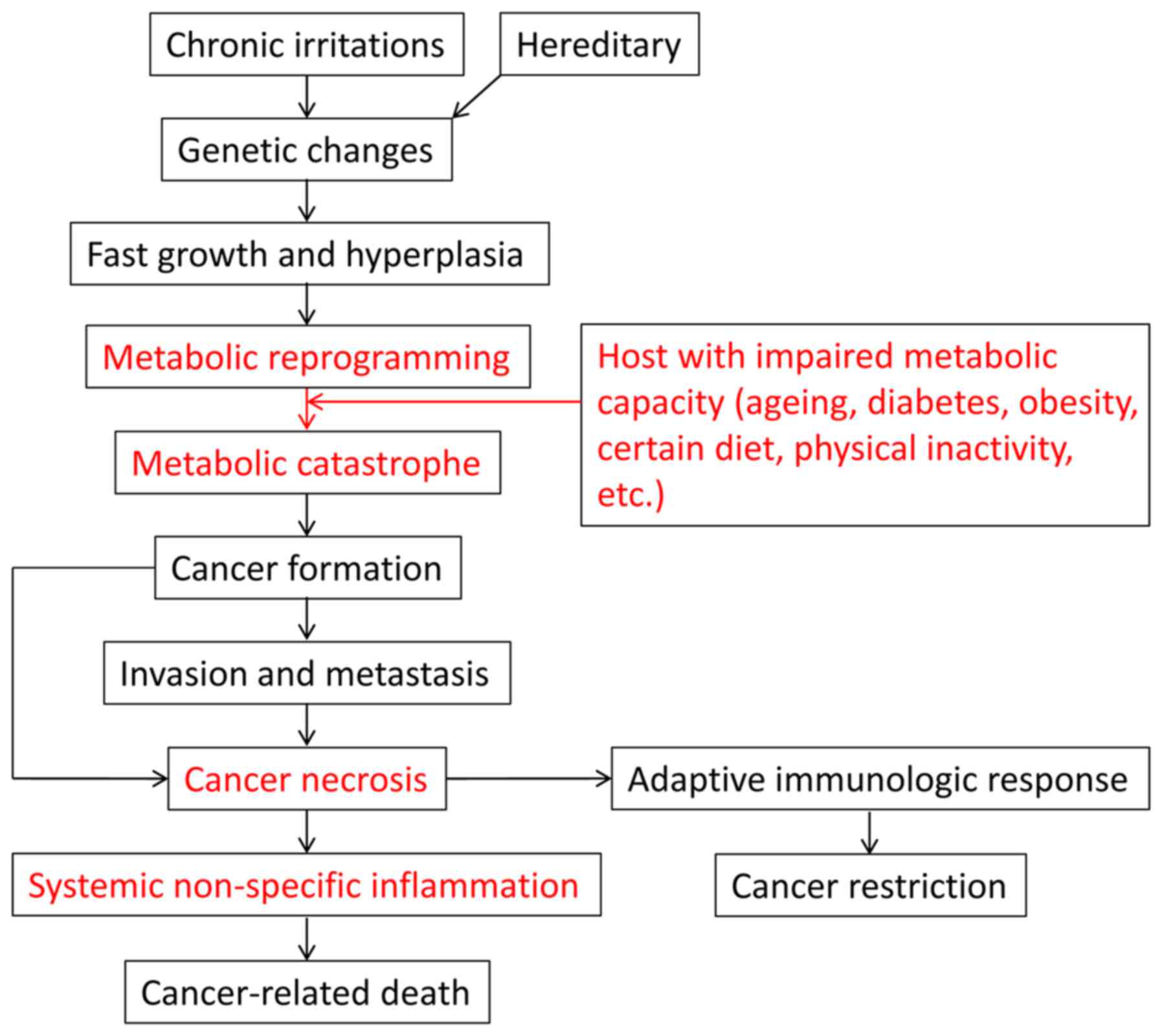
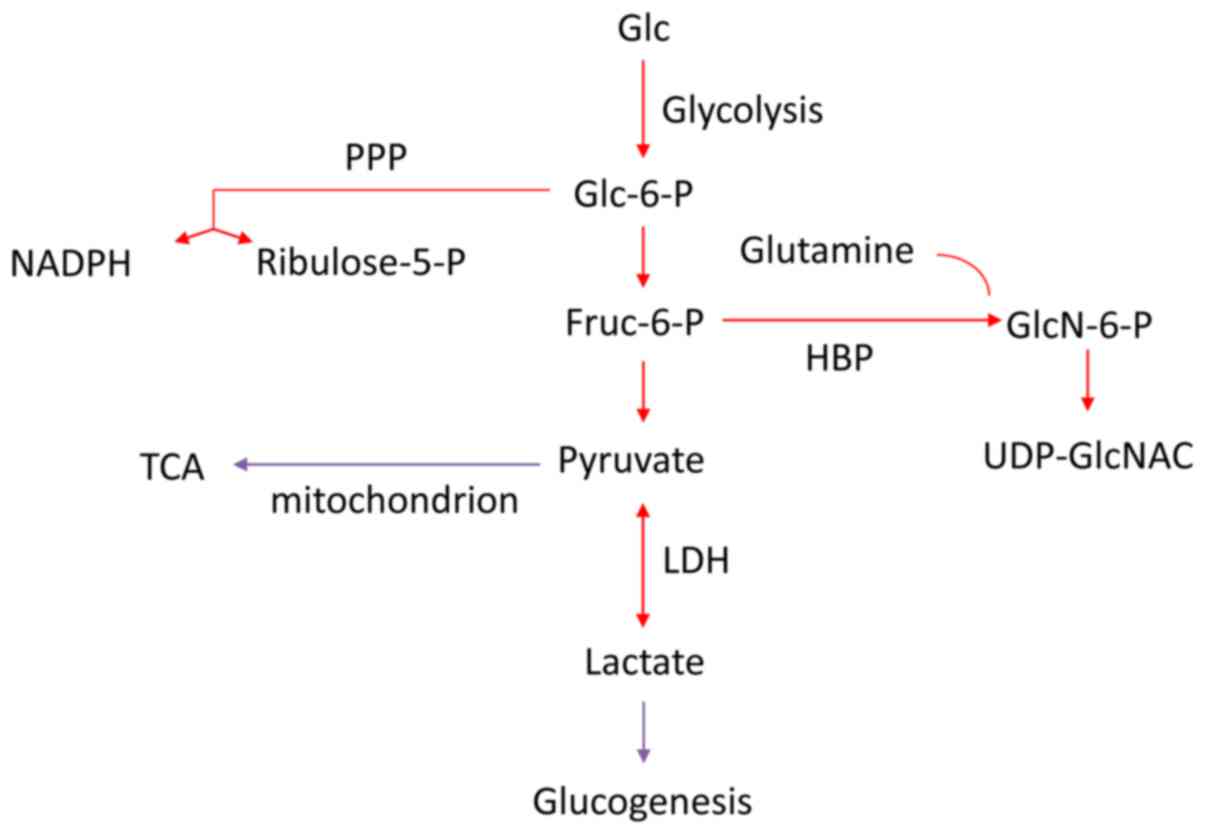
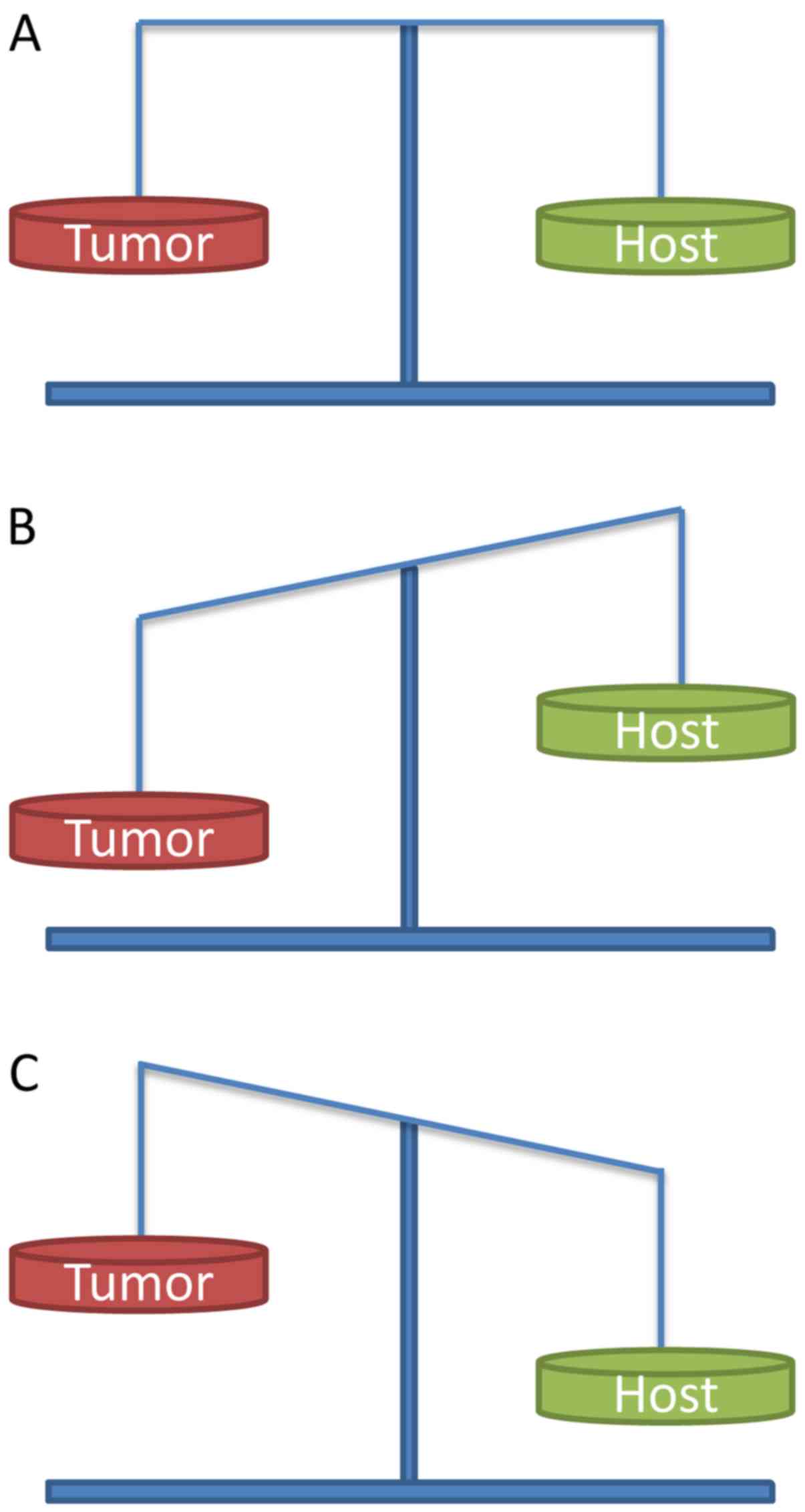
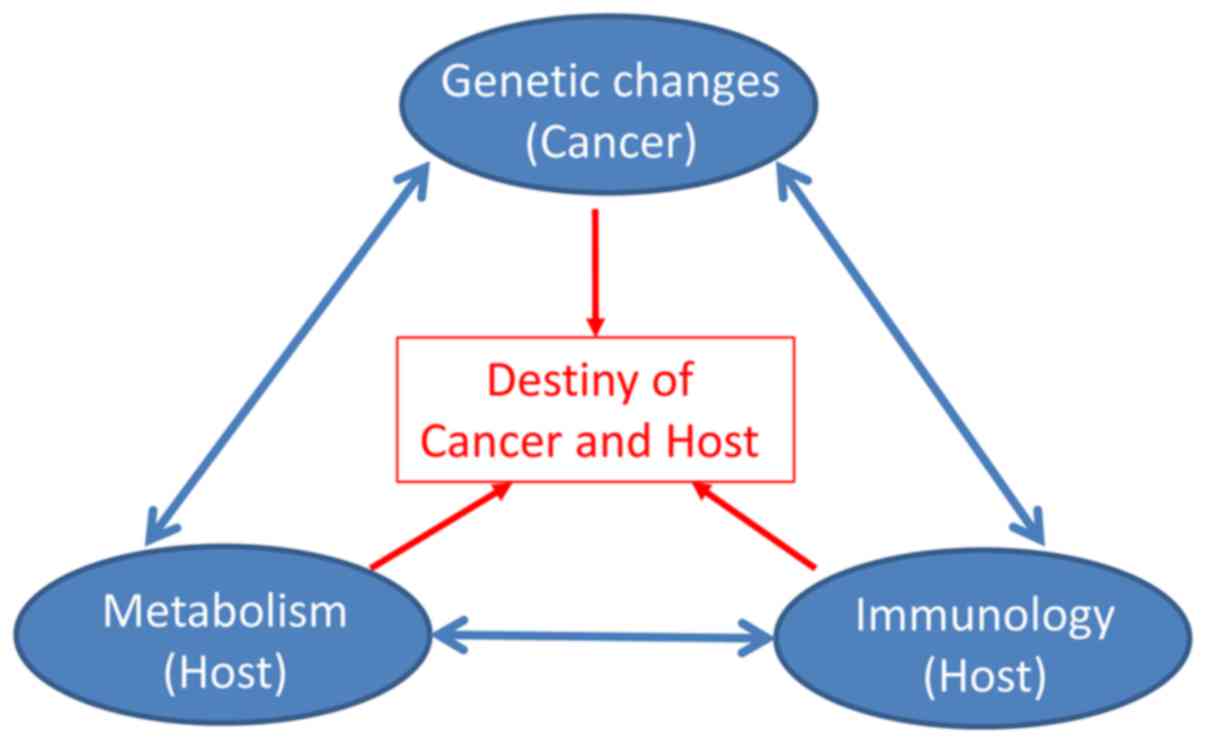
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vineis P and Wild CP: Global cancer
patterns: Causes and prevention. Lancet. 383:549–557. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Soerjomataram I, Lortet-Tieulent J, Parkin
DM, Ferlay J, Mathers C, Forman D and Bray F: Global burden of
cancer in 2008: A systematic analysis of disability-adjusted
life-years in 12 world regions. Lancet. 380:1840–1850. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Warburg O: On respiratory impairment in
cancer cells. Science. 124:269–270. 1956.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin S, DiPaola RS, Mathew R and White E:
Metabolic catastrophe as a means to cancer cell death. J Cell Sci.
