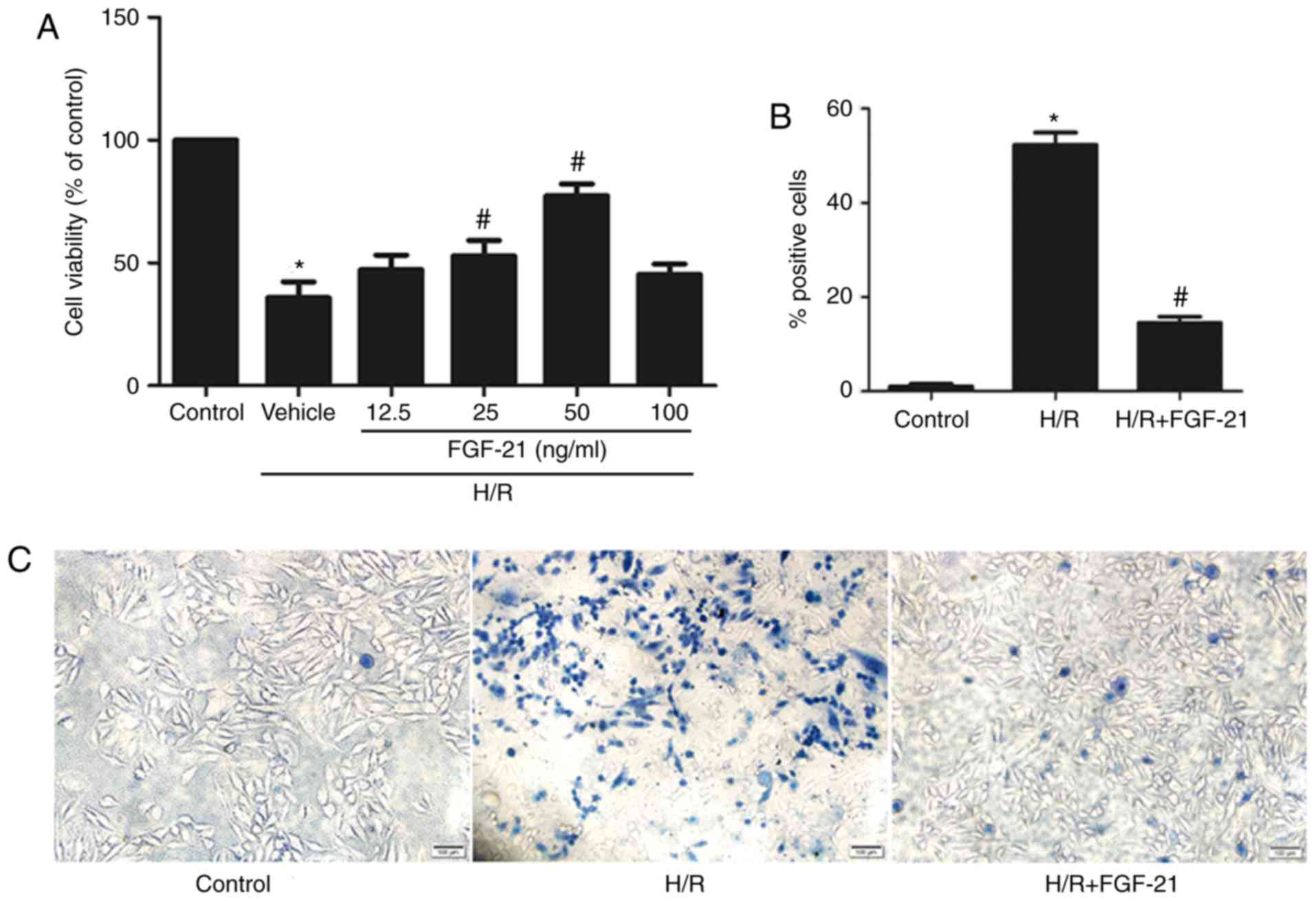
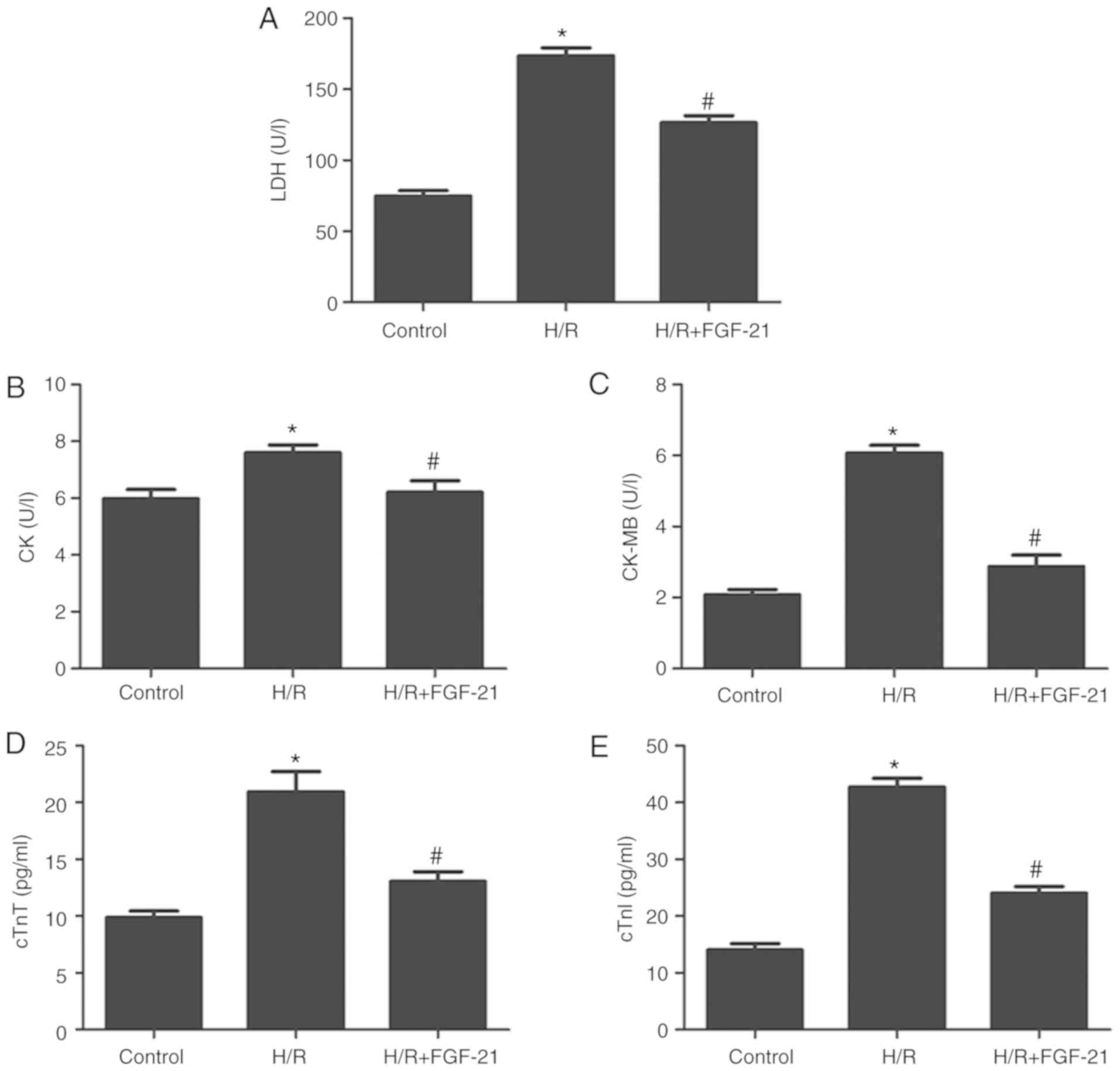
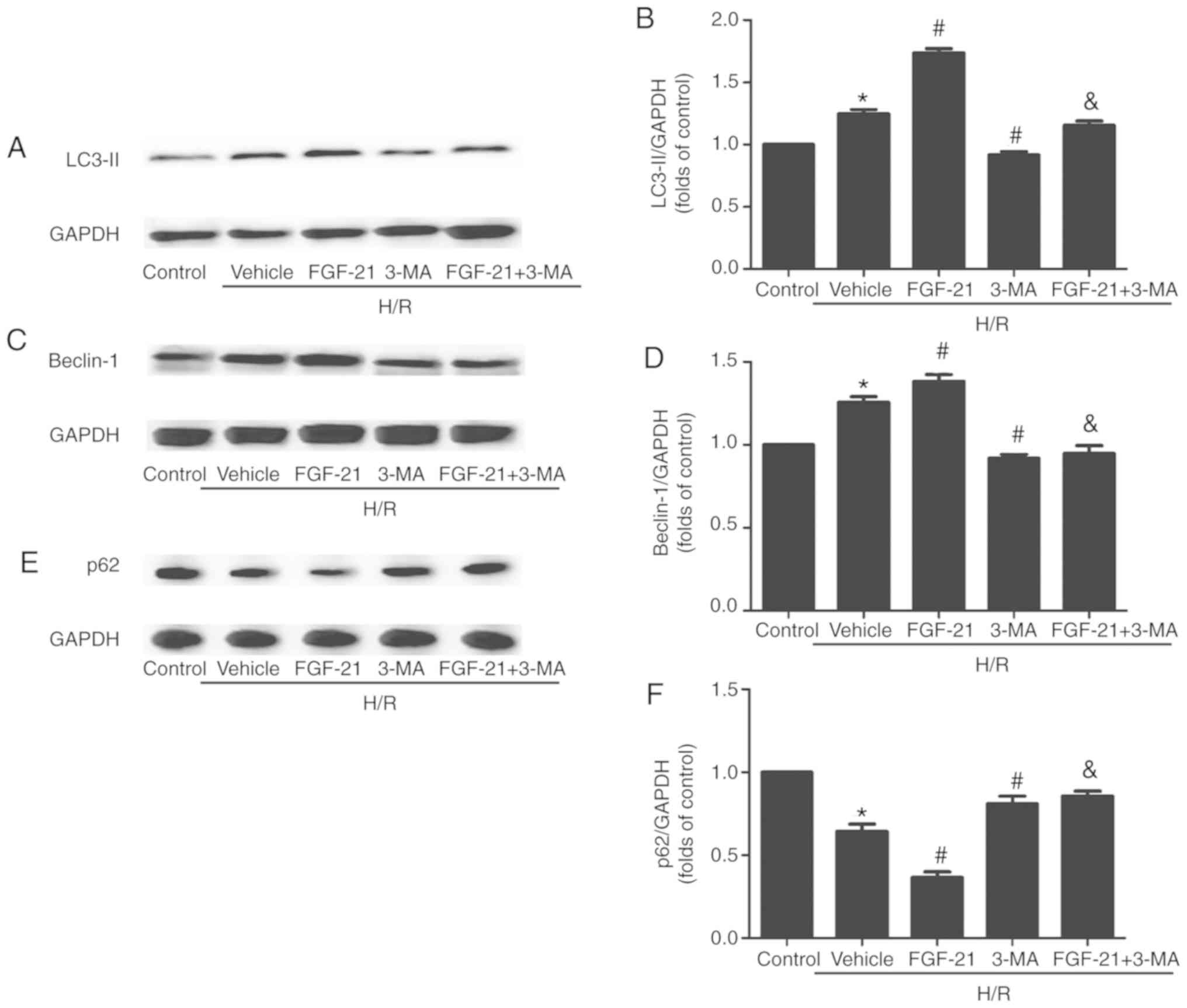
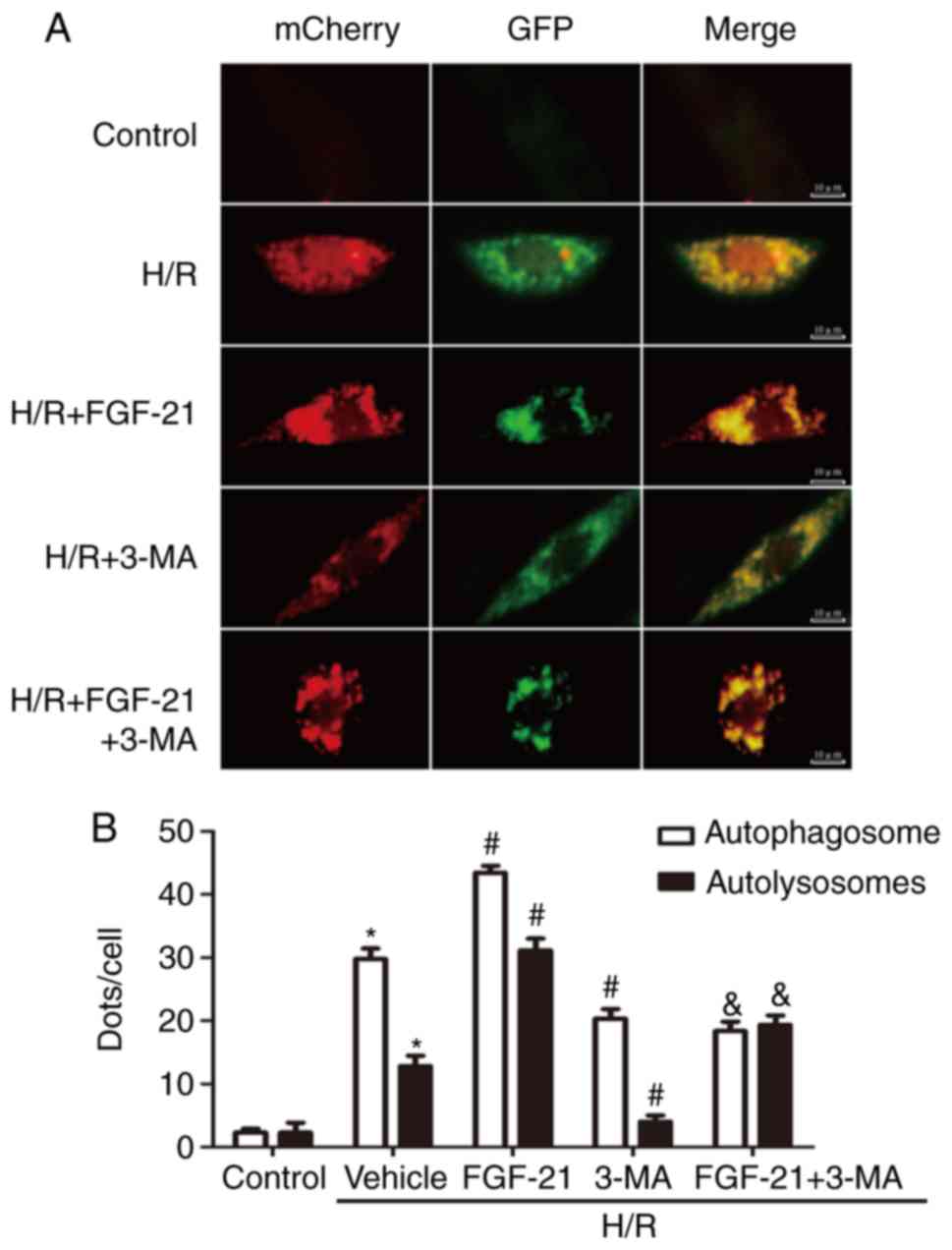
|
1
|
World Health Organization (WHO): World
health statistics 2007. WHO; Geneva: 2007
|
|
2
|
Przyklenk K, Dong Y, Undyala VV and
Whittaker P: Autophagy as a therapeutic target for
ischaemia/reperfusion injury? Concepts, controversies, and
challenges. Cardiovasc Res. 94:197–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jennings RB: Historical perspective on the
pathology of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res.
