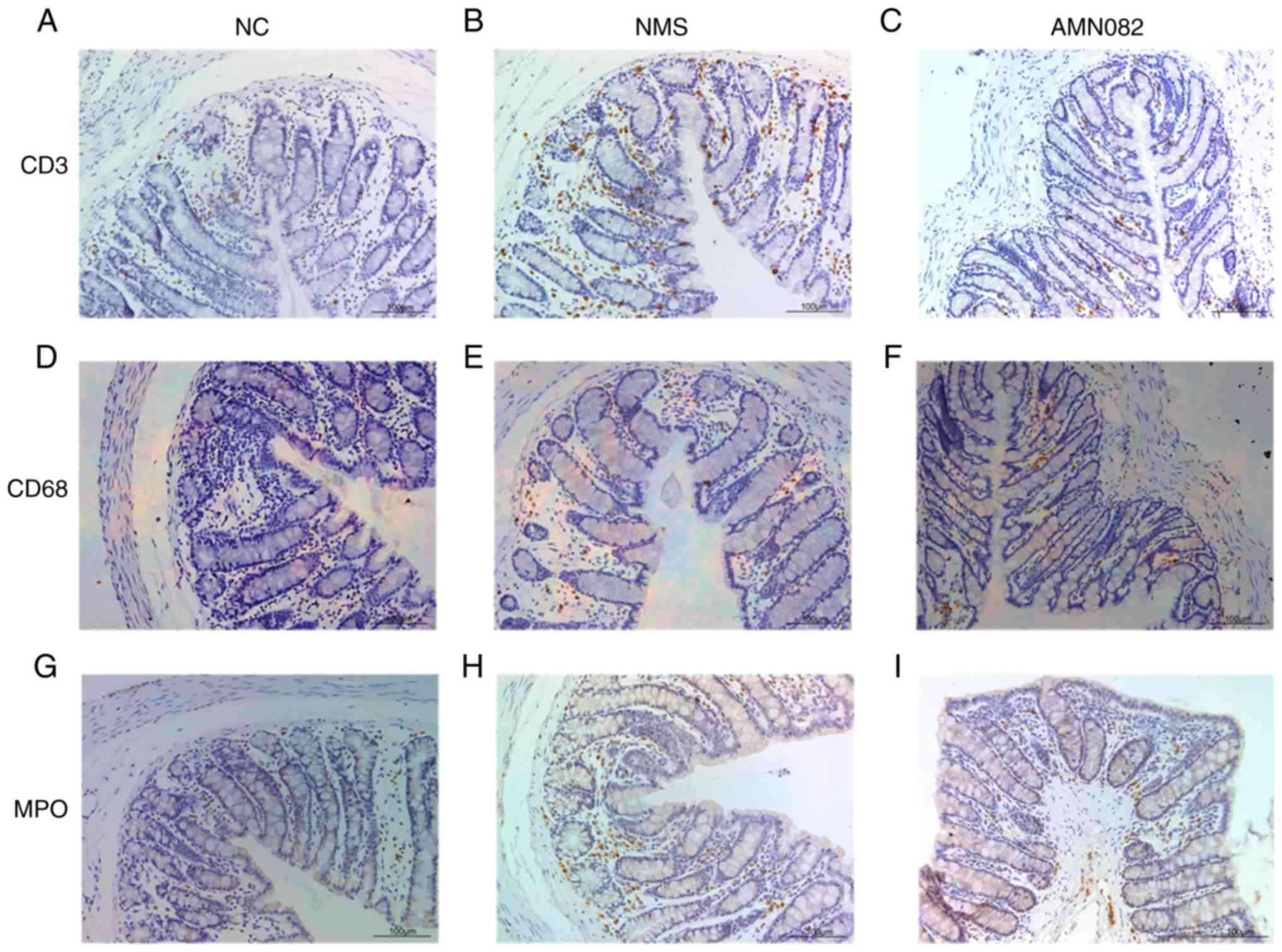
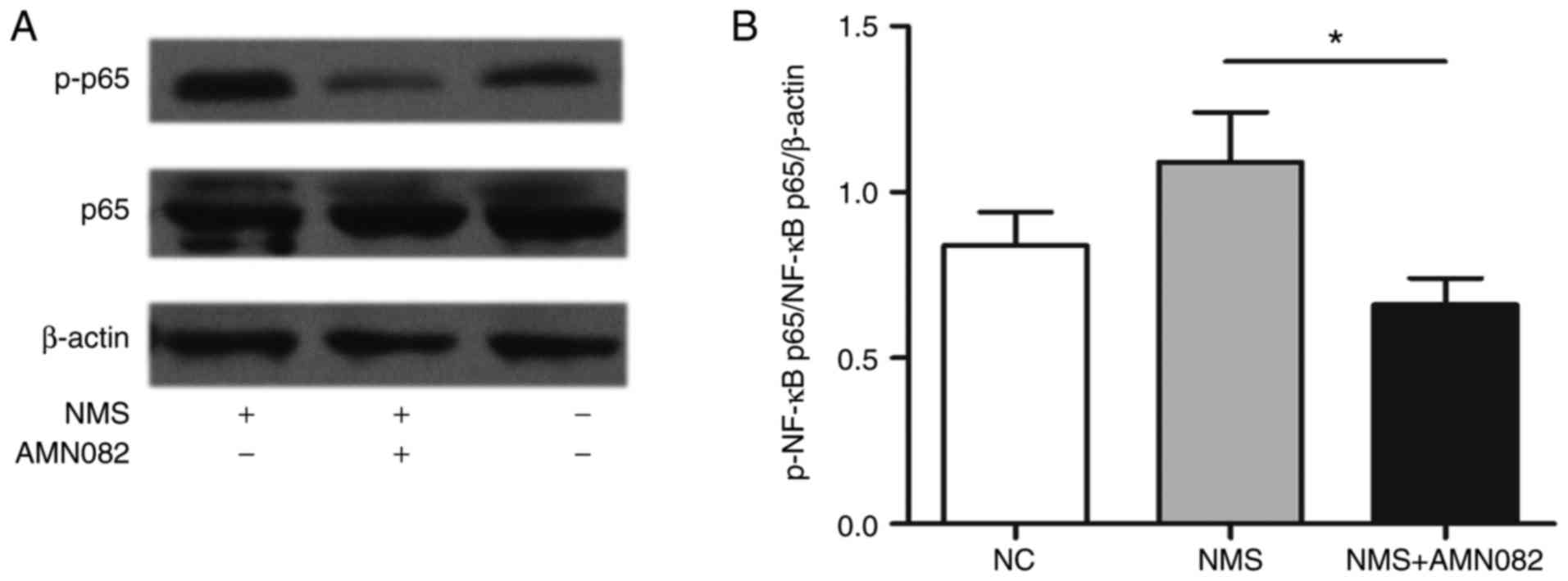
|
1
|
Zhao K, Yu L, Wang X, He Y and Lu B:
Clostridium butyricum regulates visceral hypersensitivity of
irritable bowel syndrome by inhibiting colonic mucous low grade
inflammation through its action on NLRP6. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 50:216–223. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rodiño-Janeiro BK, Vicario M,
Alonso-Cotoner C, Pascua- García R and Santos J: A review of
microbiota and irritable bowel syndrome: Future in therapies. Adv
Ther. 35:289–310. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tjong YW, Ip SP, Lao L, Wu J, Fong HH,
Sung JJ, Berman B and Che CT: Role of neuronal nitric oxide
synthase in colonic distension-induced hyperalgesia in distal colon
of neonatal maternal separated male rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
23:e666-e2782011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Coutinho SV, Plotsky PM, Sablad M, Miller
JC, Zhou H, Bayati AI, McRoberts JA and Mayer EA: Neonatal maternal
separation alters stress-induced responses to viscerosomatic
nociceptive stimuli in rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 282:G307–G316. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fernández-Montoya J, Avendaño C and
Negredo P: The glutamatergic system in primary somatosensory
neurons and its involvement in sensory input-dependent plasticity.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:E692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Julio-Pieper M, Hyland NP, Bravo JA, Dinan
TG and Cryan JF: A novel role for the metabotropic glutamate
receptor-7: Modulation of faecal water content and colonic
electrolyte transport in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 160:367–375.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Golubeva AV, Moloney RD, O'Connor RM,
Dinan TG and Cryan JF: Metabotropic glutamate receptors in central
nervous system diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 17:538–616. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Julio-Pieper M, O'Connor RM, Dinan TG and
Cryan JF: Regulation of the brain-gut axis by group III
metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 698:19–30. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kłak K, Pałucha A, Brański P, Sowa M and
Pilc A: Combined administration of PHCCC, a positive allosteric
modulator of mGlu4 receptors and ACPT-I, mGlu III receptor agonist
evokes antidepressant-like effects in rats. Amino Acids.
