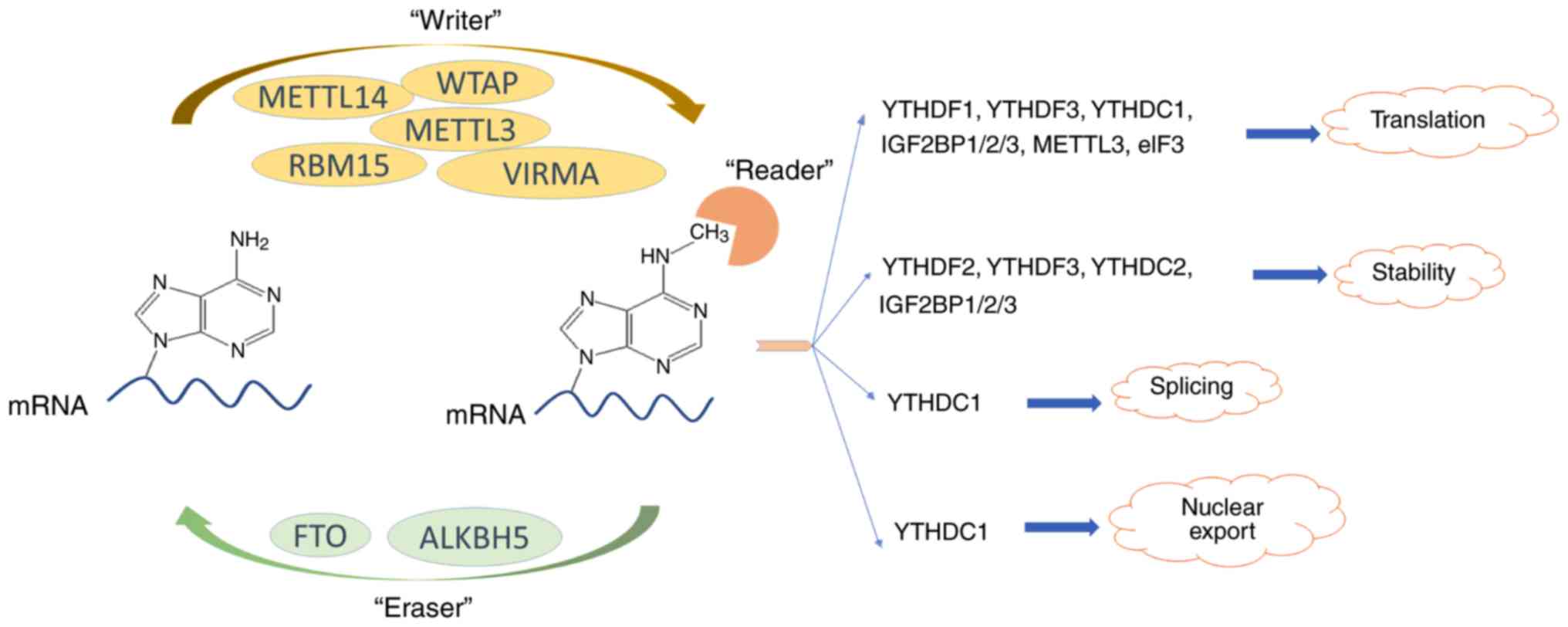
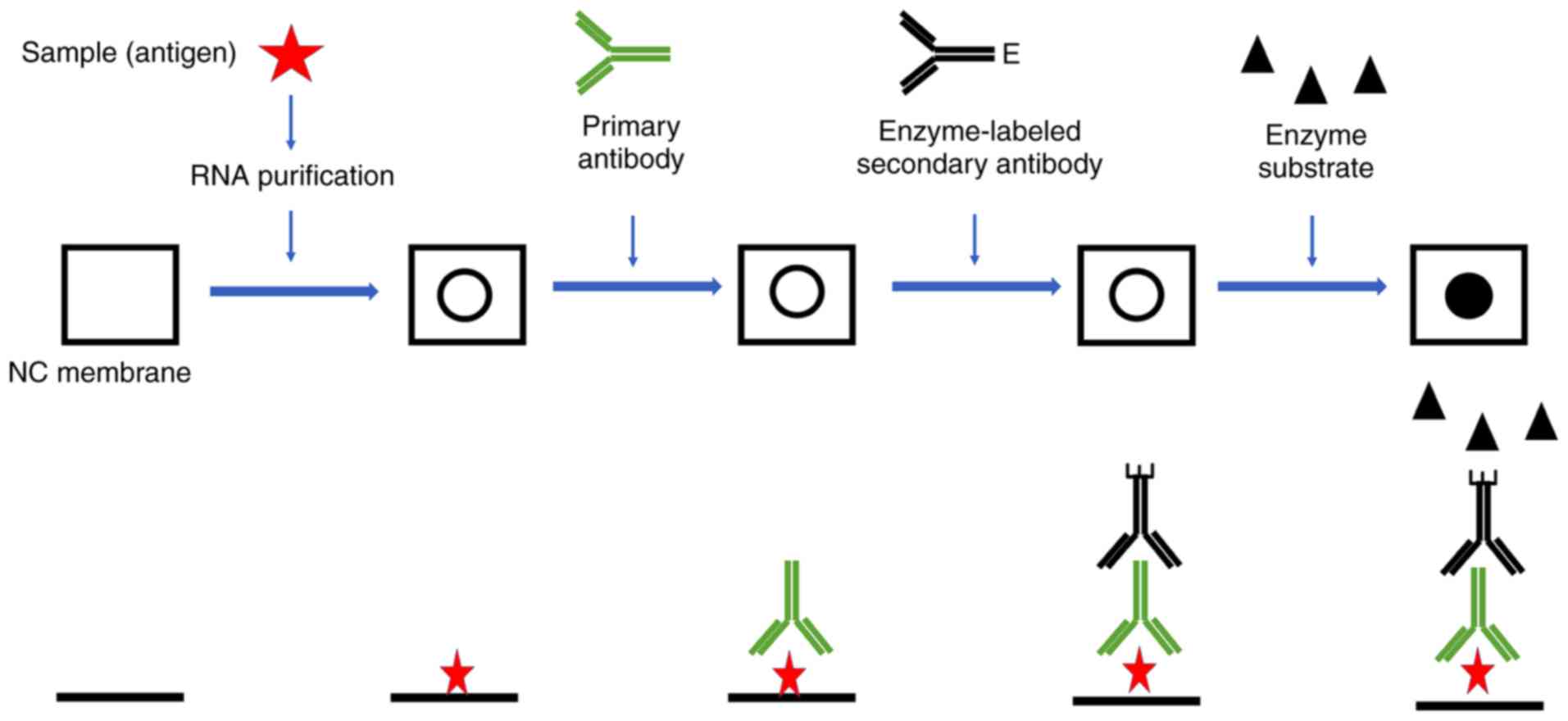
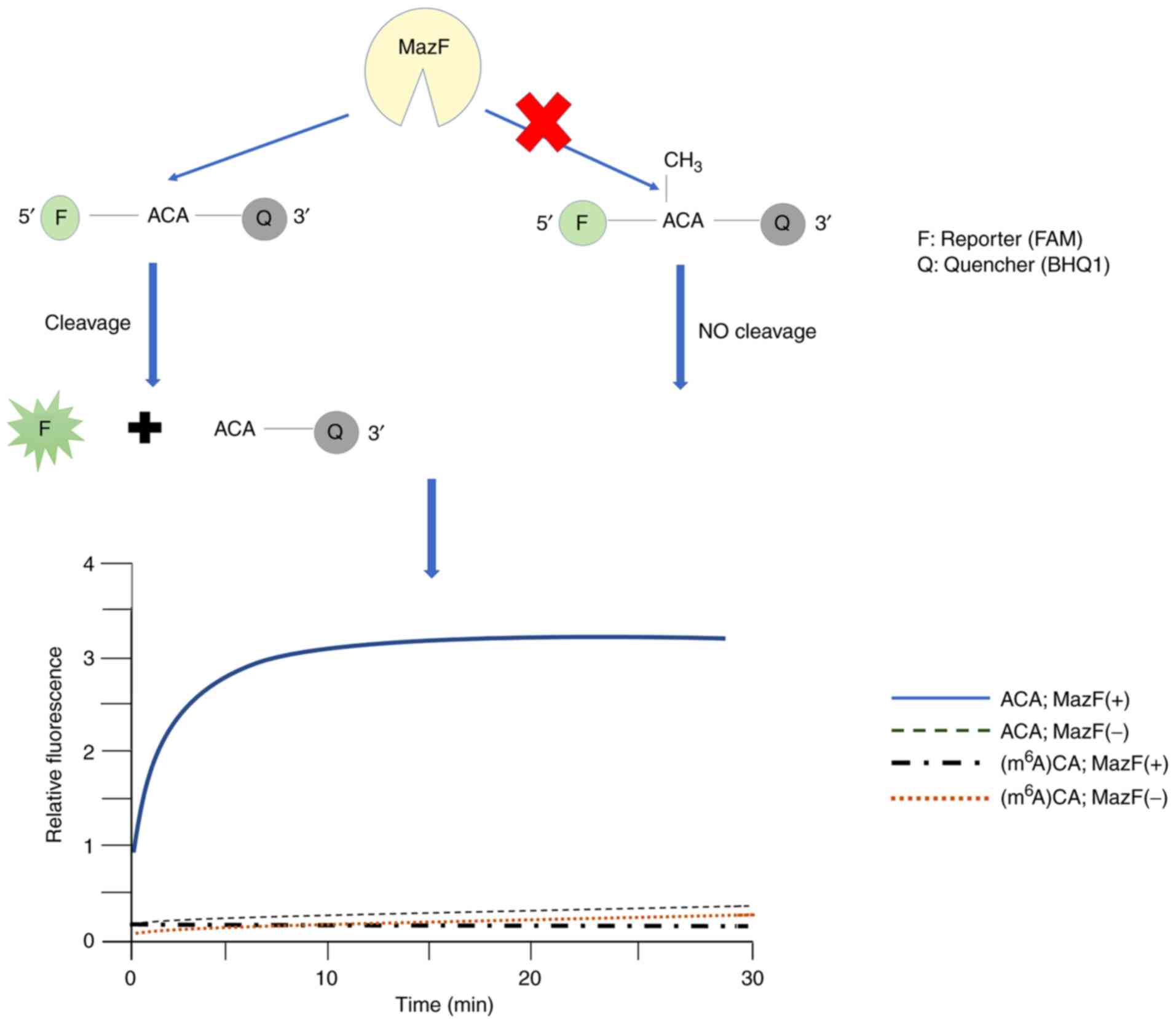
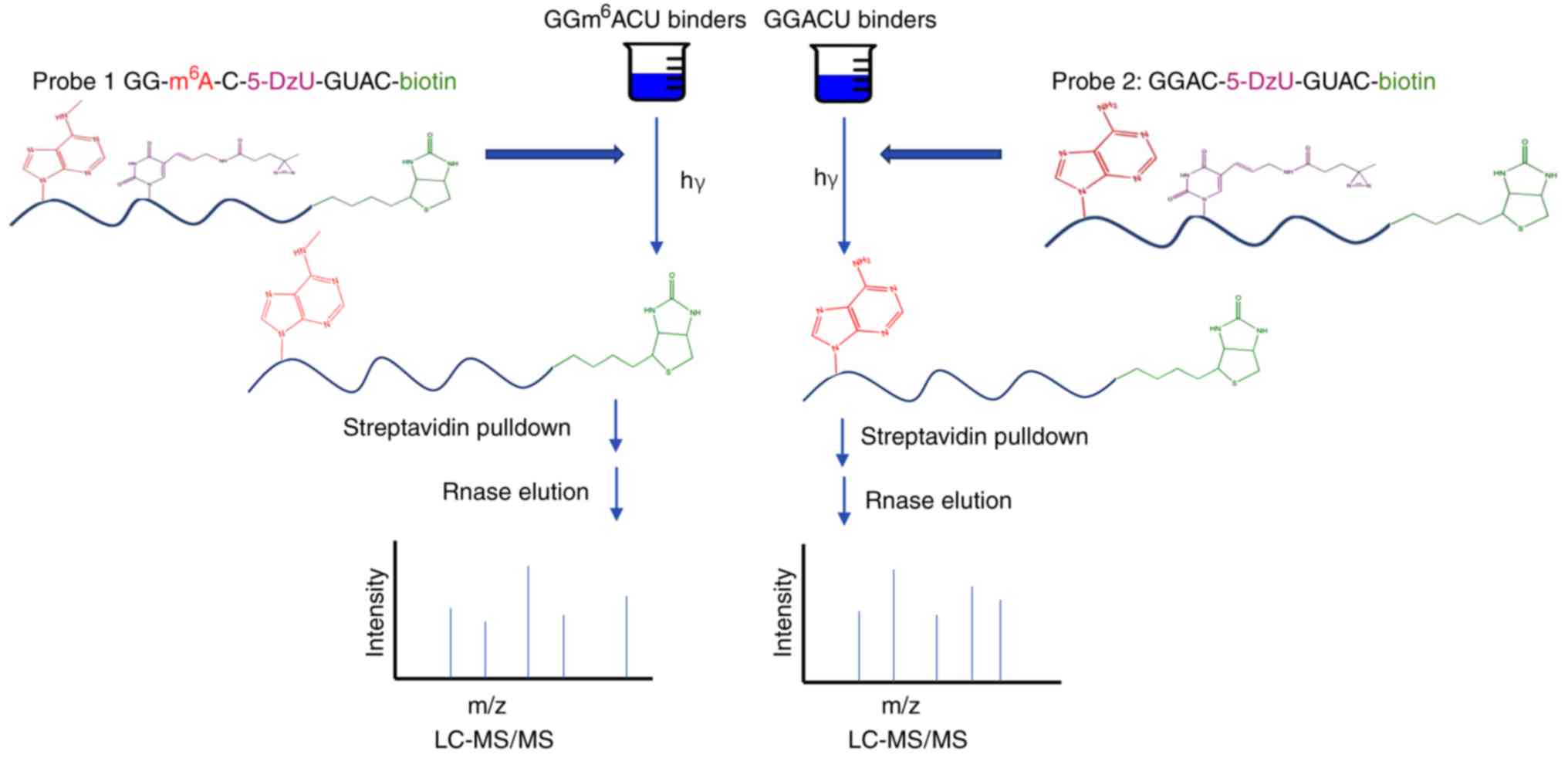
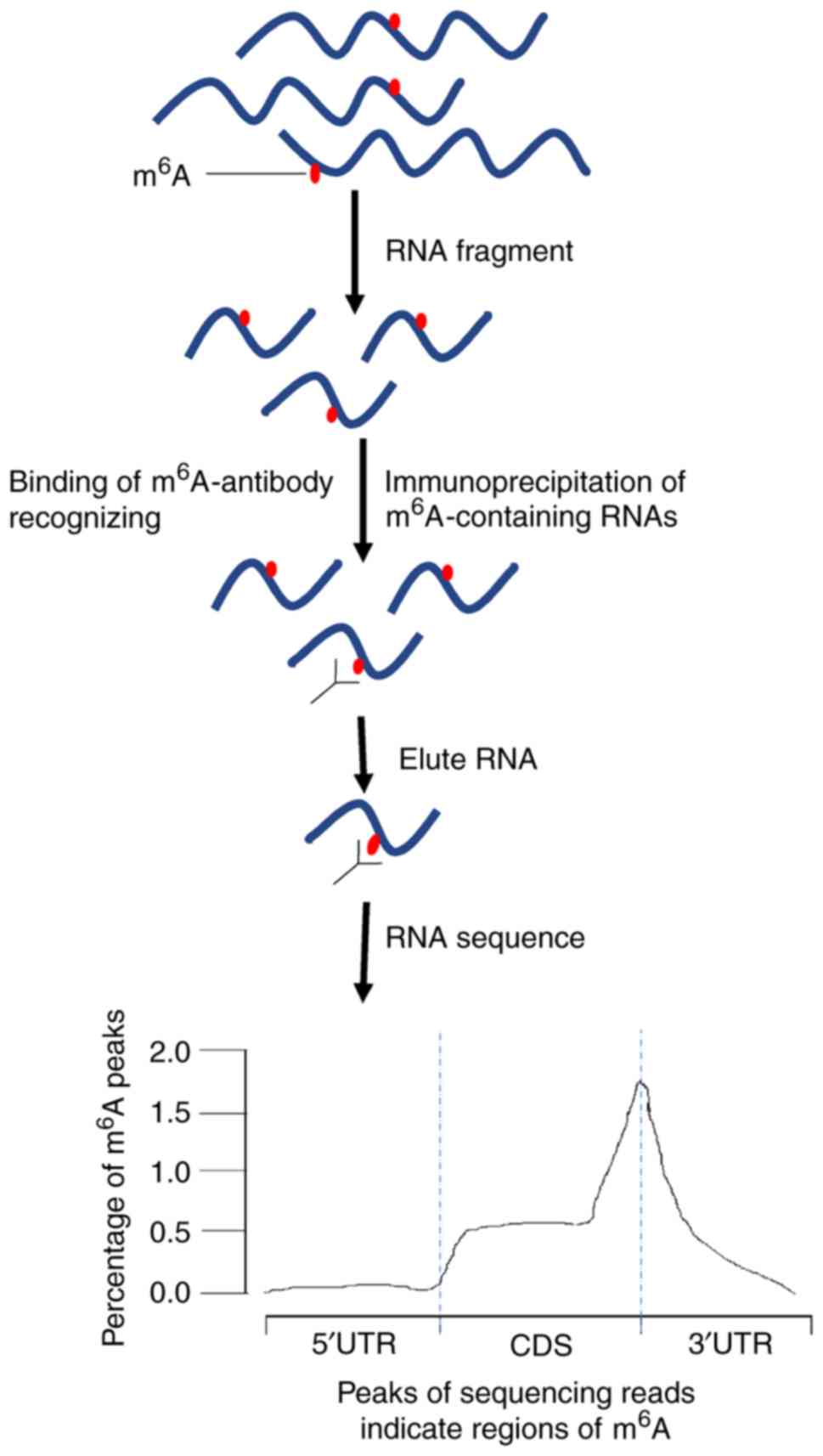
