|
1
|
Geller DS and Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: A
review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin Adv
Hematol Oncol. 8:705–718. 2010.
|
|
2
|
He H, Ni J and Huang J: Molecular
mechanisms of chemoresistance in osteosarcoma (Review). Oncol Lett.
7:1352–1362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu JJ, Liu S, Wang JG, Zhu W, Hua YQ, Sun
W and Cai ZD: Telangiectatic osteosarcoma: A review of literature.
Onco Targets Ther. 6:593–602. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McQueen P, Ghaffar S, Guo Y, Rubin EM, Zi
X and Hoang BH: The Wnt signaling pathway: Implications for therapy
in osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:1223–1232. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin CH, Ji T, Chen CF and Hoang BH: Wnt
signaling in osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 804:33–45. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McManus MM, Weiss KR and Hughes DP:
Understanding the role of Notch in osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol.
804:67–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Graziano AC, Cardile V, Avola R, Vicario
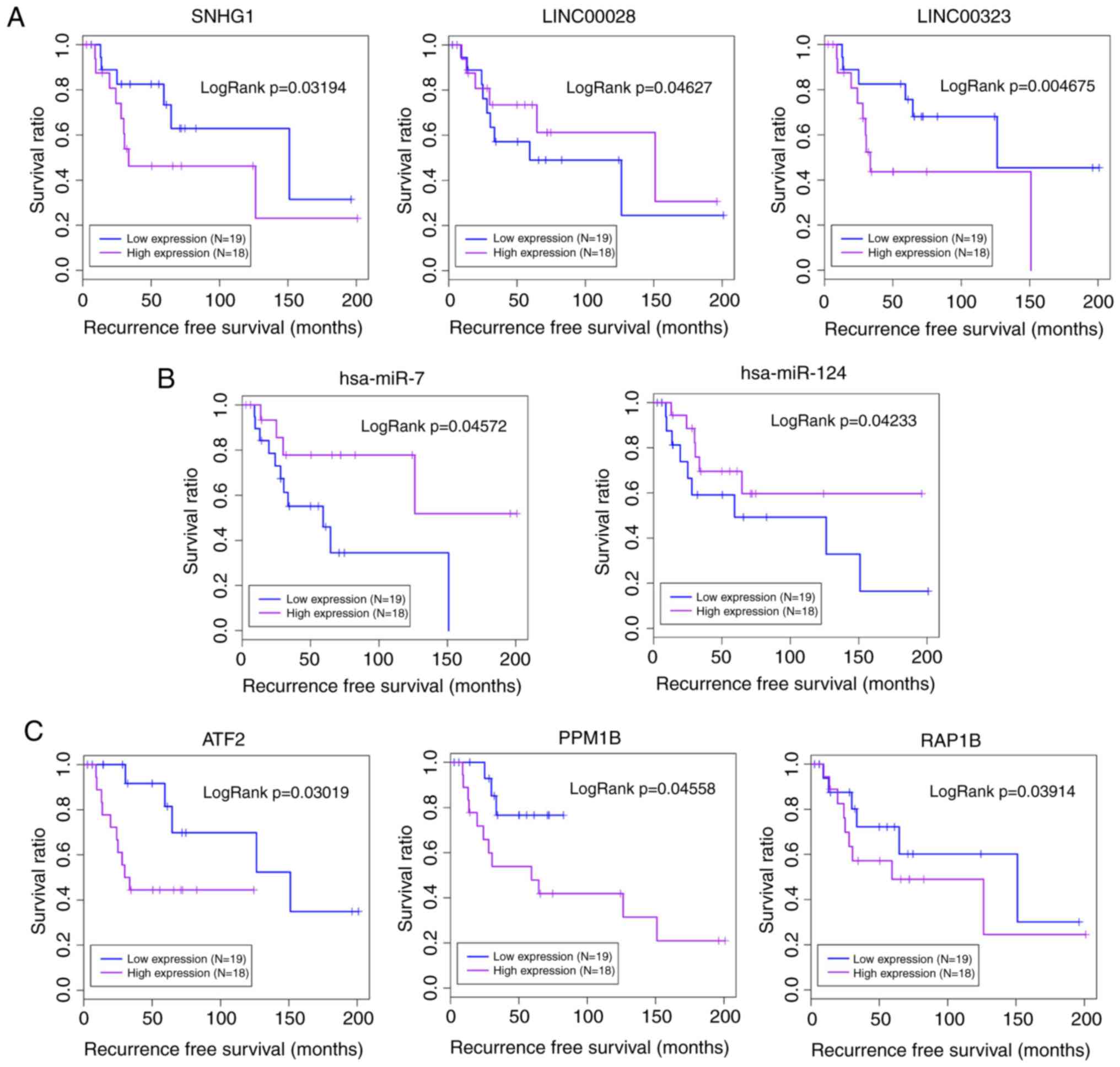
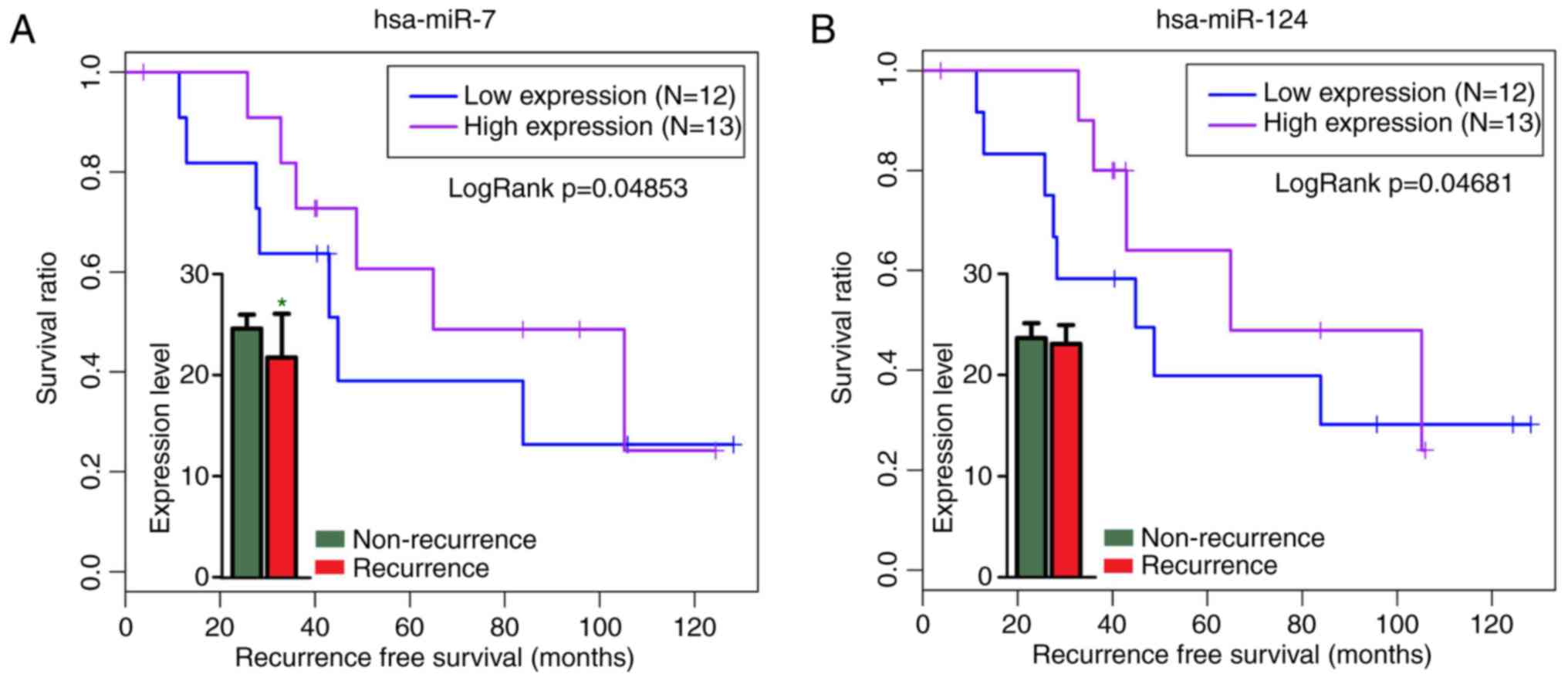
N, Parenti C, Salvatorelli L, Magro G and Parenti R: Wilms' tumor
gene 1 silencing inhibits proliferation of human osteosarcoma MG-63
cell line by cell cycle arrest and apoptosis activation.
Oncotarget. 8:13917–13931. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang F, Yan T, Guo W, Sun K, Wang S, Bao
X, Liu K, Zheng B, Zhang H and Ren T: Novel oncogene COPS3
interacts with beclin1 and Raf-1 to regulate metastasis of
osteosarcoma through autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1352018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan LH, Wang W, Yeung W, Deng Y, Yuan P
and Mak KK: Hedgehog signaling induces osteosarcoma development
through Yap1 and H19 overexpression. Oncogene. 33:4857–4866. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhou S, Yu L, Xiong M and Dai G: LncRNA
SNHG12 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in osteosarcoma by
upregulating Notch2 by sponging miR-195-5p. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 495:1822–1832. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang S, Li Z, Li D, Yang
S, Zhang H, Zeng X and Liu J: LncRNA FAL1 is a negative prognostic
biomarker and exhibits pro-oncogenic function in osteosarcoma. J
Cell Biochem. 119:8481–8489. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian ZZ, Guo XJ, Zhao YM and Fang Y:
Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA MEG3 acts as a
potential predictor biomarker in progression and poor prognosis of
osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15138–15142. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Wang Y and Kong D: Knockdown of lncRNA
MEG3 inhibits viability, migration, and invasion and promotes
apoptosis by sponging miR-127 in osteosarcoma cell. J Cell Biochem.