32:169–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Stachowicz K, Brañski P, Kłak K, van der
Putten H, Cryan JF, Flor PJ and Andrzej P: Selective activation of
metabotropic G-protein-coupled glutamate 7 receptor elicits
anxiolytic-like effects in mice by modulating GABAergic
neurotransmission. Behav Pharmacol. 19:597–603. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M and Pasricha PJ: A
new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats
induced by colon irritation during postnatal development.
Gastroenterology. 119:1276–1285. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palucha A, Klak K, Branski P, van der
Putten H, Flor PJ and Pilc A: Activation of the mGlu7 receptor
elicits antidepressant-like effects in mice. Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 194:555–562. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shah E, Rezaie A, Riddle M and Pimentel M:
Psychological disorders in gastrointestinal disease: Epiphenomenon,
cause or consequence. Ann Gastroenterol. 27:224–230. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Gros DF, Antony MM, McCabe RE and Swinson
RP: Frequency and severity of the symptoms of irritable bowel
syndrome across the anxiety disorders and depression. J Anxiety
Disord. 23:290–296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yan C, Xin-Guang L, Hua-Hong W, Jun-Xia L
and Yi-Xuan L: Effect of the 5HT4 receptor and serotonin
transporter on visceral hypersensitivity in rats. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 45:948–954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hoffman JM, Tyler K, MacEachern SJ,
Balemba OB, Johnson AC, Brooks EM, Zhao H, Swain GM, Moses PL,
Galligan JJ, et al: Activation of colonic mucosal 5-HT(4) receptors
accelerates propulsive motility and inhibits visceral
hypersensitivity. Gastroenterology. 142:844–854. e8442012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paragomi P, Rahimian R, Kazemi MH,
Gharedaghi MH, Khalifeh-Soltani A, Azary S, Javidan AN, Moradi K,
Sakuma S and Dehpour AR: Antinociceptive and antidiarrheal effects
of pioglitazone in a rat model of diarrhoea-predominant irritable
bowel syndrome: Role of nitric oxide. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
41:118–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J: Correlation between
anxiety-depression status and cytokines in diarrhea-predominant
irritable bowel syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 6:93–96. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 1996
|
|
21
|
van den Wijngaard RM, Stanisor OI, van
Diest SA, Welting O, Wouters MM, Cailotto C, de Jonge WJ and
Boeckxstaens GE: Susceptibility to stress induced visceral
hypersensitivity in maternally separated rats is transferred across
generations. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:e780-e7902013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li L, Xie R, Hu S, Wang Y, Yu T, Xiao Y,
Jiang X, Gu J, Hu CY and Xu GY: Upregulation of cystathionine
beta-synthetase expression by nuclear factor-kappa B activation
contributes to visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats with
neonatal maternal deprivation. Mol Pain. 8:892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsumoto K, Takagi K, Kato A, Ishibashi
T, Mori Y, Tashima K, Mitsumoto A, Kato S and Horie S: Role of
transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) channels in
visceral nociception and hypersensitivity. Exp Neurol. 285:41–50.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van den Wijngaard RM, Stanisor OI, van
Diest SA, Welting O, Wouters MM, de Jonge WJ and Boeckxstaens GE:
Peripheral α-helical CRF (9-41) does not reverse stress-induced
mast cell dependent visceral hypersensitivity in maternally
separated rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 24:274–282. e1112012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li X, Xi ZX and Markou A: Metabotropic
glutamate 7 (mGlu7) receptor: A target for medication development
for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Neuropharmacology.
