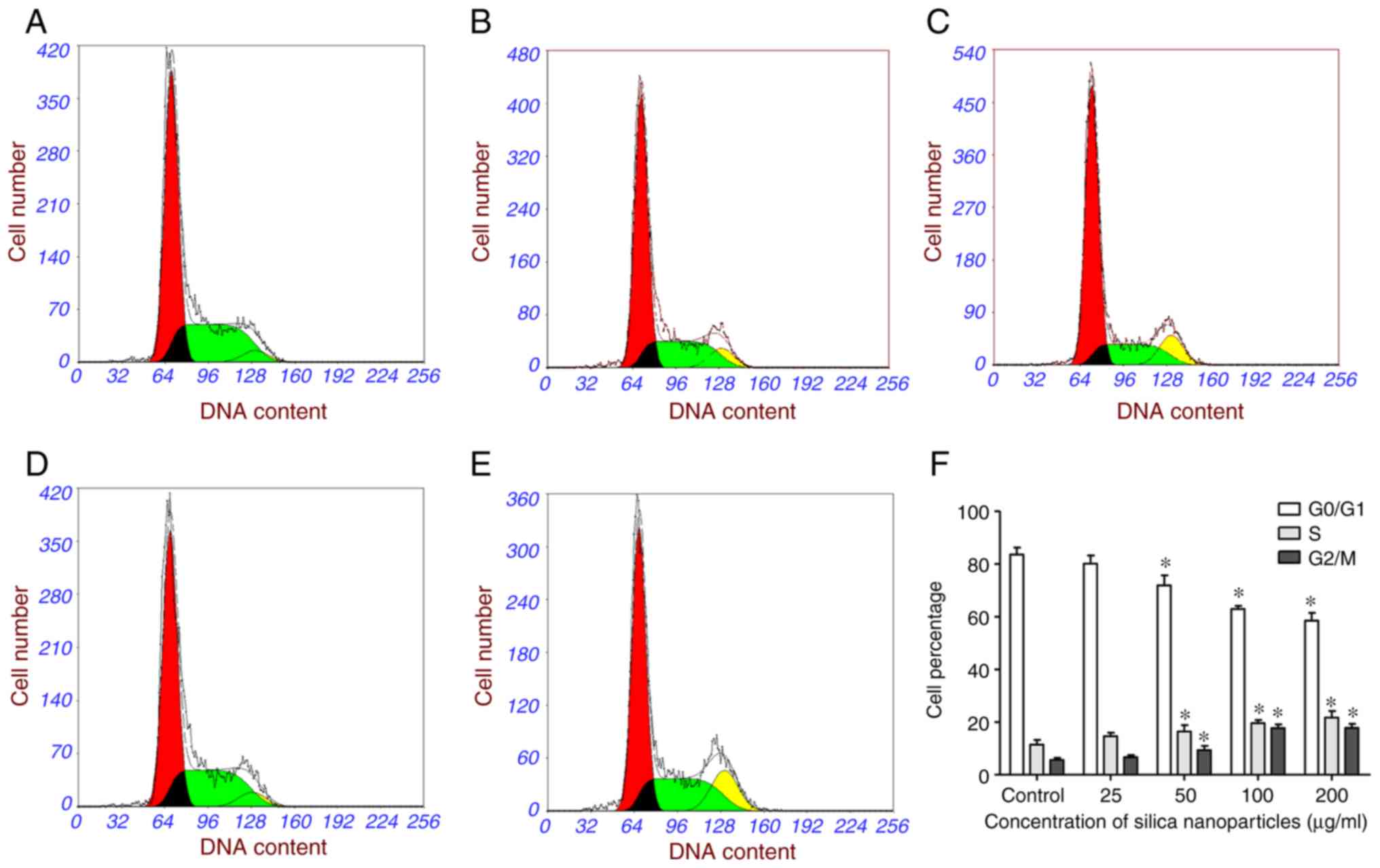
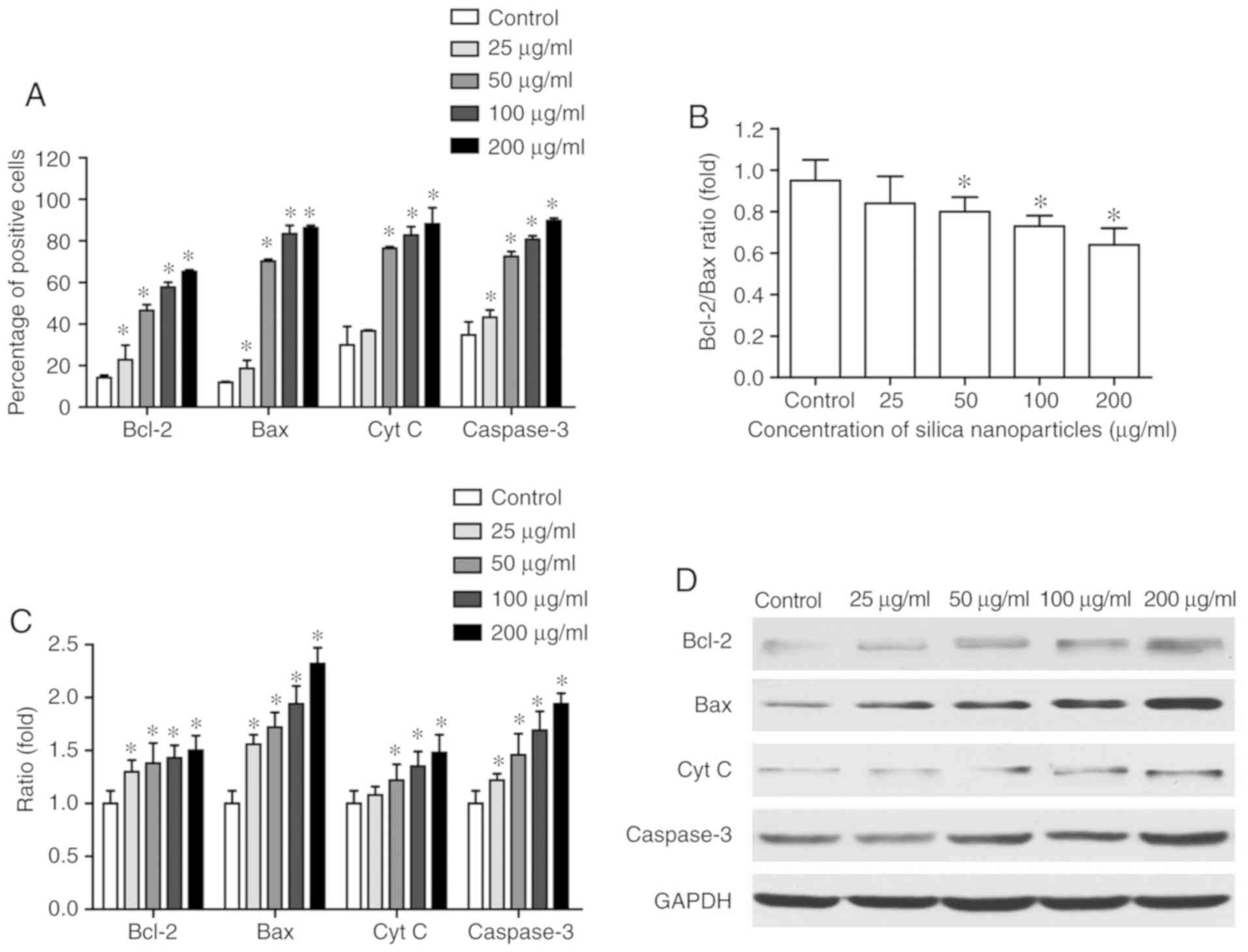
|
1
|
Powers KW, Brown SC, Krishna VB, Wasdo SC,
Moudgil BM and Roberts SM: Research strategies for safety
evaluation of nanomaterials. Part VI. Characterization of nanoscale
particles for toxicological evaluation. Toxicol Sci. 90:296–303.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu X, Qian J, Zhou H, Gan Q, Tang W, Lu J,
Yuan Y and Liu C: In vitro cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis
by silica nanoparticles in human HepG2 hepatoma cells. Int J
Nanomedicine. 6:1889–1901. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar P, Tambe P, Paknikar KM and Gajbhiye
V: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cutting-edge theranostics:
Advancement from merely a carrier to tailor-made smart delivery
platform. J Control Release. 287:35–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park JH, Dumani DS, Arsiwala A, Emelianov
S and Kane RS: Tunable aggregation of gold-silica janus
nanoparticles to enable contrast-enhanced multiwavelength
photoacoustic imaging in vivo. Nanoscale. 10:15365–15370. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Müller K, Fedosov D and Gompper G:
Margination of micro- and nano‑particles in blood flow and its
effect on drug delivery. Sci Rep. 4:48712014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mebert AM, Baglole CJ, Desimone MF and
Maysinger D: Nanoengineered silica: Properties, applications and
toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 31:753–770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pietroiusti A, Stockmann-Juvala H,
Lucaroni F and Savolainen K: Nanomaterial exposure, toxicity, and
impact on human health. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed
Nanobiotechnol. Feb 23–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Laux P, Tentschert J, Riebeling C,
Braeuning A, Creutzenberg O, Epp A, Fessard V, Haas KH, Haase A,
Hund-Rinke K, et al: Nanomaterials: Certain aspects of application,
risk assessment and risk communication. Arch Toxicol. 92:121–141.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Guo M, Xu X, Yan X, Wang S, Gao S and Zhu
S: In vivo biodistribution and synergistic toxicity of silica
nanoparticles and cadmium chloride in mice. J Hazard Mater.
