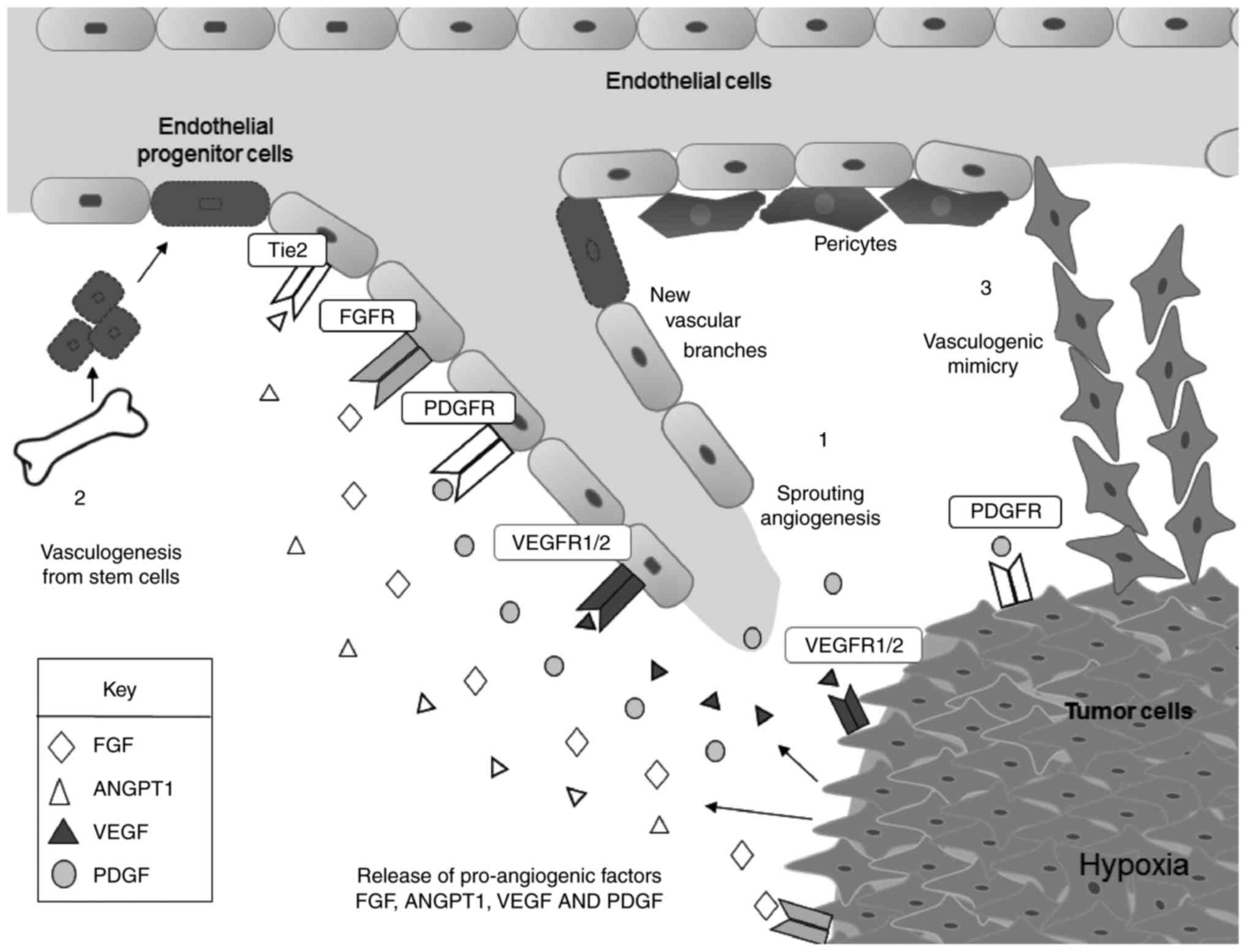
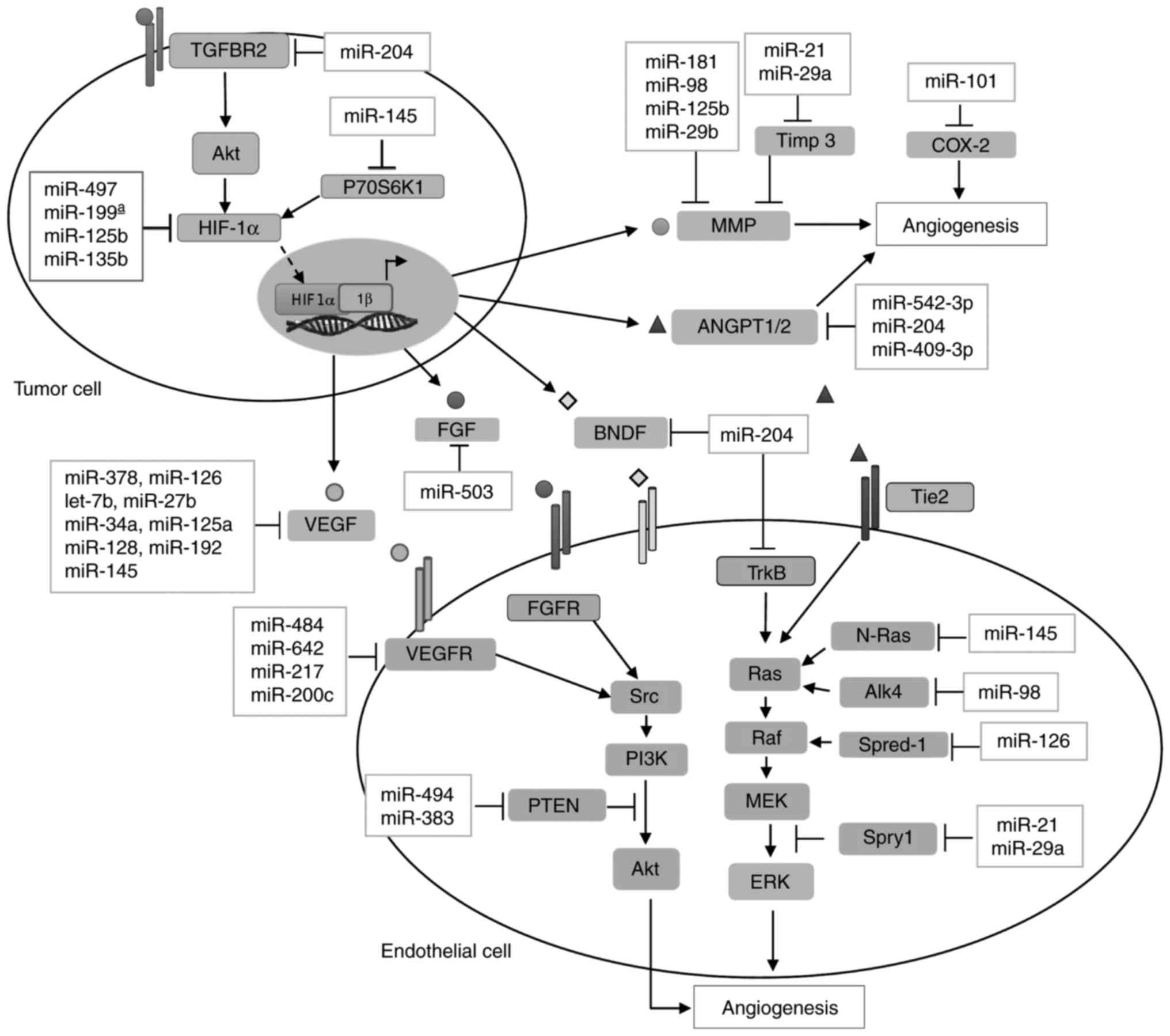
|
1
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA,
Gardner LM, Pe’er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS and Hendrix MJ: Vascular
channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro:
Vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 155:739–752. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cai X, Hagedorn CH and Cullen BR: Human
microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts
that can also function as mRNAs. RNA. 10:1957–1966. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H and
Kim VN: The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing.
Genes Dev. 18:3016–3027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruby JG, Jan CH and Bartel DP: Intronic
microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature.
448:83–86. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E,
Norman J, Cooch N, Nishikura K and Shiekhattar R: TRBP recruits the
Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing.
Nature. 436:740–744. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sen GL and Blau HM: Argonaute 2/RISC
resides in sites of mammalian mRNA decay known as cytoplasmic
bodies. Nat Cell Biol. 7:633–636. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vecchione A, Belletti B, Lovat F, Volinia
S, Chiappetta G, Giglio S, Sonego M, Cirombella R, Onesti EC,
Pellegrini P, et al: A microRNA signature defines chemoresistance
in ovarian cancer through modulation of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:9845–9850. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borges NM, do Vale Elias M, Fook-Alves VL,
Andrade TA, de Conti ML, Macedo MP, Begnami MD, Campos AH, Etto LY,
Bortoluzzo AB, et al: Angiomirs expression profiling in diffuse
large B-Cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 7:4806–4816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Suárez Y and Sessa WC: MicroRNAs as novel
regulators of angiogenesis. Circ Res. 104:442–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suzuki HI, Katsura A, Matsuyama H and
Miyazono K: MicroRNA regulons in tumor microenvironment. Oncogene.
