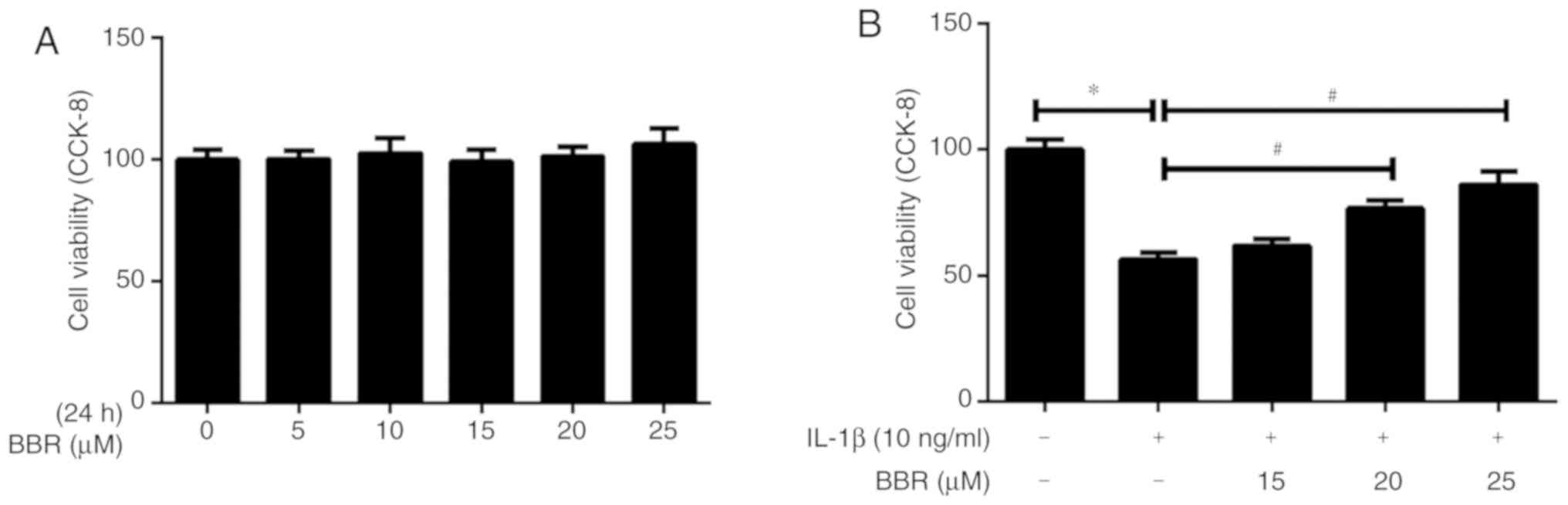
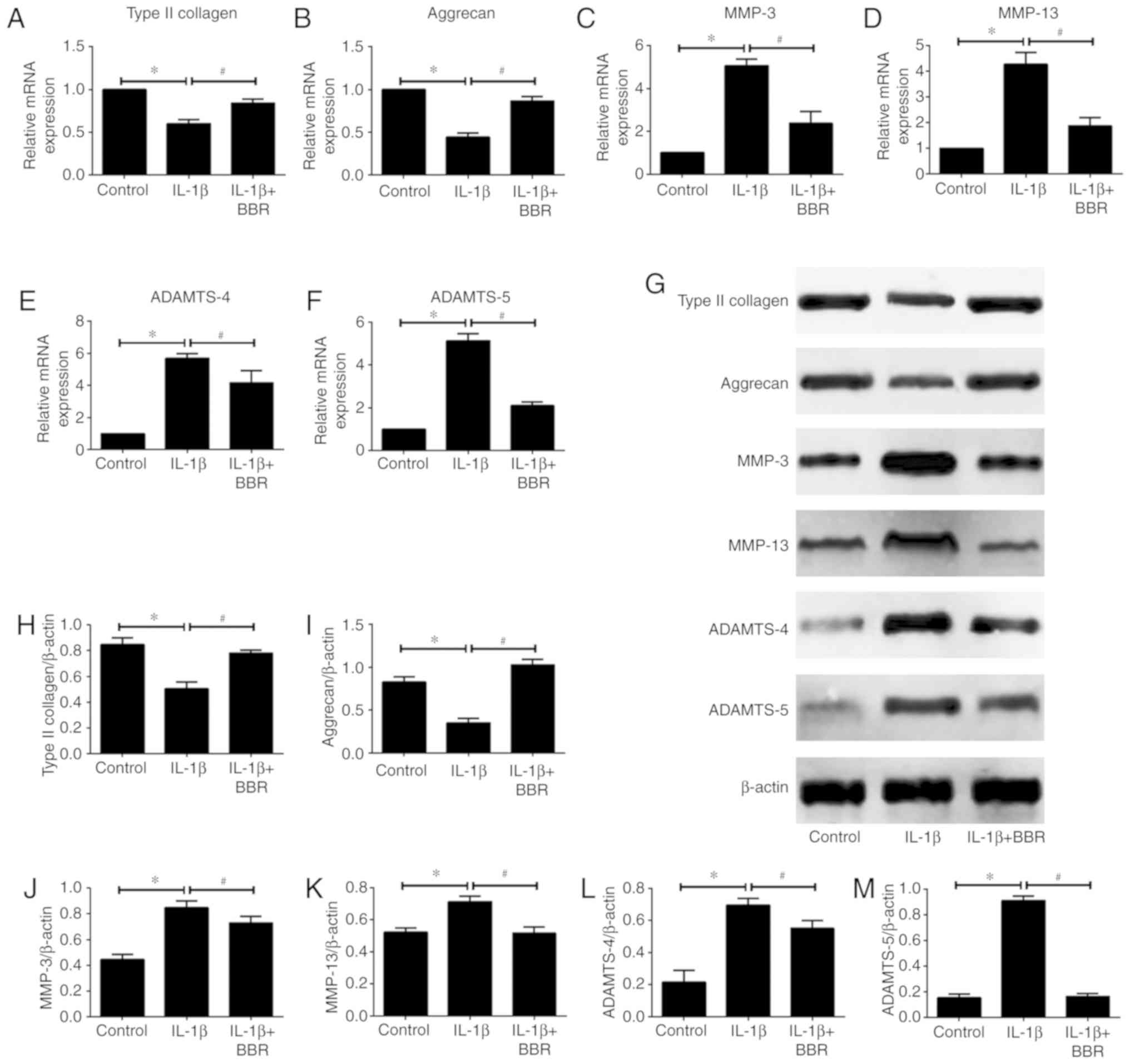
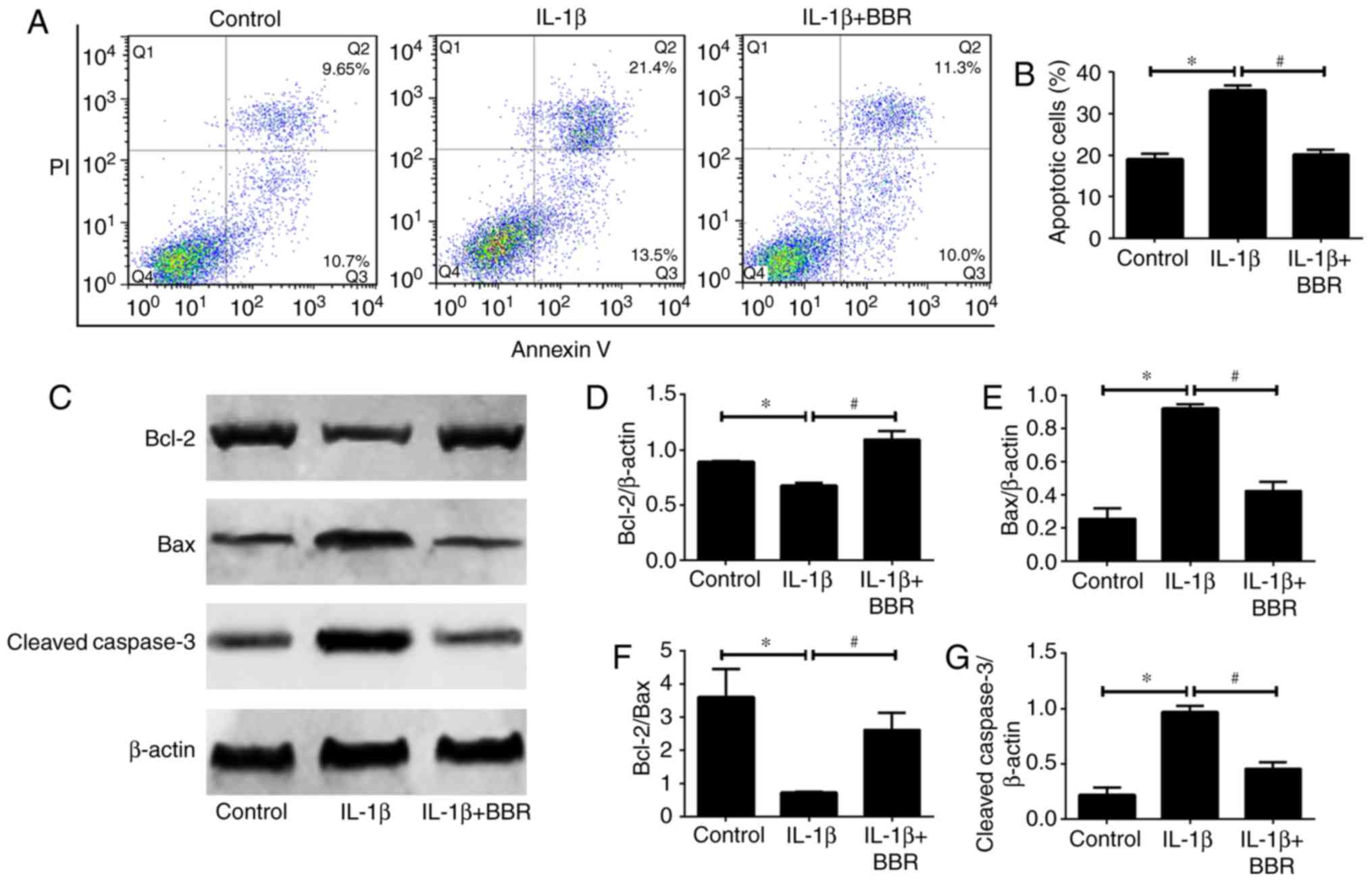
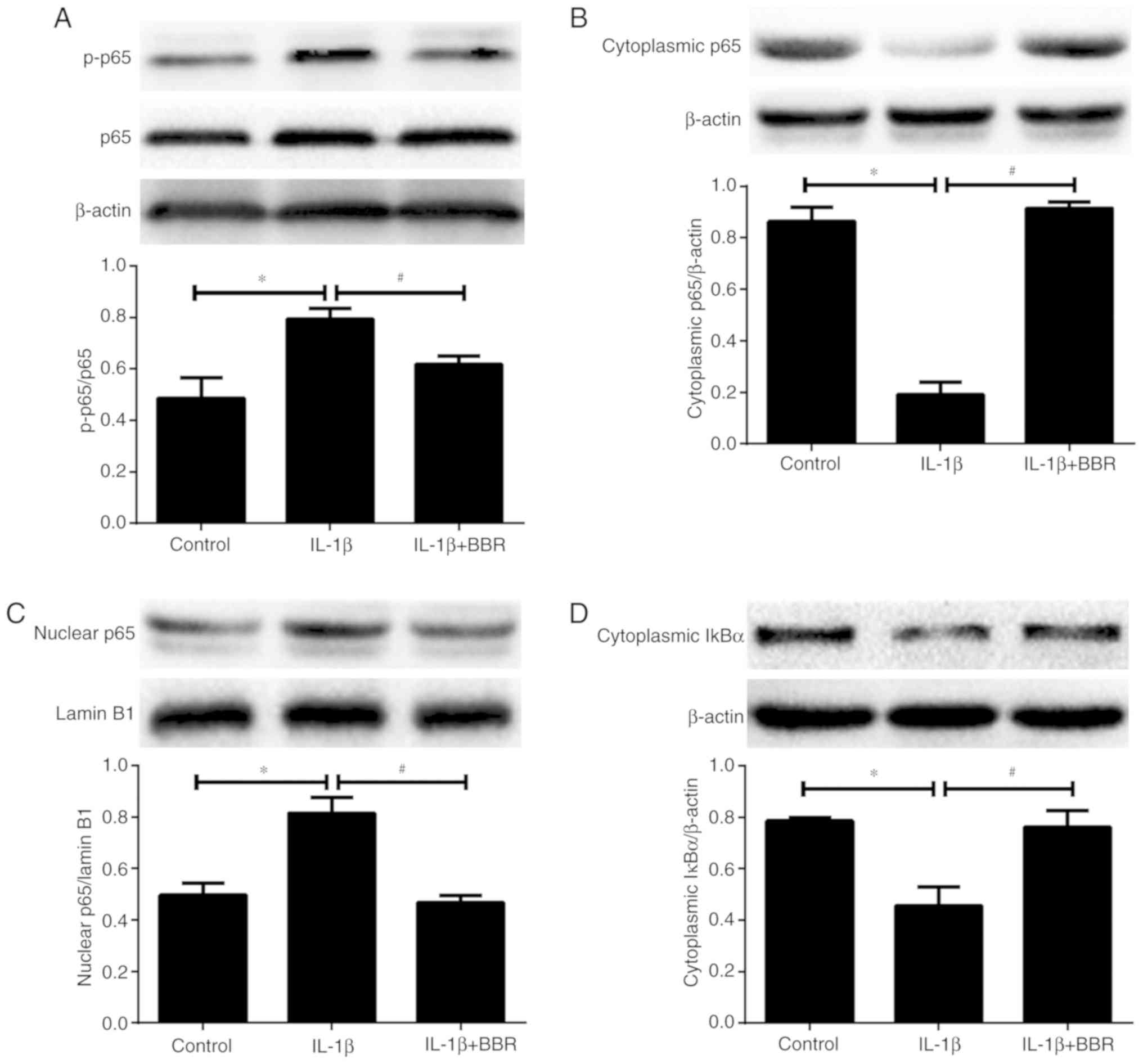
|
1
|
Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA,
Comstock BA, Hollingworth W and Sullivan SD: Expenditures and
health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA.
299:656–664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R,
Raininko R, Viikari-Juntura E and Lamminen A: Low back pain in
relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:487–492. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pattappa G, Li Z, Peroglio M, Wismer N,
Alini M and Grad S: Diversity of intervertebral disc cells:
Phenotype and function. J Anat. 221:480–496. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakai D and Grad S: Advancing the cellular
and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 84:159–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang W, Yu XH, Wang C, He WS, Zhang SJ,
