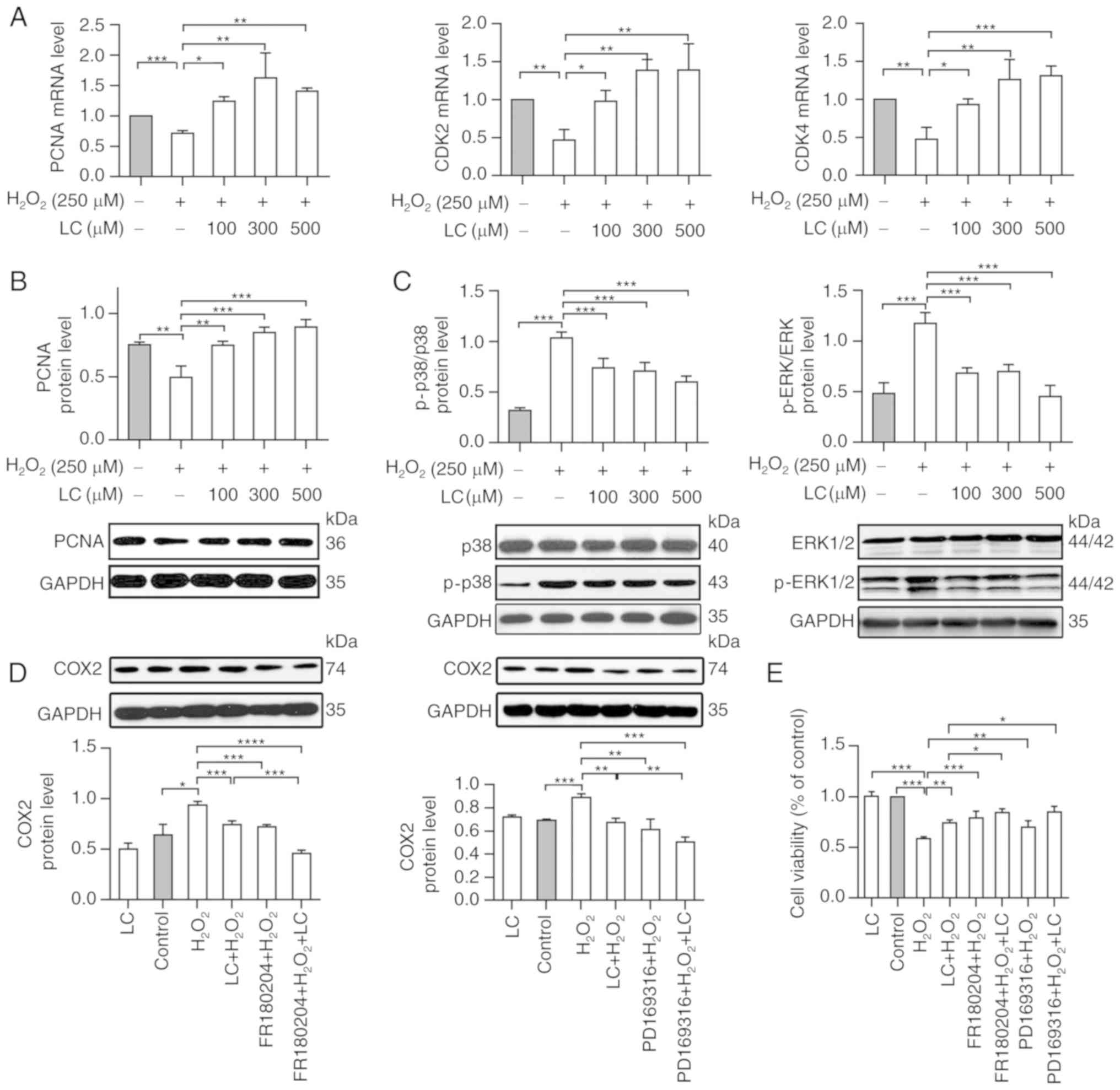
|
1
|
Nagai N, Ito Y and Takeuchi N: Correlation
between hyper-sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide and low defense
against Ca(2+) influx in cataractogenic lens of Ihara cataract
rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1005–1010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zuercher J, Neidhardt J, Magyar I, Labs S,
Moore AT, Tanner FC, Waseem N, Schorderet DF, Munier FL,
Bhattacharya S, et al: Alterations of the 5′ untranslated region of
SLC16A12 lead to age-related cataract. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
51:3354–3361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang D, Zhang X, Rong S, Sha Q, Liu P,
Han T and Pan H: Serum antioxidative enzymes levels and oxidative
stress products in age-related cataract patients. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2013:5878262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mok JW, Chang DJ and Joo CK: Antiapoptotic
effects of anthocyanin from the seed coat of black soybean against
oxidative damage of human lens epithelial cell induced by
H2O2. Curr Eye Res. 39:1090–1098. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujii J, Ikeda Y, Kurahashi T and Homma T:
Physiological and pathological views of peroxiredoxin 4. Free Radic
Biol Med. 83:373–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamada S and Guo X: Peroxiredoxin 4
(PRDX4): Its critical in vivo roles in animal models of metabolic
syndrome ranging from atherosclerosis to nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Pathol Int. 68:91–101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim DH, Park CH, Park D, Choi YJ, Park MH,
Chung KW, Kim SR, Lee JS and Chung HY: Ginsenoside Rc modulates
Akt/FoxO1 pathways and suppresses oxidative stress. Arch Pharm Res.