34:3085–3094. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison
EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV and Hannon
G: Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 35:215–217.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, Sandusky GE, Zhang
Q and Zhao G: Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during
mouse development. J Biol Chem. 280:9330–9335. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Yu J,
Gerber SA, Harrison KD, Pober JS, Iruela-Arispe ML, Merkenschlager
M and Sessa WC: Dicer-dependent endothelial microRNAs are necessary
for postnatal angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:14082–14087. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM and
Dimmeler S: Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA
expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 101:59–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS
and Sessa WC: Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression
and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 100:1164–1173.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poliseno L, Tuccoli A, Mariani L,
Evangelista M, Citti L, Woods K, Mercatanti A, Hammond S and
Rainaldi G: MicroRNAs modulate the angiogenic properties of HUVECs.
Blood. 108:3068–3071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heusschen R, van Gink M, Griffioen AW and
Thijssen VL: MicroRNAs in the tumor endothelium: Novel controls on
the angioregulatory switchboard. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1805:87–96.
2010.
|
|
22
|
McCall M, Kent O, Yu J, Fox-Talbot K,
Zaiman A and Halushka M: MicroRNA profiling of diverse endothelial
cell types. BMC Med Genomics. 4:782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen G, Li X, Jia Y, Piazza G and Xi Y:
Hypoxia-regulated microRNAs in human cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:336–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Beijnum J, Giovannetti E, Poel D,
Nowak-Sliwinska P and Griffioe A: miRNAs: micro-managers of
anticancer combination therapies. Angiogenesis. 20:269–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Siegel R, Miller K and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parker L, Schmidt M, Jin S, Gray A, Beis
D, Pham T, Frantz G, Palmieri S, Hillan K, Stainier D, et al: The
endothelial-cell-derived secreted factor Egfl7 regulates vascular
tube formation. Nature. 428:754–758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meister J and Schmidt M: miR-126 and
miR-126*: New players in cancer. ScientificWorld J. 10:2090–2100.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Xie H, Zhou Z, Chen H, Hu
T, Bai Y, Shen Y, Yuan W, Jing Q and Qin Y: Endothelial-specific
intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in human breast cancer and
targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell Biochem. 351:57–164. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu YY, Sweredoski MJ, Huss D, Lansford R,
Hess S and Tirrell DA: Prometastatic GPCR CD97 is a direct target
of tumor suppressor microRNA-126. ACS Chem Biol. 9:334–338. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Yang P, Sun T, Li D, Xu X, Rui Y,
Li C, Chong M, Ibrahim T, Mercatali L, et al: miR-126 and miR-126*
repress recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells and inflammatory
monocytes to inhibit breast cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
15:284–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M and Tavazoie
SF: A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and
metastasis by cancer cells. Nature. 481:190–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Z, Cai X, Huang C, Xu J and Liu A:
miR-497 suppresses angiogenesis in breast carcinoma by targeting
HIF-1α. Oncol Rep. 35:1696–1702. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tu Y, Liu L, Zhao D, Liu Y, Ma X, Fan Y,
Wan L, Huang T, Cheng Z and Shen B: Overexpression of miRNA-497
inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR2. Sci Rep.
5:138272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fox S, Generali D and Harris A: Breast
tumour angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 9:2162017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chang S, Wang R, Akagi K, Kim K, Martin B,
Cavallone L; Kathleen Cuningham Foundation Consortium for Research
into Familial Breast Cancer (kConFab); Haines DC, Basik M, Mai P,
et al: Tumor suppressor BRCA1 epigenetically controls oncogenic
microRNA-155. Nat Med. 17:1275–1282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Danza K, De Summa S, Pinto R, Pilato B,
Palumbo O, Merla G, Simone G and Tommasi S: MiR-578 and miR-573 as
potential players in BRCA-related breast cancer angiogenesis.
Oncotarget. 6:471–483. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Kong W, He L, Coppola M, Guo J, Esposito
NN, Coppola D and Cheng JQ: MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival,
growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer.
J Biol Chem. 285:17869–17879. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kong W, He L, Richards EJ, Challa S, Xu
CX, Permuth-Wey J, Lancaster JM, Coppola D, Sellers TA, Djeu JY and
Cheng JQ: Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by
targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and
triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 33:679–689. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Foekens J, Sieuwerts A, Smid M, Look M, de
Weerd V, Boersma A, Klijn J, Wiemer E and Martens J: Four miRNAs
associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen
receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13021–13026. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao D, Tu Y, Wan L, Bu L, Huang T, Sun X,
Wang K and Shen B: In vivo monitoring of angiogenesis inhibition
via down-regulation of mir-21 in a VEGFR2-luc murine breast cancer
model using bioluminescent imaging. PLoS One. 8:e714722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mathsyaraja H, Thies K, Taffany D, Deighan
C, Liu T, Yu L, Fernandez S, Shapiro C, Otero J, Timmers C, et al:
CSF1-ETS2-induced microRNA in myeloid cells promote metastatic
tumor growth. Oncogene. 34:3651–3661. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
He T, Qi F, Jia L, Wang S, Song N, Guo L,
Fu Y and Luo Y: MicroRNA-5423 pinhibits tumour angiogenesis by
targeting angiopoietin-2. J Pathol. 232:499–508. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He T, Qi F, Jia L, Wang S, Wang C, Song N,
Fu Y, Li L and Luo Y: Tumor cell-secreted angiogenin induces
angiogenic activity of endothelial cells by suppressing miR-542-3p.