120:379–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: Why do cancers
have high aerobic glycolysis. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:891–899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu PP and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 134:703–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL and Dang CV: Otto
Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:325–337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vander Heiden MG and DeBerardinis RJ:
Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer
Biology. Cell. 168:657–669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Casás-Selves M and Degregori J: How cancer
shapes evolution, and how evolution shapes cancer. Evolution (NY).
4:624–634. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Bishop JM: Molecular themes in
oncogenesis. Cell. 64:235–248. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spandidos DA and Wilkie NM: Malignant
transformation of early passage rodent cells by a single mutated
human oncogene. Nature. 310:469–475. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spandidos DA: A unified theory for the
development of cancer. Biosci Rep. 6:691–708. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ying H, Kimmelman AC, Lyssiotis CA, Hua S,
Chu GC, Fletcher-Sananikone E, Locasale JW, Son J, Zhang H, Coloff
JL, et al: Oncogenic Kras maintains pancreatic tumors through
regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism. Cell. 149:656–670. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moussaieff A, Rouleau M, Kitsberg D, Cohen
M, Levy G, Barasch D, Nemirovski A, Shen-Orr S, Laevsky I, Amit M,
et al: Glycolysis-mediated changes in acetyl-CoA and histone
acety-lation control the early differentiation of embryonic stem
cells. Cell Metab. 21:392–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hammarström S: The carcinoembryonic
antigen (CEA) family: Structures, suggested functions and
expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol.
9:67–81. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Richardson LC and Pollack LA: Therapy
insight: Influence of type 2 diabetes on the development, treatment
and outcomes of cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2:48–53. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wellen KE, Lu C, Mancuso A, Lemons JM,
Ryczko M, Dennis JW, Rabinowitz JD, Coller HA and Thompson CB: The
hexosamine biosynthetic pathway couples growth factor-induced
glutamine uptake to glucose metabolism. Genes Dev. 24:2784–2799.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wellen KE and Thompson CB: Cellular
metabolic stress: Considering how cells respond to nutrient excess.
