|
1
|
Li X, Yue S and Luo Z: Mesenchymal stem
cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Oncotarget.
8:102600–102616. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu YM, Nepali K and Liou JP: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis: Current status, recent progress and emerging
targets. J Med Chem. 60:527–553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Knudsen L, Ruppert C and Ochs M: Tissue
remodelling in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 367:607–626.
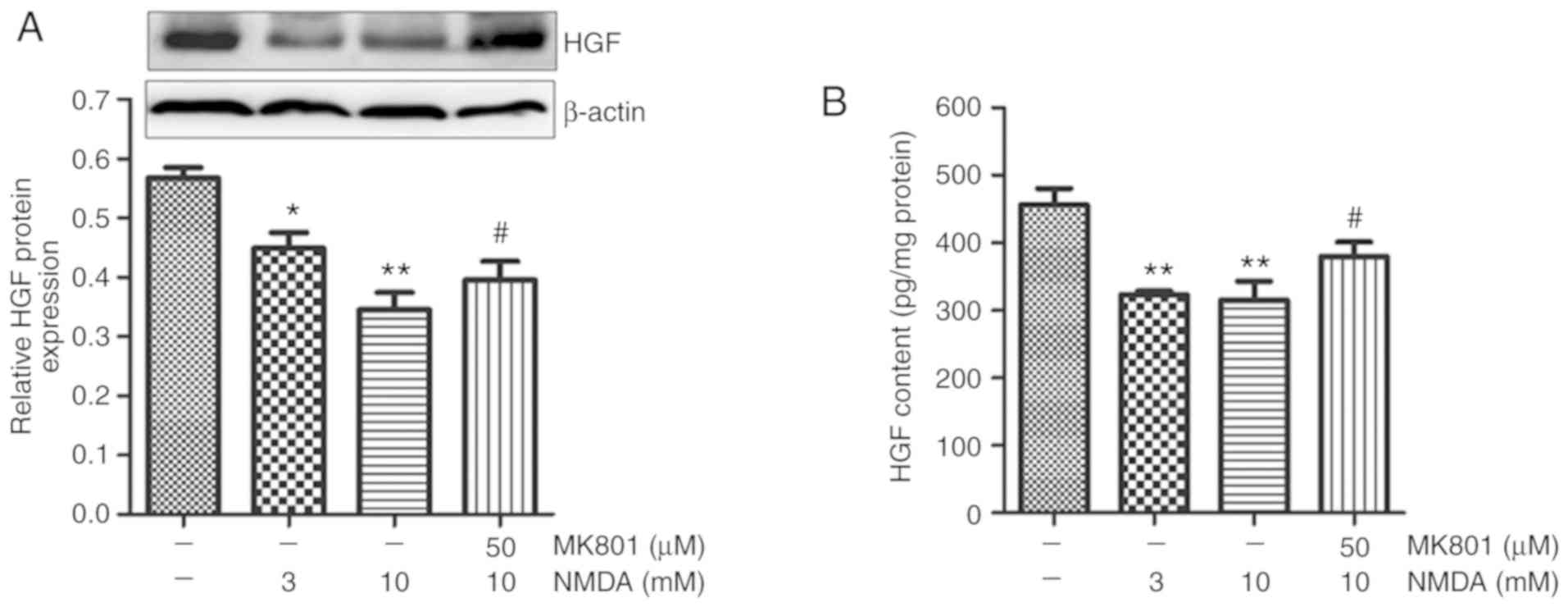
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
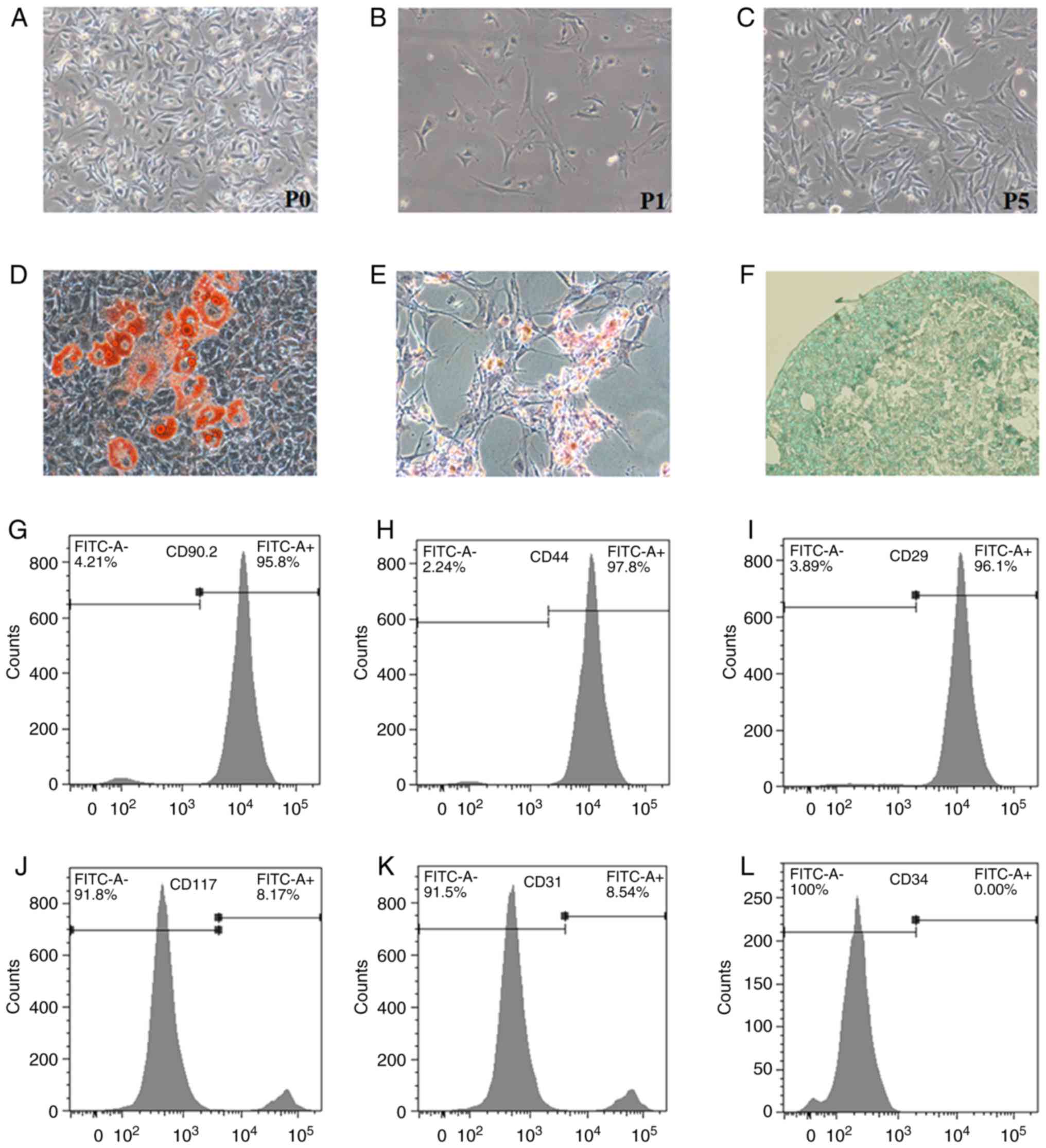
|
|
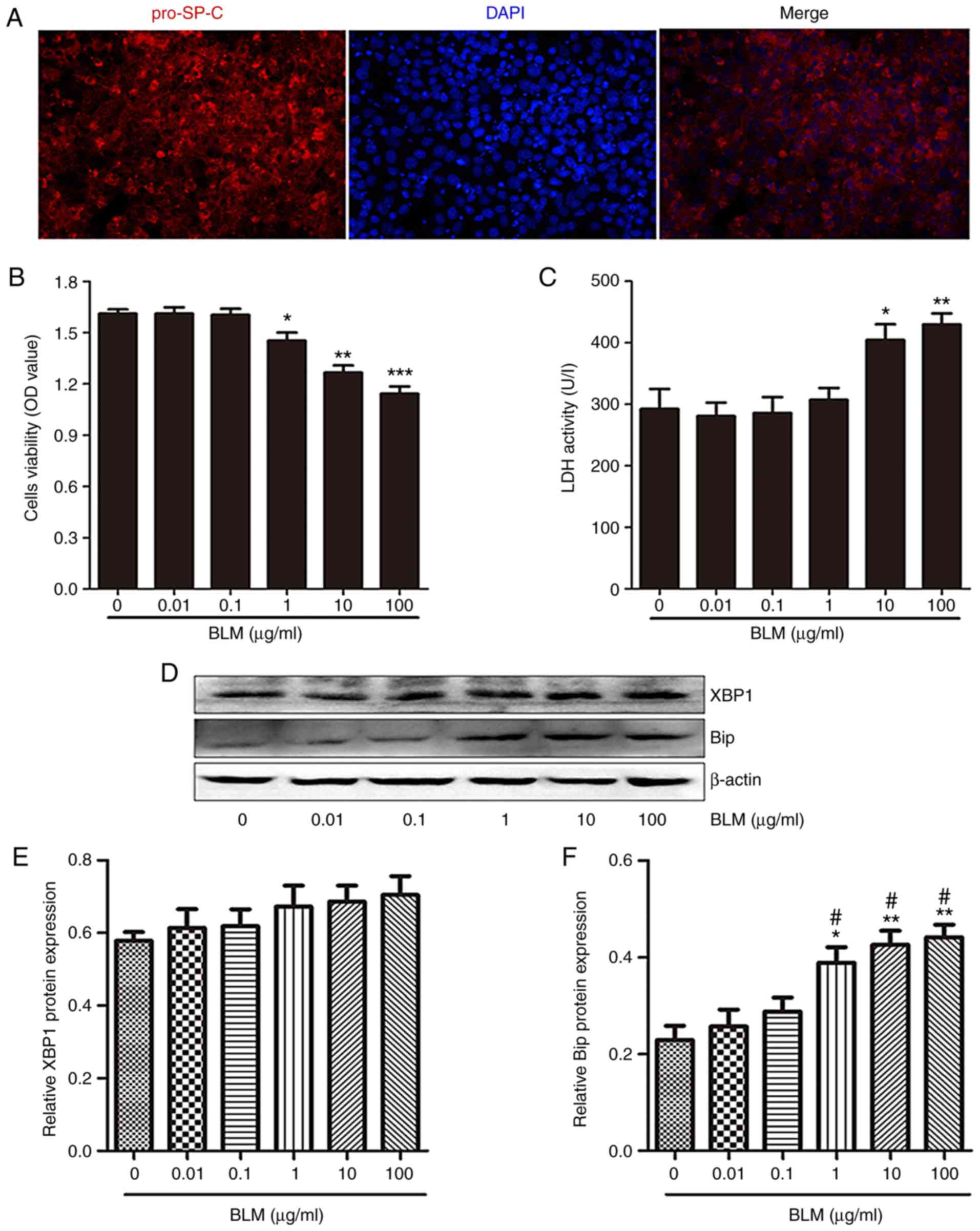
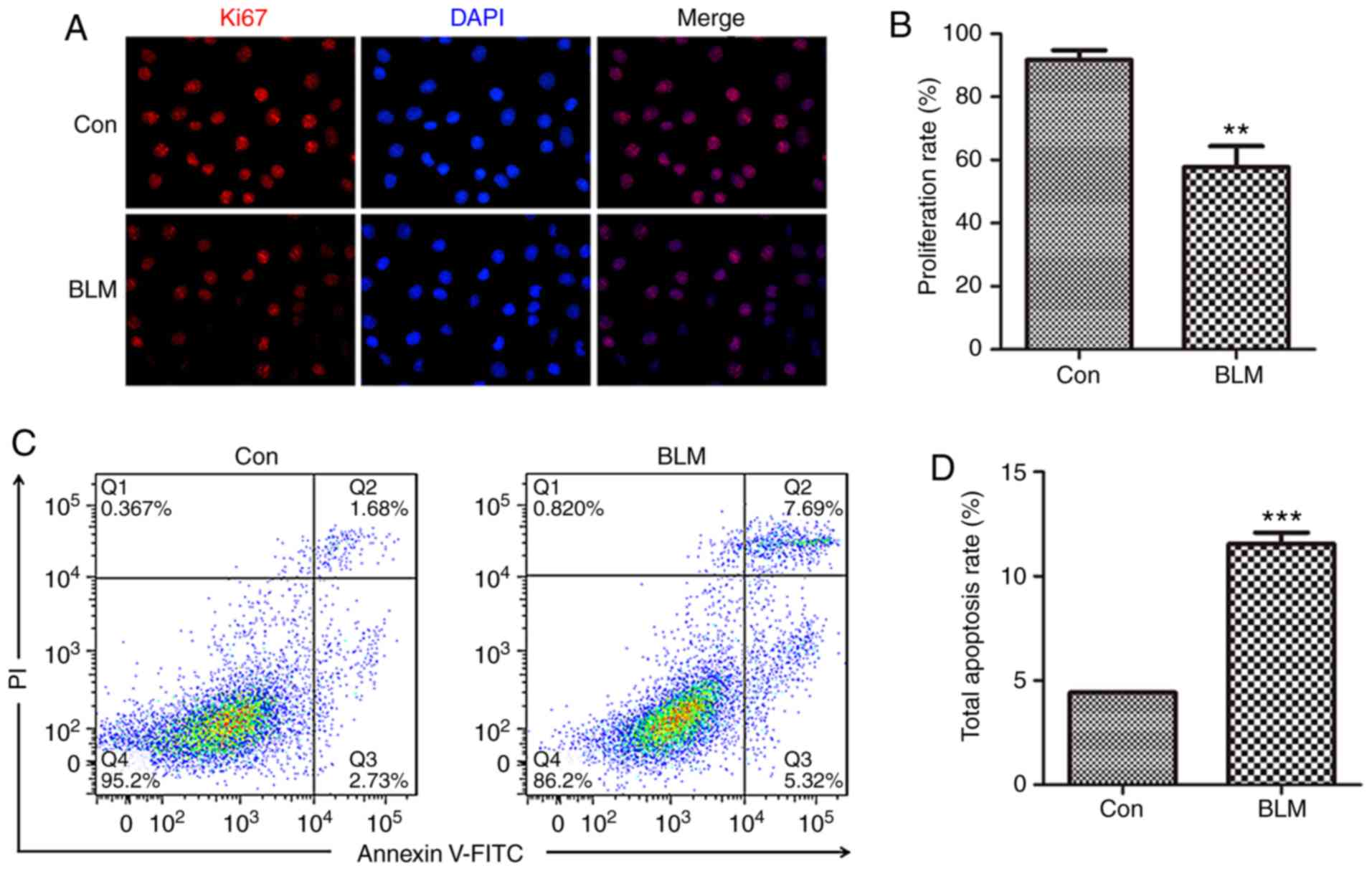
4
|
Adamson IY, Young L and Bowden DH:
Relationship of alveolar epithelial injury and repair to the
induction of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 130:377–383.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lawson WE, Crossno PF, Polosukhin VV,