Cancer Lett. 368:115–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Leidner RS, Li L and Thompson CL:
Dampening enthusiasm for circulating microRNA in breast cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e578412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li JT, Wang LF, Zhao YL, Yang T, Li W,
Zhao J, Yu F, Wang L, Meng YL, Liu NN, et al: Nuclear factor of
activated T cells 5 maintained by Hotair suppression of miR-568
upregulates S100 calcium binding protein A4 to promote breast
cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 16:4542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Flores-Pérez A, Marchat L,
Rodríguez-Cuevas S, Bautista-Piña V, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Ocampo E,
Martínez M, Palma-Flores C, Fonseca-Sánchez M, Astudillo-de la Vega
H, et al: Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by miR-204
controls angiogenesis in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 6:345042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Hardy KM, Seftor
RE and Hendrix MJ: Molecular pathways: Vasculogenic mimicry in
tumor cells: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2726–3272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Salinas-Vera YM, Marchat LA,
García-Vázquez R, González de la Rosa CH, Castañeda-Saucedo E, Tito
NN, Flores CP, Pérez-Plasencia C, Cruz-Colin JL, Carlos-Reyes Á, et
al: Cooperative multi-targeting of signaling networks by
angiomiR-204 inhibits vasculogenic mimicry in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 432:17–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer facts and
figures 2015. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; pp. 1–52. 2015
|
|
51
|
Abramson MA, Jazag A, van der Zee JA and
Whang EE: The molecular biology of pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest
Cancer Res. 1(4 Suppl 2): S7–S12. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Carr RM and Fernandez-Zapico ME:
Pancreatic cancer microenvironment, to target or not to target?
EMBO Mol Med. 8:80–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Khan S, Ansarullah, Kumar D, Jaggi M and
Chauhan SC: Targeting microRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Microplayers
in the big game. Cancer Res. 73:6541–6547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mace TA, Collins AL, Wojcik SE, Croce CM,
Lesinski GB and Bloomston M: Hypoxia induces the overexpression of
microRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res. 184:855–860.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Volinia S, Calin G, Liu C, Ambs S, Cimmino
A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner
MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ and Schmittgen
TD: Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in
pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:1046–1054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Moriyama T, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J,
Sato N, Nabae T, Takahata S, Toma H, Nagai E and Tanaka M:
MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer
cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance.
Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1067–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bao B, Ali S, Kong D, Sarkar S, Wang Z,
Banerjee S, Aboukameel A, Padhye S, Philip P and Sarkar F:
Anti-tumor activity of a novel compound-CDF is mediated by
regulating miR-21, miR-200, and PTEN in pancreatic cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e178502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kadera BE, Li L, Toste PA, Wu N, Adams C,
Dawson DW and Donahue TR: MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma tumor-associated fibroblasts promotes metastasis.
PLoS One. 8:e719782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hoffmann A, Mori R, Vallbohmer D,
Brabender J, Klein E, Drebber U, Baldus S, Cooc J, Azuma M, Metzger
R, et al: High expression of HIF1a is a predictor of clinical
outcome in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and
correlated to PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF. Neoplasia. 10:674–679. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang X, Ren H, Zhao T, Ma W, Dong J, Zhang
S, Xin W, Yang S, Jia L and Hao J: Single nucleotide polymorphism
in the microRNA-199a binding site of HIF1A gene is associated with
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma risk and worse clinical outcomes.
Oncotarget. 7:13717–1329. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chan YC, Roy S, Huang Y, Khanna S and Sen
C: The microRNA miR-199a-5p down-regulation switches on wound
angiogenesis by derepressing the v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26
oncogene homolog 1-matrix metalloproteinase-1 pathway. J Biol Chem.
287:41032–41043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Morton J, Timpson P, Karim S, Ridgway R,
Athineos D, Doyle B, Jamieson N, Oien K, Lowy A, Brunton V, et al:
Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence
in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:246–251. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Frampton A, Krell J, Jamieson N, Gall T,
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Mato Prado M, Krell D, Habib N, Castellano
L, et al: microRNAs with prognostic significance in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 51:1389–1404.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Alemar B, Izetti P, Gregório C, Macedo GS,
Castro MA, Osvaldt AB, Matte U and Ashton-Prolla P: miRNA-21 and
miRNA-34a are potential minimally invasive biomarkers for the
diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 45:84–92.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Chang T, Wentzel E, Kent O, Ramachandran
K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, Feldmann G, Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M,
Lowenstein C, et al: Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly
influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell.
