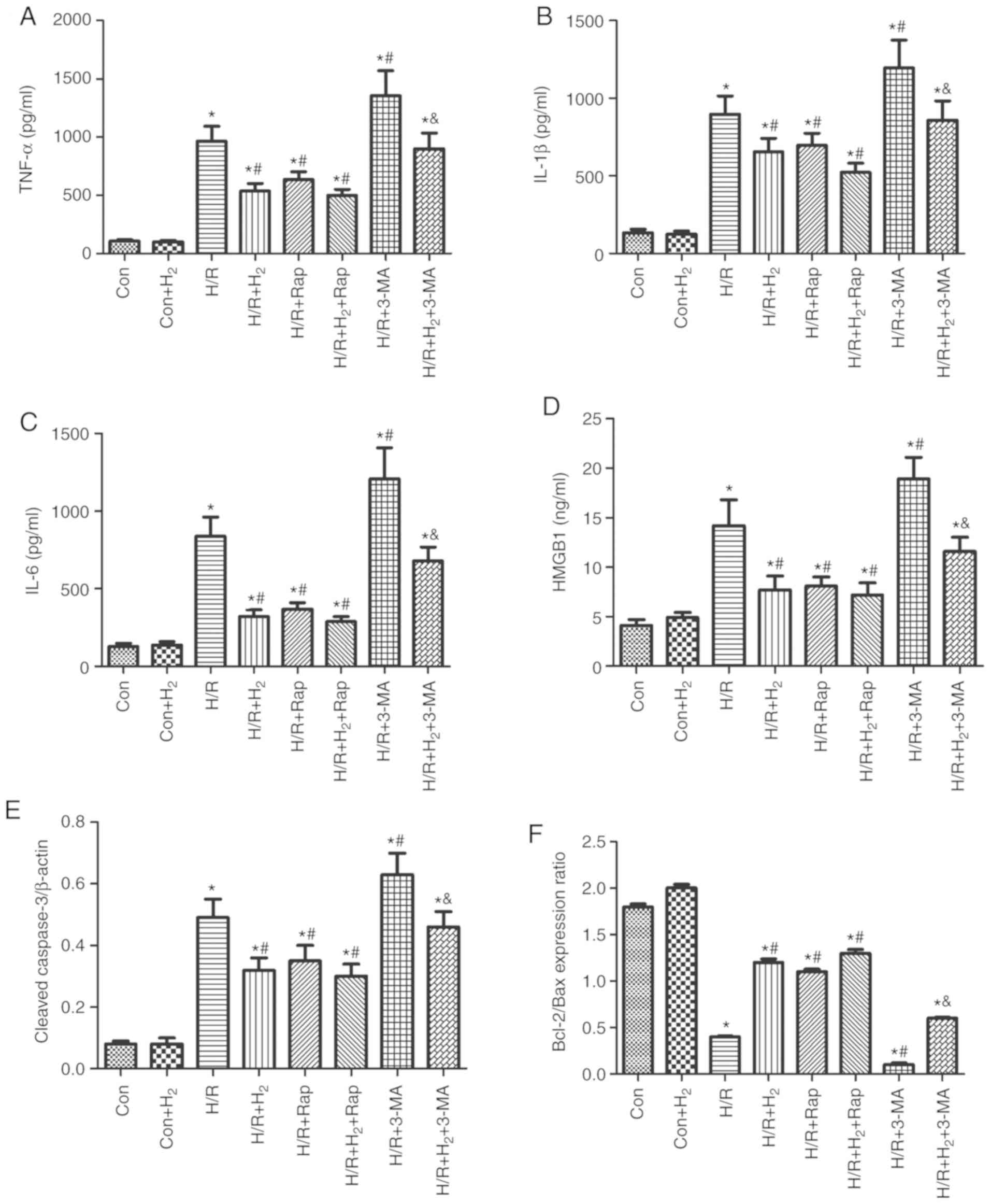
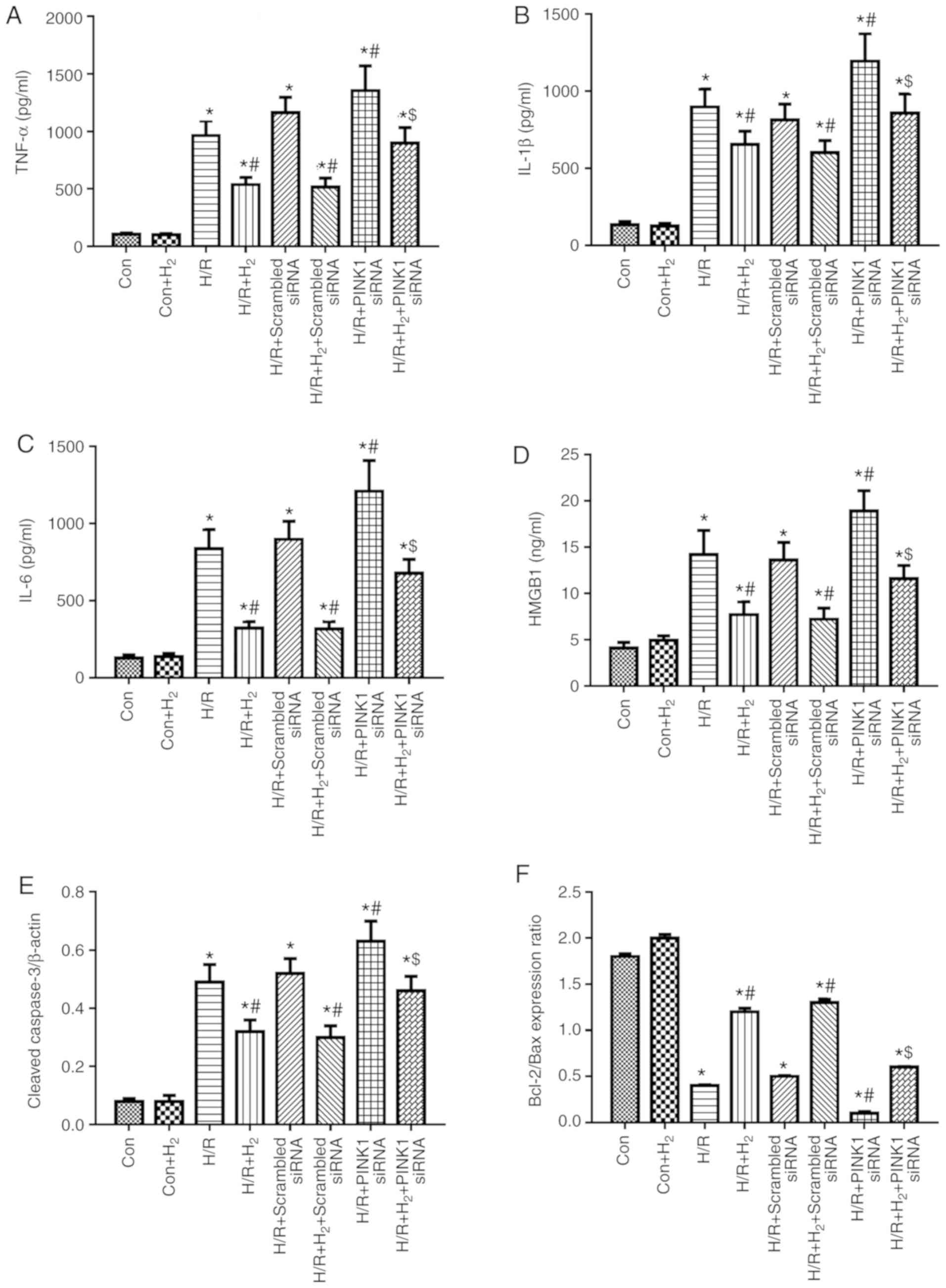
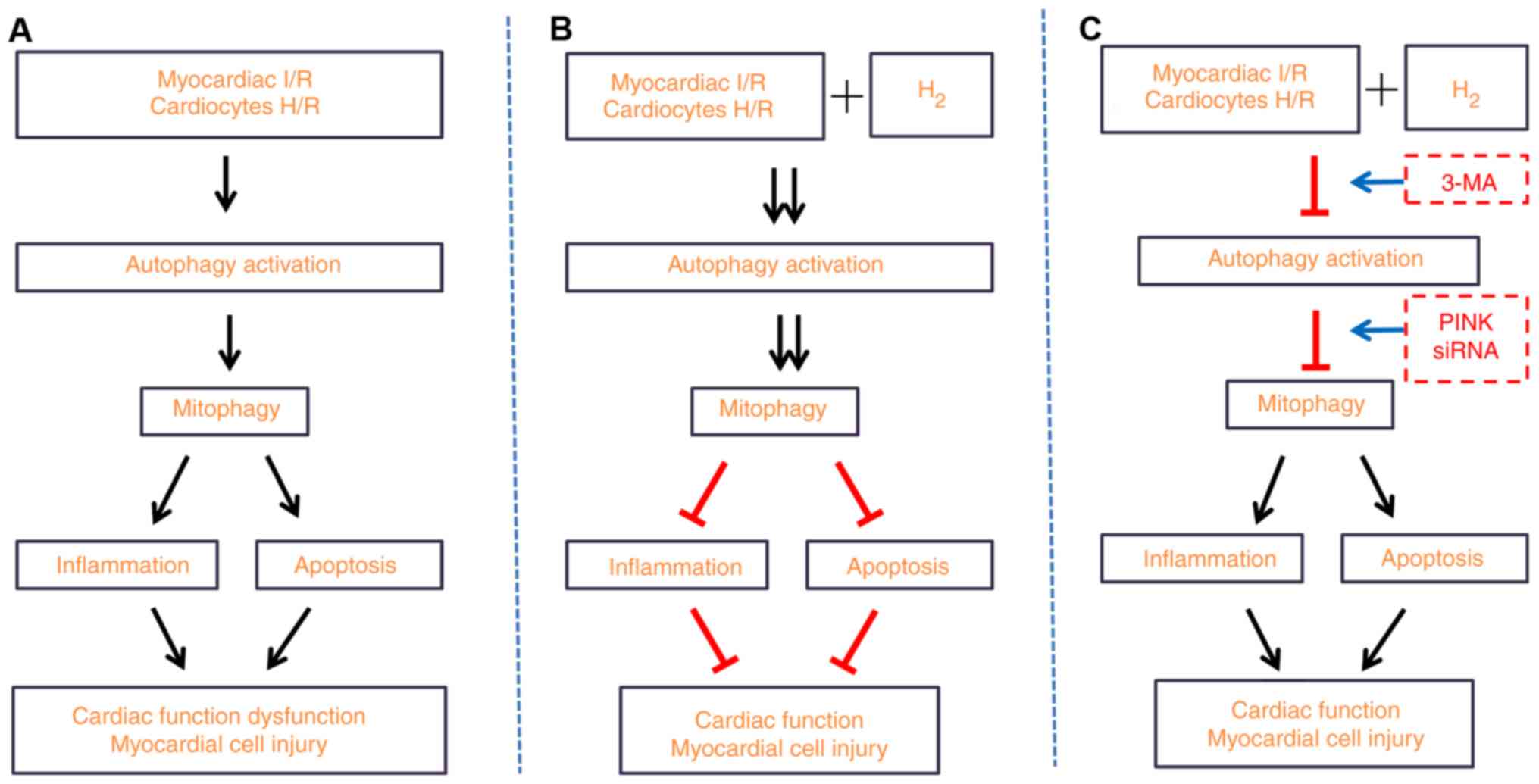
|
1
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding S, Yang Y and Mei J: Protective
effects of L-malate against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:38036572016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heusch G, Musiolik J, Gedik N and
Skyschally A: Mitochondrial STAT3 activation and cardioprotection
by ischemic postconditioning in pigs with regional myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion. Circ Res. 109:1302–1308. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Ye J, Lu X, Cheng Y, Xiang
L, Chen L, Feng W, Shi H, Yu X, et al: BFGF attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum stress and mitochondrial injury on myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion via activation of PI3K/Akt/ERK1/2 pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:595–607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pan Z, Zhao Y, Yu H, Liu D and Xu H:
Effect of hydrogen-rich saline on cardiomyocyte autophagy during
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in aged rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 95:2022–2026. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Sun Q, He B, Xiao J, Wang Z and
Sun X: Anti-inflammatory effect of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat
model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Int J
Cardiol. 148:91–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shigeta T, Sakamoto S, Li XK, Cai S, Liu