Yan YG, Zhang J, Xiang YX and Wang WJ: Interleukin-1β in
intervertebral disk degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 450:262–272.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu B, Meng C, Wang H, Jia C and Zhao Y:
Changes of proteoglycan and collagen II of the adjacent
intervertebral disc in the cervical instability models. Biomed
Pharmacother. 84:754–758. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Li K, Han X, Mao C, Zhang K, Zhao T
and Zhao J: The imbalance between TIMP3 and matrix-degrading
enzymes plays an important role in intervertebral disc
degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:507–514. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Freemont AJ: The cellular pathobiology of
the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 48:5–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yamamoto J, Maeno K, Takada T, Kakutani K,
Yurube T, Zhang Z, Hirata H, Kurakawa T, Sakai D, Mochida J, et al:
Fas ligand plays an important role for the production of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus
cells. J Orthop Res. 31:608–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen J, Xuan J, Gu YT, Shi KS, Xie JJ,
Chen JX, Zheng ZM, Chen Y, Chen XB, Wu YS, et al: Celastrol reduces
IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation
in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral
disc degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:208–219. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang Z, Chen Z, Yang S, Wang Y, Huang Z,
Gao J, Tu S and Rao Z: Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced
arthritis in rats associated with anti-inflammatory and
anti-angiogenic effects. Inflammation. 37:1789–1798. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Z, Geng YN, Jiang JD and Kong WJ:
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of berberine in the
treatment of diabetes mellitus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014.289264:2014.
|
|
14
|
Liang Y, Huang M, Jiang X, Liu Q, Chang X
and Guo Y: The neuroprotective effects of Berberine against amyloid
β-protein-induced apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons
via mitochondria-related caspase pathway. Neurosci Lett. 655:46–53.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, He X, Zhang CF, Guo CR, Wang CZ
and Yuan CS: Anti-arthritic effect of berberine on adjuvant-induced
rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:887–893.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu PF, Chen WP, Tang JL, Bao JP and Wu LD:
Protective effects of berberine in an experimental rat
osteoarthritis model. Phytother Res. 25:878–885. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao H, Zhang T, Xia C, Shi L, Wang S,
Zheng X, Hu T and Zhang B: Berberine ameliorates cartilage
degeneration in interleukin-1β-stimulated rat chondrocytes and in a
rat model of osteoarthritis via Akt signalling. J Cell Mol Med.