26:745–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vogt M, Munding J, Grüner M, Liffers ST,
Verdoodt B, Hauk J, Steinstraesser L, Tannapfel A and Hermeking H:
Frequent concomitant inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c by CpG
methylation in colorectal, pancreatic, mammary, ovarian,
urothelial, and renal cell carcinomas and soft tissue sarcomas.
Virchows Arch. 458:313–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhao T, Li J and Chen AF: MicroRNA-34a
induces endothelial progenitor cell senescence and impedes its
angiogenesis via suppressing silent information regulator 1. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E110–E116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT and Matthay RA:
Lung cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest
Med. 32:605–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bremnes RM, Camps C and Sirera R:
Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: The prognostic impact
of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and
blood. Lung Cancer. 51:143–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Korpanty G, Smyth E and Carney D: Update
on anti-angiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Are we
making progress? J Thorac Dis. 3:19–29. 2011.
|
|
72
|
Al Farsi A and Ellis P: Anti-angiogenic
therapy in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Is there
a role in subsequent lines of therapy? J Thorac Dis. 7:214–216.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chen S, Xue Y, Wu X, Le C, Bhutkar A, Bell
L, Zhang F, Langer R and Sharp PA: Global microRNA depletion
suppresses tumor angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 28:1054–1067. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Donnem T, Fenton CG, Lonvik K, Berg T,
Eklo K, Andersen S, Stenvold H, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S, Bremnes RM
and Busund LT: MicroRNA signatures in tumor tissue related to
angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 7:e296712012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu B, Peng XC, Zheng XL, Wang J and Qin
YW: MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth
of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer.
66:169–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Donnem T, Lonvik K, Eklo K, Berg T, Sorbye
SW, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S, Andersen S, Stenvold H, Bremnes RM and
Busund LT: Independent and tissue-specific prognostic impact of
miR-126 in nonsmall cell lung cancer: Coexpression with vascular
endothelial growth factor-A predicts poor survival. Cancer.
117:3193–3200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Jusufović E, Rijavec M, Keser D, Korošec
P, Sodja E, Iljazović E, Radojević Z and Košnik M: le7 and miR-126
are down-regulated in tumor tissue and correlate with microvessel
density and survival outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS
One. 7:e455772012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Chen Z, Lai TC, Jan YH, Lin FM, Wang WC,
Xiao H, Wang YT, Sun W, Cui X, Li YS, et al: Hypoxia-responsive
miRNAs target argonaute 1 to promote angiogenesis. J Clin Invest.
123:1057–1067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
et al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung
cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival.
Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens M, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hu J, Cheng Y, Li Y, Jin Z, Pan Y, Liu G,
Fu S, Zhang Y, Feng K and Feng Y: microRNA-128 plays a critical
role in human non-small cell lung cancer tumourigenesis,
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by directly targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor-C. Eur J Cancer. 50:2336–2350. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tejero R, Navarro A, Campayo M, Viñolas N,
Marrades M, Cordeiro A, Ruíz-Martínez M, Santasusagna S, Molins L,
Ramirez J and Monzó M: miR-141 and miR-200c as markers of overall
survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma.
PLoS One. 9:e1018992014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
Owen S and Souhami L: The management of
brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen LT, Xu SD, Xu H, Zhang JF, Ning JF
and Wang SF: MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung
cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and
tumor angiogenesis. Med Oncol. 9:1673–1680. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Skrzypek K, Tertil M, Golda S, Ciesl M,
Weglarczyk K, Collet G, Guichard A, Kozakowska M, Boczkowski J, Was
H, et al: Interplay between heme oxygenase-1 and miR-378 affects
non-small cell lung carcinoma growth, vascularization, and
metastasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:644–660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Mao G, Liu Y, Fang X, Liu Y, Fang L, Lin
L, Liu X and Wang N: Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes
angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis.
18:373–382. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhao WY, Wang Y, An ZJ, Shi CG, Zhu GA,
Wang B, Lu MY, Pan CK and Chen P: Downregulation of miR-497
promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting HDGF in
non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
435:466–447. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Beermann J, Napp
LC, Jabs O, Bhayadia R, Melk A, Ucar A, Chowdhury K, Lorenzen JM,
et al: Vascular importance of the miR-212/132 cluster. Eur Heart J.
35:3224–3231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Incoronato M, Urso L, Portela A, Laukkanen
MO, Soini Y, Quintavalle C, Keller S, Esteller M and Condorelli G:
Epigenetic regulation of miR-212 expression in lung cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e277222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Luo J, Meng C, Tang Y, Zhang S, Wan M, Bi
Y and Zhou X: miR-132/212 cluster inhibits the growth of lung
cancer xenografts in nude mice. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:4115–4122.