Mol Cell. 40:323–332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joslin EP, Lombard HL, Burrows RE and
Manning MD: Diabetes and cancer. N Engl J Med. 260:486–488. 1959.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pearson-Stuttard J, Zhou B, Kontis V,
Bentham J, Gunter MJ and Ezzati M: Worldwide burden of cancer
attributable to diabetes and high body-mass index: A comparative
risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 6:95–104. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Yuan C, Rubinson DA, Qian ZR, Wu C, Kraft
P, Bao Y, Ogino S, Ng K, Clancy TE, Swanson RS, et al: Survival
among patients with pancreatic cancer and long-standing or
recent-onset diabetes mellitus. J Clin Oncol. 33:29–35. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Niccoli T and Partridge L: Ageing as a
risk factor for disease. Curr Biol. 22:R741–R752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Campisi J: Aging, cellular senescence, and
cancer. Annu Rev Physiol. 75:685–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hinkal G, Parikh N and Donehower LA: Timed
somatic deletion of p53 in mice reveals age-associated differences
in tumor progression. PLoS One. 4:e66542009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
DePinho RA: The age of cancer. Nature.
408:248–254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stanta G, Campagner L, Cavallieri F and
Giarelli L: Cancer of the oldest old. What we have learned from
autopsy studies. Clin Geriatr Med. 13:55–68. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dollé ME, Snyder WK, Gossen JA, Lohman PH
and Vijg J: Distinct spectra of somatic mutations accumulated with
age in mouse heart and small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:8403–8408. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dollé ME, Giese H, Hopkins CL, Martus HJ,
Hausdorff JM and Vijg J: Rapid accumulation of genome
rearrangements in liver but not in brain of old mice. Nat Genet.
17:431–434. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miller RA: The aging immune system: Primer
and prospectus. Science. 273:70–74. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bright R: Cases and observations connected
with disease of thepancreas and duodenum. Med Chir Trans.
1833.18:1Y56 View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Everhart J and Wright D: Diabetes mellitus
as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis. JAMA.
273:1605–1609. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Larsson SC, Orsini N and Wolk A: Diabetes
mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1679–1687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bragg F, Holmes MV, Iona A, Guo Y, Du H,
Chen Y, Bian Z, Yang L, Herrington W, Bennett D, et al: China
Kadoorie Biobank Collaborative Group: Association between diabetes
and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban areas of China.
JAMA. 317:280–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Toriola AT, Stolzenberg-Solomon R,
Dalidowitz L, Linehan D and Colditz G: Diabetes and pancreatic
cancer survival: A prospective cohort-based study. Br J Cancer.
111:181–185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kleeff J, Costello E, Jackson R, Halloran
C, Greenhalf W, Ghaneh P, Lamb RF, Lerch MM, Mayerle J, Palmer D,
et al: The impact of diabetes mellitus on survival following
resection and adjuvant chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Br J
Cancer. 115:887–894. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS,
Stein KB, Derr RL, Wolff AC and Brancati FL: Long-term all-cause
mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 300:2754–2764. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cui Y and Andersen DK: Diabetes and
pancreatic cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 19:F9–F26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pollak M: Insulin and insulin-like growth
factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:915–928. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sah RP, Nagpal SJ, Mukhopadhyay D and
Chari ST: New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced
paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:423–433.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Slawson C, Copeland RJ and Hart GW:
O-GlcNAc signaling: A metabolic link between diabetes and cancer.
Trends Biochem Sci. 35:547–555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pannala R, Leirness JB, Bamlet WR, Basu A,
Petersen GM and Chari ST: Prevalence and clinical profile of
pancreatic cancer- associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology.
134:981–987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pannala R, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, Timmons
LJ, Ransom J, de Andrade M, Petersen GM and Chari ST: Temporal
association of changes in fasting blood glucose and body mass index
with diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol.