Roldan J, Cheng DS, Lane KB, Blackwell TR, Xu C, Markin C, Ware LB,
et al: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in alveolar epithelial cells is
prominent in IPF: Association with altered surfactant protein
processing and herpesvirus infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 294:L1119–L1126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhong Q, Zhou B, Ann DK, Minoo P, Liu Y,
Banfalvi A, Krishnaveni MS, Dubourd M, Demaio L, Willis BC, et al:
Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of alveolar epithelial cells: Effects of misfolded
surfactant protein. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 45:498–509. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lawson WE, Cheng DS, Degryse AL, Tanjore
H, Polosukhin VV, Xu XC, Newcomb DC, Jones BR, Roldan J, Lane KB,
et al: Endoplasmic reticulum stress enhances fibrotic remodeling in
the lungs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:10562–10567. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao H, Wu QQ, Cao LF, Qing HY, Zhang C,
Chen YH, Wang H, Liu RY and Xu DX: Melatonin inhibits endoplasmic
reticulum stress and epithelial-mesenchymal transition during
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. PLoS One.
9:e972662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu J and Kaufman RJ: From acute ER stress
to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death
Differ. 13:374–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chakrabarti A, Chen AW and Varner JD: A
review of the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biotechnol
Bioeng. 108:2777–2793. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ghadiri M, Young PM and Traini D:
Cell-based therapies for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis (IPF) disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 16:375–387. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sinclair K, Yerkovich ST and Chambers DC:
Mesenchymal stem cells and the lung. Respirology. 18:397–411. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Antunes MA, Laffey JG, Pelosi P and Rocco
PR: Mesenchymal stem cell trials for pulmonary diseases. J Cell
Biochem. 115:1023–1032. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu S, Li J, Xu X, Liu A, He H, Xu J, Chen
Q, Liu S, Liu L, Qiu H and Yang Y: The hepatocyte growth
factor-expressing character is required for mesenchymal stem cells
to protect the lung injured by lipopolysaccharide in vivo. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 7:662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong LH, Jiang YY, Liu YJ, Cui S, Xia CC,
Qu C, Jiang X, Qu YQ, Chang PY and Liu F: The anti-fibrotic effects
of mesenchymal stem cells on irradiated lungs via stimulating
endogenous secretion of HGF and PGE2. Sci Rep. 5:87132015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kumar A: NMDA receptor function during
senescence: Implication on cognitive performance. Front Neurosci.