260:780–788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen N, Song ZM, Tang H, Xi WS, Cao A, Liu
Y and Wang H: Toxicological effects of Caco-2 cells following
short-term and long-term exposure to Ag nanoparticles. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:pii: E974. 2016
|
|
11
|
Ahamed M: Silica nanoparticles-induced
cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in cultured A431 and
A549 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 32:186–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lewinski N, Colvin V and Drezek R:
Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small. 4:26–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E and
Oberdörster J: Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from
studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect.
123:823–839. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yoshida T, Yoshioka Y, Tochigi S, Hirai T,
Uji M, Ichihashi K, Nagano K, Abe Y, Kamada H, Tsunoda S, et al:
Intranasal exposure to amorphous nanosilica particles could
activate intrinsic coagulation cascade and platelets in mice. Part
Fibre Toxicol. 10:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du Z, Zhao D, Jing L, Cui G, Jin M, Li Y,
Liu X, Liu Y, Du H, Guo C, et al: Cardiovascular toxicity of
different sizes amorphous silica nanoparticles in rats after
intratracheal instillation. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 13:194–207. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin W, Huang YW, Zhou XD and Ma Y: In
vitro toxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 217:252–259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Kim BG, Park SJ,
Kim HW, Lee KH, Park SB, Lee JK and Cho MH: Toxicity and tissue
distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in mice. Toxicol Sci.
89:338–347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu J, Wang C, Sun J and Xue Y:
Neurotoxicity of silica nanoparticles: Brain localization and
dopaminergic neurons damage pathways. ACS Nano. 5:4476–4489. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Erren TC, Glende CB, Morfeld P and
Piekarski C: Is exposure to silica associated with lung cancer in
the absence of silicosis? A meta-analytical approach to an
important public health question. Int Arch Occup Environ Health.
82:997–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mignotte B and Vayssiere JL: Mitochondria
and apoptosis. Eur J Biochem. 252:1–15. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahmad J, Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Alrokayan
SA, Siddiqui MA, Musarrat J and Al-Khedhairy AA: Apoptosis
induction by silica nanoparticles mediated through reactive oxygen
species in human liver cell line HepG2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
259:160–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gopinath P, Gogoi SK, Sanpui P, Paul A,
Chattopadhyay A and Ghosh SS: Signaling gene cascade in silver
nanoparticle induced apoptosis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
77:240–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katiyar SK, Roy AM and Baliga MS:
Silymarin induces apoptosis primarily through a p53-dependent
pathway involving Bcl-2/Bax, cytochrome c release, and caspase
activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:207–216. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry
DE and Oltvai ZN: Bcl-2/Bax: A rheostat that regulates an
anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 4:327–332.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke E and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu Y, Duan J, Yu Y, Li Y, Liu X, Zhou X,
Ho KF, Tian L and Sun Z: Silica nanoparticles induce autophagy and
autophagic cell death in HepG2 cells triggered by reactive oxygen
species. J Hazard Mater. 270:176–186. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Buratti S and Lavine JE: Drugs and the
liver: Advances in metabolism, toxicity, and therapeutics. Curr
Opin Pediatr. 14:601–607. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu T, Li L, Teng X, Huang X, Liu H, Chen
D, Ren J, He J and Tang F: Single and repeated dose toxicity of
mesoporous hollow silica nanoparticles in intravenously exposed
mice. Biomaterials. 32:1657–1668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yoshida T, Yoshioka Y, Matsuyama K,
Nakazato Y, Tochigi S, Hirai T, Kondoh S, Nagano K, Abe Y, Kamada
H, et al: Surface modification of amorphous nanosilica particles
suppresses nano-silica-induced cytotoxicity, ROS generation, and
DNA damage in various mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
427:748–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun L, Li Y, Liu X, Jin M, Zhang L, Du Z,
Guo C, Huang P and Sun Z: Cytotoxicity and mitochondrial damage
caused by silica nanoparticles. Toxicol In Vitro. 25:1619–1629.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Q, Xue Y and Sun J: Kupffer
cell-mediated hepatic injury induced by silica nanoparticles in
vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:1129–1140. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li N, Duan Y, Hong M, Zheng L, Fei M, Zhao
X, Wang J, Cui Y, Liu H, Cai J, et al: Spleen injury and apoptotic
pathway in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticules. Toxicol
Lett. 195:161–168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Isoda K, Tetsuka E, Shimizu Y, Saitoh K,
Ishida I and Tezuka M: Liver injury induced by thirty‑ and
fifty‑nanometer‑diameter silica nanoparticles. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:370–375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhu Z, Li E, Liu Y, Gao Y, Sun H, Ma G,
Wang Z, Liu X, Wang Q, Qu X, et al: Inhibition of Jak-STAT3 pathway
enhances bufalin-induced apoptosis in colon cancer SW620 cells.
