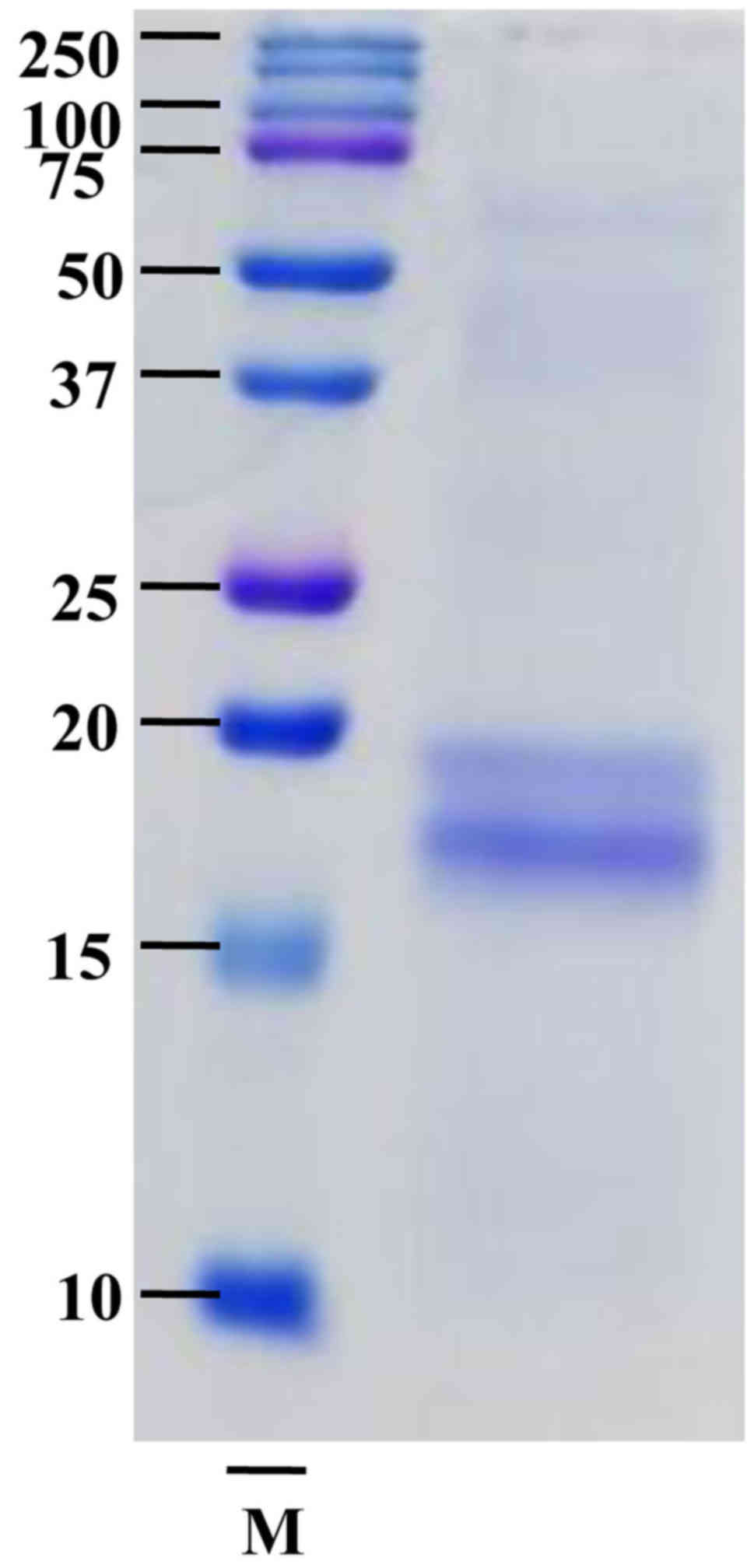
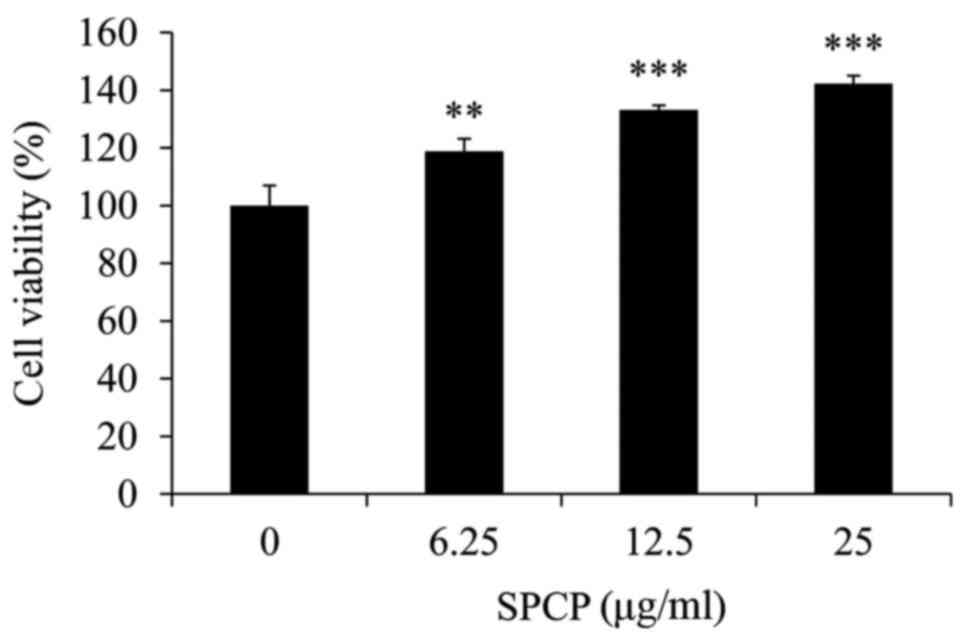