113:428–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y and Ren J: Targeting autophagy for
the therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors in
ischemia/reper-fusion heart injury. Circulation. 129:1088–1091.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Planavila A, Redondo-Angulo I and
Villarroya F: FGF21 and cardiac physiopathology. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 6:1332015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cheung BM and Deng HB: Fibroblast growth
factor 21: A promising therapeutic target in obesity-related
diseases. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 12:659–666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu S, Wu Y, Ye X, Ma L, Qi J, Yu D, Wei
Y, Lin G, Ren G and Li D: FGF21 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease by inducing autophagy. Mol Cell Biochem. 420:107–119.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanajak P, Sa-Nguanmoo P, Wang X, Liang G,
Li X, Jiang C, Chattipakorn SC and Chattipakorn N: Fibroblast
growth factor 21 (FGF21) therapy attenuates left ventricular
dysfunction and metabolic disturbance by improving FGF21
sensitivity, cardiac mitochondrial redox homoeostasis and
structural changes in pre-diabetic rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
217:287–299. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Luo F, Guo Y, Ruan G and Li X: Metformin
promotes cholesterol efflux in macrophages by up-regulating FGF21
expression: A novel anti-atherosclerotic mechanism. Lipids Health
Dis. 15:1092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng P, Zhang F, Yu L, Lin X, He L, Li X,
Lu X, Yan X, Tan Y and Zhang C: Physiological and pharmacological
roles of FGF21 in cardiovascular diseases. J Diabetes Res.
2016:15402672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Planavila A, Redondo-Angulo I, Ribas F,
Garrabou G, Casademont J, Giralt M and Villarroya F: Fibroblast
growth factor 21 protects the heart from oxidative stress.
Cardiovasc Res. 106:19–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu SQ, Tefft BJ, Roberts DT, Zhang LQ,
Ren Y, Li YC, Huang Y, Zhang D, Phillips HR and Wu YH:
Cardioprotective proteins upregulated in the liver in response to
experimental myocardial ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
303:H1446–H1458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:651–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lavandero S, Troncoso R, Rothermel BA,
Martinet W, Sadoshima J and Hill JA: Cardiovascular autophagy:
Concepts, controversies, and perspectives. Autophagy. 9:1455–1466.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao M, Sun L, Yu XJ, Miao Y, Liu JJ, Wang
H, Ren J and Zang WJ: Acetylcholine mediates AMPK-dependent
autophagic cytoprotection in H9c2 cells during
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:601–613.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Cheng Y, Gu J, Wang S, Zhou S,
Wang Y, Tan Y, Feng W, Fu Y, Mellen N, et al: Fenofibrate increases
cardiac autophagy via FGF21/SIRT1 and prevents fibrosis and
inflammation in the hearts of Type 1 diabetic mice. Clin Sci
(Lond). 130:625–641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rühlmann C, Wölk T, Blümel T, Stahn L,
Vollmar B and Kuhla A: Long-term caloric restriction in
ApoE-deficient mice results in neuroprotection via Fgf21-induced
AMPK/mTOR pathway. Aging. 8:2777–2789. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Yu P, Zhang C, Gao CY, Ma T, Zhang H, Zhou
MM, Yang YW, Yang L and Kong LY: Anti-proliferation of
triple-negative breast cancer cells with physagulide P: ROS/JNK
signaling pathway induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death.
Oncotarget. 8:64032–64049. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D,
Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM and Das DK: Cardioprotection
by resveratrol: A novel mechanism via autophagy involving the
mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 86:103–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Lin CH, Wu WS, Lin MT, Liu WP, Hsu RB and
Chang CP: Attenuating ischemia-induced H9c2 myoblasts apoptosis by
therapeutic hypothermia. Am J Med Sci. 339:258–265. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Au KW, Kou CY, Woo AY, Chim SS, Fung KP,
Cheng CH, Waye MM and Tsui SK: Calcyclin binding protein promotes
DNA synthesis and differentiation in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. J
Cell Biochem. 98:555–566. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR and Gottlieb
RA: Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion
injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 281:29776–29787. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Decker RS and Wildenthal K: Lysosomal
alterations in hypoxic and reoxygenated hearts. I. Ultrastructural
and cytochemical changes. Am J Pathol. 98:425–444. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR and Gottlieb
RA: The interplay between pro-death and pro-survival signaling
pathways in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Apoptosis meets
autophagy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 20:445–462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ling Y, Chen G, Deng Y, Tang H, Ling L,
Zhou X, Song X, Yang P, Liu Y, Li Z, et al: Polydatin
post-treatment alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury
by promoting autophagic flux. Clin Sci (Lond). 130:1641–1653. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sagrillo-Fagundes L, Assunção Salustiano
EM, Ruano R, Markus RP and Vaillancourt C: Melatonin modulates
autophagy and inflammation protecting human placental trophoblast
from hypoxia/reoxygenation. J Pineal Res. 4:e125202018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu F, Zhang J, Qian J, Wu G and Ma Z:
Baicalin attenuates liverhypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inducing
autophagy. Exp Ther Med. 2:657–664. 2018.