119:669–679. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou Q, Chen F, Fei Z, Zhao J, Liang Y,
Pan W, Liu X and Zheng D: Genetic variants of lncRNA HOTAIR
contribute to the risk of osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:19928–19934.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma B, Li M, Zhang L, Huang M, Lei JB, Fu
GH, Liu CX, Lai QW, Chen QQ and Wang YL: Upregulation of long
non-coding RNA TUG1 correlates with poor prognosis and disease
status in osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 37:4445–4455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li F, Cao L, Hang D, Wang F and Wang Q:
Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP is up-regulated and associated with poor
prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:11414–11420. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA
language. Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kelly AD, Haibe-Kains B, Janeway KA, Hill
KE, Howe E, Goldsmith J, Kurek K, Perez-Atayde AR, Francoeur N, Fan
JB, et al: MicroRNA paraffin-based studies in osteosarcoma reveal
reproducible independent prognostic profiles at 14q32. Genome Med.
5:22013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bolstad B: PreprocessCore: A collection of
pre-processing functions. R package version 1. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data Bioinformatics computational biology Solutions
Using R Bioconductor. Springer; pp. 397–420. 2005
|
|
21
|
Rao Y, Lee Y, Jarjoura D, Ruppert AS, Liu
CG, Hsu JC and Hagan JP: A comparison of normalization techniques
for microRNA microarray data. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol.
7:Article222008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yates B, Braschi B, Gray KA, Seal RL,
Tweedie S and Bruford EA: http://Genenames.orgurisimpleGenenames.org: The HGNC
and VGNC resources in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:D619–D625. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gosling C: Encyclopedia of distances.
Reference Rev. 24:1–583. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Wang P, Wang Y, Hang B, Zou X and Mao JH:
A novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict
survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55343–55351.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang Da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nature Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 12:42015.
|
|
30
|
Lee YY, Kim TJ, Kim JY, Choi CH, Do IG,
Song SY, Sohn I, Jung SH, Bae DS, Lee JW and Kim BG: Genetic
profiling to predict recurrence of early cervical cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 131:650–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeggari A, Marks DS and Larsson E:
miRcode: A map of putative microRNA target sites in the long
non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics. 28:2062–2063. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ, Sciaky
D, King BL, McMorran R, Wiegers J, Wiegers TC and Mattingly CJ: The
comparative toxicogenomics database: Update 2017. Nucleic Acids
Res. 45:D972–D978. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
He JP, Hao Y, Wang XL, Yang XJ, Shao JF,
Guo FJ and Feng JX: Review of the molecular pathogenesis of
osteosarcoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5967–5976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang B, Su Y, Yang Q, Lv D, Zhang W, Tang
K, Wang H, Zhang R and Liu Y: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR promotes tumor growth and metastasis in human osteosarcoma.
Mol Cells. 38:432–440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP
and Yao J: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits
osteo-sarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 14:2311–2325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen HJ, Lin CM, Lee CY, Shih NC, Peng SF,
Tsuzuki M, Amagaya S, Huang WW and Yang JS: Kaempferol suppresses
cell metastasis via inhibition of the ERK-p38-JNK and AP-1
signaling pathways in U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep.
30:925–932. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheng DD, Zhu B, Li SJ, Yuan T, Yang QC
and Fan CY: Down-regulation of RPS9 inhibits osteosarcoma cell
growth through inactivation of MAPK signaling pathway. J Cancer.
8:2720–2728. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng S, Zhang X, Huang N, Qiu Q, Jin Y
and Jiang D: Down-regulation of S100A9 inhibits osteosarcoma cell
growth through inactivating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. BMC
Cancer. 16:2532016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li L, Liang S, Wasylishen AR, Zhang Y,
Yang X, Zhou B, Shan L, Han X, Mu T, Wang G and Xiong S: PLA2G16
promotes osteosarcoma metastasis and drug resistance via the MAPK
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:18021–18035. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kang HM, Park BS, Kang HK, Park HR, Yu SB
and Kim IR: Delphinidin induces apoptosis and inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the ERK/p38 MAPK-signaling
pathway in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Environ Toxicol.
33:640–649. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y, Hu Q, Li G, Li L, Liang S, Zhang
Y, Liu J, Fan Z, Li L, Zhou B, et al: ONZIN upregulation by mutant
p53 contributes to osteosarcoma metastasis through the CXCL5-MAPK
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1099–1111. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Geng S, Zhang X, Chen J, Liu X, Zhang H,
Xu X, Ma Y, Li B, Zhang Y, Bi Z and Yang C: The tumor suppressor
role of miR-124 in osteosarcoma. PLoS one. 9:e915662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shouying L, Changxi Z, Changbao Z, Qiuhe
S, Ming W, Ye L and Huaijie A: Low-expression of miR-7 promotes
cell proliferation and exhibits prognostic value in osteosarcoma
patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9035–9041. 2017.
|
|
48
|
Wang J, Cao L, Wu J and Wang Q: Long
non-coding RNA SNHG1 regulates NOB1 expression by sponging miR-326
and promotes tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 52:77–88.
2018.
|
|
49
|
Jiang Z, Jiang C and Fang J: Up-regulated
lnc-SNHG1 contributes to osteosarcoma progression through
sequestration of miR-577 and activation of WNT2B/Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:238–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|