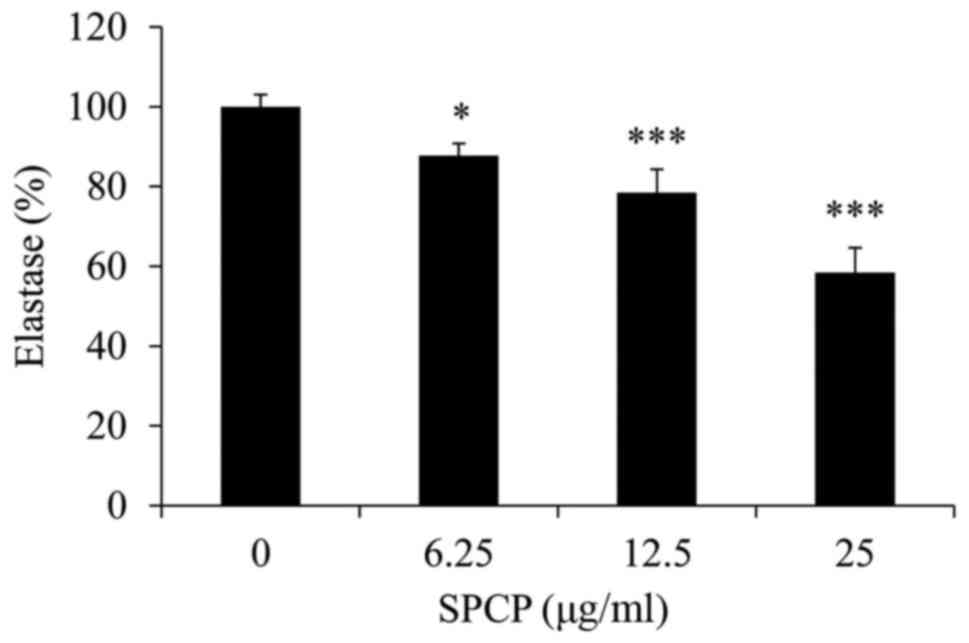
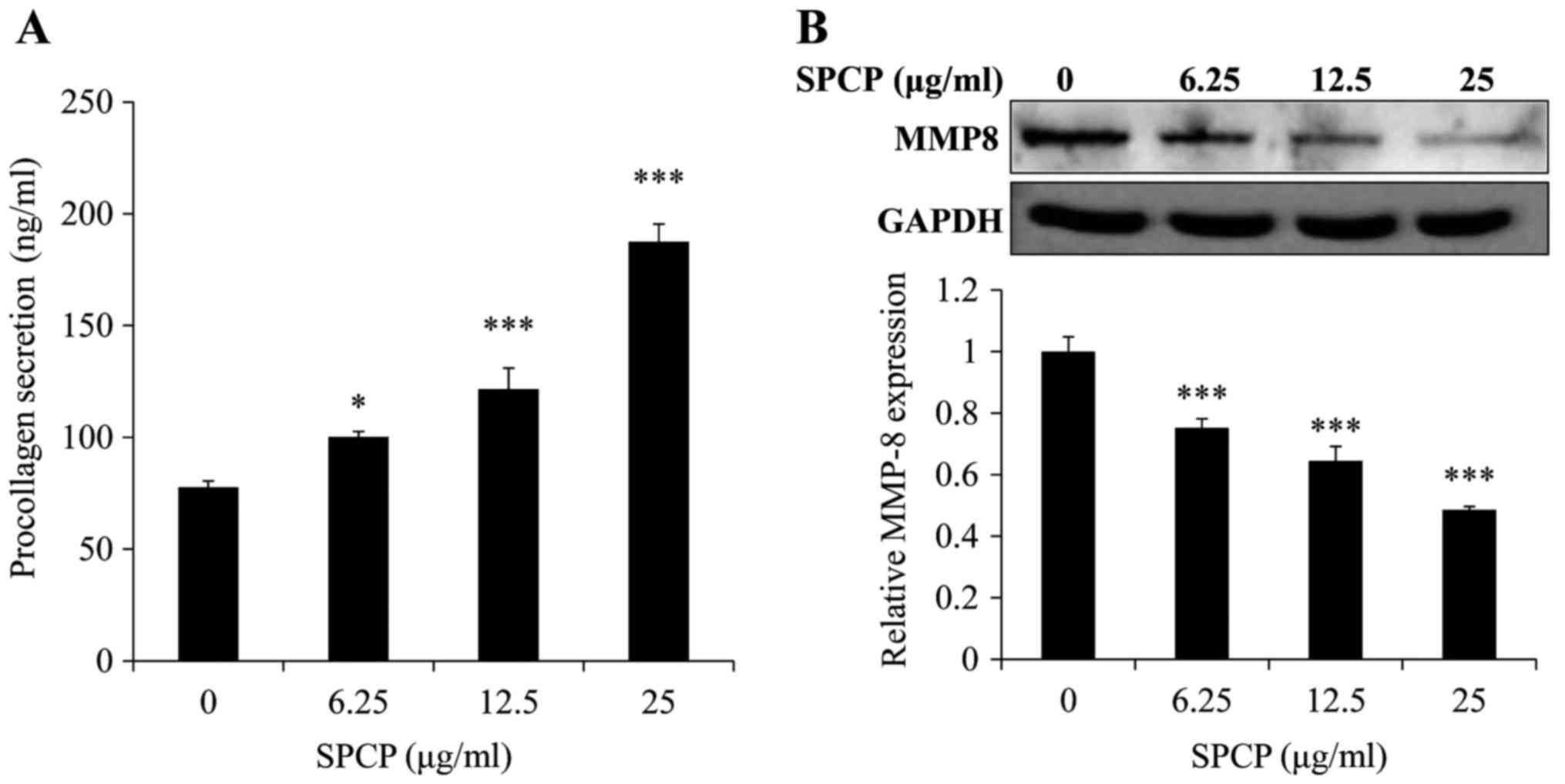