104:2318–2325. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pannala R, Basu A, Petersen GM and Chari
ST: New-onset diabetes: A potential clue to the early diagnosis of
pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 10:88–95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Luo G, Liu C, Guo M, Cheng H, Lu Y, Jin K,
Liu L, Long J, Xu J, Lu R, et al: Potential biomarkers in Lewis
negative patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 265:800–805.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Luo G, Liu C, Guo M, Long J, Liu Z, Xiao
Z, Jin K, Cheng H, Lu Y, Ni Q, et al: CA199-Low&Lewis(+)
pancreatic cancer: A unique subtype. Cancer Lett. 385:46–50. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Esteghamati A, Hafezi-Nejad N, Zandieh A,
Sheikhbahaei S, Emamzadeh-Fard S and Nakhjavani M: CA 19-9 is
associated with poor glycemic control in diabetic patients: Role of
insulin resistance. Clin Lab. 60:441–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kim SH, Baek CO, Lee KA, Park TS, Baek HS
and Jin HY: Clinical implication of elevated CA 19-9 level and the
relationship with glucose control state in patients with type 2
diabetes. Endocrine. 46:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
McWilliams RR and Petersen GM: Overweight,
obesity, and pancreatic cancer: Beyond risk alone. JAMA.
301:2592–2593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bianchini F, Kaaks R and Vainio H:
Overweight, obesity, and cancer risk. Lancet Oncol. 3:565–574.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Calle EE and Kaaks R: Overweight, obesity
and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat
Rev Cancer. 4:579–591. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yuan C, Bao Y, Wu C, Kraft P, Ogino S, Ng
K, Qian ZR, Rubinson DA, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci EL, et al:
Prediagnostic body mass index and pancreatic cancer survival. J
Clin Oncol. 31:4229–4234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K
and Thun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a
prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med.
348:1625–1638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hu FB, Willett WC, Li T, Stampfer MJ,
Colditz GA and Manson JE: Adiposity as compared with physical
activity in predicting mortality among women. N Engl J Med.
351:2694–2703. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gukovsky I, Li N, Todoric J, Gukovskaya A
and Karin M: Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: Common features
in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
Gastroenterology. 144:1199–1209. e11942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, He G, Ali SR,
Holzer RG, Osterreicher CH, Takahashi H and Karin M: Dietary and
genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by
enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell. 140:197–208. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Weindruch R and Walford RL: Dietary
restriction in mice beginning at 1 year of age: Effect on life-span
and spontaneous cancer incidence. Science. 215:1415–1418. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dhahbi JM, Kim HJ, Mote PL, Beaver RJ and
Spindler SR: Temporal linkage between the phenotypic and genomic
responses to caloric restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:5524–5529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kalaany NY and Sabatini DM: Tumours with
PI3K activation are resistant to dietary restriction. Nature.
458:725–731. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lee C, Safdie FM, Raffaghello L, Wei M,
Madia F, Parrella E, Hwang D, Cohen P, Bianchi G and Longo VD:
Reduced levels of IGF-I mediate differential protection of normal
and cancer cells in response to fasting and improve
chemotherapeutic index. Cancer Res. 70:1564–1572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Raffaghello L, Lee C, Safdie FM, Wei M,
Madia F, Bianchi G and Longo VD: Starvation-dependent differential
stress resistance protects normal but not cancer cells against
high-dose chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:8215–8220.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sheen JH, Zoncu R, Kim D and Sabatini DM:
Defective regulation of autophagy upon leucine deprivation reveals
a targetable liability of human melanoma cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cancer Cell. 19:613–628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS,
Kita K, Ochi T, Zeller KI, De Marzo AM, Van Eyk JE, Mendell JT, et
al: c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial
glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature.
458:762–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Son J, Lyssiotis CA, Ying H, Wang X, Hua
S, Ligorio M, Perera RM, Ferrone CR, Mullarky E, Shyh-Chang N, et
al: Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a
KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature. 496:101–105. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Maddocks OD, Berkers CR, Mason SM, Zheng
L, Blyth K, Gottlieb E and Vousden KH: Serine starvation induces
stress and p53-dependent metabolic remodelling in cancer cells.
