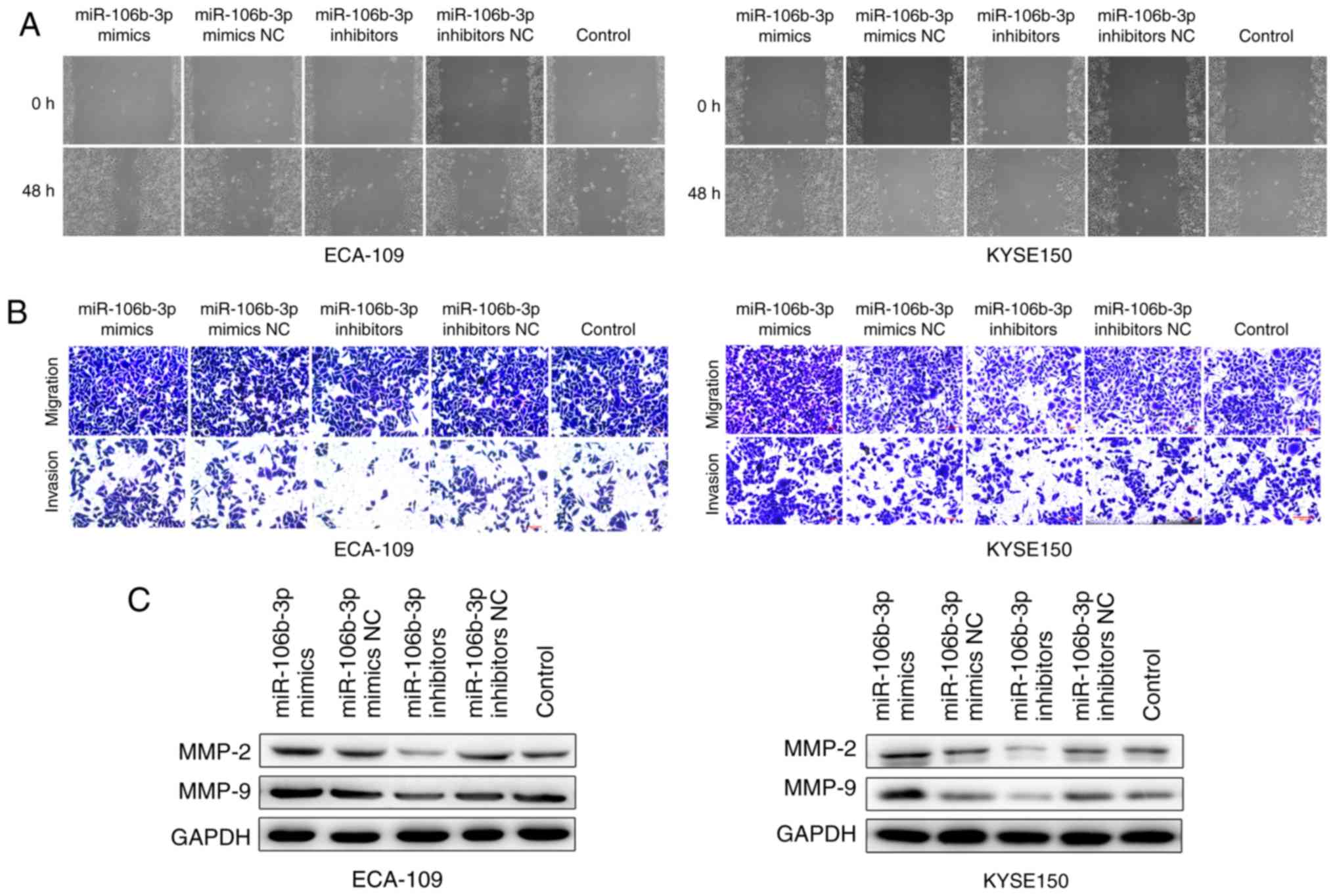
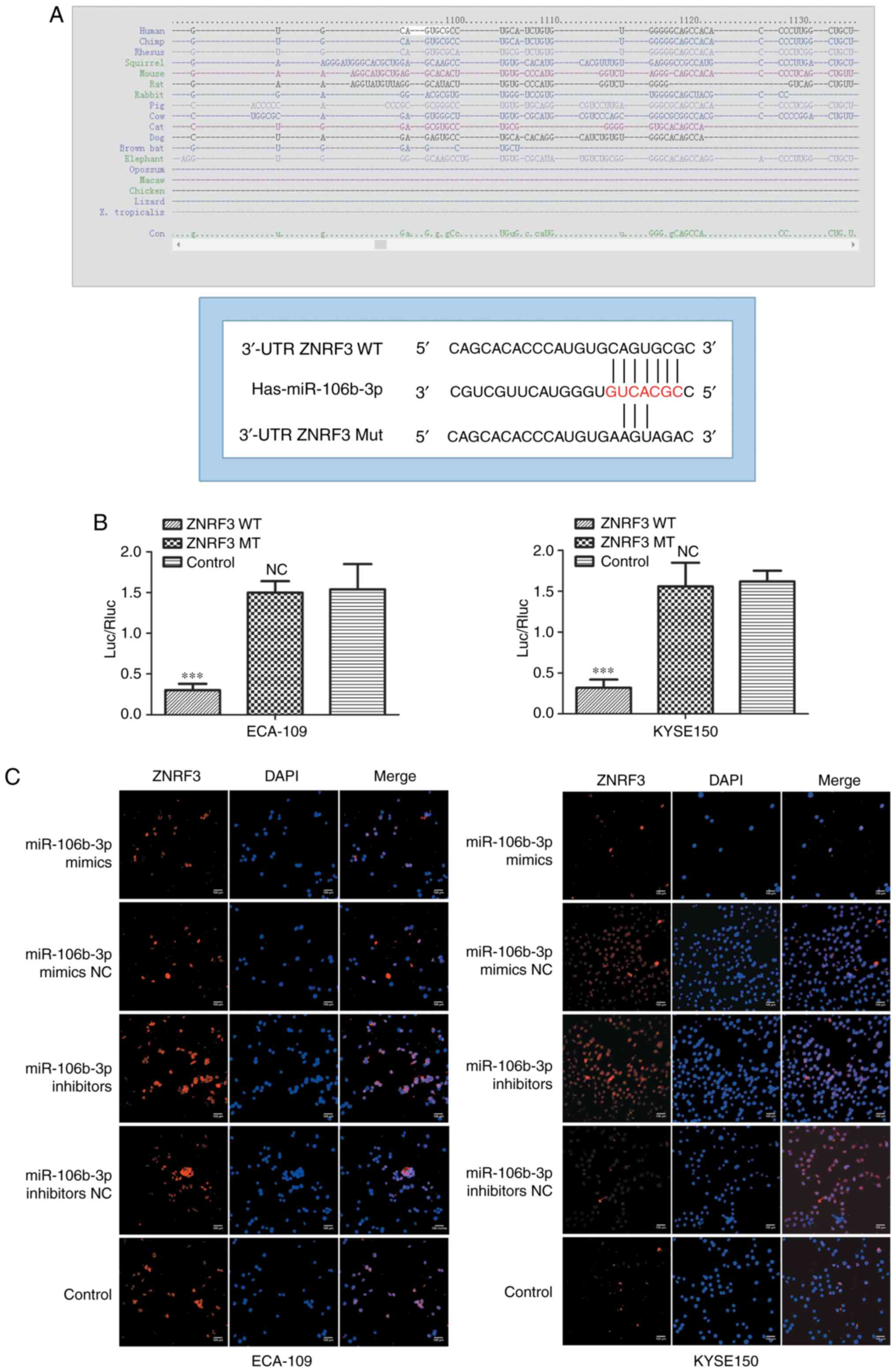
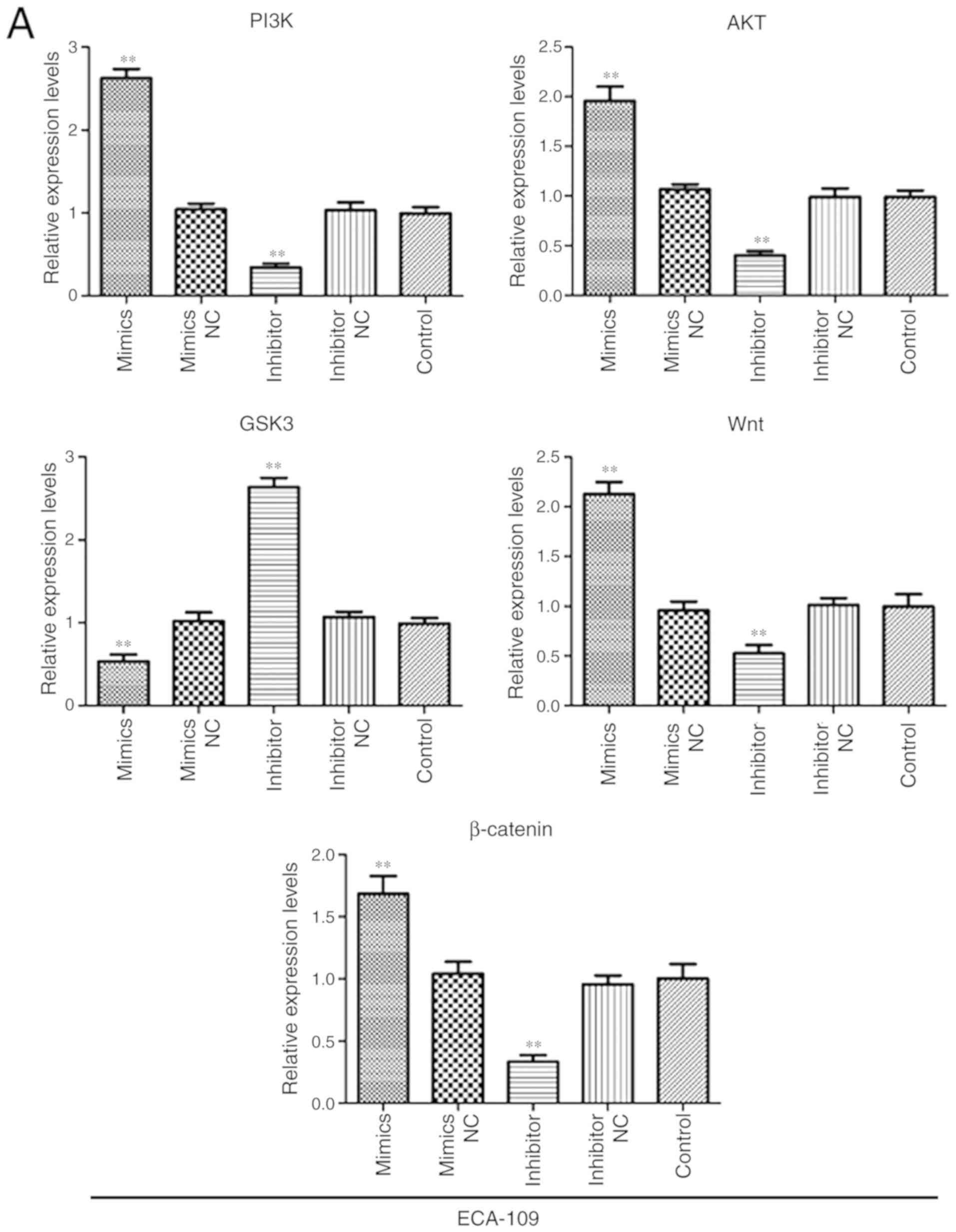
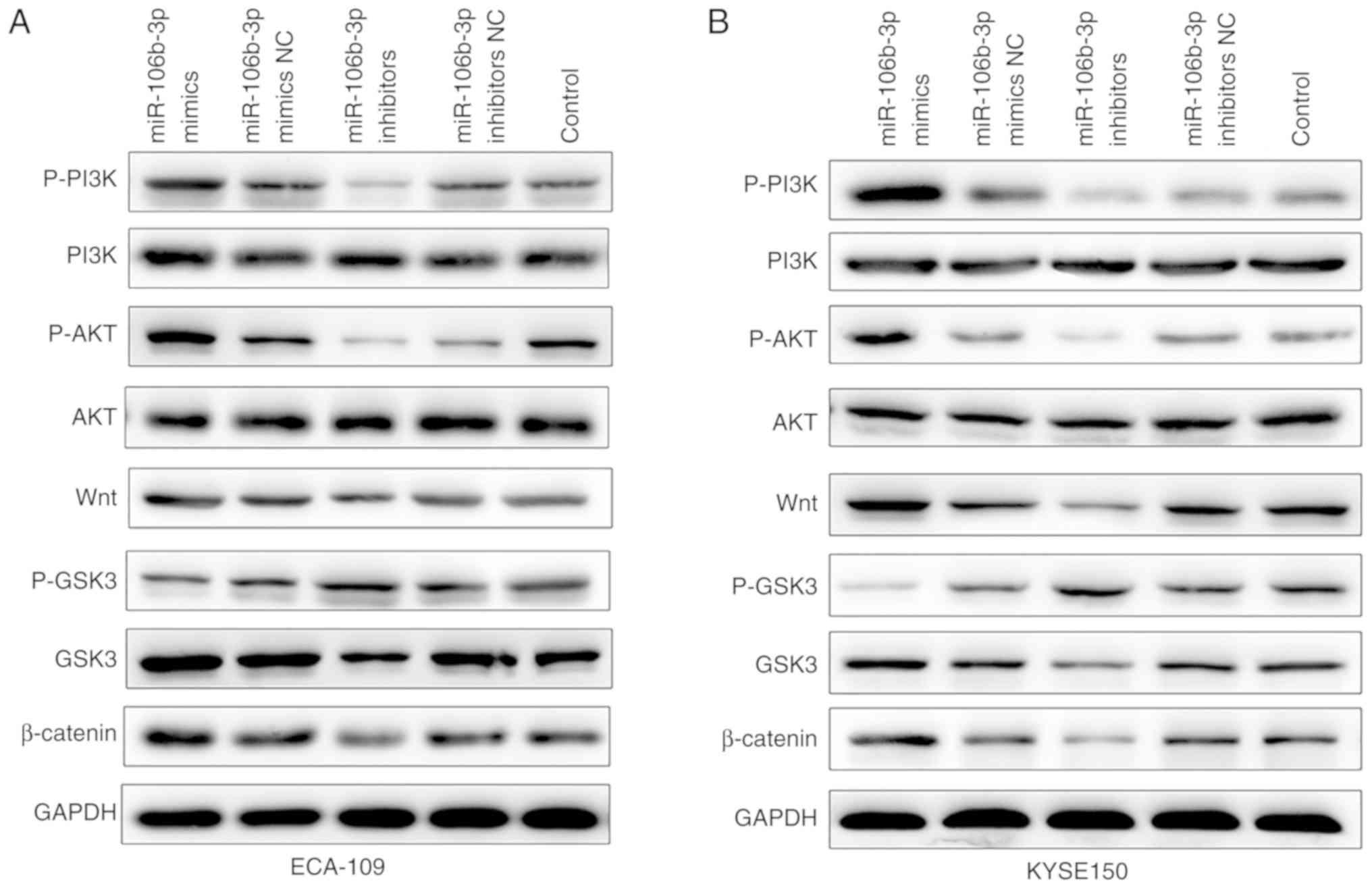
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mccann J: Esophageal cancers: Changing
character, increasing incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:497–498.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Da F, Xi J, Ji Z, Liu T, Ma Y,
Zhao Y, Dong L, Wang Q and Shen X: Expression and clinical
significance of UCH37 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Dig Dis Sci. 57:2310–2317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kausar T, Ahsan A, Hasan MR, Lin L, Beer
DG and Ralhan R: Sperm protein 17 is a novel marker for predicting