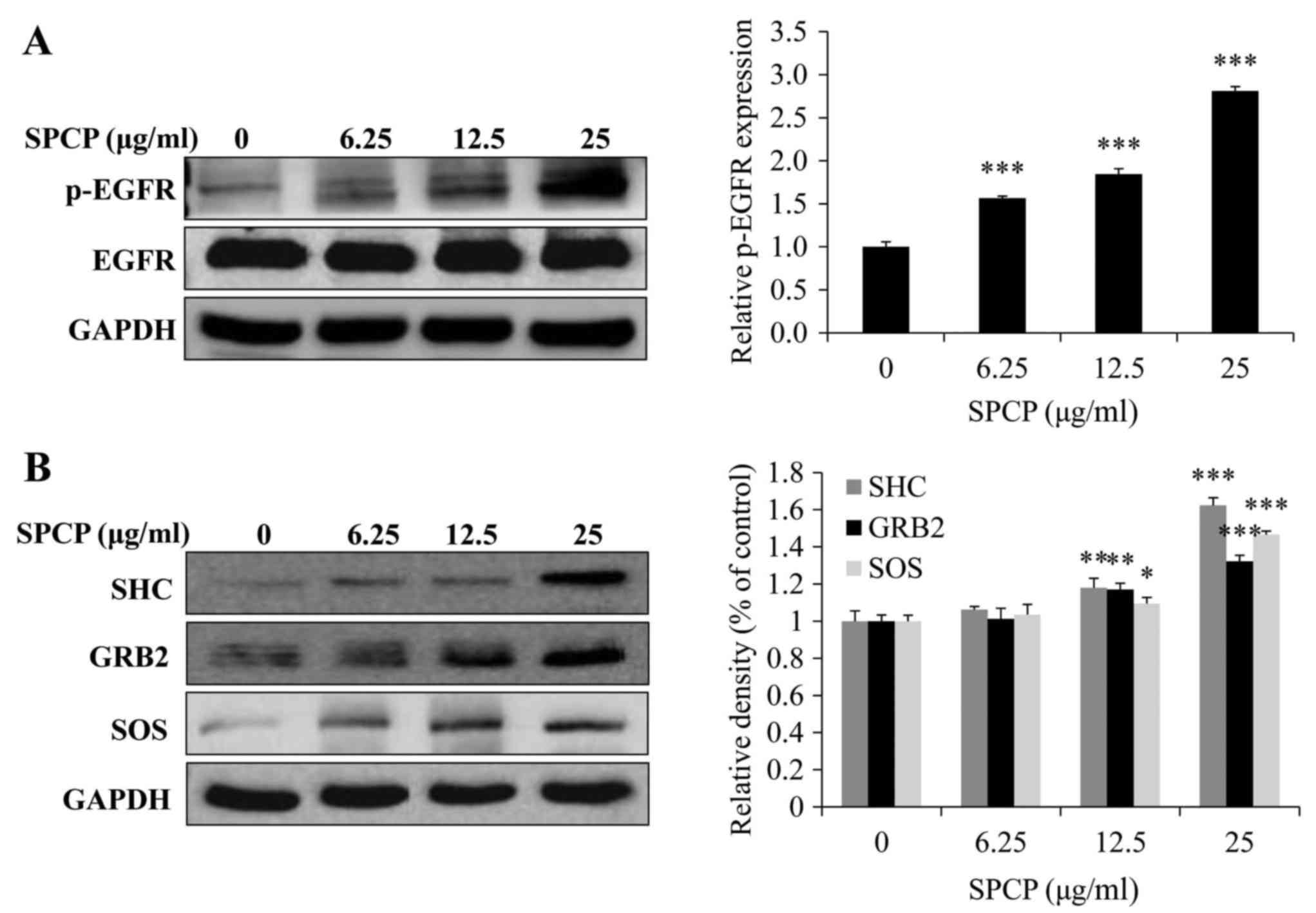
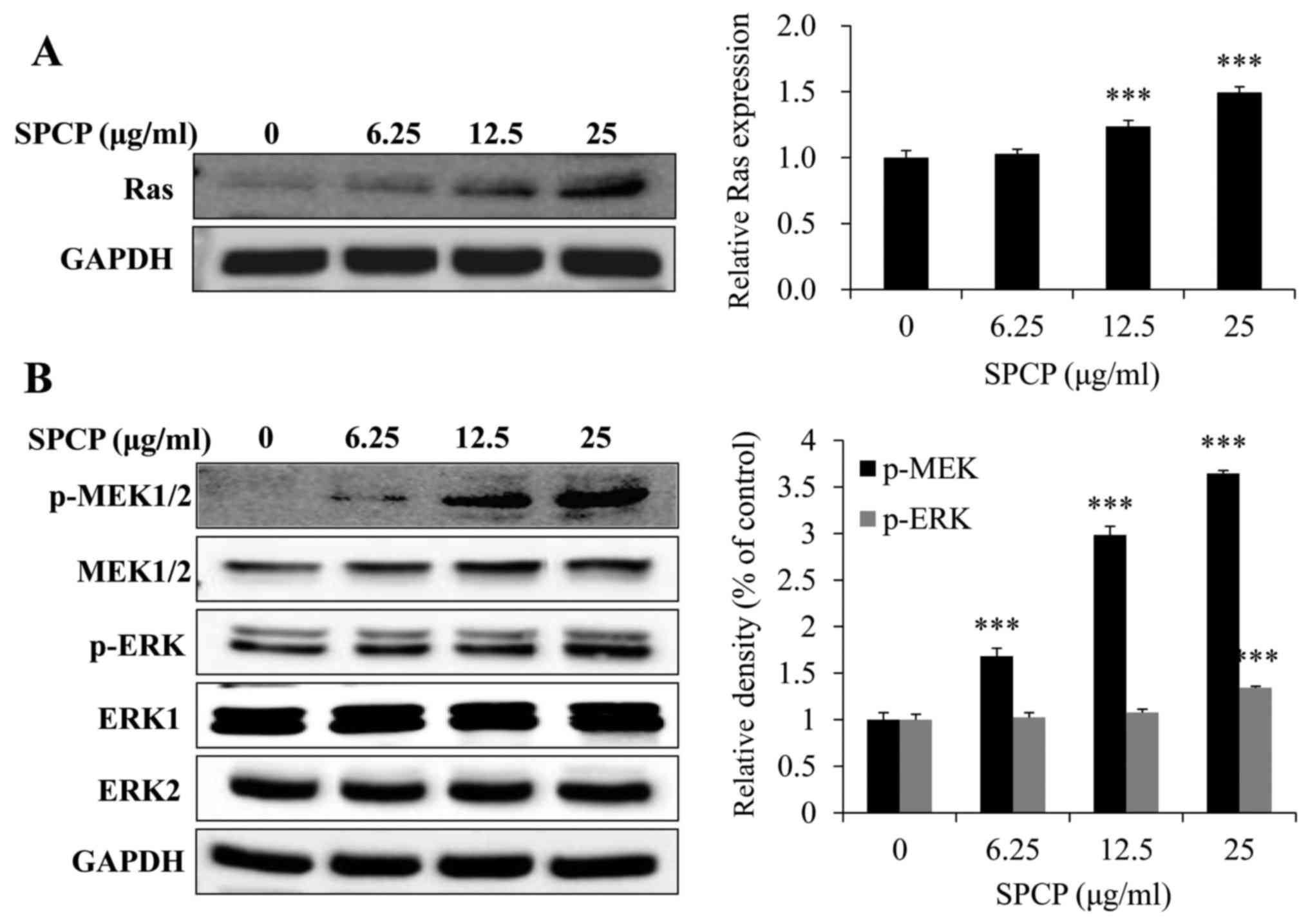
|
1
|
Wu X, Li R, Zhao Y and Liu Y: Separation
of polysaccharides from Spirulina platensis by HSCCC with
ethanol-ammonium sulfate ATPS and their antioxidant activities.