18:283–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Liu SQ, Yu L, He B, Wu SH, Zhao Q,
Xia SQ and Mei HJ: Berberine prevents nitric oxide-induced rat
chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degeneration in a rat
osteoarthritis model via AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling. Apoptosis.
20:1187–1199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Zheng Z, Wang J, Tang C, Khor S,
Chen J, Chen X, Zhang Z, Tang Q, Wang C, et al: Berberine
suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation in
nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in a
rodent model. Int J Biol Sci. 14:682–692. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M,
Hodler J and Boos N: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
26:1873–1878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kang L, Hu J, Weng Y, Jia J and Zhang Y:
Sirtuin 6 prevents matrix degradation through inhibition of the
NF-κB pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res.
352:322–332. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Purmessur D, Walter BA, Roughley PJ,
Laudier DM, Hecht AC and Iatridis J: A role for TNFα in
intervertebral disc degeneration: A non-recoverable catabolic
shift. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:151–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roelofs PD, Deyo RA, Koes BW, Scholten RJ
and van Tulder MW: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for low
back pain: An updated Cochrane review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
33:1766–1774. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Phillips FM, Reuben J and Wetzel FT:
Intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to a lumbar fusion. An
experimental rabbit model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 84:289–294. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang B, Xu L, Zhuo N and Shen J:
Resveratrol protects against mitochondrial dysfunction through
autophagy activation in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 493:373–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chandirasegaran G, Elanchezhiyan C, Ghosh
K and Sethupathy S: Berberine chloride ameliorates oxidative
stress, inflammation and apoptosis in the pancreas of
Streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother.
95:175–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jimbo K, Park JS, Yokosuka K, Sato K and
Nagata K: Positive feedback loop of interleukin-1beta upregulating
production of inflammatory mediators in human intervertebral disc
cells in vitro. J Neurosurg Spine. 2:589–595. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Johnson ZI, Schoepflin ZR, Choi H, Shapiro
IM and Risbud MV: Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cells Mater. 30:104–116;
discussion 116–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang WJ, Yu XH, Wang C, Yang W, He WS,
Zhang SJ, Yan YG and Zhang J: MMPs and ADAMTSs in intervertebral
disc degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 448:238–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kang L, Yang C, Yin H, Zhao K, Liu W, Hua
W, Wang K, Song Y, Tu J, Li S, et al: MicroRNA-15b silencing
inhibits IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degradation by
targeting SMAD3 in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biotechnol Lett.
39:623–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han Y, Li X, Yan M, Yang M, Wang S, Pan J,
Li L and Tan J: Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes
calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through
ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. Mar 23–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cheng X, Zhang L, Zhang K, Zhang G, Hu Y,
Sun X, Zhao C, Li H, Li YM and Zhao J: Circular RNA VMA21 protects
against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c
and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. Ann Rheum Dis.
77:770–779. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen J, Xu S, Zhou H, Liu H, Jiang W, Hao
J and Hu Z: IL-1β induces apoptosis and autophagy via mitochondria
pathway in human degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep.
7:410672017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang CC, Zhou JS, Hu JG, Wang X, Zhou XS,
Sun BA, Shao C and Lin Q: Effects of IGF-1 on IL-1β-induced
apoptosis in rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
7:441–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wuertz K, Vo N, Kletsas D and Boos N:
Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: The
roles of NF-κB and MAP kinases. Eur Cell Mater. 23:103–119;
discussion 119–120. 2012.
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Wang X, Pan H, Yang H, Li X, Zhang
K, Wang H, Zheng Z, Liu H and Wang J: Resistin promotes CCL4
expression through toll-like receptor-4 and activation of the
p38-MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways: Implications for
intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
25:341–350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|