2014.
|
|
92
|
Cui H, Seubert B, Stahl E, Dietz H,
Reuning U, Moreno-Leon L, Ilie M, Hofman P, Nagase H, Mari B and
Krüger A: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a
pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells
and their exosomes. Oncogene. 34:3640–3650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Pesta M, Kulda V, Kucera R, Pesek M,
Vrzalova J, Liska V, Pecen L, Treska V, Safranek J, Prazakova M, et
al: Prognostic significance of TIMP-1 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:4031–4038. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer facts and
figures 2016. Atlanta, Ga: American Cancer Society; 2016
|
|
95
|
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Schetter AJ, Okugawa Y,
Harris CC, Boland CR and Goel A: Identification of a
metastasis-specific MicroRNA signature in human colorectal cancer.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 107:dju4922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yamaguchi T, Iijima T, Wakaume R,
Takahashi K, Matsumoto H, Nakano D, Nakayama, Y Mori T, Horiguchi S
and Miyaki M: Underexpression of miR-126 and miR-20b in hereditary
and nonhereditary colorectal tumors. Oncology. 87:58–66. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z,
Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J and Jiang B: Epigenetic silencing of miR-126
contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hansen TF, Andersen CL, Nielsen BS,
Spindler KL, Sørensen FB, Lindebjerg J, Brandslund I and Jakobsen
A: Elevated microRNA-126 is associated with high vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression levels and high
microvessel density in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2:1101–1106.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Hansen TF, Christensen Rd, Andersen RF,
Sørensen FB, Johnsson A and Jakobsen A: MicroRNA-126 and epidermal
growth factor-like domain 7-an angiogenic couple of importance in
metastatic colorectal cancer. Results from the Nordic ACT trial Br
J Cancer. 109:1243–1251. 2013.
|
|
100
|
Yu W, Wang Z, Shen LI and Wei Q:
Circulating microRNA-21 as a potential diagnostic marker for
colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. 4:237–244.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T,
Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M, Nenutil R and Vyzula R: Altered
expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to
clinico-pathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology.
72:397–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Nielsen S, Jørgensen S, Fog JU, Søkilde R,
Christensen IJ, Hansen U, Brünner N, Baker A, Møller S and Nielsen
HJ: High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal cancers
predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon cancer
patients. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:27–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Nagao Y, Hisaoka M, Matsuyama A, Kanemitsu
S, Hamada T, Fukuyama T, Nakano R, Uchiyama A, Kawamoto M,
Yamaguchi K and Hashimoto H: Association of microRNA-21 expression
with its targets, PDCD4 and TIMP3, in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 25:112–121. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Song MS and Rossi JJ: The anti-miR21
antagomir, a therapeutic tool for colorectal cancer, has a
potential synergistic effect by perturbing an
angiogenesis-associated miR30. Front Genet. 4:3012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bridge G, Monteiro R, Henderson S, Emuss
V, Lagos D, Georgopoulou D, Patient R and Boshoff C: The
microRNA-30 family targets DLL4 to modulate endothelial cell
behavior during angiogenesis. Blood. 120:5063–5072. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hellström M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ, Wallgard
E, Coultas L, Lindblom P, Alva J, Nilsson AK, Karlsson L, Gaiano N,
et al: Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip
cells during angiogenesis. Nature. 445:776–780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Miyanaga K, Kato Y, Nakamura T, Matsumura
M, Amaya H, Horiuchi T, Chiba Y and Tanaka K: Expression and role
of thrombospondin-1 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
22:3941–3948. 2002.
|
|
108
|
Diosdado B, van de Wiel A, Terhaar Sive
Droste S, Mongera S, Postma C, Meijerink WJ, Carvalho B and Meijer
GA: MiR-17-92 cluster is associated with 13q gain and c-myc
expression during colorectal adenoma to adenocarcinoma progression.
Br J Cancer. 101:707–714. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D,
Sevignani C, Wentzel E, Furth E, Lee M, Enders H, Mendell T and
Thomas-Tikhonenko A: Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a
Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet. 38:1060–1065. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Amodeo V, Bazan V, Fanale D, Insalaco L,
Caruso S, Cicero G, Bronte G, Rolfo C, Santini D and Russo A:
Effects of anti-miR-182 on TSP-1 expression in human colon cancer
cells: There is a sense in antisense? Expert Opin Ther Targets.