37:813–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kubo E, Shibata T, Singh DP and Sasaki H:
Roles of TGF β and FGF signals in the lens: Tropomyosin regulation
for posterior capsule opacity. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E30932018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schey KL, Petrova RS, Gletten RB and
Donaldson PJ: The role of aquaporins in ocular lens homeostasis.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:E26932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dahm R: Dying to see. Sci Am. 291:82–89.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Traina G: The neurobiology of
acetyl-L-carnitine. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 21:1314–1329. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nutrients Editorial Office: Erratum:
l-Carnitine supplementation in recovery after exercise; Nutrients
2018, 10, 349. Nutrients. 10:E5412018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mishra A, Reddy IJ, Gupta PS and Mondal S:
L-carnitine mediated reduction in oxidative stress and alteration
in transcript level of antioxidant enzymes in sheep embryos
produced in vitro. Reprod Domest Anim. 51:311–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng R, Su Z, Hua X, Zhang Z, Li DQ and
Pflugfelder SC: Osmoprotectants suppress the production and
activity of matrix metalloproteinases induced by hyperosmolarity in
primary human corneal epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 20:1243–1252.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mitchell SL, Uppal K, Williamson SM, Liu
K, Burgess LG, Tran V, Umfress AC, Jarrell KL, Cooke Bailey JN,
Agarwal A, et al: The carnitine shuttle pathway is altered in
patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:4978–4985. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Werner E, Wang H and Doetsch PW: Opposite
roles for p38MAPK-driven responses and reactive oxygen species in
the persistence and resolution of radiation-induced genomic
instability. PLoS One. 9:e1082342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bai J, Yang F, Dong L and Zheng Y: Ghrelin
protects human lens epithelial cells against oxidative
stress-induced damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:19104502017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akasaki Y, Alvarez-Garcia O, Saito M,
Caramés B, Iwamoto Y and Lotz MK: FoxO transcription factors
support oxidative stress resistance in human chondrocytes.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:3349–3358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patel H, Chen J and Kavdia M: Induced
peroxidase and cytoprotective enzyme expressions support adaptation
of HUVECs to sustain subsequent H2O2
exposure. Microvasc Res. 103:1–10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhu L, Li J, Wu D and Li B: The protective
effect of beta-casomor-phin-7 via promoting Foxo1 activity and
nuclear translocation in human lens epithelial cells. Cutan Ocul
Toxicol. 37:267–274. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shamsi FA, Chaudhry IA, Boulton ME and
Al-Rajhi AA: L-carnitine protects human retinal pigment epithelial
cells from oxidative damage. Curr Eye Res. 32:575–584. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thrimawithana TR, Rupenthal ID, Räsch SS,
Lim JC, Morton JD and Bunt CR: Drug delivery to the lens for the
management of cataracts. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 126:185–194. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuan X, Marcano DC, Shin CS, Hua X,
Isenhart LC, Pflugfelder SC and Acharya G: Ocular drug delivery
nanowafer with enhanced therapeutic efficacy. ACS Nano.
9:1749–1758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao C, Fu MJ and Qiu LH: Molecular
cloning and functional characterization of cyclin E and CDK2 from
penaeus monodon. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kanska J, Zakhour M, Taylor-Harding B,
Karlan BY and Wiedemeyer WR: Cyclin E as a potential therapeutic
target in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
143:152–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chou HC, Wen LL, Chang CC, Lin CY, Jin L
and Juan SH: From the cover: l-Carnitine via PPARγ- and
Sirt1-dependent mechanisms attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and renal fibrosis caused by perfluorooctanesulfonate.
Toxicol Sci. 160:217–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baierle M, Nascimento SN, Moro AM, Brucker
N, Freitas F, Gauer B, Durgante J, Bordignon S, Zibetti M, Trentini
CM, et al: Relationship between inflammation and oxidative stress
and cognitive decline in the institutionalized elderly. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2015:8041982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dogru M, Kojima T, Simsek C and Tsubota K:
Potential role of oxidative stress in ocular surface inflammation
and dry eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:DES163–DES168.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hua X, Chi W, Su L, Li J, Zhang Z and Yuan
X: ROS-induced oxidative injury involved in pathogenesis of fungal
keratitis via p38 MAPK activation. Sci Rep. 7:104212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu D, Zhu H, Fu Q, Xu S, Sun W, Chen G and
Lv X: Ketamine delays progression of oxidative and damaged cataract
through regulating HMGB-1/NF-κB in lens epithelial cells.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 40:303–308. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jia Z, Song Z, Zhao Y, Wang X and Liu P:
Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract protects human lens epithelial
cells from oxidative stress via reducing NF-κB and MAPK protein
expression. Mol Vis. 17:210–217. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yao K, Ye P, Zhang L, Tan J, Tang X and
Zhang Y: Epigallocatechin gallate protects against oxidative
stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human lens
epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 14:217–223. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|