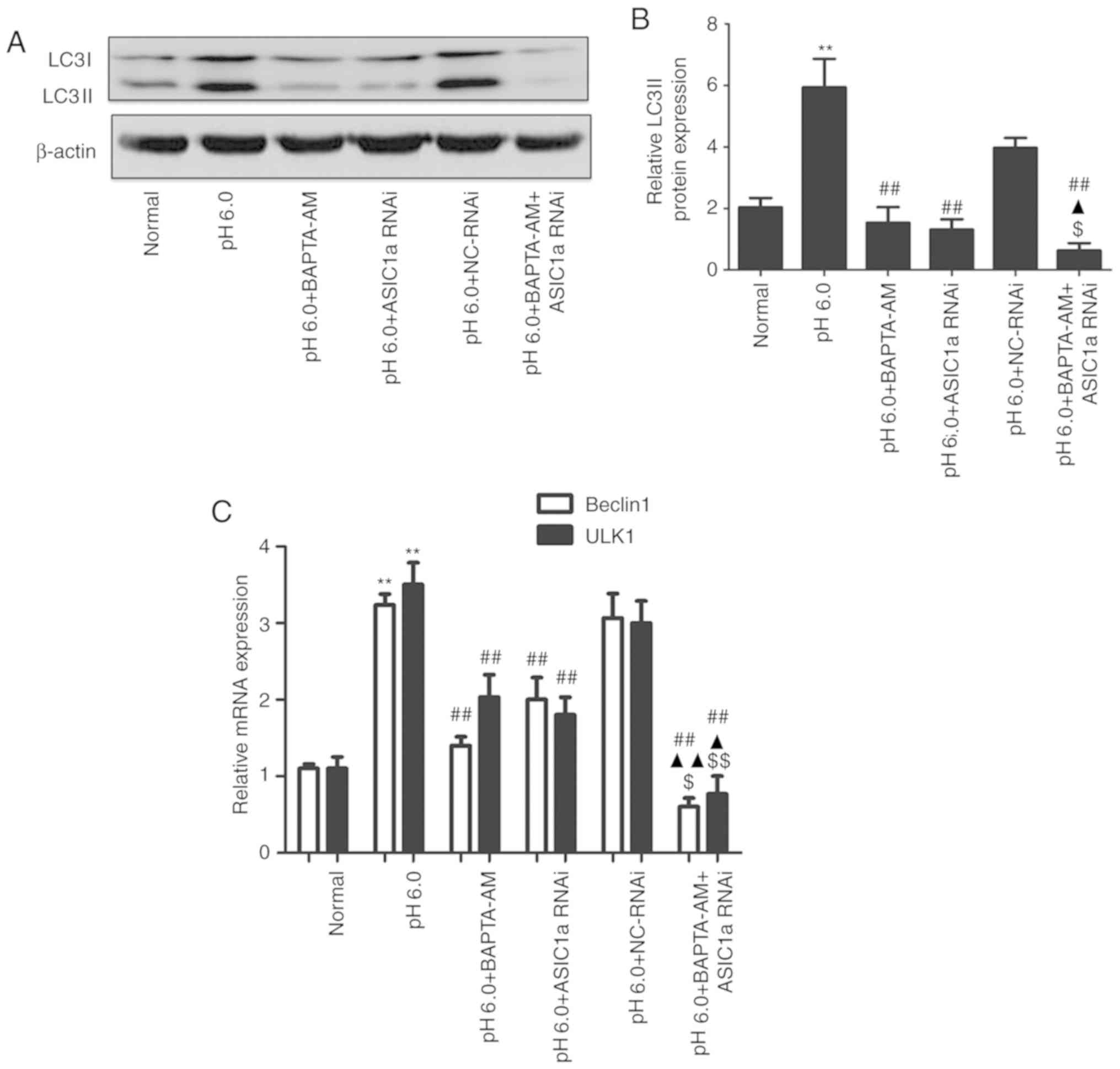
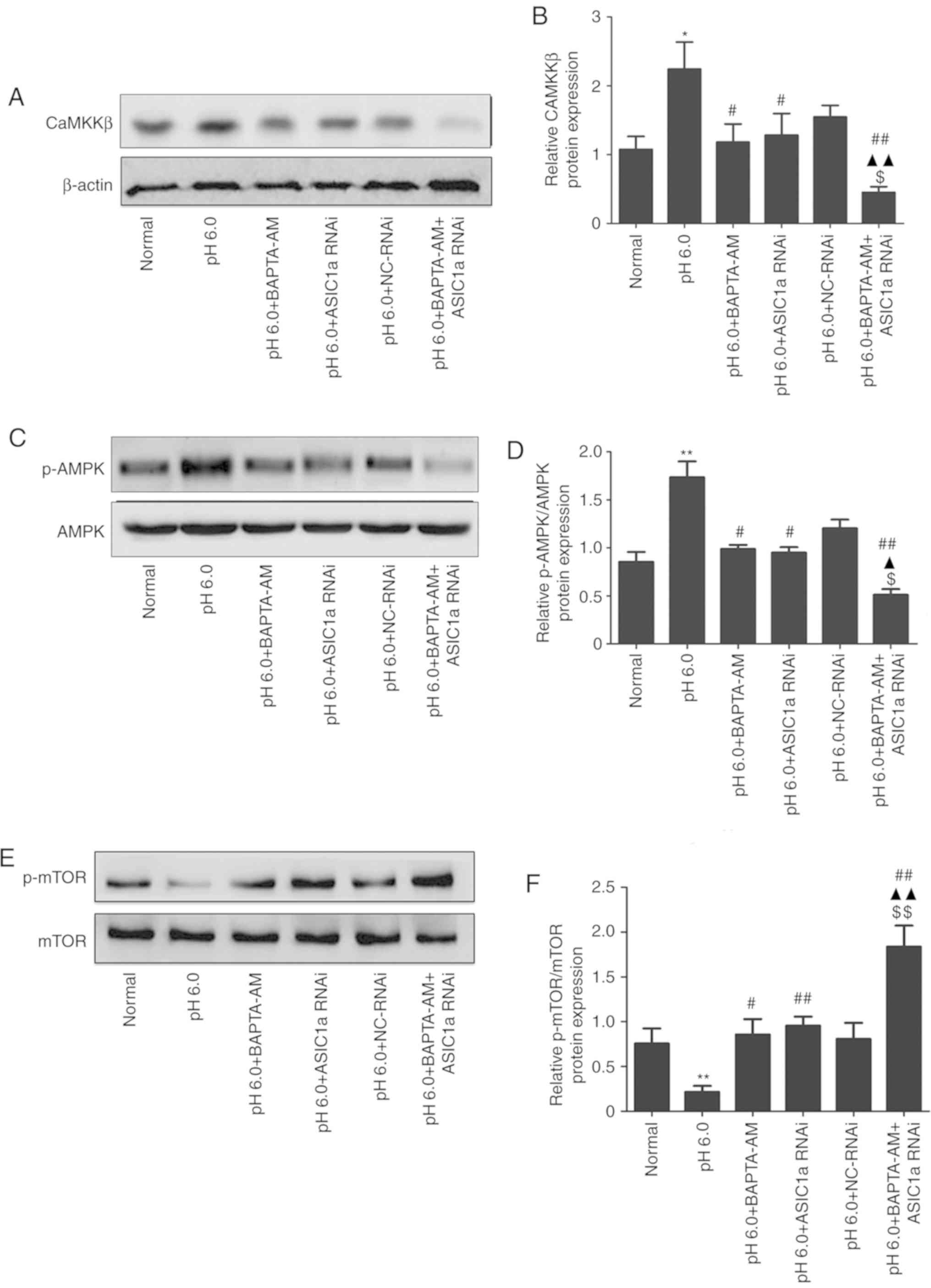
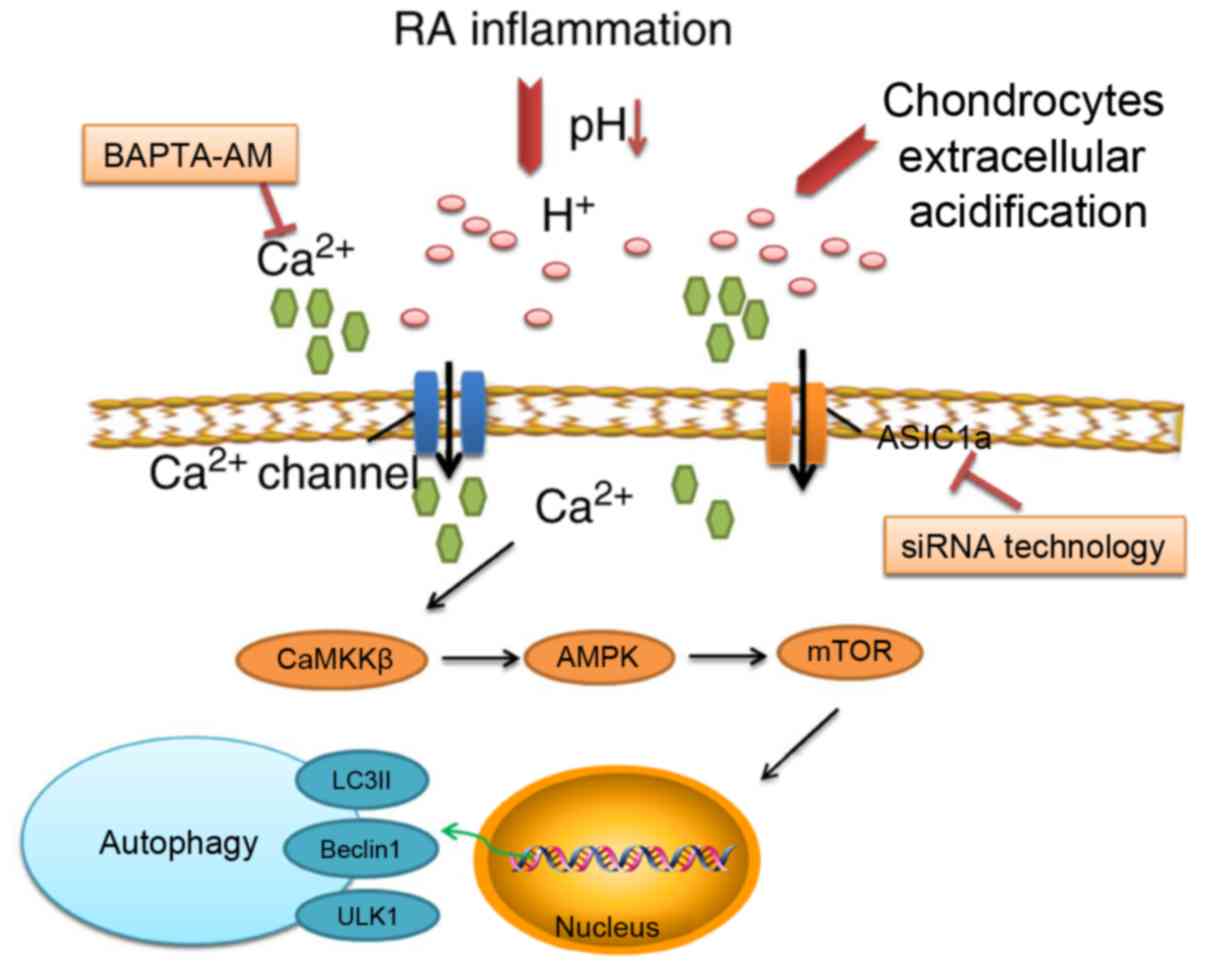
|
1
|
Scott DL, Wolfe F and Huizinga TW:
Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 376:1094–1108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malemud CJ: Chondrocyte apoptosis in
rheumatoid arthritis: Is preventive therapy possible? Immunotherapy
(Los Angel). 1:1022015.
|
|
3
|
Chang J, Wang W, Zhang H, Hu Y, Wang M and
Yin Z: The dual role of autophagy in chondrocyte responses in the
pathogenesis of articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis.
Int J Mol Med. 32:1311–1318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F,
Heurteaux C and Lazdunski M: A proton-gated cation channel involved
in acid-sensing. Nature. 386:173–177. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen CC, England S, Akopian AN and Wood
JN: A sensory neuron-specific, proton-gated ion channel. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:10240–10245. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lingueglia E, de Weille JR, Bassilana F,
Heurteaux C, Sakai H, Waldmann R and Lazdunski M: A modulatory
subunit of acid sensing ion channels in brain and dorsal root
ganglion cells. J Biol Chem. 272:29778–29783. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiong ZG, Chu XP and Simon RP:
Ca2+ -permeable acid-sensing ion channels and ischemic
brain injury. J Membr Biol. 209:59–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu W, Chen FH, Yuan FL, Zhang TY, Wu FR,
Rong C, Jiang S, Tang J, Zhang CC and Lin MY: Blockade of
acid-sensing ion channels protects articular chondrocytes from
acid-induced apoptotic injury. Inflamm Res. 61:327–335. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rong C, Chen FH, Jiang S, Hu W, Wu FR,
Chen TY and Yuan FL: Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels by
amiloride protects rat articular chondrocytes from acid-induced
apoptosis via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Cell Biol Int.