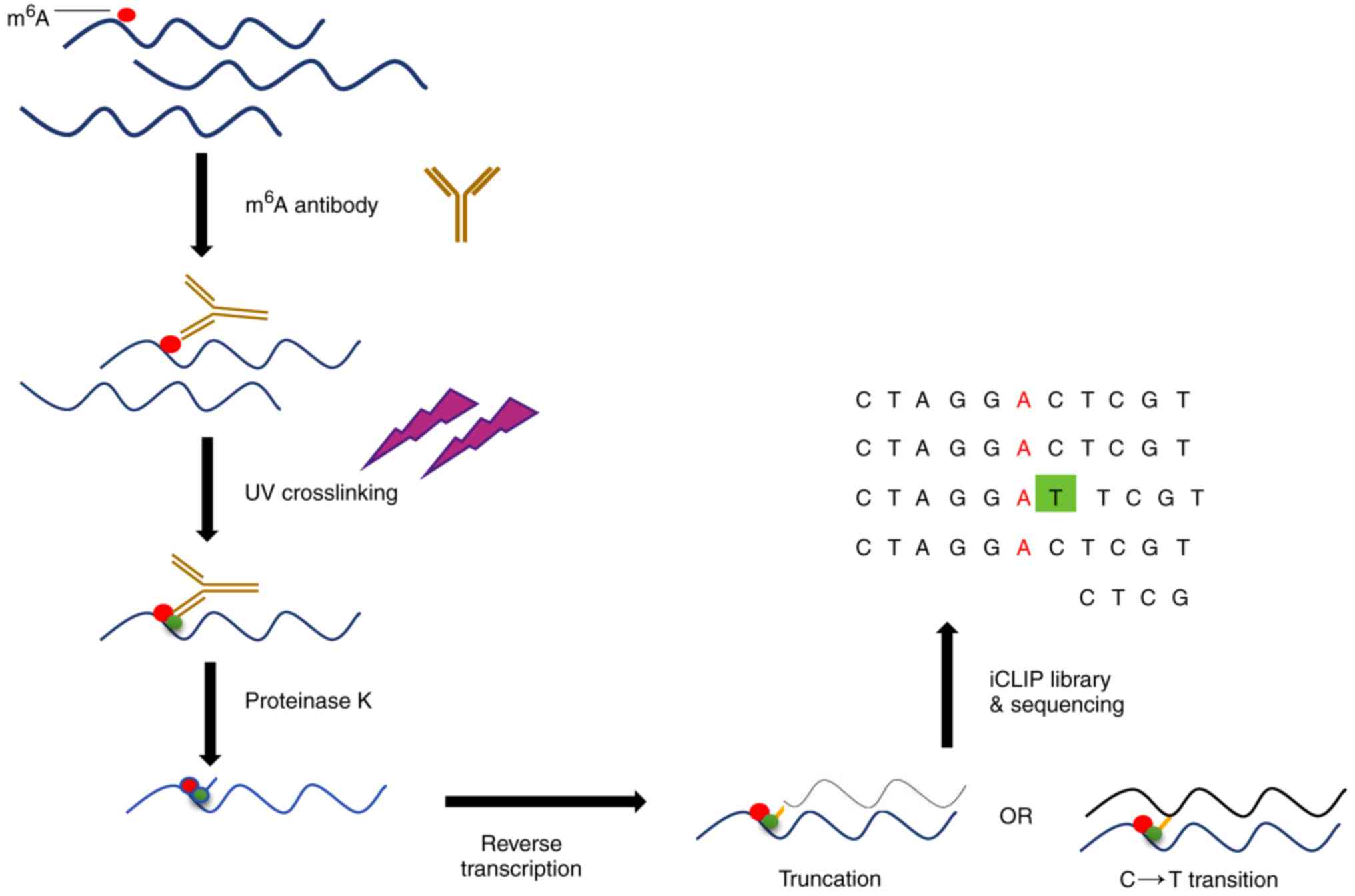
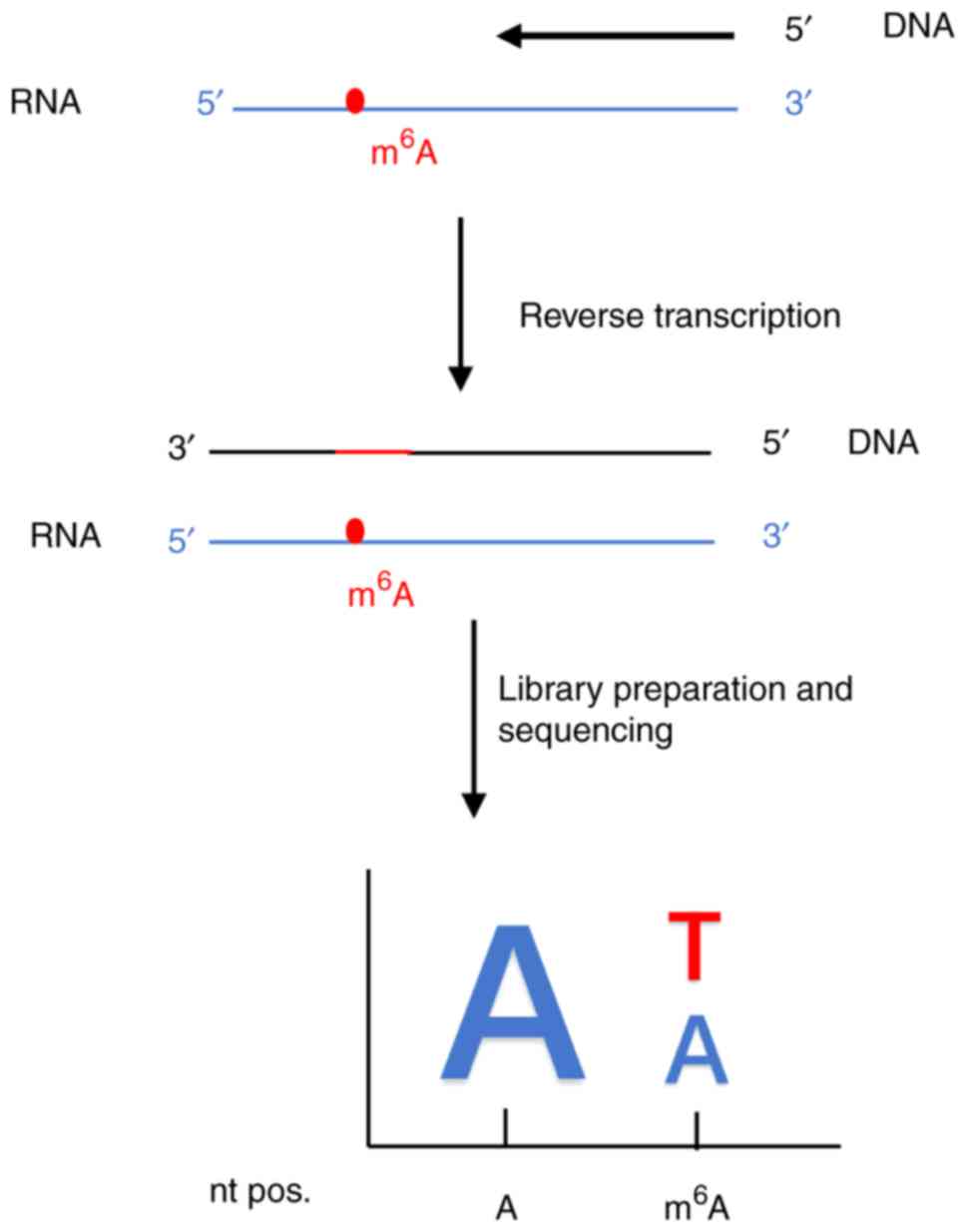
|
1
|
He C: Grand challenge commentary: RNA
epigenetics. Nat Chem Biol. 6:863–865. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meye KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O,
Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation
reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.
149:1635–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S,
Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al: Topology of the human
and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature.
