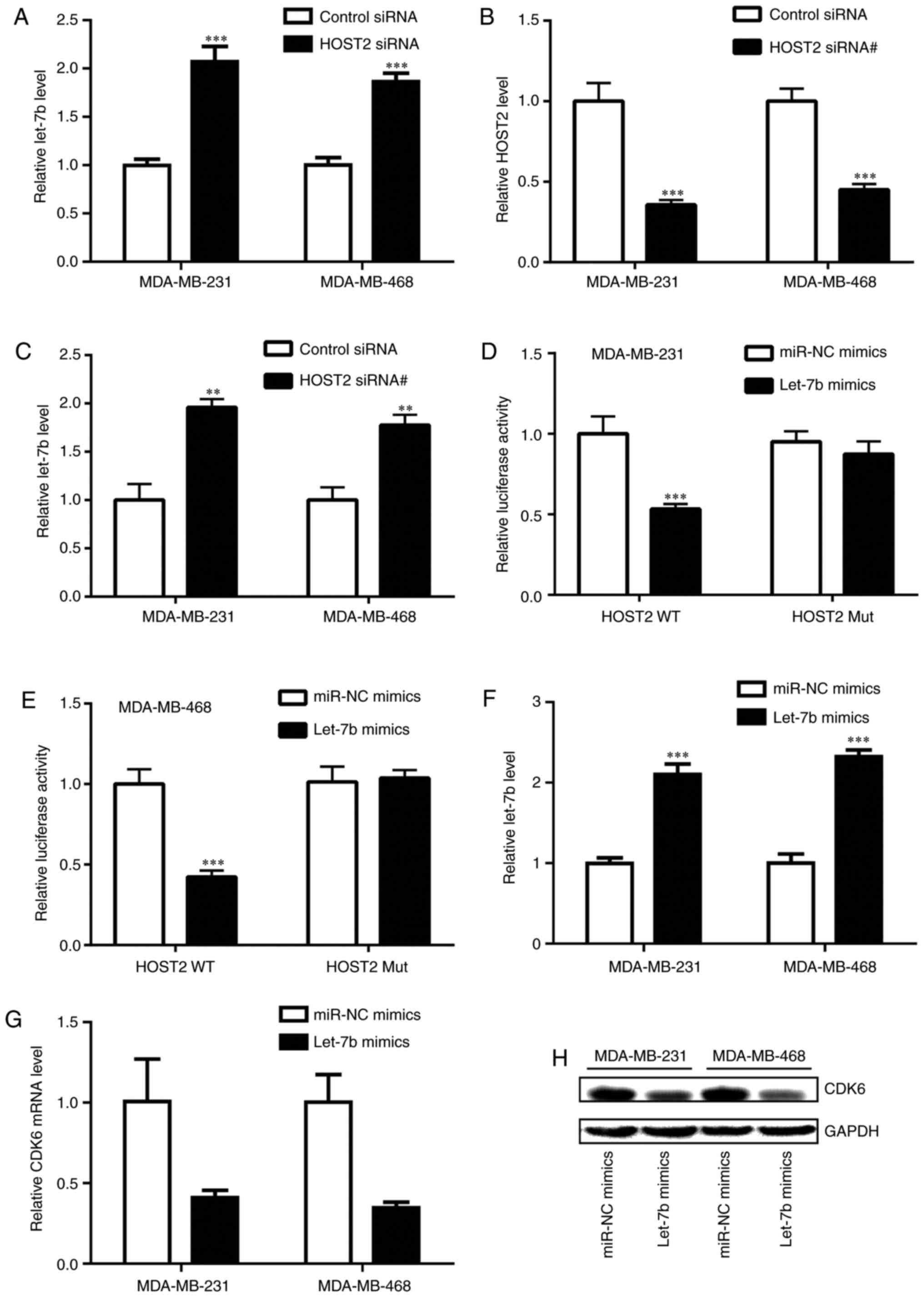
|
1
|
Schettini F, Buono G, Cardalesi C,
Desideri I, De Placido S and Del Mastro L: Hormone receptor/human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: Where we
are now and where we are going. Cancer Treat Rev. 46:20–26. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zheng S, Bai JQ, Li J, Fan JH, Pang Y,
Song QK, Huang R, Yang HJ, Xu F, Lu N and Qiao YL: The pathologic
characteristics of breast cancer in China and its shift during
1999-2008: a national-wide multicenter cross-sectional image over
10 years. Int J Cancer. 131:2622–2631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss P: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human
breast tumours. Nature. 490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Agrawal LS and Mayer IA: Platinum agents
in the treatment of early-stage triple-negative breast cancer: Is
it time to change practice? Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 12:654–658.