36:635–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yuan FL, Chen FH, Lu WG, Li X, Li JP, Li
CW, Xu RS, Wu FR, Hu W and Zhang TY: Inhibition of acid-sensing ion
channels in articular chondrocytes by amiloride attenuates
articular cartilage destruction in rats with adjuvant arthritis.
Inflamm Res. 59:939–947. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martínez-Borra J and López-Larrea C:
Autophagy and self-defense. Adv Exp Med Biol. 738:169–184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Vicencio JM, Kepp
O, Joza N, Tajeddine N and Kroemer G: Life, death and burial:
Multifaceted impact of autophagy. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:786–790.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He C, Zhu H, Li H, Zou MH and Xie Z:
Dissociation of Bcl-2-Beclin1 complex by activated AMPK enhances
cardiac autophagy and protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis in
diabetes. Diabetes. 62:1270–1281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ,
Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, Shen S, Kepp O, Scoazec M, Mignot
G, et al: Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced
by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science. 334:1573–1577. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rubinsztein DC: The roles of intracellular
protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature.
443:780–786. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vural A and Kehrl JH: Autophagy in
macrophages: Impacting inflammation and bacterial infection.
Scientifica (Cairo). 2014:8254632014.
|
|
17
|
Zhou XJ and Zhang H: Autophagy in
immunity: Implications in etiology of autoimmune/autoinflammatory
diseases. Autophagy. 8:1286–1299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wojtkowiak JW and Gillies RJ: Autophagy on
acid. Autophagy. 8:1688–1689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caramés B, Hasegawa A, Taniguchi N, Miyaki
S, Blanco FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces
severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:575–581.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Ureshino RP, Rocha KK, Lopes GS,
Bincoletto C and Smaili SS: Calcium signaling alterations,
oxidative stress, and autophagy in aging. Antioxid Redox Signal.
21:123–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM and Kim DH:
mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584:1287–1295. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seldin MM, Lei X, Tan SY, Stanson KP, Wei
Z and Wong GW: Skeletal muscle-derived myonectin activates the
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway to suppress autophagy
in liver. J Biol Chem. 288:36073–36082. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Feng Z, Cui S, Hou K, Tang L, Zhou
J, Cai G, Xie Y, Hong Q, Fu B and Chen X: Rapamycin upregulates
autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR-ULK1 pathway, resulting in reduced
podocyte injury. PLoS One. 8:e637992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sarkar S, Ravikumar B, Floto RA and
Rubinsztein DC: Rapamycin and mTOR-independent autophagy inducers
ameliorate toxicity of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin and
related proteinopathies. Cell Death Differ. 16:46–56. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Høyer-Hansen M, Bastholm L, Szyniarowski
P, Campanella M, Szabadkai G, Farkas T, Bianchi K, Fehrenbacher N,
Elling F, Rizzuto R, et al: Control of macroautophagy by calcium,
calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-beta, and Bcl-2. Mol Cell.