World J Surg Oncol. 10:2282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L and Li N: Toxic
potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 311:622–627.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kipen HM and Laskin DL: Smaller is not
always better: Nanotechnology yields nanotoxicology. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 289:L696–L697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Hu L, Yu D and Gao C: Influence
of silica particle internalization on adhesion and migration of
human dermal fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 31:pp. 8465pp. 84742010,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ryman-Rasmussen JP, Riviere JE and
Monteiro-Riviere NA: Surface coatings determine cytotoxicity and
irritation potential of quantum dot nanoparticles in epidermal
keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 127:143–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chan WT, Liu CC, Chiang Chiau JS, Tsai ST,
Liang CK, Cheng ML, Lee HC, Yeung CY and Hou SY: In vivo
toxicologic study of larger silica nanoparticles in mice. Int J
Nanomedicine. 12:3421–3432. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cui W, Li J, Zhang Y, Rong H, Lu W and
Jiang L: Effects of aggregation and the surface properties of gold
nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and cell growth. Nanomedicine.
8:46–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Guo C, Ma R, Liu X, Chen T, Li Y, Yu Y,
Duan J, Zhou X, Li Y and Sun Z: Silica nanoparticles promote
oxLDL-induced macrophage lipid accumulation and apoptosis via
endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling. Sci Total Environ.
631-632:570–579. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nishimori H, Kondoh M, Isoda K, Tsunoda S,
Tsutsumi Y and Yagi K: Silica nanoparticles as hepatotoxicants. Eur
J Pharm Biopharm. 72:496–501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nishimori H, Kondoh M, Isoda K, Tsunoda S,
Tsutsumi Y and Yagi K: Histological analysis of 70-nm silica
particles-induced chronic toxicity in mice. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
72:626–629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
So SJ, Jang IS and Han CS: Effect of
micro/nano silica particle feeding for mice. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.
8:5367–5371. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yu Y, Duan J, Yu Y, Li Y, Zou Y, Yang Y,
Jiang L, Li Q and Sun Z: Autophagy and autophagy dysfunction
contribute to apoptosis in HepG2 cells exposed to nanosilica.
Toxicol Res (Camb). 5:871–882. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Duan J, Yu Y, Li Y, Yu Y, Li Y, Zhou X,
Huang P and Sun Z: Toxic effect of silica nanoparticles on
endothelial cells through DNA damage response via Chk1-dependent
G2/M checkpoint. PLoS One. 8:pp. e620872013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN and Van
Bockstaele DR: Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 36:165–175.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Stark GR and Taylor WR: Analyzing the G2/M
checkpoint. Methods Mol Biol. 280:51–82. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cuddihy AR and O'Connell MJ: Cell-cycle
responses to DNA damage in G2. Int Rev Cytol. 222:99–140. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ly JD, Grubb R and Lawen A: The
mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an
update. Apoptosis. 8:115–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: The
pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 305:626–629.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li Y, Sun L, Jin M, Du Z, Liu X, Guo C, Li
Y, Huang P and Sun Z: Size-dependent cytotoxicity of amorphous
silica nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Toxicol In
Vitro. 25:1343–1352. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pucci B, Adams CS, Fertala J, Snyder BC,
Mansfield KD, Tafani M, Freeman T and Shapiro IM: Development of
the terminally differentiated state sensitizes epiphyseal
chondrocytes to apoptosis through caspase-3 activation. J Cell
Physiol. 210:609–615. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Krętowski R, Kusaczuk M, Naumowicz M,
Kotyńska J, Szynaka B and Cechowska-Pasko M: The effects of silica
nanoparticles on apoptosis and autophagy of glioblastoma cell
lines. Nanomaterials (Basel). 7. pii: E230. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gross A, Mcdonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Brenner C, Cadiou H, Vieira HL, Zamzami N,
Marzo I, Xie Z, Leber B, Andrews D, Duclohier H, Reed JC and
Kroemer G: Bcl-2 and Bax regulate the channel activity of the
mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene.
19:329–336. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gao C and Wang AY: Significance of
increased apoptosis and Bax expression in human small intestinal
adenocarcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 57:1139–1148. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|