Carbohydr Polym. 173:465–472. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vo TS, Ngo DH, Kang KH, Park SJ and Kim
SK: The role of peptides derived from Spirulina maxima in
downregulation of FcεRI-mediated allergic responses. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 58:2226–2234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang B, Cai T, Liu Q, Whitney JCC, Du M,
Ma Q, Zhang R, Yang L, Cole SPC and Cai Y: Preparation and
evaluation of spirulina polysaccharide nanoemulsions. Int J Mol
Med. 42:1273–1282. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yogianti F, Kunisada M, Nakano E, Ono R,
Sakumi K, Oka S, Nakabeppu Y and Nishigori C: Inhibitory effects of
dietary Spirulina platensis on UVB-induced skin inflammatory
responses and carcinogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 134:2610–2619.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu Q, Liu L, Miron A, Klímová B, Wan D and
Kuča K: The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory
activities of Spirulina: An overview. Arch Toxicol. 90:1817–1840.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nawrocka D, Kornicka K, Śmieszek A and
Marycz K: Spirulina platensis improves mitochondrial function
impaired by elevated oxidative stress in adipose-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells (ASCs) and intestinal epithelial cells
(IECs), and enhances insulin sensitivity in equine metabolic
syndrome (EMS) horses. Mar Drugs. 15:2372017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vázquez-Velasco M, González-Torres L,
López-Gasco P, Bastida S, Benedí J, Sánchez-Reus MI, González-Muñoz
MJ and Sánchez-Muniz FJ: Liver oxidation and inflammation in Fa/Fa
rats fed glucomannan/spirulina-surimi. Food Chem. 159:215–221.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Al-Dhabi NA and Valan Arasu M:
Quantification of phyto-chemicals from commercial Spirulina
products and their antioxidant activities. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2016:1–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E and
Isambert A: Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng.
101:87–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SK, Ravichandran YD, Khan SB and Kim
YT: Prospective of the cosmeceuticals derived from marine
organisms. Biotechnol Bioproc E. 13:511–523. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xiong ZM, O'Donovan M, Sun L, Choi JY, Ren
M and Cao K: Anti-aging potentials of methylene blue for human skin
longevity. Sci Rep. 7:24752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoseini SM, Kalantari A, Afarideh M,
Noshad S, Behdadnia A, Nakhjavani M and Esteghamati A: Evaluation
of plasma MMP-8, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 identifies candidate
cardiometabolic risk marker in metabolic syndrome: Results from
double-blinded nested case-control study. Metabolism. 64:527–538.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tundis R, Loizzo MR, Bonesi M and
Menichini F: Potential role of natural compounds against skin
aging. Curr Med Chem. 22:1515–1538. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pham QL, Jang HJ and Kim KB: Anti-wrinkle
effect of fermented black ginseng on human fibroblasts. Int J Mol
Med. 39:681–686. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Na J, Bak DH, Im SI, Choi H, Hwang JH,
Kong SY, No YA, Lee Y and Kim BJ: Anti-apoptotic effects of
glycosaminoglycans via inhibition of ERK/AP-1 signaling in
TNF-α-stimulated human dermal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med.
41:3090–3098. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meinke MC, Nowbary CK, Schanzer S, Vollert
H, Lademann J and Darvin ME: Influences of orally taken
carotenoid-rich curly kale extract on collagen I/elastin index of
the skin. Nutrients. 9:7752017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Rittié L and Fisher GJ: UV-light-induced
signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res Rev. 1:705–720. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jadoon S, Karim S, Bin Asad MH, Akram MR,
Khan AK, Malik A, Chen C and Murtaza G: Anti-aging potential of
phytoextract loaded-pharmaceutical creams for human skin cell
longevity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:7096282015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Herman MP, Sukhova GK, Libby P, Gerdes N,
Tang N, Horton DB, Kilbride M, Breitbart RE, Chun M and Schönbeck
U: Expression of neutrophil collagenase (matrix
metalloproteinase-8) in human atheroma: A novel collagenolytic
pathway suggested by transcriptional profiling. Circulation.
104:1899–1904. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burke KE: Mechanisms of aging and
development-A new understanding of environmental damage to the skin
and prevention with topical antioxidants. Mech Ageing Dev.