2014.
|
|
6
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pinto R, De Summa S, Pilato B and Tommasi
S: DNA methylation and miRNAs regulation in hereditary breast
cancer: Epigenetic changes, players in transcriptional and
post-transcriptional regulation in hereditary breast cancer. Curr
Mol Med. 14:45–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Maruyama R and Suzuki H: Long noncoding
RNA involvement in cancer. BMB Rep. 45:604–611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li JP, Liu LH, Li J, Chen Y, Jiang XW,
Ouyang YR, Liu YQ, Zhong H, Li H and Xiao T: Microarray expression
profile of long noncoding RNAs in human osteosarcoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 433:200–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lv M, Xu P, Wu Y, Huang L, Li W, Lv S, Wu
X, Zeng X, Shen R, Jia X, et al: LncRNAs as new biomarkers to
differentiate triple negative breast cancer from non-triple
negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:13047–13059. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rinn JL and Chang HY: Genome regulation by
long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:145–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu RT, Cao JL, Yan CQ, Wang Y, An CJ and
Lv HT: Effects of LncRNA-HOST2 on cell proliferation, migration,
invasion and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
SMMC-7721. Biosci Rep. 37:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhong Y, Gao D, He S, Shuai C and Peng S:
Dysregulated expression of long noncoding RNAs in ovarian cancer.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 26:1564–1570. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Mammalian
cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:630–641. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lim S and Kaldis P: Cdks, cyclins and
CKIs: roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development.
140:3079–3093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Qi X, Zhang DH, Wu N, Xiao JH, Wang X and
Ma W: ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical
implications. J Med Genet. 52:710–718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lu PW, Li L, Wang F and Gu YT: Effects of
long non-coding RNA HOST2 on cell migration and invasion by
regulating microRNA let-7b in breast cancer. J Cell Biochem.
119:4570–4580. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Palma G, Frasci G, Chirico A, Esposito E,
Siani C, Saturnino C, Arra C, Ciliberto G, Giordano A and D'Aiuto
M: Triple negative breast cancer: Looking for the missing link
between biology and treatments. Oncotarget. 6:26560–26574. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oakman C, Viale G and Di Leo A: Management
of triple negative breast cancer. Breast. 19:312–321. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, He Q, Hu Z, Feng Y, Fan L, Tang
Z, Yuan J, Shan W, Li C, Hu X, et al: Long noncoding RNA LINP1
regulates repair of DNA double-strand breaks in triple-negative
breast cancer. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 23:522–530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Lin A, Li C, Xing Z, Hu Q, Liang K, Han L,
Wang C, Hawke DH, Wang S, Zhang Y, et al: The LINK-A lncRNA
activates normoxic HIF1alpha signalling in triple-negative breast
cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 18:213–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Regulation of
apoptosis by long non-coding RNA GAS5 in breast cancer cells:
implications for chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
145:359–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rangel LB, Sherman-Baust CA, Wernyj RP,
Schwartz DR, Cho KR and Morin PJ: Characterization of novel human
ovarian cancer-specific transcripts (HOSTs) identified by serial
analysis of gene expression. Oncogene. 22:7225–7232. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao Y, Meng H, Liu S, Hu J, Zhang Y, Jiao
T, Liu Y, Ou J, Wang D, Yao L, et al: LncRNA-HOST2 regulates cell
biological behaviors in epithelial ovarian cancer through a
mechanism involving microRNA let-7b. Hum Mol Genet. 24:841–852.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Li X, Meng FB, Wang ZX, Zhao RT
and Yang CY: Effects of the long non-coding RNA HOST2 on the
proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of human
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:320–330. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tadesse S, Yu M, Kumarasiri M, Le BT and
Wang S: Targeting CDK6 in cancer: State of the art and new
insights. Cell Cycle. 14:3220–3230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu YH, Yao J, Chan LC, Wu TJ, Hsu JL,
Fang YF, Wei Y, Wu Y, Huang WC, Liu CL, et al: Definition of
PKC-alpha, CDK6, and MET as therapeutic targets in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 74:4822–4835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Li D, Zhang W, Guo M and Zhan Q:
Long non-coding RNA gadd7 interacts with TDP-43 and regulates Cdk6
mRNA decay. EMBO J. 31:4415–4427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Z, Wang W, Jiang J, Bao E, Xu D, Zeng
Y, Tao L and Qiu J: Downregulation of GAS5 promotes bladder cancer
cell proliferation, partly by regulating CDK6. PLoS One.
8:e739912013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kawasaki Y, Komiya M, Matsumura K, Negishi
L, Suda S, Okuno M, Yokota N, Osada T, Nagashima T, Hiyoshi M, et
al: MYU, a target lncRNA for Wnt/c-Myc signaling, mediates
induction of CDK6 to promote cell cycle progression. Cell Rep.
16:2554–2564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|