9:4732015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Griffin WR III, Haun HL, Hazelbaker CL,
Ramachandra VS and Becker HC: Increased extracellular glutamate in
the nucleus accumbens promotes excessive ethanol drinking in
ethanol dependent mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 39:707–717. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li X, Li C, Tang Y, Huang Y, Cheng Q,
Huang X, Zhao F, Hao C, Feng D, Xu J, et al: NMDA receptor
activation inhibits the anti-fibrotic effect of BM-MSCs on
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 315:L404–L421. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xu S, De Becker A, Van Camp B,
Vanderkerken K and Van Riet I: An improved harvest and in vitro
expansion protocol for murine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:1059402010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Della Latta V, Cecchettini A, Del RS and
Morales MA: Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction:
From biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol Res.
97:122–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schroder M and Kaufman RJ: The mammalian
unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem. 74:739–789. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T
and Mori K: XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in
response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription
factor. Cell. 107:881–891. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mulugeta S, Nguyen V, Russo SJ, Muniswamy
M and Beers MF: A surfactant protein C precursor protein BRICHOS
domain mutation causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, proteasome
dysfunction, and caspase 3 activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
32:521–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mulugeta S, Maguire JA, Newitt JL, Russo
SJ, Kotorashvili A and Beers MF: Misfolded BRICHOS SP-C mutant
proteins induce apoptosis via caspase-4- and cytochrome c-related
mechanisms. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L720–L729.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nita I, Hostettler K, Tamo L, Medová M,
Bombaci G, Zhong J, Allam R, Zimmer Y, Roth M, Geiser T and Gazdhar
A: Hepatocyte growth factor secreted by bone marrow stem cell
reduce ER stress and improves repair in alveolar epithelial II
cells. Sci Rep. 7:419012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cahill EF, Kennelly H, Carty F, Mahon BP
and English K: Hepatocyte growth factor is required for mesenchymal
stromal cell protection against bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:1307–1318. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schrier DJ, Kunkel RG and Phan SH: The
role of strain variation in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 127:63–66. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang R, Ibarra-Sunga O, Verlinski L, Pick
R and Uhal BD: Abrogation of bleomycin-induced epithelial apoptosis
and lung fibrosis by captopril or by a caspase inhibitor. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 279:L143–L151. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wallach-Dayan SB, Izbicki G, Cohen PY,
Gerstl-Golan R, Fine A and Breuer R: Bleomycin initiates apoptosis
of lung epithelial cells by ROS but not by Fas/FasL pathway. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L790–L796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Korfei M, Ruppert C, Mahavadi P, Henneke
I, Markart P, Koch M, Lang G, Fink L, Bohle RM, Seeger W, et al:
Epithelial endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in sporadic
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
178:838–846. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao J, Dennis JE, Muzic RF, Lundberg M and
Caplan AI: The dynamic in vivo distribution of bone marrow-derived
mesen-chymal stem cells after infusion. Cells Tissues Organs.
169:12–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, Spears
W, Roman J and Brigham KL: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
33:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen Q, Chen B, Xiao Z, Zhao L, Xu X, Wan
X, Jin M, Dai J and Dai H: Paracrine factors from mesenchymal stem
cells attenuate epithelial injury and lung fibrosis. Mol Med Rep.
11:2831–2837. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Seedorf G, Metoxen AJ, Rock R, Markham N,
Ryan S, Vu T and Abman SH: Hepatocyte growth factor as a downstream
mediator of vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent
preservation of growth in the developing lung. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 310:L1098–L1110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Liu Y, Peng X, Liu W, Zhao F, Feng
D, Han J, Huang Y, Luo S, Li L, et al: NMDA receptor antagonist
attenuates bleomycin-induced acute lung injury. PLoS One.
10:e1258732015.
|
|
38
|
Shang LH, Luo ZQ, Deng XD, Wang MJ, Huang
FR, Feng DD and Yue SJ: Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
and its effect on nitric oxide production of rat alveolar
macrophages. Nitric Oxide. 23:327–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tang F, Yue S, Luo Z, Feng D, Wang M, Qian
C, Zhen X and Duan Y: Role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in
hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Pediatr Pulmonol. 40:437–444. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang M, Luo Z, Liu S, Li L, Deng X, Huang
F, Shang L, Jian C and Yue S: Glutamate mediates hyperoxia-induced
newborn rat lung injury through N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Am
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 40:260–267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|