|
|
29
|
Palmen M, Daemen MJ, De Windt LJ, Willems
J, Dassen WR, Heeneman S, Zimmermann R, Van Bilsen M and Doevendans
PA: Fibroblast growth factor-1 improves cardiac functional recovery
and enhances cell survival after ischemia and reperfusion: A
fibroblast growth factor receptor, protein kinase C, and tyrosine
kinase-dependent mechanism. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:1113–1123. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang ZS, Padua RR, Ju H, Doble BW, Jin Y,
Hao J, Cattini PA, Dixon IM and Kardami E: Acute protection of
ischemic heart by FGF-2: Involvement of FGF-2 receptors and protein
kinase C. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 282:H1071–H1080. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang ZS, Srisakuldee W, Soulet F, Bouche
G and Kardami E: Non-angiogenic FGF-2 protects the ischemic heart
from injury, in the presence or absence of reperfusion. Cardiovasc
Res. 62:154–166. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu MH, Li GH, Peng LJ, Qu SL, Zhang Y,
Peng J, Luo XY, Hu HJ, Ren Z, Liu Y, et al: PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a
signaling mediates cardioprotection of FGF-2 against hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
414:57–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Singla DK, Singla RD, Abdelli LS and Glass
C: Fibroblast growth factor-9 enhances M2 macrophage
differentiation and attenuates adverse cardiac remodeling in the
infarcted diabetic heart. PLoS One. 10:e01207392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu SQ, Roberts D, Kharitonenkov A, Zhang
B, Hanson SM, Li YC, Zhang LQ and Wu YH: Endocrine protection of
ischemic myocardium by FGF21 from the liver and adipose tissue. Sci
Rep. 3:27672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Joki Y, Ohashi K, Yuasa D, Shibata R, Ito
M, Matsuo K, Kambara T, Uemura Y, Hayakawa S, Hiramatsu-Ito M, et
al: FGF21 attenuates pathological myocardial remodeling following
myocardial infarction through the adiponectin-dependent mechanism.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:124–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Patel V, Adya R, Chen J, Ramanjaneya M,
Bari MF, Bhudia SK, Hillhouse EW, Tan BK and Randeva HS: Novel
insights into the cardio-protective effects of FGF21 in lean and
obese rat hearts. PLoS One. 9:e871022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chanoit G, Lee S, Xi J, Zhu M, McIntosh
RA, Mueller RA, Norfleet EA and Xu Z: Exogenous zinc protects
cardiac cells from reperfusion injury by targeting mitochondrial
permeability transition pore through inactivation of glycogen
synthase kinase-3beta. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
295:H1227–H1233. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cong WT, Ling J, Tian HS, Ling R, Wang Y,
Huang BB, Zhao T, Duan YM, Jin LT and Li XK: Proteomic study on the
protective mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 to
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 91:973–984.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han MM, Wang WF, Liu MY, Li DS, Zhou B, Yu
YH and Ren GP: FGF-21 protects H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress injury. Yao Xue Xue Bao.
49:470–475. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aita VM, Liang XH, Murty VV, Pincus DL, Yu
W, Cayanis E, Kalachikov S, Gilliam TC and Levine B: Cloning and
genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene
on chromosome 17q21. Genomics. 59:59–65. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang S, Guo Y, Zhang W, Zhang J, Zhang Y
and Xu P: Effect of FGF-21 on implant bone defects through
hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1259–1267. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|