C, Kurokawa R, Nakazawa A, Kasahara M and Uemoto S: Luminal
injection of hydrogen-rich solution attenuates intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation. 99:500–507.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li J, Hong Z, Liu H, Zhou J, Cui L, Yuan
S, Chu X and Yu P: Hydrogen-rich saline promotes the recovery of
renal function after ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via
anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 7:1062016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shimada S, Wakayama K, Fukai M, Shimamura
T, Ishikawa T, Fukumori D, Shibata M, Yamashita K, Kimura T, Todo
S, et al: Hydrogen gas ameliorates hepatic reperfusion injury after
prolonged cold preservation in isolated perfused rat liver. Artif
Organs. 40:1128–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang R, Wu J, Chen Z, Xia F, Sun Q and Liu
L: Postconditioning with inhaled hydrogen promotes survival of
retinal ganglion cells in a rat model of retinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Brain Res. 1632:82–90. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, Liu W, Liu Y, Zhang
JH, Denoble PJ, Tao H and Sun X: Hydrogen-rich saline protects
myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 234:1212–1219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cabigas EB, Somasuntharam I, Brown ME, Che
PL, Pendergrass KD, Chiang B, Taylor WR and Davis ME:
Over-expression of catalase in myeloid cells confers acute
protection following myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci.