485:201–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Desrosiers R, Friderici K and Rottman F:
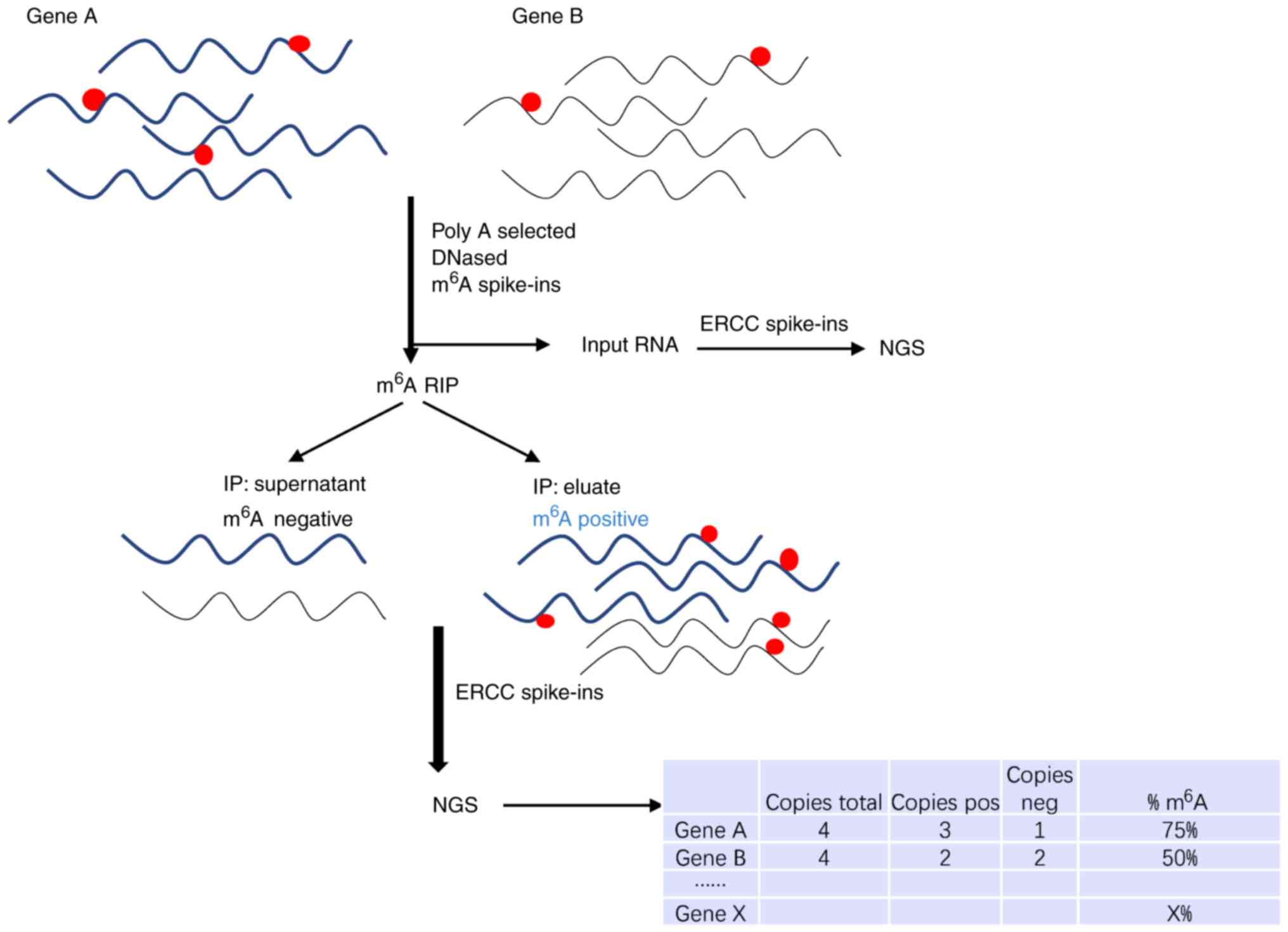
Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from
novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 71:3971–3975.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
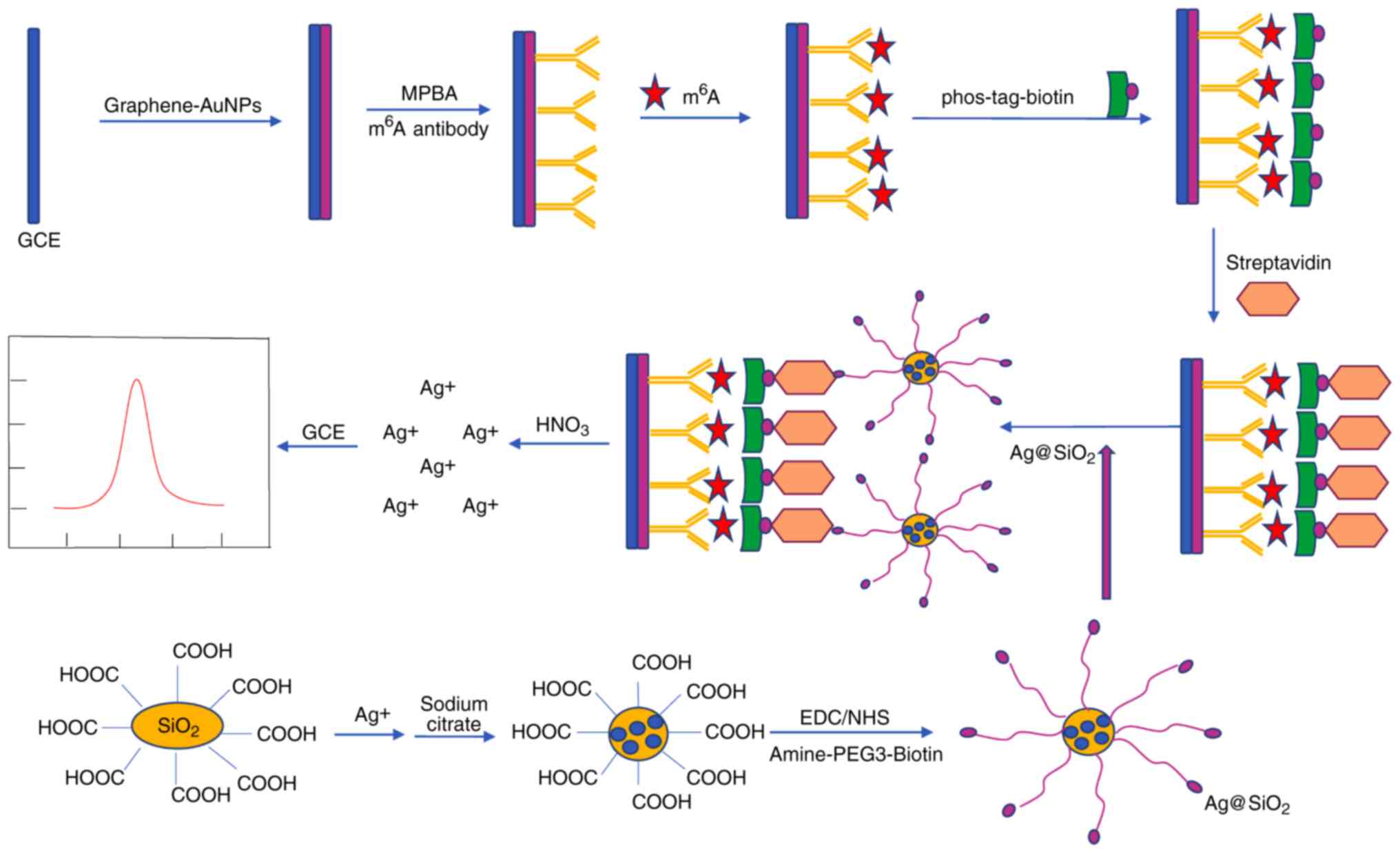
|
|
5
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Modified nucleosides
and bizarre 5′-termini in mouse myeloma mRNA. Nature. 255:28–33.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
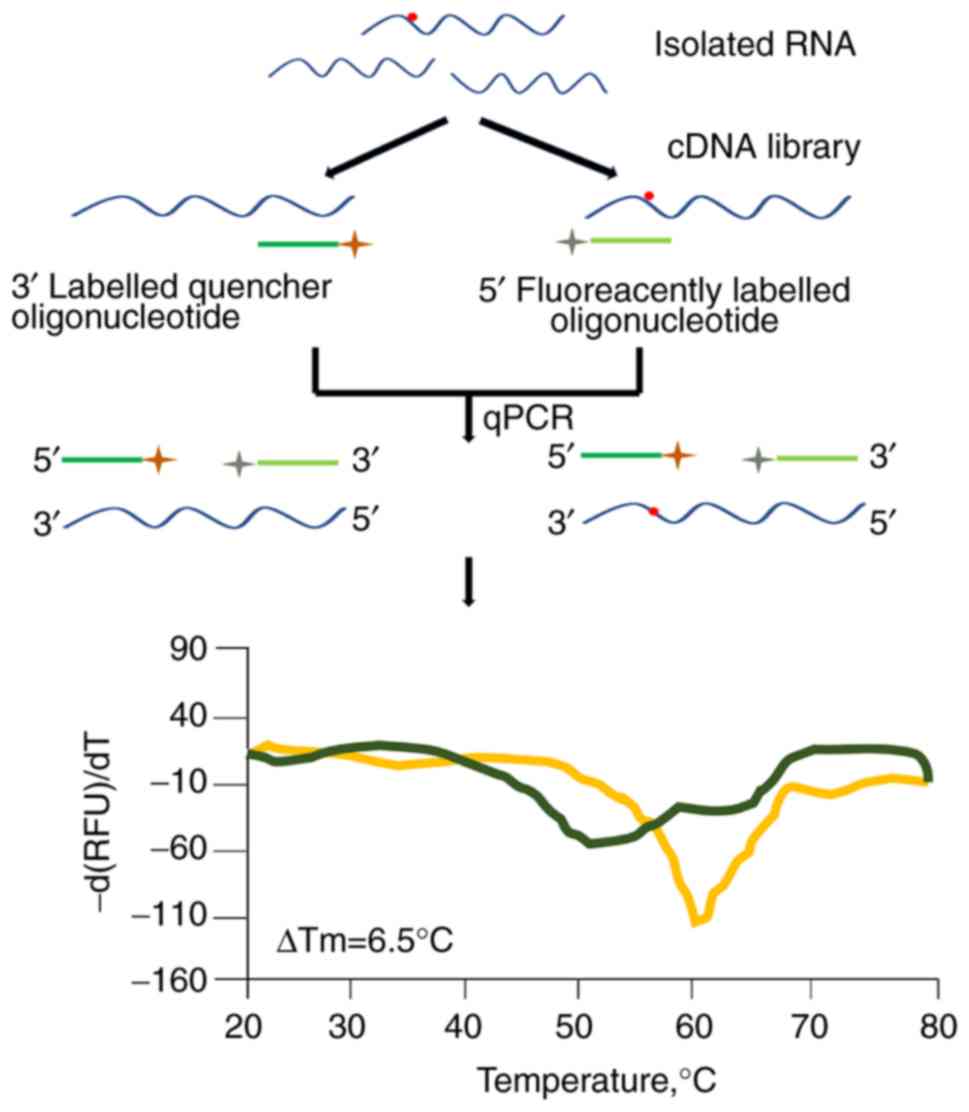
|
6
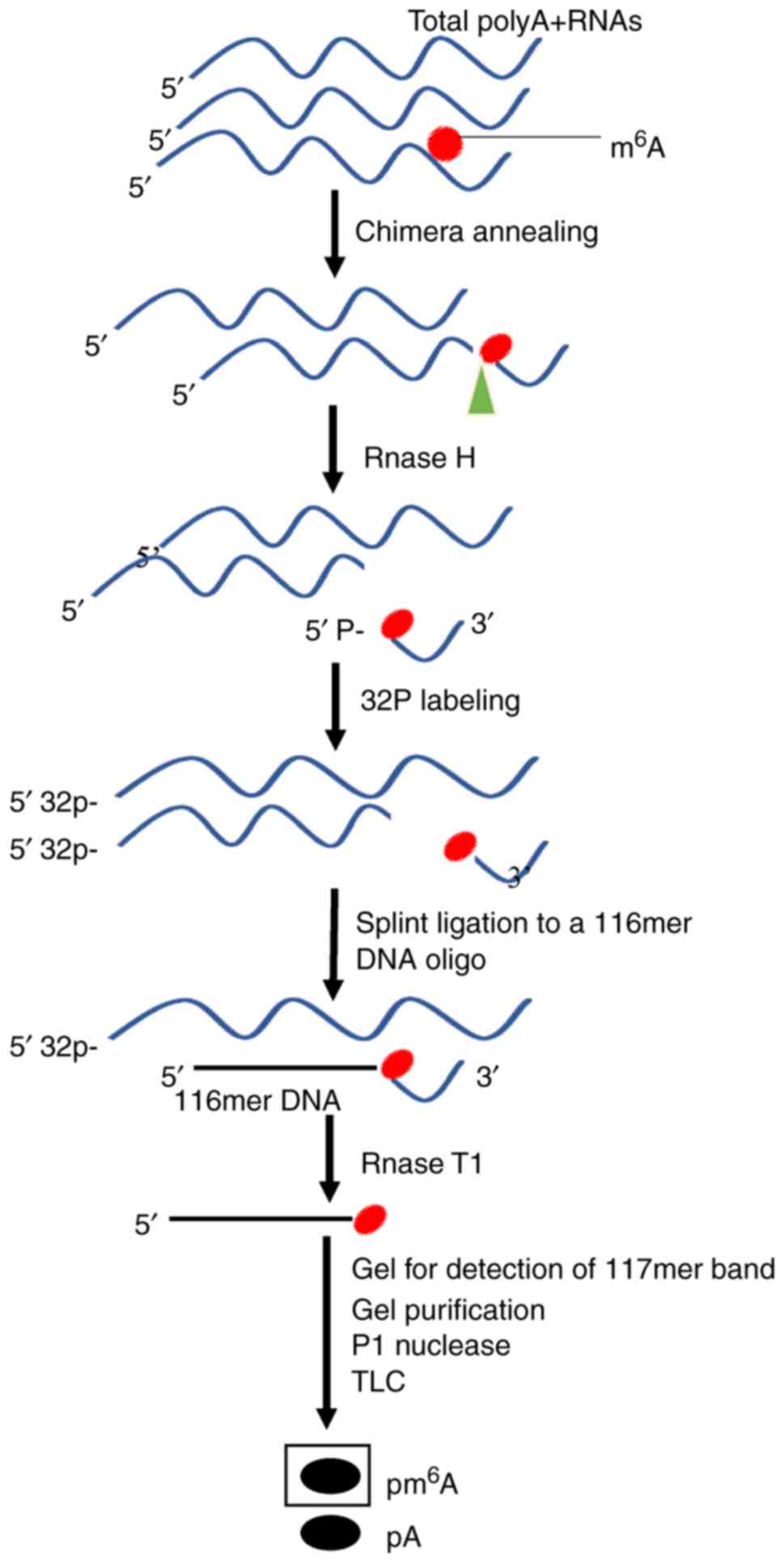
|
Wei CM, Gershowitz A and Moss B:
Methylated nucleotides block 5′ terminus of HeLa cell messenger
RNA. Cell. 4:379–386. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Narayan P and Rottman FM: Methylation of
mRNA. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 65:255–285. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dubin DT and Taylor RH: The methylation
state of poly A-containing messenger RNA from cultured hamster
cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2:1653–1668. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haugland RA and Cline MG:
Post-transcriptional modifications of oat coleoptile ribonucleic
acids. 5′-Terminal capping and methylation of internal nucleosides
in poly(A)-rich RNA. Eur J Biochem. 104:271–277. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Niu Y, Zhao X, Wu YS, Li MM, Wang XJ and
Yang YG: N6-methyl-adenosine (m6A) in RNA: An old modification with
a novel epigenetic function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
11:8–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, Matera
AG and Rottman FM: Purification and cDNA cloning of the
AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA
(N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA. 3:1233–1247. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X,
Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, et al: Mammalian WTAP is
a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine
methyltransferase. Cell Res. 24:177–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang
T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N,
Cacchiarelli D, et al: Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two
distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell
Rep. 8:284–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ear J and Lin S: RNA methylation regulates
hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell development. J Genet
Genomics. 44:473–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang P, Doxtader KA and Nam Y: Structural
basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14
methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 63:306–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A,
Jackson C, Guttman M and Jaffrey SR: m(6)A RNA methylation promotes
XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 537:369–373.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pendleton KE, Chen B, Liu K, Hunter OV,
Xie Y, Tu BP and Conrad NK: The U6 snRNA m6A
Methyltransferase METTL16 Regulates SAM Synthetase Intron
Retention. Cell. 169:824–835.e814. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang
Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG and He C: N6-methyladenosine in
nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat
Chem Bio. 7:885–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P,
Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al: ALKBH5
is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and
mouse fertility. Mol cell. 49:18–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han
D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H and He C: N(6)-methyladenosine
modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell.
161:1388–1399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han
D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, et al:
N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability.
Nature. 505:117–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao
YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, et al: Nuclear m(6)A
reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 61:507–519. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, Wang X,
Zhou T, Cui Y, Sha J, Huang X, Guerrero L, Xie P, et al: YTHDC1
mediates nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine methylated
mRNAs. Elife. 6:e313112017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Theler D, Dominguez C, Blatter M, Boudet J
and Allain FH: Solution structure of the YTH domain in complex with
N6-methyladenosine RNA: A reader of methylated RNA. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:13911–13919. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saletore Y, Meyer K, Korlach J, Vilfan ID,
Jaffrey S and Mason CE: The birth of the Epitranscriptome:
Deciphering the function of RNA modifications. Genome Biol.
13:1752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aschenbrenner J, Werner S, Marchand V,
Adam M, Motorin Y, Helm M and Marx A: Engineering of a DNA
polymerase for direct m6A sequencing. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
57:417–421. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Molinie B, Wang J, Lim KS, Hillebrand R,
Lu ZX, Van Wittenberghe N, Howard BD, Daneshvar K, Mullen AC, Dedon
P, et al: m6A level and isoform characterization sequencing
(m6A-LAICseq) reveals the census and complexity of the m6A
epitranscriptome. Nat Methods. 13:692–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagarajan A, Janostiak R and Wajapeyee N:
Dot blot analysis for measuring global
N6-methyladenosine modification of RNA. Methods Mol
Biol. 1870:263–271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Arguello AE, DeLiberto AN and Kleiner RE:
RNA chemical proteomics reveals the N6-methyladenosine
(m6A)-regulated protein-RNA interactome. J Am Chem Soc.
139:17249–17252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin H, Wang H, Jiang W, Zhou Y and Ai S:
Electrochemical immunosensor for N6-methyladenosine detection in
human cell lines based on biotin-streptavidin system and
silver-SiO2 signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron.
90:494–500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO,
Meydan C, Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Single-nucleotide-resolution
mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods.