17:1249–1261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L and Chen C:
Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human
tissues. BMC Genomics. 8:1662007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Sundaram P, Hultine S, Smith LM, Dews M,
Fox JL, Biyashev D, Schelter JM, Huang Q, Cleary MA, Volpert OV and
Thomas-Tikhonenko A: p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits
thrombospondin-1 and promotes angiogenesis in colon cancers. Cancer
Res. 71:7490–7501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Braun CJ, Zhang X, Savelyeva I, Wolff S,
Moll UM, Schepeler T, Ørntoft TF, Andersen CL and Dobbelstein M:
p53-responsive micrornas 192 and 215 are capable of inducing cell
cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 68:10094–10104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Xue G, Yan HL, Zhang Y, Hao LQ, Zhu XT,
Mei Q and Sun SH: c-Myc-mediated repression of miR-15-16 in hypoxia
is induced by increased HIF-2α and promotes tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis by upregulating FGF2. Oncogene. 34:1393–1406. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Dai L, Wang W, Zhang S, Jiang Q, Wang R,
Dai L, Cheng L, Yang Y, Wei YQ and Deng HX: Vector-based
miR-15a/16-1 plasmid inhibits colon cancer growth in vivo. Cell
Biol Int. 36:765–770. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Fang Y, Liang X, Jiang W, Li J, Xu J and
Cai X: Cyclin b1 suppresses colorectal cancer invasion and
metastasis by regulating e-cadherin. PLoS One. 10:e01268752015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Planutis K, Planutiene M and Holcombe F: A
novel signaling pathway regulates colon cancer angiogenesis through
Norrin. Sci Rep. 4:56302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang B, Li W, Liu H, Yang L, Liao Q, Cui
S, Wang H and Zhao L: miR-29b suppresses tumor growth and
metastasis in colorectal cancer via downregulating Tiam1 expression
and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Death Dis.
17:e13352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Subramanian M, Rao SR, Thacker P,
Chatterjee S and Karunagaran D: MiR-29b downregulates canonical Wnt
signaling by suppressing coactivators of β-catenin in human
colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:1974–1984.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ding Q, Chang CJ, Xie X, Xia W, Yang Y,
Wang SC, Wang Y, Xia J, Chen L, Cai C, et al: APOBEC3G promotes
liver metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model of colorectal cancer
and predicts human hepatic metastasis. J Clin Invest.
121:4526–4536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Colangelo T, Fucci A, Votino C, Sabatino
L, Pancione M, Laudanna C, Binaschi M, Bigioni M, Maggi A, Parente
D, et al: MicroRNA-130b promotes tumor development and is
associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia.
15:1086–1099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Panigrahy D, Singer S, Shen LQ,
Butterfield CE, Freedman DA, Chen EJ, Moses MA, Kilroy S, Duensing
S, Fletcher C, et al: PPARgamma ligands inhibit primary tumor
growth and metastasis by inhibiting angiogenesis. J Clin Invest.
110:923–932. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Urbich C, Kaluza D, Frömel T, Knau A,
Bennewitz K, Boon RA, Bonauer A, Doebele C, Boeckel JN,
Hergenreider E, et al: MicroRNA-27a/b controls endothelial cell
repulsion and angiogenesis by targeting semaphorin 6A. Blood.
119:1607–1616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Veliceasa D, Biyashev D, Qin G, Misener S,
Mackie AR, Kishore R and Volpert OV: Therapeutic manipulation of
angiogenesis with miR-27b. Vasc Cell. 24:62015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Abdelrahim
M, Abudayyeh A, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Wu F, Mertens-Talcott S,
Vanderlaag K, Cho D, et al: Oncogenic microRNA-27a is a target for
anticancer agent methyl
2-cyano-3,11-dioxo-18beta-olean-1,12-dien-30-oate in colon cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 125:1965–1974. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Pathi S, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G,
Sreevalsan S, Anand S, Thatcher GR and Safe S: GT-094, a NO-NSAID,
inhibits colon cancer cell growth by activation of a reactive
oxygen species-microRNA-27a: ZBTB10-specificity protein pathway.
Mol Cancer Res. 9:195–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Colangelo T, Polcaro G, Ziccardi P, Pucci
B, Muccillo L, Galgani M, Fucci A, Milone MR, Budillon A,
Santopaolo M, et al: Proteomic screening identifies calreticulin as
a miR-27a direct target repressing MHC class I cell surface
exposure in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 25:e21202016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Bao Y, Chen Z, Guo Y, Feng Y, Li Z, Han W,
Wang J, Zhao W, Jiao Y, Li K, et al: Tumor suppressor microRNA-27a
in colorectal carcinogenesis and progression by targeting SGPP1 and
Smad2. PLoS One. 9:e1059912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ye J, Wu X, Wu D, Wu P, Ni C, Zhang Z,
Chen Z, Qiu F, Xu J and Huang J: miRNA-27b targets vascular
endothelial growth factor C to inhibit tumor progression and
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e606872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver
JL, Are C, Brattain M and Wang J: MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver
metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene. 33:5332–5340. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
131
|
Yin Y, Yan ZP, Lu NN, Xu Q, He J, Qian X,
Yu J, Guan X, Jiang BH and Liu LZ: Downregulation of miR-145
associated with cancer progression and VEGF transcriptional
activation by targeting N-RAS and IRS1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1829:239–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li
D, Lai L and Jiang BH: MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer
cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:761–774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
133
|
Bustin SA, Dorudi S, Phillips SM, Feakins
RM and Jenkins PJ: Local expression of insulin-like growth factor-I
affects angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 23:130–138.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Qian X, Yu J, Yin Y, He J, Wang L, Li Q,
Zhang LQ, Li CY, Shi ZM, Xu Q, et al: MicroRNA-143 inhibits tumor
growth and angiogenesis and sensitizes chemosensitivity to
oxaliplatin in colorectal cancers. Cell Cycle. 12:1385–1394. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang H, Hao Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Li J, Yin
S, Sun C, Ma M, Huang Y and Xi JJ: Genome-wide functional screening
of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer
metastasis. Nat Commun. 2:5542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Lin RL and Zhao LJ: Mechanistic basis and
clinical relevance of the role of transforming growth factor-β in
cancer. Cancer Biol Med. 12:385–393. 2015.