15:9036–9050. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Xie K, Han H, Li Y, Liu L, Yang T
and Yu Y: Molecular hydrogen protects mice against polymicrobial
sepsis by ameliorating endothelial dysfunction via an Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:643–654. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qi L, Pan H, Li D, Fang F, Chen D and Sun
H: Luteolin improves contractile function and attenuates apoptosis
following ischemia-reperfusion in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Eur J
Pharmacol. 668:201–207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong J, Xue FS, Yuan YJ, Wang Q, Liao X
and Wang WL: Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: A possible
approach to protect against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.
Chin Med J (Engl). 123:2720–2726. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Speyer CL and Ward PA: Role of endothelial
chemokines and their receptors during inflammation. J Invest Surg.
24:18–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Naidu BV, Farivar AS, Woolley SM, Grainger
D, Verrier ED and Mulligan MS: Novel broad-spectrum chemokine
inhibitor protects against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Heart Lung Transplant. 23:128–134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konstantinidis K, Whelan RS and Kitsis RN:
Mechanisms of cell death in heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1552–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Movassagh M and Foo RS: Simplified
apoptotic cascades. Heart Fail Rev. 13:111–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Liu B, Li T, Zhu Y, Luo G, Jiang
Y, Tang F, Jian Z and Xiao Y: AMPK activation serves a critical
role in mitochondria quality control via modulating mitophagy in
the heart under chronic hypoxia. Int J Mol Med. 41:69–76. 2018.
|
|
22
|
Bian X, Teng T, Zhao H, Qin J, Qiao Z, Sun
Y, Liun Z and Xu Z: Zinc prevents mitochondrial superoxide
generation by inducing mitophagy in the setting of
hypoxia/reoxygenation in cardiac cells. Free Radic Res. 52:80–91.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Eiyama A and Okamoto K:
PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 33:95–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kubli DA, Cortez MQ, Moyzis AG, Najor RH,
Lee Y and Gustafsson AB: PINK1 is dispensable for mitochondrial
recruitment of parkin and activation of mitophagy in cardiac
myocytes. PLoS One. 10:pp. e01307072015, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dorn GN III: Parkin-dependent mitophagy in
the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 95:42–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Hoshino A, Mita Y, Okawa Y, Ariyoshi M,
Iwai-Kanai E, Ueyama T, Ikeda K, Ogata T and Matoba S: Cytosolic
p53 inhibits Parkin-mediated mitophagy and promotes mitochondrial
dysfunction in the mouse heart. Nat Commun. 4:23082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kubli DA, Zhang X, Lee Y, Hanna RA,
Quinsay MN, Nguyen CK, Jimenez R, Petrosyan S, Murphy AN and
Gustafsson AB: Parkin protein deficiency exacerbates cardiac injury
and reduces survival following myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem.