12:767–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weng Li Z, Su H, Weng R, Zuo X, Li Z,
Huang C, Nachtergaele H, Dong S, Hu LC, et al: FTO plays an
oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a
N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell.
31:127–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Yue M, Wang J, Kumar S,
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Zhang Z, Ogawa Y, Kellis M, Duester G and Zhao
JC: N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates
embryonic neural stem cell self-renewal through histone
modifications. Nat Neurosci. 21:195–206. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Imanishi M, Tsuji S, Suda A and Futaki S:
Detection of N6-methyladenosine based on the
methyl-sensitivity of MazF RNA endonuclease. Chem Commun (Camb).
53:12930–12933. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mishima E, Jinno D, Akiyama Y, Itoh K,
Nankumo S, Shima H, Kikuchi K, Takeuchi Y, Elkordy A, Suzuki T, et
al: Immuno-Northern blotting: Detection of RNA modifications by
using antibodies against modified nucleosides. PLoS One.
10:e01437562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mishima E and Abe T: Immuno-northern
blotting: Detection of modified RNA using gel separation and
antibodies to modified nucleosides. Methods Mol Biol. 1870:179–187.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen W, Feng P, Ding H and Lin H:
Identifying N6-methyladenosine sites in the Arabidopsis
thaliana transcrip-tome. Mol Genet Genomics. 291:2225–2229. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Golovina AY, Dzama MM, Petriukov KS,
Zatsepin TS, Sergiev PV, Bogdanov AA and Dontsova OA: Method for
site-specific detection of m6A nucleoside presence in RNA based on
high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:e27.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lopez CM, Lloyd AJ, Leonard K and
Wilkinson MJ: Differential effect of three base modifications on
DNA thermostability revealed by high resolution melting. Anal Chem.
84:7336–7342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu N, Parisien M, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C
and Pan T: Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at
single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA.
19:1848–1856. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jacob R, Zander S and Gutschner T: The
dark side of the epitranscriptome: Chemical modifications in long
non-coding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E23872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li X, Zhu P, Ma S, Song J, Bai J, Sun F
and Yi C: Chemical pulldown reveals dynamic pseudouridylation of
the mammalian transcriptome. Nat Chem Biol. 11:592–597. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Antanaviciute A, Baquero-Perez B, Watson
CM, Harrison SM, Lascelles C, Crinnion L, Markham AF, Bonthron DT,
Whitehouse A and Carr IM: M6aViewer: Software for the detection,
analysis, and visualization of N6-methyladenosine peaks
from m6A-seq/ME-RIP sequencing data. RNA. 23:1493–1501.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cui X, Meng J, Zhang S, Chen Y and Huang
Y: A novel algorithm for calling mRNA m6A peaks by modeling
biological variances in MeRIP-seq data. Bioinformatics.