|
|
137
|
Xiao F, Qiu H, Cui H, Ni X, Li J, Liao W,
Lu L and Ding K: MicroRNA-885-3p inhibits the growth of HT-29 colon
cancer cell xenografts by disrupting angiogenesis via targeting
BMPR1A and blocking BMP/Smad/Id1 signaling. Oncogene. 34:1968–1978.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Yamada N, Tsujimura N, Kumazaki M,
Shinohara H, Taniguchi K, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T and Akao Y: Colorectal
cancer cell-derived microvesicles containing microRNA-1246 promote
angiogenesis by activating Smad 1/5/8 signaling elicited by PML
down-regulation in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1839:1256–1272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Wang Y, Kim S and Kim IM: Regulation of
metastasis by microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 4:1432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Dwivedi SK, Mustafi SB, Mangala LS, Jiang
D, Pradeep S, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Ling H, Ivan C, Mukherjee P,
Calin GA, et al: Therapeutic evaluation of microRNA-15a and
microRNA-16 in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 7:15093–15104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Nusrat O, Belotte J, Fletcher NM, Memaj I,
Saed MG, Diamond MP and Saed GM: The role of angiogenesis in the
persistence of chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Reprod
Sci. 23:1484–1492. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
He J, Jing Y, Li W, Qian X, Xu Q, Li FS,
Liu LZ, Jiang BH and Jiang Y: Roles and mechanism of miR-199a and
miR-125b in tumor angiogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e566472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H and Shi
H: MicroRNA-497 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor a through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2127–2133. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Chan JK, Kiet TK, Blansit K, Ramasubbaiah
R, Hilton JF, Kapp DS and Matei D: MiR-378 as a biomarker for
response to anti-angiogenic treatment in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 133:568–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Lai Y, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Shu Y, Luo X,
Yang Y, Wang X, Yang G, Li L and Feng Y: The microRNA-27a:
ZBTB10-specificity protein pathway is involved in follicle
stimulating hormone-induced VEGF, Cox2 and survivin expression in
ovarian epithelial cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:776–784. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Korpal M and Kang Y: The emerging role of
miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 5:115–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Pecot C, Rupaimoole R, Yang D, Akbani R,
Ivan C, Lum C, Wu S, Han HD, Shah MY, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, et al:
Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat Commun.
4:24272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Imam JS, Plyler JR, Bansal H, Prajapati S,
Bansal S, Rebeles J, Chen HI, Chang YF, Panneerdoss S, Zoghi B, et
al: Genomic loss of tumor suppressor miRNA-204 promotes cancer cell
migration and invasion by activating AKT/mTOR/Rac1 signaling and
actin reorganization. PLoS One. 7:e523972012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Zhu AX, Duda DG, Sahani DV and Jain RK:
HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:292–301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA,
Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW, Chang TC, Vivekanandan P,
Torbenson M, Clark KR, et al: Therapeutic microRNA delivery
suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell.
137:1005–1017. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
van Zandwijk N, Pavlakis N, Kao SC, Linton
A, Boyer MJ, Clarke S, Huynh Y, Chrzanowska A, Fulham MJ, Bailey
DL, et al: Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in
patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A
first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet
Oncol. 18:1386–1396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Kumar B, Yadav A, Lang J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor growth and tumor
angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e376012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Yu G, Yao W, Xiao W, Li H, Xu H and Lang
B: MicroRNA-34a functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA and
suppresses angiogenesis in bladder cancer by directly targeting
CD44. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:7792014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Arunachalam G, Lakshmanan AP, Samuel SM,
Triggle CR and Ding H: Molecular interplay between microRNA-34a and
Sirtuin1 in hyperglycemia-mediated impaired angiogenesis in
endothelial cells: Effects of metformin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
356:314–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M,
Kang YK, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S and Hong DS: Phase
I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice
weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
35:180–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|