66:12–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xiao J, Shao L, Shen J, Jiang W, Feng Y,
Zheng P and Liu F: Effects of ketanserin on experimental colitis in
mice and macrophage function. Int J Mol Med. 37:659–668. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao J, Lu Z, Sheng J, Song Y, Jiang W,
Liu F and Zheng P: 5-fluorouracil attenuates dextran sodium
sulfate-induced acute colitis in mice. Mol Med Rep. 13:2821–2828.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karrasch T and Jobin C: NF-kappaB and the
intestine: Friend or foe. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14:114–124. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wouters MM: Histamine antagonism and
postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity. Gut. 63:1836–1837.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hornby PJ: Receptors and transmission in
the brain-gut axis. II. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the
brain-gut axis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
280:G1055–G1060. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang HJ, Yoo BC, Lim SB, Jeong SY, Kim WH
and Park JG: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 expression in
colorectal carcinoma and its prognostic significance. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:3288–3295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tong Q and Kirchgessner AL: Localization
and function of metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 in the enteric
nervous system. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
285:G992–G1003. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Gao J and Wei L: Changes of
expressions of NR2A and NR2B in anterior cingulate cortex of
post-inflammatory visceral hypersensitive rats. Chin J
Gastroenteml. 15:330–334. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
35
|
Pałucha-Poniewiera A, Szewczyk B and Pilc
A: Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in the
antidepressant-like activity of the mGlu5 antagonist MTEP and the
mGlu7 agonist AMN082 in the FST in rats. Neuropharmacology.
82:59–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang WY, Wang H, Luo Y, Jia LJ, Zhao JN,
Zhang HH, Ma ZW, Xue QS and Yu BW: The effects of metabotropic
glutamate receptor 7 allosteric agonist N,
N'-dibenzhydrylethane-1,2- diamine dihydrochloride on developmental
sevoflurane neurotoxicity: Role of extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1 and 2 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Neuroscience. 205:167–177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ohman L and Simrén M: Pathogenesis of IBS:
Role of inflammation, immunity and neuroimmune interactions. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:163–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li YQ, Zhang HN, Zuo XL, Yuan HP, Lu XF
and Li MJ: Study on the shifting of Thl/Th2 balance of large
intestinal mueosa in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Chin J
of Dig. 24:728–731. 2004.In Chinese.
|
|
39
|
Kühn R, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K
and Müller W: Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic
enterocolitis. Cell. 75:263–274. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
O'Malley D, Liston M, Hyland NP, Dinan TG
and Cryan JF: Colonic soluble mediators from the maternal
separation model of irritable bowel syndrome activate submucosal
neurons via an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300:G241–G252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen ZY, Zhang XW, Yu L, Hua R, Zhao XP,
Qin X and Zhang YM: Spinal toll-like receptor 4-mediated signalling
pathway contributes to visceral hypersensitivity induced by
neonatal colonic irritation in rats. Eur J Pain. 19:176–186. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Rodella L, Rezzani R, Agostini C and
Bianchi R: Induction of NADPH-diaphorase activity in the rat
periaqueductal gray matter after nociceptive visceral stimulation.
Brain Res. 793:333–336. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
de Waal Malefyt R, Haanen J, Spits H,
Roncarolo MG, te Velde A, Figdor C, Johnson K, Kastelein R, Yssel H
and de Vries JE: Interleukin 10 (IL-10) and viral IL-10 strongly
reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing
the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of
class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med.
174:915–924. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Akiho H, Deng Y, Blennerhassett P,
Kanbayashi H and Collins SM: Mechanisms underlying the maintenance
of muscle hypercontractility in a model of postinfective gut
dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 129:131–141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|