32:i378-i3852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meng J, Lu Z, Liu H, Zhang L, Zhang S,
Chen Y, Rao MK and Huang Y: A protocol for RNA methylation
differential analysis with MeRIP-Seq data and exomePeak
R/Bioconductor package. Methods. 69:274–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu H, Wang H, Wei Z, Zhang S, Hua G,
Zhang SW, Zhang L, Gao SJ, Meng J, Chen X and Huang Y: MeT-DB V2.0:
Elucidating context-specific functions of N6-methyl-adenosine
methyltran-scriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D281–D287. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhou C, Molinie B, Daneshvar K, Pondick
JV, Wang J, Van Wittenberghe N, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC and Mullen
AC: Genome-wide maps of m6A circRNAs identify widespread and
cell-type-specific methylation patterns that are distinct from
mRNAs. Cell Rep. 20:2262–2276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang M, Li Q and Xie Y: A Bayesian
hierarchical model for analyzing methylated RNA immunoprecipitation
sequencing data. Quant Biol. 6:275–286. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Rana AP and Tuck MT: Analysis and in vitro
localization of internal methylated adenine residues in
dihydrofolate reductase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:4803–4808.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ehrlich M, Gama-Sosa MA, Carreira LH,
Ljungdahl LG, Kuo KC and Gehrke CW: DNA methylation in thermophilic
bacteria: N4-methylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and
N6-methyladenine. Nucleic Acids Res. 13:1399–1412. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Clancy MJ, Shambaugh ME, Timpte CS and
Bokar JA: Induction of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
leads to the formation of N6-methyladenosine in mRNA: A potential
mechanism for the activity of the IME4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res.
30:4509–4518. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Shi Y, Yang X,
Xiao W, Hao YJ, Ping XL, Chen YS, Wang WJ, et al: FTO-dependent
demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is
required for adipogenesis. Cell Res. 24:1403–1419. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi
J, Millán-Zambrano G, Robson SC, Aspris D, Migliori V, Bannister
AJ, Han N, et al: Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia
by m6A-dependent translation control. Nature.
552:126–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tang Li X, Huang J, Wang W, Li F, Qin P,
Qin C, Zou Z, Wei Q, Hua JL, et al: The M6A methyltransferase
METTL3: Acting as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:96103–96116. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Miao Z, Xin N, Wei B, Hua X, Zhang G, Leng
C, Zhao C, Wu D, Li J, Ge W, et al: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is
detected in RNA from mouse brain tissues. Brain Res. 1642:546–552.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rona G, Scheer I, Nagy K, Pálinkás HL,
Tihanyi G, Borsos M, Békési A and Vértessy BG: Detection of uracil
within DNA using a sensitive labeling method for in vitro and
cellular applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:e282016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Wehr NB and Levine RL: Quantitation of
protein carbonylation by dot blot. Anal Biochem. 423:241–245. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jaffrey SR and Kharas MG: Emerging links
between m6A and misregulated mRNA methylation in cancer. Genome
Med. 9:22017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Kwok CT, Marshall AD, Rasko JE and Wong
JJ: Genetic alterations of m6A regulators predict poorer
survival in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 10:392017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhang C, Zhi WI, Lu H, Samanta D, Chen I,
Gabrielson E and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate
pluripotency factor expression by ZNF217- and ALKBH5-mediated
modulation of RNA methylation in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:64527–64542. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Inouye M: The discovery of mRNA
interferases: Implication in bacterial physiology and application
to biotechnology. J Cell Physiol. 209:670–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gerstberger S, Hafner M and Tuschl T: A
census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 15:829–845.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Licatalosi DD, Mele A, Fak JJ, Ule J,
Kayikci M, Chi SW, Clark TA, Schweitzer AC, Blume JE, Wang X, et
al: HITS-CLIP yields genome-wide insights into brain alternative
RNA processing. Nature. 456:464–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dubinsky L, Krom BP and Meijler MM:
Diazirine based photoaffinity labeling. Bioorg Med Chem.
20:554–570. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Kauer JC, Erickson-Viitanen S, Wolfe HR Jr
and DeGrado WF: p-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine, a new photoreactive
amino acid. Photolabeling of calmodulin with a synthetic
calmodulin-binding peptide. J Biol Chem. 261:10695–10700.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhu T, Roundtree IA, Wang P, Wang X, Wang
L, Sun C, Tian Y, Li J, He C and Xu Y: Crystal structure of the YTH
domain of YTHDF2 reveals mechanism for recognition of
N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 24:1493–1496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu C, Wang X, Liu K, Roundtree IA, Tempel
W, Li Y, Lu Z, He C and Min J: Structural basis for selective
binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain. Nat Chem Biol.
10:927–929. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu
PJ, Liu C and He C: YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of
N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 27:315–328.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Luo GZ, MacQueen A, Zheng G, Duan H, Dore
LC, Lu Z, Liu J, Chen K, Jia G, Bergelson J and He C: Unique
features of the m6A methylome i. Arabidopsis thaliana Nat Commun.
5:56302014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Piekna-Przybylska D, Decatur WA and
Fournier MJ: The 3D rRNA modification maps database: With
interactive tools for ribosome analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:D178–D183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang
Z and Zhao JC: N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes
developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol.
16:191–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A,
Skabkin MA, Elemento O, Pestova TV, Qian SB and Jaffrey SR: 5′ UTR
m(6)a promotes cap-independent translation. Cell. 163:999–1010.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R and
Gregory RI: The m(6)a methyltransferase Mettl3 promotes translation
in human cancer cells. Mol Cell. 62:335–345. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G and He C:
Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible
m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 15:293–306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang
Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang W and Ye L: HBXIP-elevated
methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer
via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 415:11–19.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun
G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, et al: m6A RNA methylation
regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem
cells. Cell Rep. 18:2622–2634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li Y, Zheng D, Wang F, Xu Y, Yu H and
Zhang H: Expression of demethylase genes, fto and alkbh1, is
associated with prognosis of gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Wang X, Li Z, Kong B, Song C, Cong J, Hou
J and Wang S: Reduced m6A mRNA methylation is correlated
with the progression of human cervical cancer. Oncotarget.
8:98918–98930. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhou J, Wang J, Hong B, Ma K, Xie H, Li L,
Zhang K, Zhou B, Cai L and Gong K: Gene signatures and prognostic
values of m6A regulators in clear cell renal cell carcinoma-a
retrospective study using TCGA database. Aging (Albany NY).
11:1633–1647. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J,
Cheng CL, Tsang LH, Ho DW, Chiu DK, Lee JM, et al: RNA
N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer
progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing
of SOCS2. Hepatology. 67:2254–2270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|