cisplatin response in esophageal squamous cancer cell lines. Int J
Cancer. 126:1494–1503. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Qin YR, Tang H, Xie F, Liu H, Zhu Y, Ai J,
Chen L, Li Y, Kwong DL, Fu L and Guan XY: Characterization of
tumor-suppressive function of SOX6 in human esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:46–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang JG, Shi Y, Hong DF, Song M, Huang D,
Wang CY and Zhao G: MiR-148b suppresses cell proliferation and
invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting WNT1/β-catenin
pathway. Sci Rep. 5:80872015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang Y and Lee CG: MicroRNA and
cancer-focus on apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 13:12–23. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai K, Wang Y and Bao X: MiR-106b promotes
cell proliferation via targeting RB in laryngeal carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 30:732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, Lioudmer P,
Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Miller K, Kilic E, Erbersdobler A, Weikert
S and Jung K: miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for
bladder cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn.
15:695–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li BK, Huang PZ, Qiu JL, Liao YD, Hong J
and Yuan YF: Upregulation of microRNA-106b is associated with poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 9:2262014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slaby O, Jancovicova J, Lakomy R, Svoboda
M, Poprach A, Fabian P, Kren L, Michalek J and Vyzula R: Expression
of miRNA-106b in conventional renal cell carcinoma is a potential
marker for prediction of early metastasis after nephrectomy. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
J Clin Invest. 139:871–890. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Dieudonné FX, Marion A, Marie PJ and
Modrowski D: Targeted inhibition of T-cell factor activity promotes
syndecan-2 expression and sensitization to doxorubicin in
osteosarcoma cells and bone tumors in mice. J Bone Miner Res.