Nature. 493:542–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Knott SRV, Wagenblast E, Khan S, Kim SY,
Soto M, Wagner M, Turgeon MO, Fish L, Erard N, Gable AL, et al:
Asparagine bioavailability governs metastasis in a model of breast
cancer. Nature. 554:378–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jain M, Nilsson R, Sharma S, Madhusudhan
N, Kitami T, Souza AL, Kafri R, Kirschner MW, Clish CB and Mootha
VK: Metabolite profiling identifies a key role for glycine in rapid
cancer cell proliferation. Science. 336:1040–1044. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gladden LB: Lactate metabolism: A new
paradigm for the third millennium. J Physiol. 558:5–30. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Feron O: Pyruvate into lactate and back:
From the Warburg effect to symbiotic energy fuel exchange in cancer
cells. Radiother Oncol. 92:329–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sonveaux P, Végran F, Schroeder T, Wergin
MC, Verrax J, Rabbani ZN, De Saedeleer CJ, Kennedy KM, Diepart C,
Jordan BF, et al: Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively
kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3930–3942.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lisanti MP and
Sotgia F: Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy
and biomass to anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth. Semin
Cancer Biol. 25:47–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Goodwin ML, Jin H, Straessler K, Smith-Fry
K, Zhu JF, Monument MJ, Grossmann A, Randall RL, Capecchi MR and
Jones KB: Modeling alveolar soft part sarcomagenesis in the mouse:
A role for lactate in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell.
26:851–862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Doherty JR and Cleveland JL: Targeting
lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J Clin Invest.
123:3685–3692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shime H, Yabu M, Akazawa T, Kodama K,
Matsumoto M, Seya T and Inoue N: Tumor-secreted lactic acid
promotes IL-23/ IL-17 proinflammatory pathway. J Immunol.
180:7175–7183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ryan DP, Hong TS and Bardeesy N:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:1039–1049. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zong WX and Thompson CB: Necrotic death as
a cell fate. Genes Dev. 20:1–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow. Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Vakkila J and Lotze MT: Inflammation and
necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:641–648. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Vanharanta S and Massagué J: Origins of
metastatic traits. Cancer Cell. 24:410–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Oskarsson T, Batlle E and Massagué J:
Metastatic stem cells: Sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell
Stem Cell. 14:306–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Peinado H, Zhang H, Matei IR, Costa-Silva
B, Hoshino A, Rodrigues G, Psaila B, Kaplan RN, Bromberg JF, Kang
Y, et al: Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for
metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:302–317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O’Connor ST, Li S, Chin AR, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
88
|
Pascual G, Domínguez D and Benitah SA: The
contributions of cancer cell metabolism to metastasis. Dis Model
Mech. 11:112018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Dupuy F, Tabariès S, Andrzejewski S, Dong
Z, Blagih J, Annis MG, Omeroglu A, Gao D, Leung S, Amir E, et al:
PDK1-dependent metabolic reprogramming dictates metastatic
potential in breast cancer. Cell Metab. 22:577–589. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I,
Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, Jatoi A, Loprinzi C, MacDonald N,
Mantovani G, et al: Definition and classification of cancer
cachexia: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 12:489–495.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Baracos VE, Martin L, Korc M, Guttridge DC
and Fearon KC: Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
4:171052018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Argilés JM, Busquets S, Stemmler B and
López-Soriano FJ: Cancer cachexia: Understanding the molecular
basis. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:754–762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Fearon KC, Glass DJ and Guttridge DC:
Cancer cachexia: Mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell
Metab. 16:153–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
McMillan DC: Systemic inflammation,
nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr Opin
Clin Nutr Metab Care. 12:223–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Hotchkiss RS, Strasser A, McDunn JE and
Swanson PE: Cell death. N Engl J Med. 361:1570–1583. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kroemer G and Jäättelä M: Lysosomes and
autophagy in cell death control. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:886–897. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, Metabolism, and Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
McQuade Li J, Siemer T, Napetschnig AB,
Moriwaki J, Hsiao K, Damko YS, Moquin E, Walz D, McDermott TA, et
al: The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling
complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 150:339–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Majno G and Joris I: Apoptosis, oncosis,
and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am J Pathol. 146:3–15.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray
K, Anderson D, Chen G, Mukherjee C, Shi Y, Gélinas C, Fan Y, et al:
Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis,
inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 10:51–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Edwards JG, Swinson DE, Jones JL, Muller
S, Waller DA and O’Byrne KJ: Tumor necrosis correlates with
angiogenesis and is a predictor of poor prognosis in malignant
mesothelioma. Chest. 124:1916–1923. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Lee SE, Byun SS, Oh JK, Lee SC, Chang IH,
Choe G and Hong SK: Significance of macroscopic tumor necrosis as a
prognostic indicator for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
176:1332–1337; discussion 1337-1338. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Tomes L, Emberley E, Niu Y, Troup S,
Pastorek J, Strange K, Harris A and Watson PH: Necrosis and hypoxia
in invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 81:61–69.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Richards CH, Mohammed Z, Qayyum T, Horgan
PG and McMillan DC: The prognostic value of histological tumor
necrosis in solid organ malignant disease: A systematic review.