288:915–926. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Ma Z, Hu W, Wang D, Jiang S, Fan
C, Di S, Liu D, Sun Y and Yi W: Caveolin-1/-3: Therapeutic targets
for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol.
111:452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mao X, Wang T, Liu Y, Irwin MG, Ou JS,
Liao XL, Gao X, Xu Y, Ng KF, Vanhoutte PM and Xia Z:
N-acetylcysteine and allopurinol confer synergy in attenuating
myocardial ischemia injury via restoring HIF-1alpha/HO-1 signaling
in diabetic rats. PLoS One. 8. pp. e689492013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pan Z, Zhao Y, Yu H, Liu D and Xu H:
Effect of hydrogen-rich saline on cardiomyocyte autophagy during
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in aged rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 95:2022–2026. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rossello X, Lobo-Gonzalez M and Ibanez B:
Pathophysiology and therapy of myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion
syndrome. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. Jun 7–2019, Epub ahead
of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hinojar R, Foote L, Ucar EA, Dabir D,
Schnackenburg B, Higgins DM, Schaeffter T, Nagel E and Puntmann V:
Myocardial T2 mapping for improved detection of inflammatory
myocardial involvement in acute and chronic myocarditis. J
Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 16(Suppl 1): pp. O632014, View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Xu P, Cai X, Zhang W, Li Y, Qiu P, Lu D
and He X: Flavonoids of Rosa roxburghii Tratt exhibit
radioprotection and anti-apoptosis properties via the
Bcl-2(Ca(2+))/caspase-3/PARP-1 pathway. Apoptosis. 21:1125–1143.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen DF,
Gautier CA, Shen J, Cookson MR and Youle RJ: PINK1 is selectively
stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol.
8:pp. e10002982010, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moyzis AG, Sadoshima J and Gustafsson AB:
Mending a broken heart: The role of mitophagy in cardioprotection.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 308:H183–H192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Li T, Jiao YR, Wang LH, Zhou YH and Yao
HC: Autophagy in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: Friend or
foe? Int J Cardiol. 239:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Toldo S, Marchetti C, Mauro AG, Chojnacki
J, Mezzaroma E, Carbone S, Zhang S, Van Tassell B, Salloum FN and
Abbate A: Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome limits the
inflammatory injury following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in
the mouse. Int J Cardiol. 209:215–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu H, Zhang H, Zhao W, Guo L, Li X, Li Y,
Zhang X and Sun Y: Gypenoside protects against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting cardiomyocytes apoptosis
via inhibition of chop pathway and activation of PI3K/Akt pathway
in vivo and in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:123–136. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ge M, Yao W, Yuan D, Zhou S, Chen X, Zhang
Y, Li H, Xia Z and Hei Z: Brg1-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
activation alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell
Death Dis. 8:pp. e28412017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma L, Liu H, Xie Z, Yang S, Xu W, Hou J
and Yu B: Ginsenoside Rb3 protects cardiomyocytes against
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of JNK-mediated
NF-κB pathway: A mouse cardiomyocyte model. PLoS One. 9:pp.
e1036282014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yu J, Wang L, Akinyi M, Li Y, Duan Z, Zhu
Y and Fan G: Danshensu protects isolated heart against ischemia
reperfusion injury through activation of Akt/ERK1/2/Nrf2 signaling.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:14793–14804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nandi S, Ravindran S and Kurian GA: Role
of endogenous hydrogen sulfide in cardiac mitochondrial
preservation during ischemia reperfusion injury. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:271–279. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chi J, Li Z, Hong X, Zhao T, Bie Y, Zhang
W, Yang J, Feng Z, Yu Z, Xu Q, et al: Inhalation of hydrogen
attenuates progression of chronic heart failure via suppression of
oxidative stress and P53 related to Apoptosis pathway in rats.