27:2118–2129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Q, Cao HZ and Zheng PS: LGR5 promotes
the proliferation and tumor formation of cervical cancer cells
through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
5:9092–9105. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hua HW, Jiang F, Huang Q, Liao Z and Ding
G: MicroRNA-153 promotes Wnt/β-catenin activation in hepatocellular
carcinoma through suppression of WWOX. Oncotarget. 6:3840–3847.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou DS, Wang HB, Zhou ZG, Zhang YJ, Zhong
Q, Xu L, Huang YH, Yeung SC, Chen MS and Zeng MS: TACC3 promotes
stemness and is a potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:24163–24177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zebisch M, Xu Y, Krastev C, MacDonald BT,
Chen M, Gilbert RJ, He X and Jones EY: Structural and molecular
basis of ZNRF3/RNF43 transmembrane ubiquitin ligase inhibition by
the Wnt agonist R-spondin. Nat Commun. 4:27872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y, Lan J, Wang W, Shi Q, Lan Y, Cheng
Z and Guan H: ZNRF3 acts as a tumour suppressor by the Wnt
signalling pathway in human gastric adenocarcinoma. J Mol Histol.
44:555–563. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qin H, Cai A, Xi H, Yuan J and Chen L:
ZnRF3 induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by antagonizing Wnt
and Hedgehog signaling. Panminerva Med. 57:167–175. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deng X, Wu B, Xiao K, Kang J, Xie J, Zhang
X and Fan Y: MiR-146b-5p promotes metastasis and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer by targeting
ZNRF3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:71–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang JP, Feng LL, Zhan HF, et al: Stromal
cell-derived factor 1 alpha induce epithelial mesenchymal
transition of Hela cells. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 6:933–937.
2017.
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Ren H, Jin Y and Guo Y:
ZNRF3 inhibits the invasion and tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol
Res. 25:571–577. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yau WL, Lam CS, Ng L, Chow AK, Chan ST,
Chan JY, Wo JY, Ng KT, Man K, Poon RT and Pang RW: Over-expression
of miR-106b promotes cell migration and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition process. PLoS One. 8:e578822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang TS, Yang XH, Chen X, Wang XD, Hua J,
Zhou DL, Zhou B and Song ZS: MicroRNA-106b in cancer-associated
fibroblasts from gastric cancer promotes cell migration and
invasion by targeting PTEN. FEBS Lett. 588:2162–2169. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun C, Yao X, Jiang Q and Sun X: miR-106b
targets DAB2 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation
and metastasis. Oncol Lett. 16:3063–3069. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Piao J, You K, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Li Z and
Geng L: Substrate stiffness affects epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of cervical cancer cells through miR-106b and its target
protein DAB2. Int J Oncol. 50:2033–2042. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He QY, Wang GC, Zhang H, Tong DK, Ding C,
Liu K, Ji F, Zhu X and Yang S: miR-106a-5p suppresses the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting HMGA2. DNA Cell Biol. 35:506–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang GJ, Li JS, Zhou H, Xiao HX, Li Y and
Zhou T: MicroRNA-106b promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and
invasion by directly targeting DLC1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Cubillo E, Sarrió D,
Peinado H, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Villa S, Bolós V, Jordá M, Fabra
A, Portillo F, et al: Genetic profiling of epithelial cells
expressing E-cadherin repressors reveals a distinct role for Snail,
Slug, and E47 factors in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer
Res. 66:9543–9556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Castro Alves C, Rosivatz E, Schott C,
Hollweck R, Becker I, Sarbia M, Carneiro F and Becker KF: Slug is
overexpressed in gastric carcinomas and may act synergistically
with SIP1 and Snail in the down-regulation of E-cadherin. J Pathol.
211:507–515. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Choi YS, Shim YM, Kim SH, Son DS, Lee HS,
Kim GY, Han J and Kim J: Prognostic significance of E-cadherin and
beta-catenin in resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 24:441–449. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Leung CO, Mak WN, Kai AK, Chan KS, Lee TK,
Ng IO and Lo RC: Sox9 confers stemness properties in hepatocellular
carcinoma through Frizzled-7 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Oncotarget. 7:29371–29386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yuan X, Sun X, Shi X, Wang H, Wu G, Jiang
C, Yu D, Zhang W, Xue B and Ding Y: USP39 promotes colorectal
cancer growth and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Oncol Rep. 37:2398–2404. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mao Y, Xu J, Li Z, Zhang N, Yin H and Liu
Z: The role of nuclear β-catenin accumulation in the Twist2-induced
ovarian cancer EMT. PLoS One. 8:e782002013. View Article : Google Scholar
|