25:193–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bohensky J, Leshinsky S, Srinivas V and
Shapiro IM: Chondrocyte autophagy is stimulated by HIF-1 dependent
AMPK activation and mTOR suppression. Pediatr Nephrol. 25:633–642.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Srinivas V, Bohensky J and Shapiro IM:
Autophagy: A new phase in the maturation of growth plate
chondrocytes is regulated by HIF, mTOR and AMP kinase. Cells
Tissues Organs. 189:88–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Yuan FL, Chen FH, Lu WG, Li X, Wu FR, Li
JP, Li CW, Wang Y, Zhang TY and Hu W: Acid-sensing ion channel 1a
mediates acid-induced increases in intracellular calcium in rat
articular chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 340:153–159. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiong ZG, Zhu XM, Chu XP, Minami M, Hey J,
Wei WL, MacDonald JF, Wemmie JA, Price MP, Welsh MJ and Simon RP:
Neuroprotection in ischemia: Blocking calcium-permeable
acid-sensing ion channels. Cell. 118:687–698. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T). method Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mathy-Hartert M, Martin G, Devel P,
Deby-Dupont G, Pujol JP, Reginster JY and Henrotin Y: Reactive
oxygen species down-regulate the expression of pro- inflammatory
genes by human chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 52:111–118. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Razaq S, Wilkins RJ and Urban JP: The
effect of extracellular pH on matrix turnover by cells of the
bovine nucleus pulposus. Eur Spine J. 12:341–349. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mariño G, Madeo F and Kroemer G: Autophagy
for tissue homeostasis and neuroprotection. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
23:198–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Seino D, Blanco
FJ, D’Lima D and Lotz M: Mechanical injury suppresses autophagy
regulators and pharmacologic activation of autophagy results in
chondroprotection. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1182–1192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apgp, is localized in autophago-some
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miki Y, Tanji K, Mori F, Utsumi J, Sasaki
H, Kakita A, Takahashi H and Wakabayashi K: Alteration of upstream
autophagy-related proteins (ULK1, ULK2, Beclin1, VPS34 and AMBRA1)
in lewy body disease. Brain Pathol. 26:359–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu W, Shang G, Yang S, Huang J, Xue X,
Lin Y, Zheng Y, Wang X, Wang L, Lin R, et al: Electroacupuncture
protects against ischemic stroke by reducing autophagosome
formation and inhibiting autophagy through the mTORC1-ULK1
complex-Beclin1 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:309–318. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Pandey AK, Hazari PP, Patnaik R and Mishra
AK: The role of ASIC1a in neuroprotection elicited by quercetin in
focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1383:289–299. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weng XC, Zheng JQ, Li J and Xiao WB:
Underlying mechanism of ASIC1a involved in acidosis-induced
cytotoxicity in rat C6 glioma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:1731–1736. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Khan MJ, Rizwan Alam M, Waldeck-Weiermair
M, Karsten F, Groschner L, Riederer M, Hallström S, Rockenfeller P,
Konya V, Heinemann A, et al: Inhibition of autophagy rescues
palmitic acid-induced necroptosis of endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 287:21110–21120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang SH, Shih YL, Ko WC, Wei YH and Shih
CM: Cadmium-induced autophagy and apoptosis are mediated by a
calcium signaling pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3640–3652. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Williams JA, Hou Y, Ni HM and Ding WX:
Role of intracellular calcium in proteasome inhibitor-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and cell death. Pharm Res.
30:2279–2289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Khan MT and Joseph SK: Role of inositol
trisphosphate receptors in autophagy in DT40 cells. J Biol Chem.
285:16912–16920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Decuypere JP, Bultynck G and Parys JB: A
dual role for Ca(2+) in autophagy regulation. Cell calcium.
50:242–250. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Furuta A, Tanaka M, Omata W, Nagasawa M,
Kojima I and Shibata H: Microtubule disruption with BAPTA and
dimethyl BAPTA by a calcium chelation-independent mechanism in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocr J. 56:235–243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Pfisterer SG, Mauthe M, Codogno P and
Proikas-Cezanne T: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase
(CaMK) signaling via CaMKI and AMP-activated protein kinase
contributes to the regulation of WIPI-1 at the onset of autophagy.
Mol Pharmacol. 80:1066–1075. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Khan NM, Ansari MY and Haqqi TM: Sucrose,
but not glucose, blocks IL1- beta-induced inflammatory response in
human chondrocytes by inducing autophagy via AKT/mTOR pathway. J
Cell Biochem. 118:629–639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Taneike M, Nishida K, Omiya S,
Zarrinpashneh E, Misaka T, Kitazume-Taneike R, Austin R, Takaoka M,
Yamaguchi O, Gambello MJ, et al: mTOR hyperactivation by ablation
of tuberous sclerosis complex 2 in the mouse heart induces cardiac
dysfunction with the increased number of small mitochondria
mediated through the down-regulation of autophagy. PLoS One.
11:e01526282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hirata Y and Oku Y: TRP channels are
involved in mediating hypercapnic Ca2+ responses in rat
glia-rich medullary cultures independent of extracellular pH. Cell
Calcium. 48:124–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Takahashi K, Yokota M and Ohta T:
Molecular mechanism of 2- APB- induced Ca(2)(+) influx in external
acidification in PC12. Exp Cell Res. 323:337–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|