Future Oncol. 7:1223–1235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Lotze MT and Tracey KJ: High-mobility
group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:331–342. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P and Krysko DV:
Necroptosis: The release of damage-associated molecular patterns
and its physiological relevance. Immunity. 38:209–223. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Fu B, Yachida S, Luo
M, Abe H, Henderson CM, Vilardell F, Wang Z, Keller JW, Banerjee P,
et al: DPC4 gene status of the primary carcinoma correlates with
patterns of failure in patients with pancreatic cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 27:1806–1813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Nakahashi C, Oda T, Kinoshita T, Ueda T,
Konishi M, Nakagohri T, Inoue K, Furuse J, Ochiai A and Ohkohchi N:
The impact of liver metastasis on mortality in patients initially
diagnosed with locally advanced or resectable pancreatic cancer.
Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 33:155–164. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS,
Horgan PG, McMillan DC and Clarke SJ: The systemic
inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in
patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:218–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Dvorak HF: Tumors: Wounds that do not
heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound
healing. N Engl J Med. 315:1650–1659. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, Horie T
and Kubota K: Inflammation-based prognostic score is a novel
predictor of postoperative outcome in patients with colorectal
cancer. Ann Surg. 246:1047–1051. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Luo G, Guo M, Liu Z, Xiao Z, Jin K, Long
J, Liu L, Liu C, Xu J, Ni Q, et al: Blood neutrophil-lymphocyte
ratio predicts survival in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer
treated with chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:670–676. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Ambrus JL, Ambrus CM, Mink IB and Pickren
JW: Causes of death in cancer patients. J Med. 6:61–64.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Marshall S, Bacote V and Traxinger RR:
Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced
desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine
biosyn-thesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem.
266:4706–4712. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Hart GW and Copeland RJ: Glycomics hits
the big time. Cell. 143:672–676. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wang J, Liu R, Hawkins M, Barzilai N and
Rossetti L: A nutrient-sensing pathway regulates leptin gene
expression in muscle and fat. Nature. 393:684–688. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Bond MR and Hanover JA: O-GlcNAc cycling:
A link between metabolism and chronic disease. Annu Rev Nutr.
33:205–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fuster MM and Esko JD: The sweet and sour
of cancer: Glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:526–542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Chiaradonna F, Ricciardiello F and
Palorini R: The nutrient-sensing hexosamine biosynthetic pathway as
the hub of cancer metabolic rewiring. Cells. 7:72018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Bullen JW, Balsbaugh JL, Chanda D,
Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Neumann D and Hart GW: Cross-talk between
two essential nutrient-sensitive enzymes: O-GlcNAc transferase
(OGT) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). J Biol Chem.
289:10592–10606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Pascual G, Avgustinova A, Mejetta S,
Martín M, Castellanos A, Attolini CS, Berenguer A, Prats N, Toll A,
Hueto JA, et al: Targeting metastasis-initiating cells through the
fatty acid receptor CD36. Nature. 541:41–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Shin YK, Park JS, Kim HS, Jun HJ, Kim GE,
Suh CO, Yun YS and Pyo H: Radiosensitivity enhancement by
celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 selective inhibitor, via
COX-2-dependent cell cycle regulation on human cancer cells
expressing differential COX-2 levels. Cancer Res. 65:9501–9509.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA and
Pardoll DM: Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint
blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:275–287. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|