172:123–130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shiraha H, Gupta K, Drabik K and Wells A:
Aging fibroblasts present reduced epidermal growth factor (EGF)
responsiveness due to preferential loss of EGF receptors. J Biol
Chem. 275:19343–19351. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Li Y, Zhu Q, Li T, Lu H, Wei N,
Huang Y, Shi R, Ma X, Wang X, et al: Anti-skin-aging effect of
epigallocatechin gallate by regulating epidermal growth factor
receptor pathway on aging mouse model induced by d-Galactose. Mech
Ageing Dev. 164:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao M, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY, Zhang
JH, Wang XH, Ge ZQ and Yang XM: Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK
cascade and induces proliferation of L02 cells through the
Src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal. 26:2161–2166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gerber PA, Buhren BA, Schrumpf H, Hevezi
P, Bölke E, Sohn D, Jänicke RU, Belum VR, Robert C, Lacouture ME,
et al: Mechanisms of skin aging induced by EGFR inhibitors. Support
Care Cancer. 24:4241–4248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Green MR, Basketter DA, Couchman JR and
Rees DA: Distribution and number of epidermal growth factor
receptors in skin is related to epithelial cell growth. Dev Biol.
100:506–512. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tran KT, Rusu SD, Satish L and Wells A:
Aging-related attenuation of EGF receptor signaling is mediated in
part by increased protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Exp Cell
Res. 289:359–367. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Z, Liu S and Cai Y: EGFR/MAPK signaling
regulates the proliferation of Drosophila renal and nephric stem
cells. J Genet Genomics. 42:9–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shin S, Son D, Kim M, Lee S, Roh KB, Ryu
D, Lee J, Jung E and Park D: Ameliorating effect of akebia quinata
fruit extracts on skin aging induced by advanced glycation end
products. Nutrients. 7:9337–9352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ryu J, Kwon MJ and Nam TJ: Nrf2 and NF-κB
signaling pathways contribute to porphyra-334-mediated inhibition
of UVA-induced inflammation in skin fibroblasts. Mar Drugs.
13:4721–4732. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barnes D and Sato G: Methods for growth of
cultured cells in serum-free medium. Anal Biochem. 102:255–270.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim YM, Jung HJ, Choi JS and Nam TJ:
Anti-wrinkle effects of a tuna heart H2O fraction on
Hs27 human fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 37:92–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Magadum A, Ding Y, He L, Kim T,
Vasudevarao MD, Long Q, Yang K, Wickramasinghe N, Renikunta HV,
Dubois N, et al: Live cell screening platform identifies PPARδ as a
regulator of cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair. Cell
Res. 27:1002–1019. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee J, Park A, Kim MJ, Lim HJ, Rha YA and
Kang HG: Spirulina extract enhanced a protective effect in type 1
diabetes by anti-apoptosis and anti-ROS production. Nutrients.
9:13632017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lu J, Ren DF, Wang JZ, Sanada H and
Egashira Y: Protection by dietary Spirulina platensis against
D-galactosamine--and acetaminophen-induced liver injuries. Br J
Nutr. 103:1573–1576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kepekçi RA, Polat S, Çelik A, Bayat N and
Saygideger SD: Protective effect of Spirulina platensis enriched in
phenolic compounds against hepatotoxicity induced by CCl4. Food
Chem. 141:1972–1979. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Romay Ch, González R, Ledón N, Remirez D
and Rimbau V: C-phycocyanin: A biliprotein with antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Curr Protein Pept
Sci. 4:207–216. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim MS, Song HJ, Lee SH and Lee CK:
Comparative study of various growth factors and cytokines on type I
collagen and hyaluronan production in human dermal fibroblasts. J
Cosmet Dermatol. 13:44–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tanaka M, Koyama Y and Nomura Y: Effects
of collagen peptide ingestion on UV-B-induced skin damage. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 73:930–932. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim MK, Bang CY, Yun GJ, Kim HY, Jang YP
and Choung SY: Anti-wrinkle effects of Seungma-Galgeun-Tang as
evidenced by the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-I
production and the promotion of type-1 procollagen synthesis. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 16:1162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang CY, Li XH, Zhang T, Fu J and Cui XD:
Hydrogen sulfide suppresses the expression of MMP-8, MMP-13, and
TIMP-1 in left ventricles of rats with cardiac volume overload.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:1301–1309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Corcoran RB, Ebi H, Turke AB, Coffee EM,
Nishino M, Cogdill AP, Brown RD, Della Pelle P, Dias-Santagata D,
Hung KE, et al: EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling
contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to
RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discov. 2:227–235. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|