Front Physiol. 9:10262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yue L, Li H, Zhao Y, Li J and Wang B:
Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathways
and cardiac function during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in
rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 95:1483–1487. 2015.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pan Z, Zhao Y, Yu H, Liu D and Xu H:
Effect of hydrogen-rich saline on cardiomyocyte autophagy during
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in aged rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 95:2022–2026. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yue L, Li H, Zhao Y, Li J and Wang B:
Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on Akt/GSK3β signaling pathways and
cardiac function during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in rats.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 95:1483–1487. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo J, Wang SB, Yuan TY, Wu YJ, Yan Y, Li
L, Xu XN, Gong LL, Qin HL, Fang LH and Du GH: Coptisine protects
rat heart against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
suppressing myocardial apoptosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis.
231:384–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fliss H and Gattinger D: Apoptosis in
ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res. 79:949–956. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Anselmi A, Abbate A, Girola F, Nasso G,
Biondi-Zoccai GG, Possati G and Gaudino M: Myocardial ischemia,
stunning, inflammation, and apoptosis during cardiac surgery: A
review of evidence. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 25:304–311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vukojevic K, Carev D, Sapunar D, Petrovic
D and Saraga-Babic M: Developmental patterns of caspase-3, bax and
bcl-2 proteins expression in the human spinal ganglia. J Mol
Histol. 39:339–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dong JW, Zhu HF, Zhu WZ, Ding HL, Ma TM
and Zhou ZN: Intermittent hypoxia attenuates ischemia/reperfusion
induced apoptosis in cardiac myocytes via regulating Bcl-2/Bax
expression. Cell Res. 13:385–391. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li R, Geng HH, Xiao J, Qin XT, Wang F,
Xing JH, Xia YF, Mao Y, Liang JW and Ji XP: MiR-7a/b attenuates
post-myocardial infarction remodeling and protects H9c2
cardiomyoblast against hypoxia-induced apoptosis involving Sp1 and
PARP-1. Sci Rep. 6:290822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang YQ, Chang GL, Wang Y, Zhang DY, Cao
L and Liu J: Geniposide prevents hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced
apoptosis in H9c2 cells: Improvement of mitochondrial dysfunction
and activation of GLP-1R and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:407–421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bao W, Hu E, Tao L, Boyce R, Mirabile R,
Thudium DT, Ma XL, Willette RN and Yue TL: Inhibition of Rho-kinase
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc
Res. 61:548–558. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sun D, Huang J, Zhang Z, Gao H, Li J, Shen
M, Cao F and Wang H: Luteolin limits infarct size and improves
cardiac function after myocardium ischemia/reperfusion injury in
diabetic rats. PLoS One. 7:pp. e334912012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ahn J and Kim J: Mechanisms and
consequences of inflammatory signaling in the myocardium. Curr
Hypertens Rep. 14:510–516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Woldbaek PR, Tønnessen T, Henriksen UL,
Florholmen G, Lunde PK, Lyberg T and Christensen G: Increased
cardiac IL-18 mRNA, pro-IL-18 and plasma IL-18 after myocardial
infarction in the mouse; a potential role in cardiac dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Res. 59:122–131. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang JJ, Peng K, Zhang J, Meng XW and Ji
FH: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning may attenuate myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by down-regulating the HMGB1
TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS One. 12:pp. e01720062017,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Cao QH, Liu F, Yang ZL, Fu XH, Yang ZH,
Liu Q, Wang L, Wan XB and Fan XJ: Prognostic value of autophagy
related proteins ULK1, Beclin 1, ATG3, ATG5, ATG7, ATG9, ATG10,
ATG12, LC3B and p62/SQSTM1 in gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res.
8:3831–3847. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
de Vries RL and Przedborski S: Mitophagy
and Parkinson's disease: Be eaten to stay healthy. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 55:37–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF and Youle
RJ: Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and
promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol. 183:795–803. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lee Y, Lee HY, Hanna RA and Gustafsson AB:
Mitochondrial autophagy by Bnip3 involves Drp1-mediated
mitochondrial fission and recruitment of Parkin in cardiac
myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1924–H931. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Billia F, Hauck L, Konecny F, Rao V, Shen
J and Mak TW: PTEN-inducible kinase 1 (PINK1)/Park6 is
indispensable for normal heart function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:9572–9577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhao Y, Tang Y, Suo C, Liu D, Li S and Li
H: Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on endoplasmic reticulum stress
during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 94:3024–3028. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|